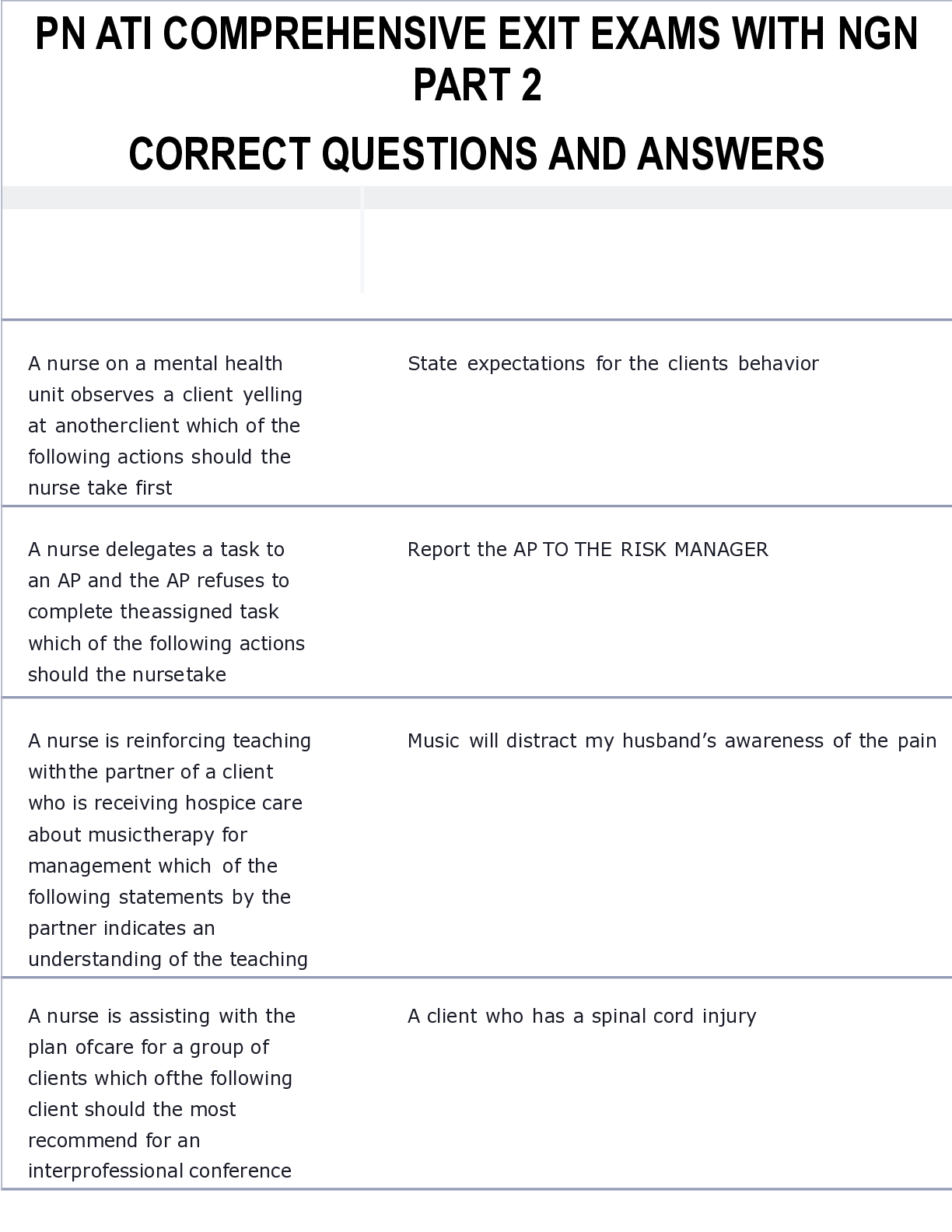
PN ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAMS WITH NGN PART 2 CORRECT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 31.5

HOME WORK QUESIONS Nursing 101 september paper 2020
$ 10
I HUMAN CASE WEEK 10 TESTICULAR PAIN
$ 40
.png)
STAT 111 Solution 2 - HBS with complete solution 2020
$ 6

IT 1223SP4 Study Guide 2021
$ 5

TEST BANK FOR PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: A PRACTICAL APPROACH 3rd Edition By Lachel Story A+ 2025
$ 9.5

WGU C785 Biochem - Module 1 - All Questions | Questions with 100% Correct Answers | Verified | Latest Update
$ 7
.png)
MATH 225N Week 8 Final Exam (Version 1)

.png)


























