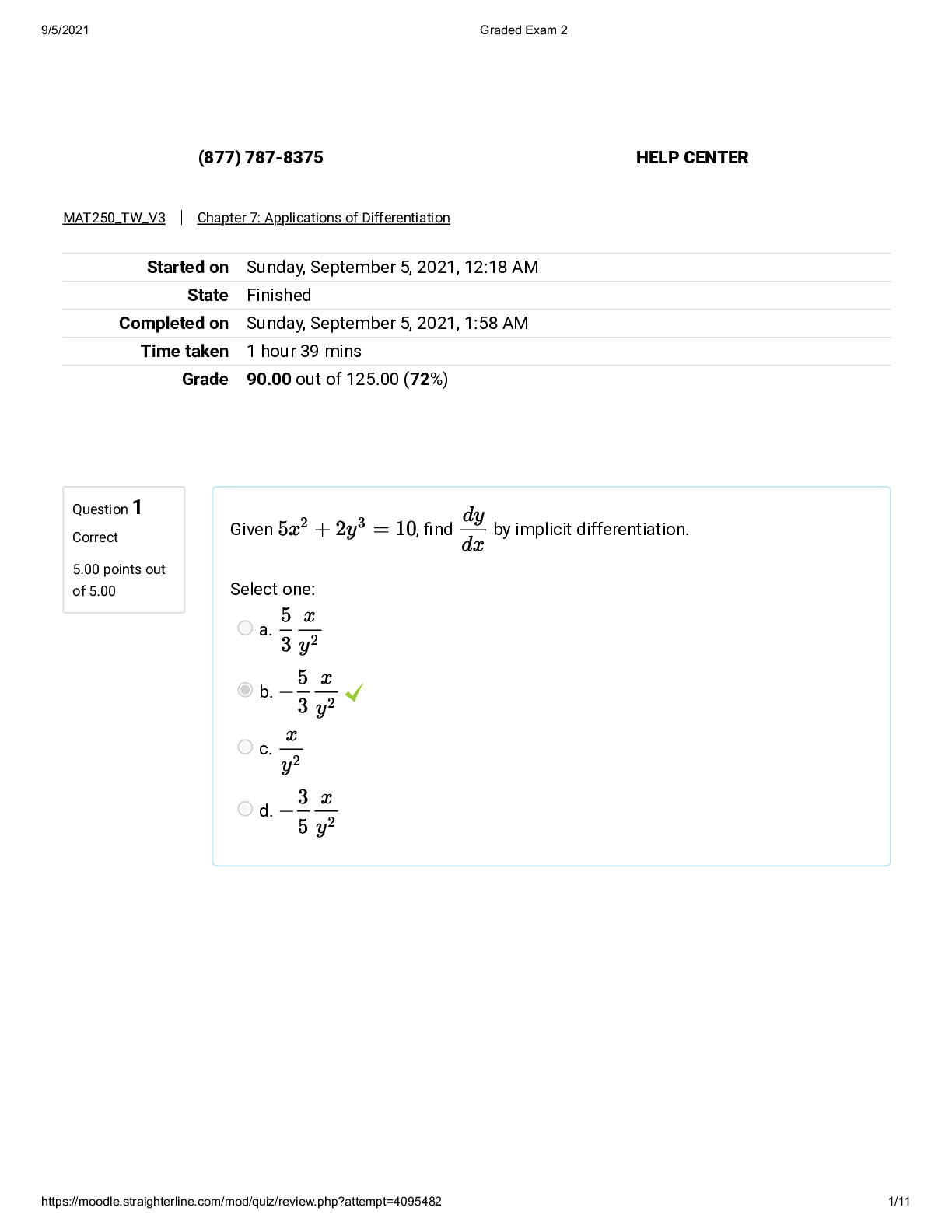
Voluntary vs involuntary admission: Voluntary admission clients chooses admissions to
a mental health facility in order to obtain treatment, voluntary admission has the right to
apply for a release at any time. Involun
...
Voluntary vs involuntary admission: Voluntary admission clients chooses admissions to
a mental health facility in order to obtain treatment, voluntary admission has the right to
apply for a release at any time. Involuntary patients enter the facility against their will.
Admission is up to 60 days. They have the right to refuse treatment.
Know psychoanalysis, psychotherapy, use of positive/negative reinforcement:
Psychoanalysis is a therapeutic process of assessing unconscious thoughts and feelings
and resolving conflict by talking to a psychoanalyst, may takes months to years, due to
the length and insurance, this cannot be the only therapy. First developed by SIGMUND
FREUD to resolve internal conflicts which occurs from early childhood experiences. Past
relationships are a common focus for therapy. Psychotherapy involves more verbal
therapist-to-client interaction than classic psychoanalysis. Client and therapy
develop a trusting relationship to explore the client’s problems.
Psychodynamic psychotherapy: employs the same tools as psychoanalysis, but it
focuses more on the client’s present state rather than his early life.
Interpersonal psychotherapy IPT: assist the client in addressing specific
problems, role-relationship, bereavement.
Cognitive therapy: based on cognitive model, individual thoughts and behaviors
to solve current problems, it treats depression, anxiety, eating disorders, other
issues that can improve by changing a client’s attitude toward life experiences.
Behavioral therapy: teaches the client ways to decrease anxiety or avoidant
behavior and give clients an opportunity to practice techniques, reduce anxiety
and relaxation and training models, successful for client who have phobia,
substance use or addictive disorder.
Dialectical behavioral therapy; is a cognitive-behavioral therapy for clients who
have a personality disorder and exhibit self-injury behaviors.
Positive reinforcement: Operant conditioning, the client receives positive rewards
for positive behavior.
Negative reinforcement: A
[Show More]



.png)