BIO 171 Microbiology Module 1. Portage Learning.Module1.1: Introduction
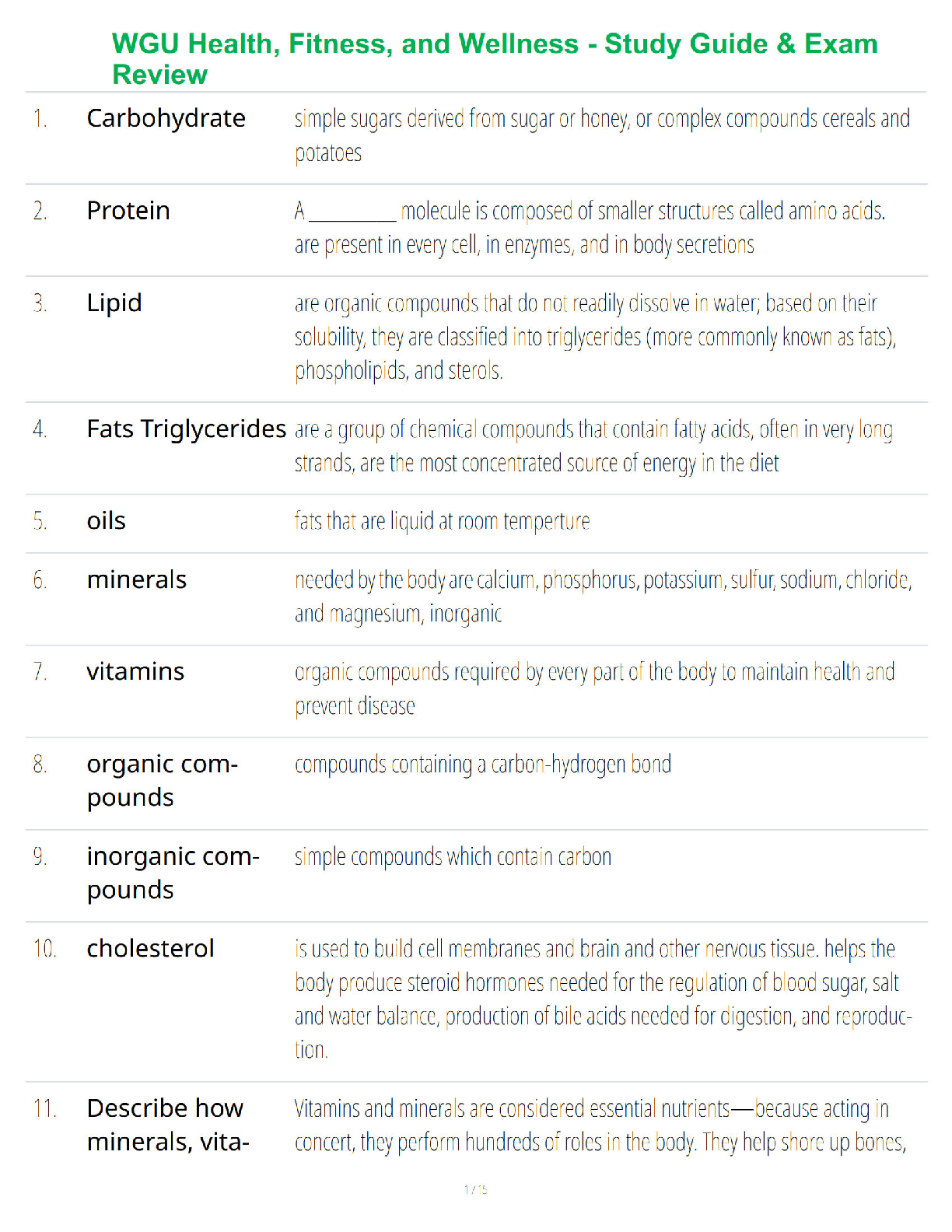
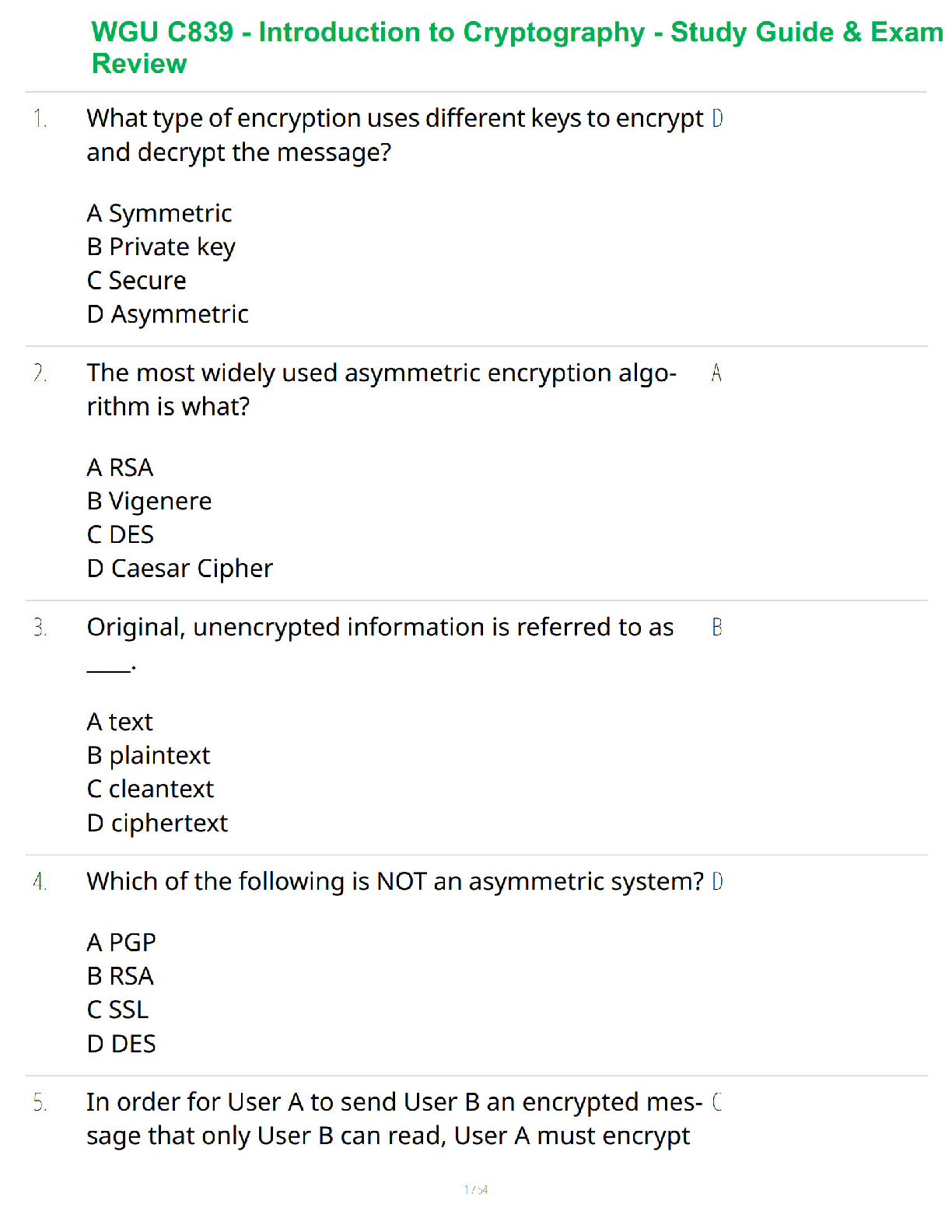
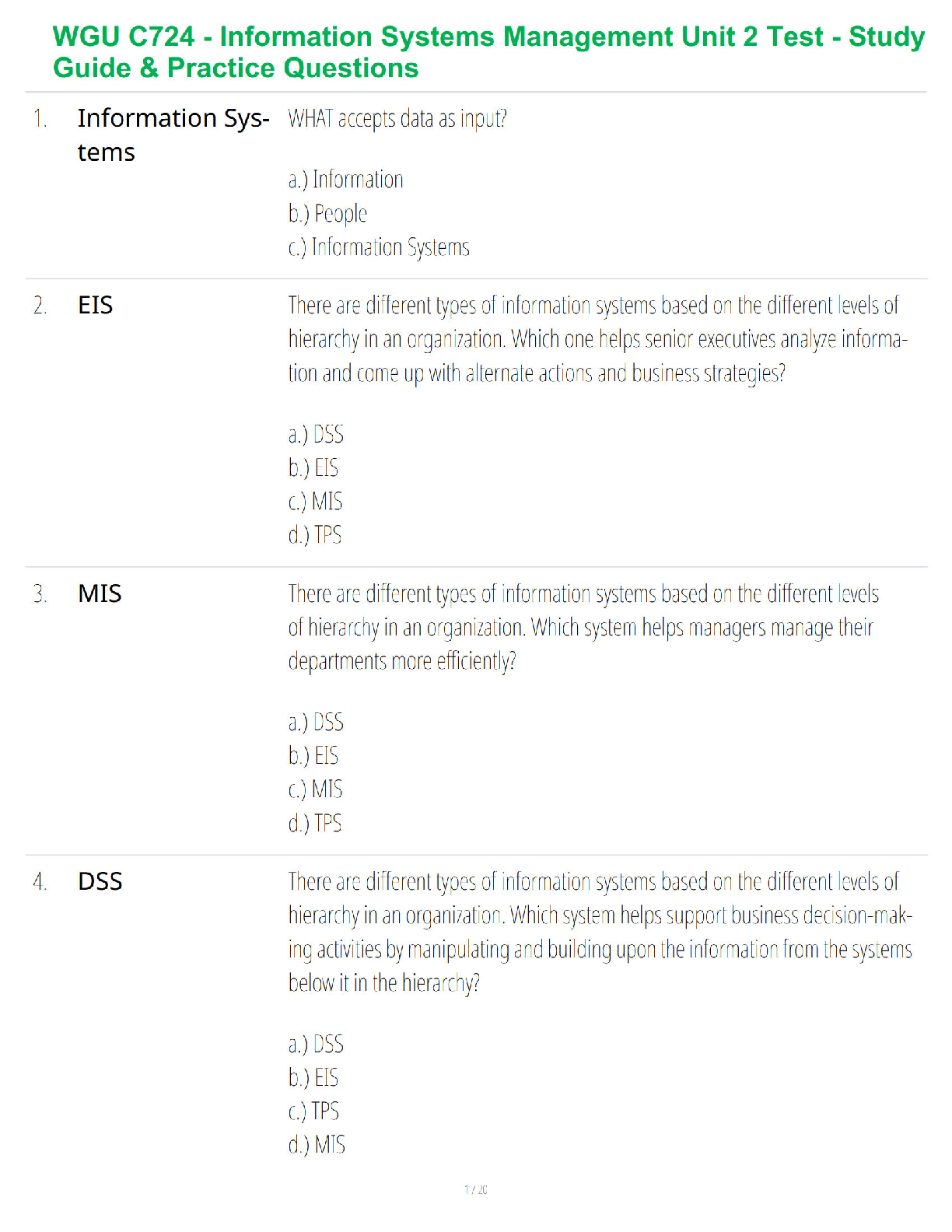
- What is microbiology?
• It is the study of biological processes at the micro (microscopic) level.
These microorganisms usually consist of a sin
...
BIO 171 Microbiology Module 1. Portage Learning.Module1.1: Introduction
- What is microbiology?
• It is the study of biological processes at the micro (microscopic) level.
These microorganisms usually consist of a single cell, so they are too small
to study with just your eyes.
- Examples would include bacteria, archaeons, fungi, protozoa, and algae.
• Although they are also microscopic, viruses are not living, so they are not
considered microorganisms. However, viruses can be classified as
microbes, a more general term that includes microorganisms and viruses.
Taken together, microbiology is the study of microbes.
• Despite being invisible to the naked eye, microbes play a complex role in
our world. For instance, microbes can be beneficial in a variety of ways
ranging from aiding in food digestion to protecting us when we are exposed
to potentially harmful foreign invaders to helping crops grow. However,
microbes can also be detrimental, as harmful strains of bacteria, fungi,
protozoa, and viruses kill millions of people each year and sicken even
more.
Module1.4: Macromolecules
- A microorganism usually consists of a single cell. At the most generalized
level, all cells are comprised of macromolecules—complex molecules that are
composed of smaller subunits.
- There are four main types of macromolecules found in cells: (1) proteins, (2)
nucleic acids, (3) lipids, and (4) polysaccharides.
1
Thursday, February 25, 2021
• Proteins are polymers (a large molecule comprised of many smaller
subunits) of amino acids, and they are the most abundant form of
macromolecule.
- Proteins may facilitate the movement of materials in or out of a cell.
- Some can act as enzymes that catalyze, or speed up, biochemical
processes.
- Others play a structural role, while other proteins, such as filaments,
enable movement.
- There is remarkable diversity within cells because of the way proteins are
formed by varying combinations of amino acids.
• Note: There are 20 different amino acids, and the order and length in
which they are assembled give rise to different protein sizes, structures,
and functions. Each protein has its own unique sequence of amino
acids, which is known as the primary structure of the protein.
- Titin, the largest known protein, is made up of about 33,000 amino
acids
- Of the twenty amino acids, it should also be noted that 9 are
considered essential amino acids, as the human body cannot produce
them—they must instead be taken in from the environment through
other sources (i.e.) the food you eat.
• Nucleic acids are chemical molecules that carry genetic information within
the cell. There are two major types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic
acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
- DNA contains a vast amount of hereditary information and is responsible
for the inheritable characteristics of living organisms.
[Show More]