ECON 102 MIDTER EXAM
Points Awarded 54.00
Points Missed 6.00
Percentage 90.0%
1.
A firm’s product price multiplied by the total number of items sold is called
A) profit
B) explicit cost
C) total reve
...
ECON 102 MIDTER EXAM
Points Awarded 54.00
Points Missed 6.00
Percentage 90.0%
1.
A firm’s product price multiplied by the total number of items sold is called
A) profit
B) explicit cost
C) total revenue
D) implicit cost
Table for Individual Question Feedback
2.
The short run is a situation such that
A) all inputs to production may vary in quantity.
B) the firm has sufficient time to add new capital to its production process.
C) at least one input to production is fixed in quantity.
D) the firm cannot alter the number of workers it hires.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
3.
Consider the figure above. Which of the following correctly identifies each curve?
A) A=MC, B=ATC, C=AVC, D=AFC
B) A=AVC, B=ATC, C=MC, D=AFC
C) A=MC, B=AVC, C=ATC, D=AFC
D) A=ATC, B=AFC, C=AVC, D=MC
Table for Individual Question Feedback
4.
Labor Output Variable
Cost Fixed
Cost Total
Cost
0 0 12
1 10 5
2 18 22
3 24 15
4 28 20 32
Consider the table above. What is the average total cost at 3 units of labor?
A) $9
B) $1
C) $1.13
D) $27
Table for Individual Question Feedback
5.
Consider the graph above. Each short run average total cost curve represents a different
A) none of these
B) firm: firm A, firm B and firm C.
C) factory size: small, medium or large.
D) time horizon: short, medium or long run.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
6.
The graph above represents
A) the marginal revenue product of labor
B) the marginal product of labor
C) the marginal cost of production
D) the average cost of production
Table for Individual Question Feedback
7.
Consider the table above. What is the price of the final good?
A) $1
B) $4
C) $10
D) $30
Table for Individual Question Feedback
8.
Norman has an upward sloping labor supply curve. If the opportunity cost of leisure rises for Norman, he will work
A) less
B) more information is needed to answer the question
C) the same amount
D) more
Table for Individual Question Feedback
9.
You own a bread bakery on College Avenue. The baking ovens you own are considered to be
A) productive goods
B) investment goods
C) final goods
D) capital goods
Table for Individual Question Feedback
10.
Your bagel shop uses both capital and labor in the production of bagels. In this production process capital and labor are complements. You install a new oven and the marginal product of capital increases. As a result
A) labor becomes more productive
B) the wage falls
C) labor becomes less productive
D) the rental rate of capital falls
Table for Individual Question Feedback
11.
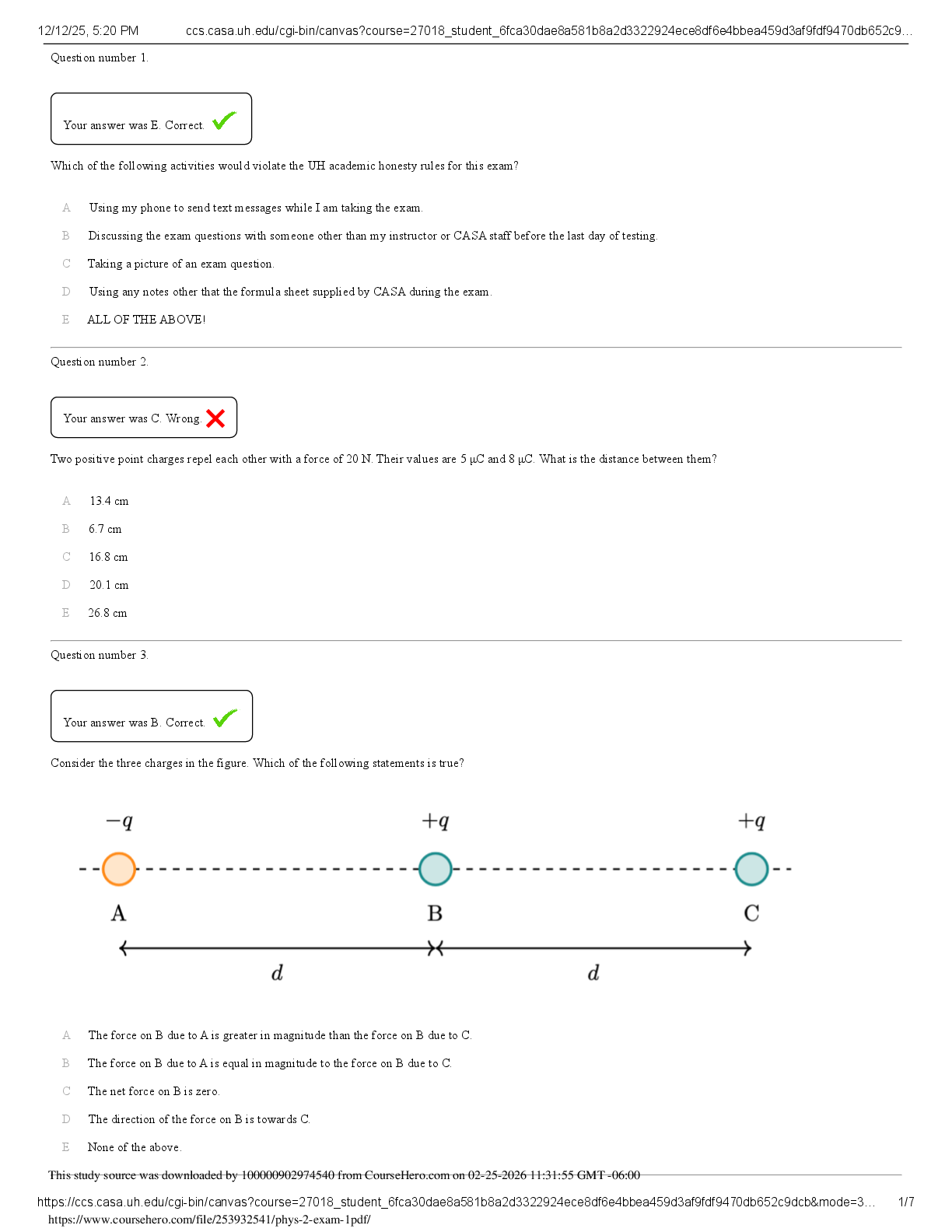
In the above figure, assume that S0 represents the industry supply curve and D0 represents the demand curve in a perfectly competitive market. What can be said about the demand curve that an individual firm faces?
A) An individual firm will face a vertical demand curve at 250.
B) An individual firm will face the demand curve indicated by D0.
C) An individual firm will face a horizontal demand curve at $1.25.
D) An individual firm will face a downward sloping demand curve starting at $1.25.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
12.
The above figure represents the cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is $4, then
A) the firm will be making zero economic profit.
B) the firm will be making positive economic profit.
C) the firm will be making negative economic profit.
D) the firm will shut down.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
13.
In the above figure, the left hand side graph represents a perfectly competitive industry and the right hand side graph represents a perfectly competitive firm. As the demand curve increases from D0 to D1,
A) the firm's output decreases from 9 to 8.
B) the firm's output decreases from 11 to 9.
C) the firm's output increases from 8 to 9.
D) the firm's output increases from 9 to 11.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
14.
If a perfectly competitive firm is making positive economic profits, then
A) it is operating in the short run.
B) it is operating in the long run.
C) it is producing at its minimum average total cost.
D) it is producing at its minimum average variable cost.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
15.
In a perfectly competitive industry, price equals marginal cost. Which of the following is NOT an implication of this?
A) Competitive firms maximize profits.
B) The product will be produced at the minimum average total cost in the long run.
C) The price of the product accurately reflects its cost to society.
D) A competitive firm sells its product at the opportunity cost of the product.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
16.
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by: P = 40 –Q, where P is the price of the good and Q is the quantity demanded. The marginal cost of production is constant and is equal to $2. There are no fixed costs of production. What price should the monopolist charge in order to maximize profit?
A) $2.
B) $38.
C) $42.
D) $21.
E) None of these.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
17.
A profit-maximizing monopolist with a positive marginal cost of production will always
A) produce on the elastic part of the demand curve.
B) produce on the inelastic part of the demand curve.
C) produce a higher level of output than a competitive firm.
D) produce where demand is unitary elastic.
E) earn a positive economic profit.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
18.
Suppose a monopolist faces the following demand curve: What is the marginal revenue of the 6th unit of output?
Price Quantity
$90
0
$80 1
$70 2
$60 3
$50 4
$40 5
$30 6
$20 7
A) $40
B) $10
C) $-10
D) $30
E) None of these.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
19.
Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a monopolist is -1. If price equals $10, then marginal revenue equals
A) $0
B) None of these.
C) $5
D) $10
E) $20
Table for Individual Question Feedback
20.
When a firm is able to charge each consumer exactly what they are willing to pay for a good, this is called
A) 1st degree price discrimination.
B) None of these.
C) 3rd degree price discrimination.
D) 2nd degree price discrimination.
E) 4th degree price discrimination.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
Submitted by ROBERTSON, KRISTI (KLR5625) on 4/3/2016 9:21:07 PM
Points Awarded 32.50
Points Missed 7.50
Percentage 81.2%
1.
You are operating a firm in a perfectly competitive market. In the short run, you have fixed costs of $30. Your variable costs are given in the following table:
Q TVC
0 0
1 70
2 120
3 150
4 190
5 270
6 360
Complete the following table:
Market Price Profit maximizing level of output Profit
$48
$52
$75
$85
Table for Individual Question Feedback
4.5/12.0
2.
A monopolist faces a demand curve given by
P = 105 – 3Q
where P is the price of the good and Q is the quantity demanded.
The marginal cost of production is constant and is equal to $15. There are no fixed costs of production.
Hint: To answer the following questions, it may be helpful to draw a graph!
What quantity should the monopolist produce in order to maximize profit?
What price should the monopolist charge in order to maximize profit?
How much profit will the monopolist make?
What is the deadweight loss created by this monopoly? (Hint: compare the monopoly outcome with the perfectly competitive outcome).
Monopoly deadweight loss =
If the market were perfectly competitive, what quantity would be produced?
Table for Individual Question Feedback
10.0/10.0
3.
Senior citizens can buy movie tickets at a lower price than the general public. This is an example of
A) demand discrimination.
B) price discrimination.
C) price differentiation.
D) age discrimination.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
4.
Which of the following is NOT necessary in order for a monopolist to practice effective price discrimination?
A) The marginal cost of providing the same good to different groups of buyers must be different.
B) The monopolist must have a downward sloping demand curve.
C) The buyers in various markets must face different price elasticities of demand.
D) The monopolist must be able to segregate its market into different submarkets.
Table for Individual Question Feedback
5.
Suppose a competitive firm can sell its output for $9 per unit. The following table gives the firm’s short run production function.
Labor Output
0 0
1 8
2 20
3 35
4 44
5 51
6 54
In the table below, you will determine several points on the firm’s demand curve for labor. To do this, you must determine how many workers the firm should hire for different values of the wage rate in order to maximize profit. Complete the table below:
Wage Rate
per Worker Quantity Demanded of Workers
$25
$60
$75
$90
Table for Individual Question Feedback
[Show More]