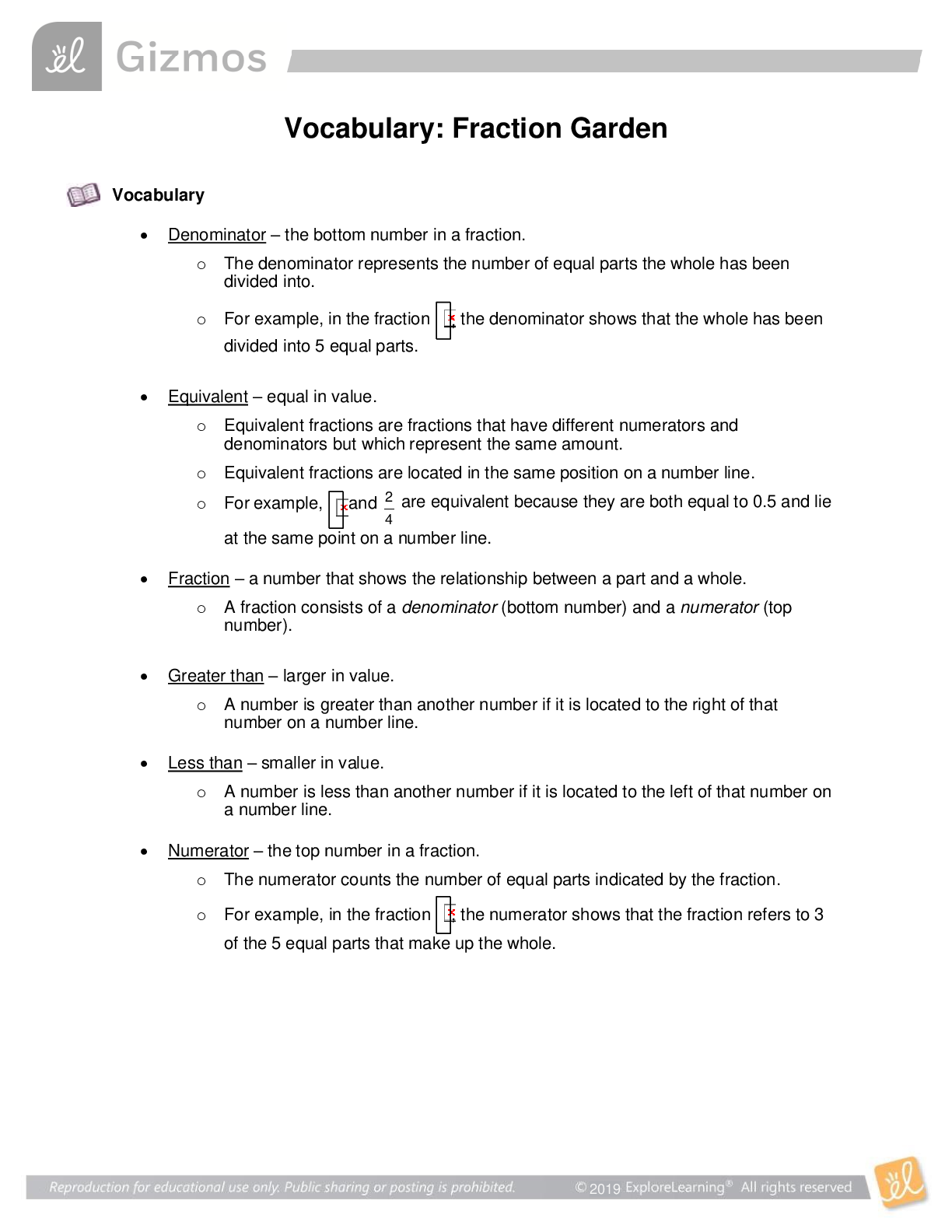
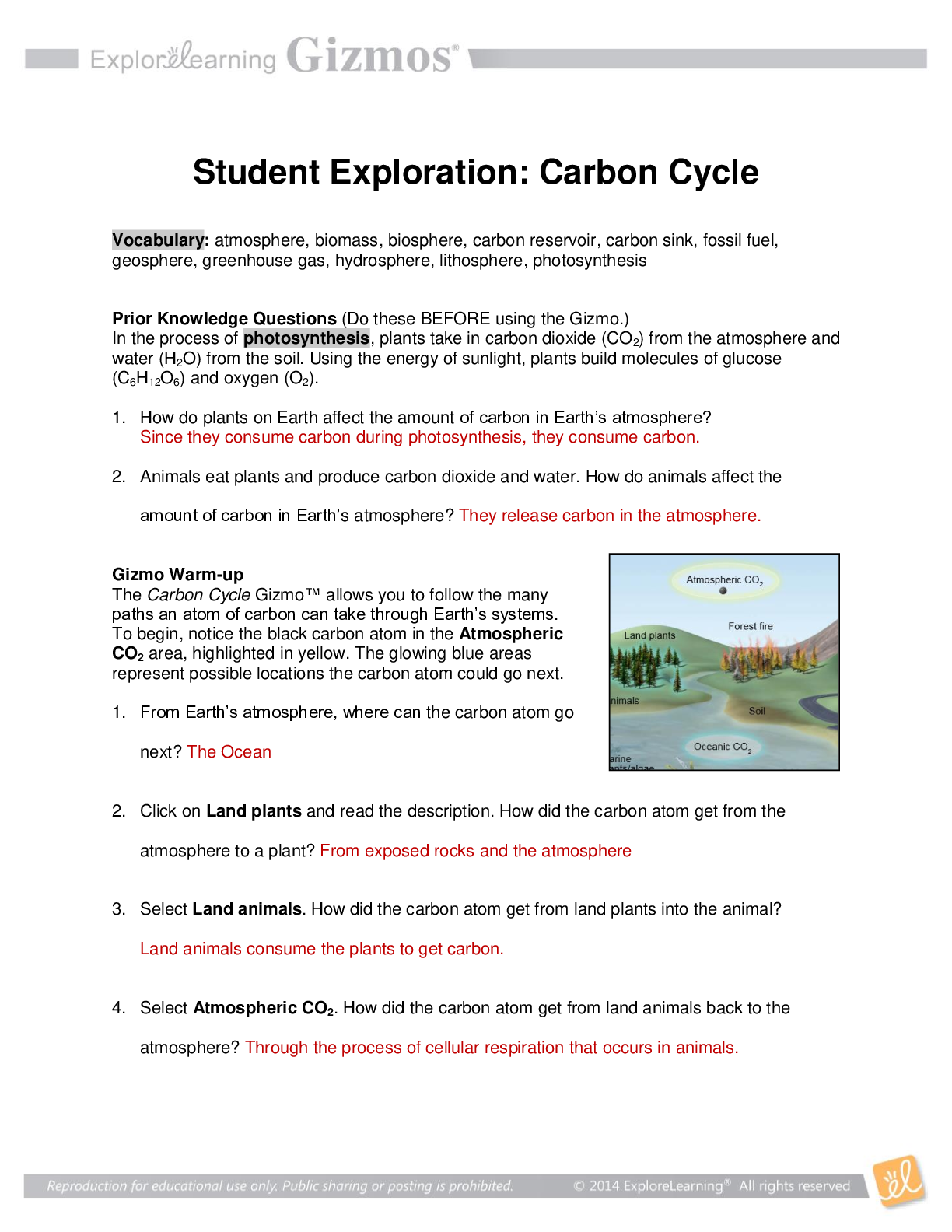
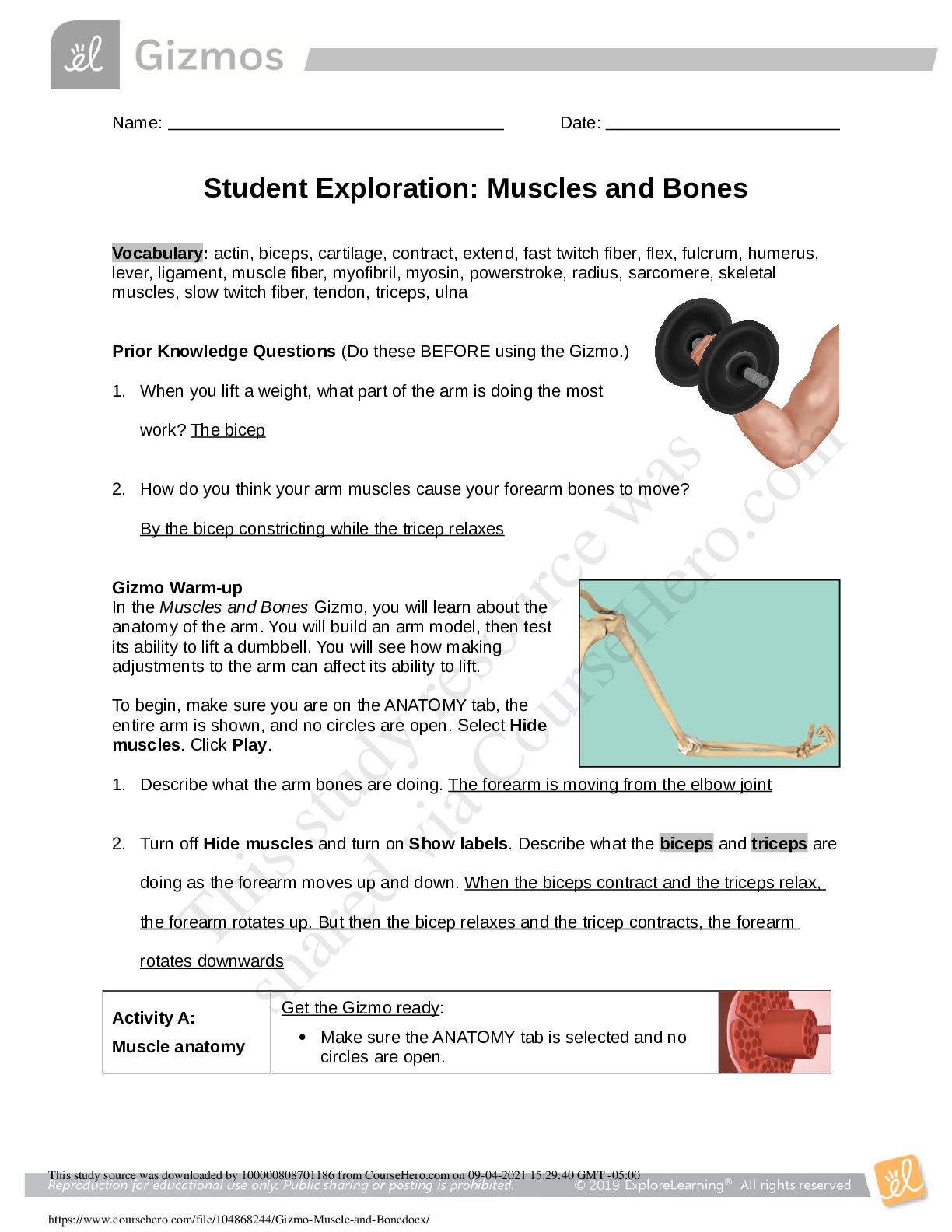
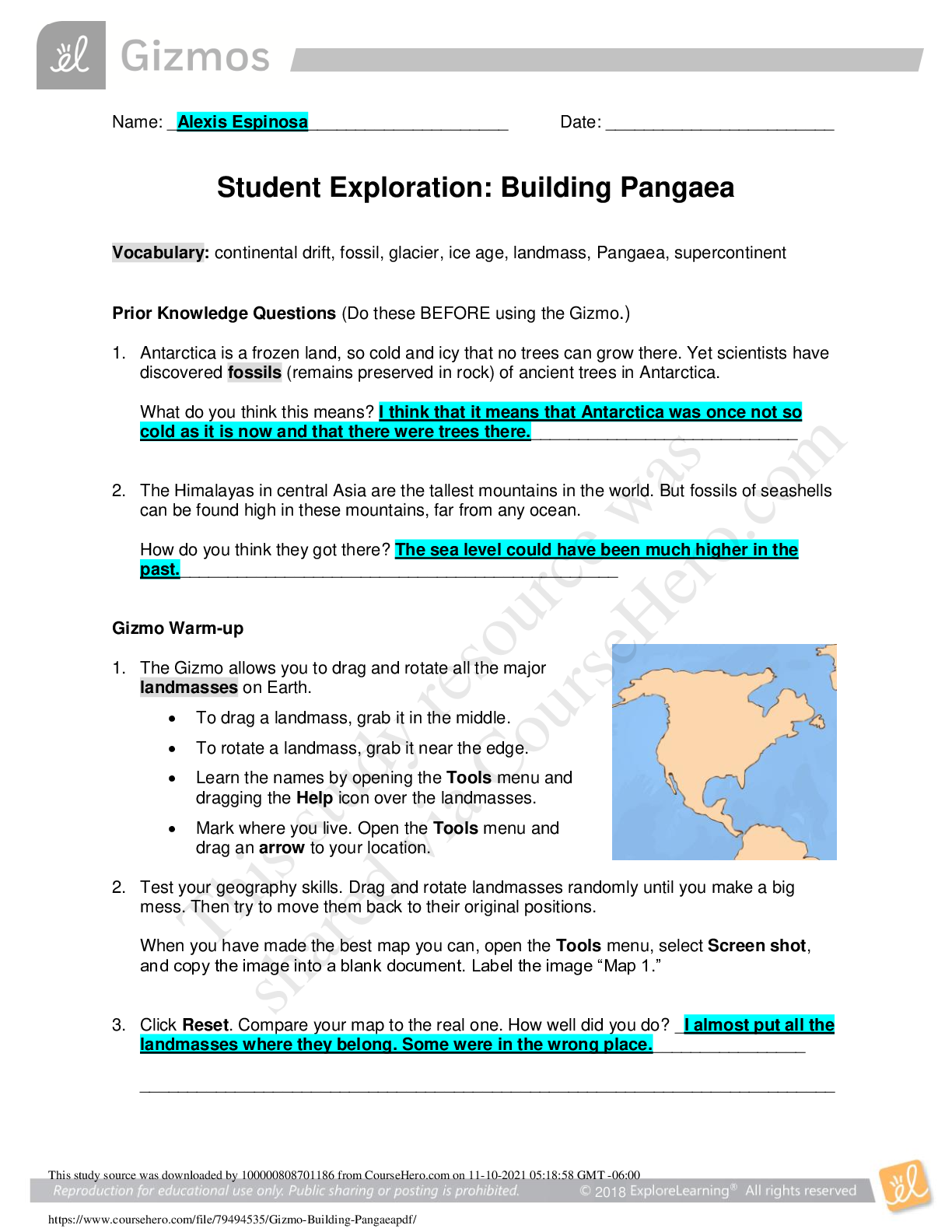
Student Exploration: Waves
Vocabulary: amplitude, compression, crest, frequency, longitudinal wave, medium, period,
power, rarefaction, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, wave speed
Prior Knowledge Questions (
...
Student Exploration: Waves
Vocabulary: amplitude, compression, crest, frequency, longitudinal wave, medium, period,
power, rarefaction, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, wave speed
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
1. A buoy is anchored to the ocean floor. A large wave approaches
the buoy. How will the buoy move as the wave goes by?
The buoy will move because the wave will push it.
2. The two images show side views of ocean waves. How are the two sets of waves different?
The two images showing the two
different sides of the ocean waves
are different because the first image
of the wave is higher than the
second image of the ocean wave.
Gizmo Warm-up
Ocean swells are an example of waves. In the Waves Gizmo™,
you will observe wave motion on a model of a spring. The hand
can move the spring up and down or back and forth.
To begin, check that the Type of wave is Transverse, Amplitude is 20.0 cm, Frequency is
0.75 Hz, Tension is 3.0 N, and Density is 1.0 kg/m. Click Play ( ).
1. How would you describe the motion of a transverse wave? In my opinion, I think that the
motion of this transverse wave is moving at right angles. Because, the speed stays the
same and the wave power doesn’t change either.
Click Pause ( ). Notice the crests (high points) and troughs (low points) of the wave.
2. Click Reset ( ). For the Type of wave, choose Longitudinal. Increase the Amplitude to
20.0 cm, and click Play. How would you describe the motion of a longitudinal wave?
I think, that the motion of this longitudinal wave is a wave that is going said to side but in a
slow speed.
Click Pause. Notice the compressions in the wave where the coils of the spring model are
close together and the rarefactions where the coils are spread apart.
[Show More]
 Exploration Waves.png)









 Exploration Natural Selection 1 Brandon Trigg.png)