BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Modul 2 Exam Questions with correct answers (All)
Modul 2 Exam Questions with correct answers
Document Content and Description Below
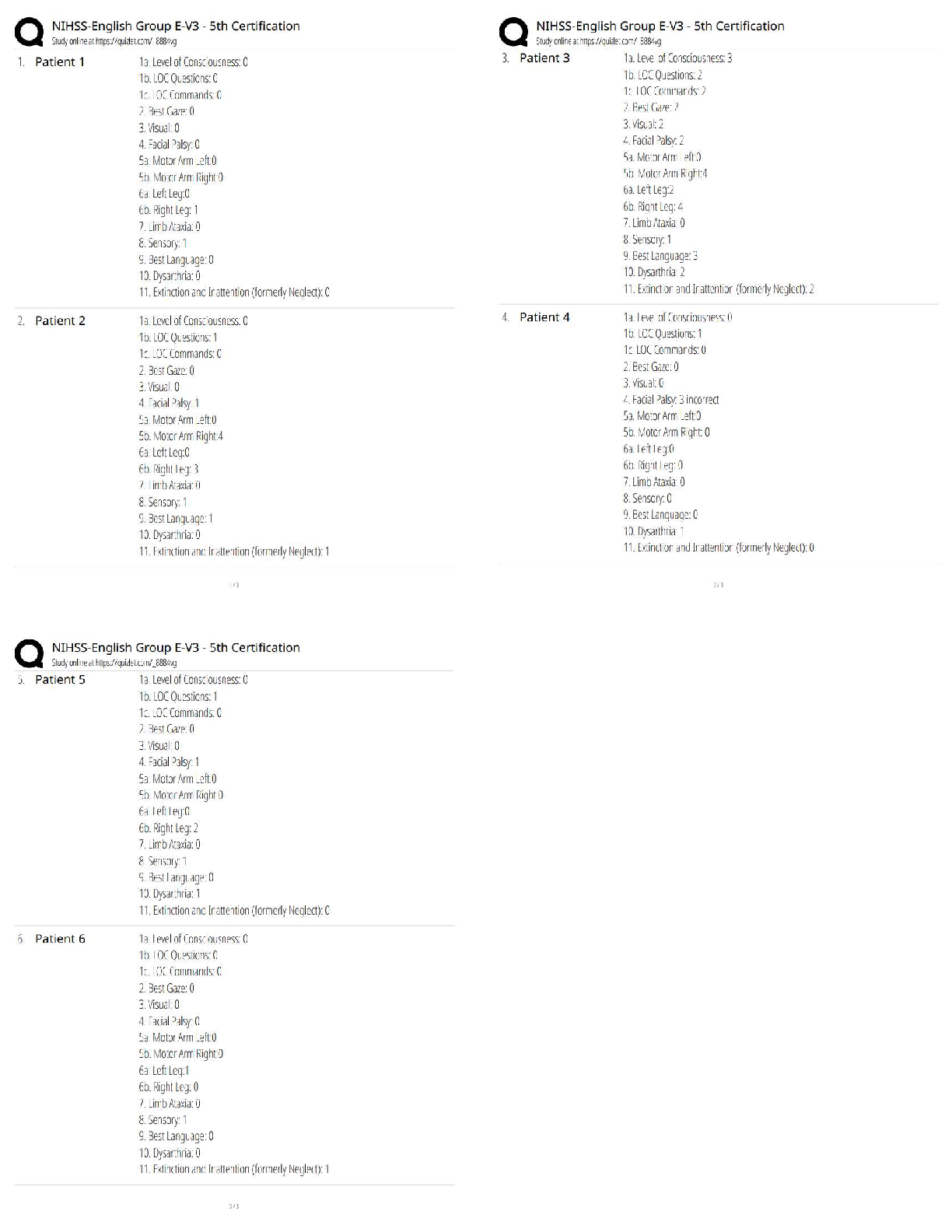
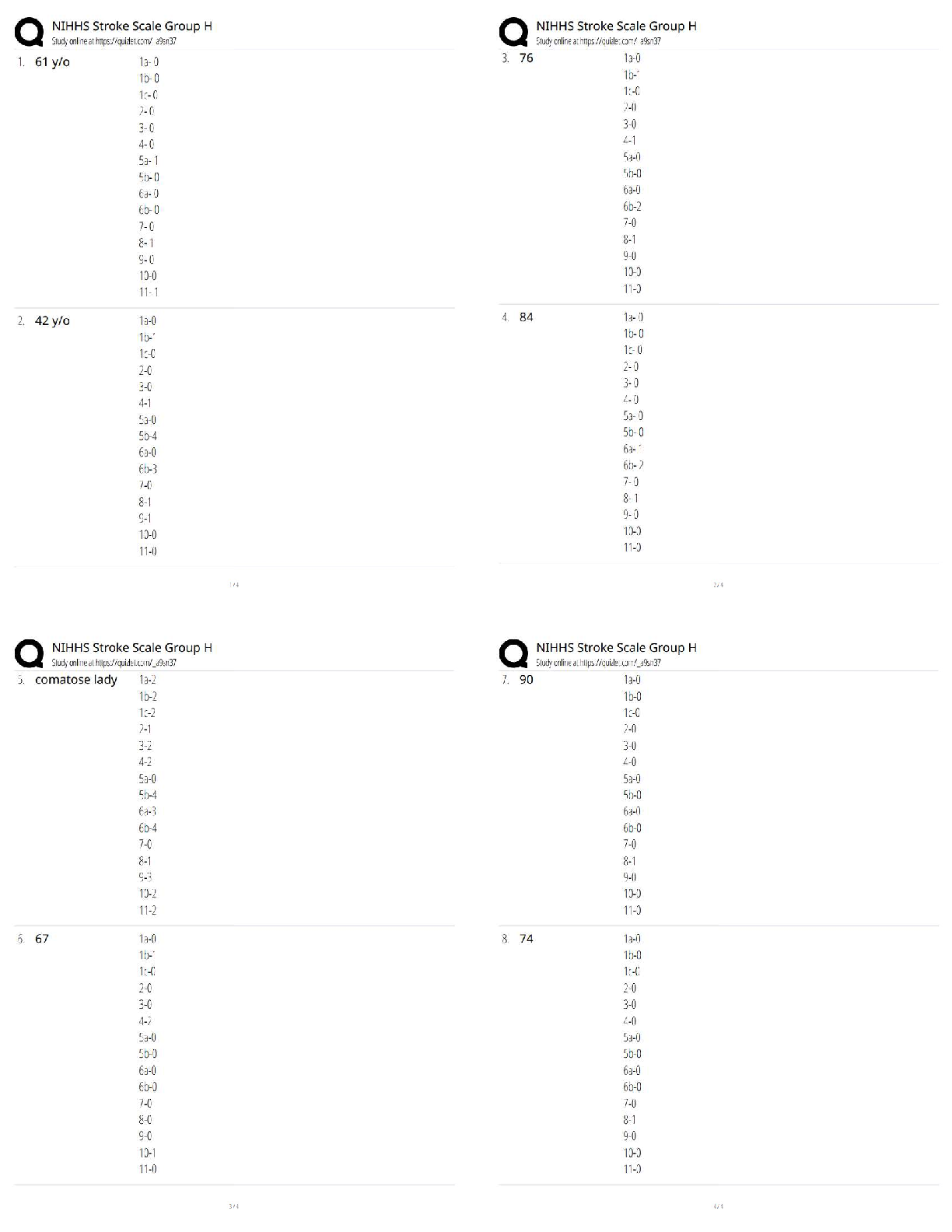
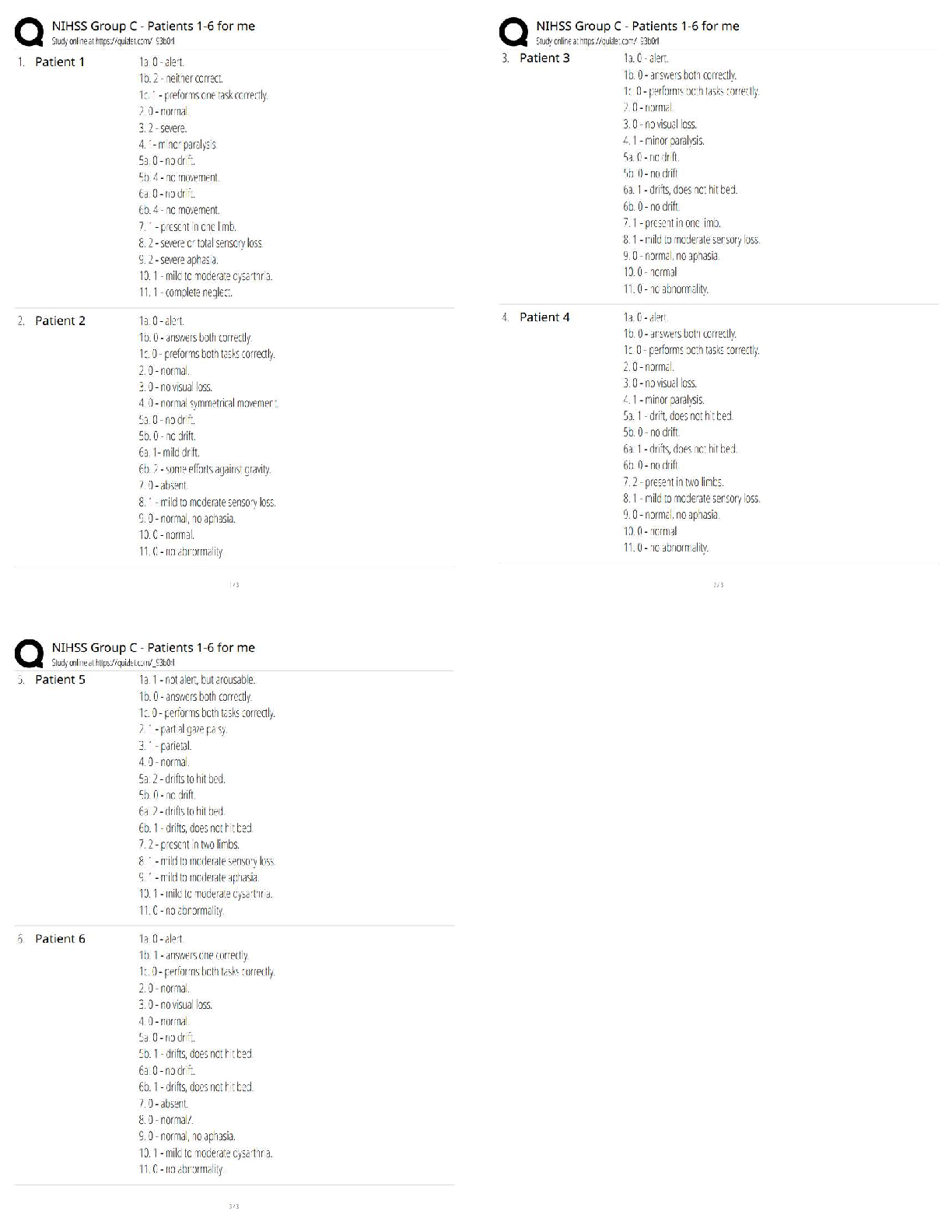
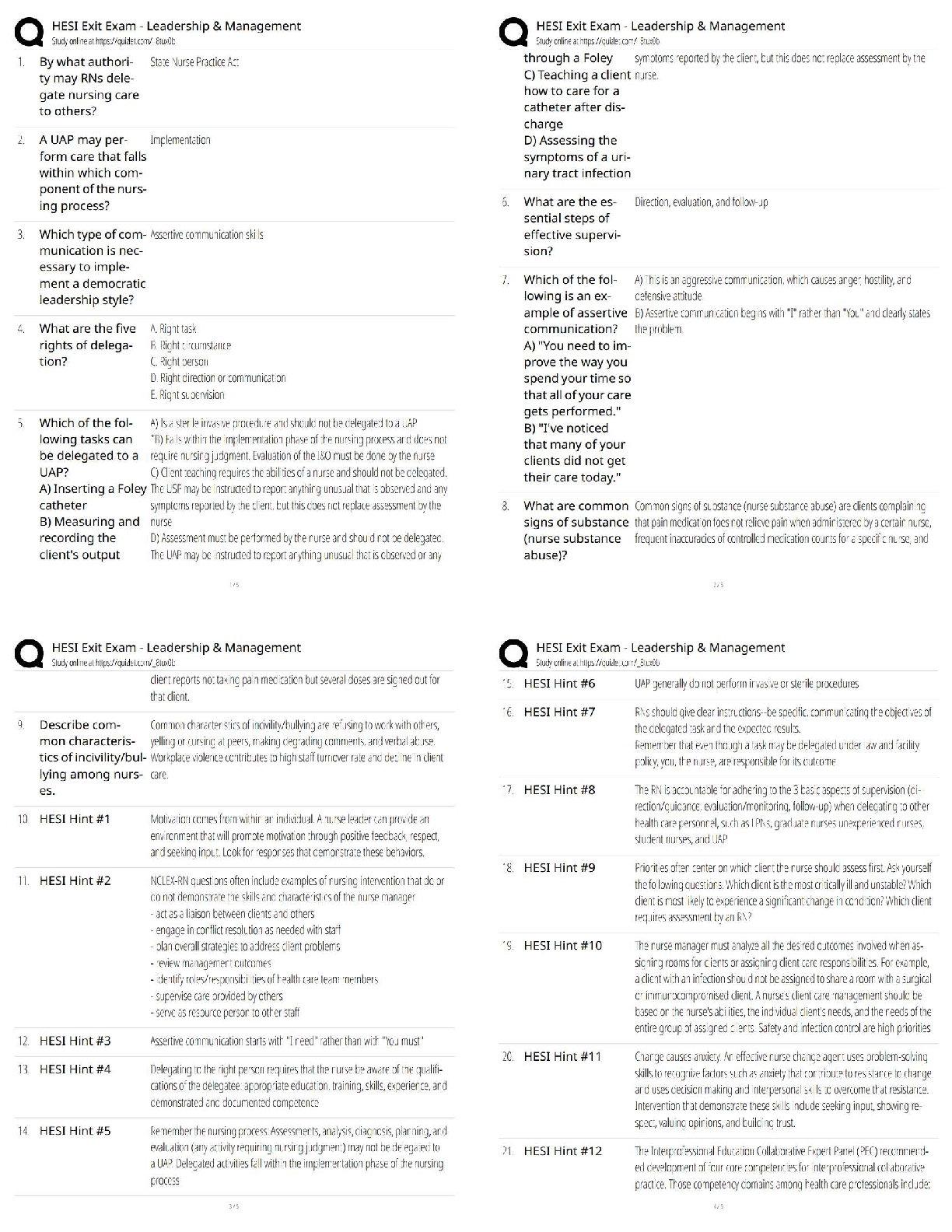
Question 1 4 / 4 pts How many lobes does the right human lung have? Your Answer: Three lobes. Three Lobes Question 2 3 / 3 pts Air and food pass in which one of the following areas: Trachea ... Nasopharynx Correct! Oropharynx Alveoli Question 3 3 / 3 pts Rings of cartilage line much of the respiratory tract. In which of one the following would cartilage NOT be found? Trachea Larynx Bronchi Correct! Alveoli Question 4 10 / 10 pts Label the following five items from the diagram: Label B- ___________ Label D- __________ Label E- __________ Label F- __________ Label G- __________ Your Answer: Label B- Oral Cavity Label D - Epiglottis Label E- Glottis Label F- Trachea Label G- Esophagus Label B- Oral Cavity Label D- Epiglottis Label E- Glottis Label F- Trachea Label G- Esophagus Question 5 5 / 5 pts Note: Essay answers must clearly be in your own words. Explain what happens to the epiglottis during swallowing. Why? Your Answer: When we swallow the epiglottis moves to block the entrance of food particles into our larynx and lungs. The muscles of the larynx pull upward to assist with this movement. They tightly close during swallowing. This prevents food from entering our lungs. The trachea is closed by the epiglottis. The epiglottis moves inferiorly, covering the trachea. This is to prevent food or liquid from entering the lungs. Question 6 5 / 5 pts Note: Essay answers must clearly be in your own words. Explain at least two differences between Type I and Type II alveolar cells. Your Answer: The type I cells is a complex branched cell with multiple cytoplasmic plates that are greatly attenuated and realatively devoid of organelles. Type I cells the very thin simple squamous epithelium of the alveoli junction with capillaries. Make up roughly 95 % of aleveolar epithelial cells. The Type II cells act as the 'caretaker' of the alveolar compartment. Type II produce and secrete pulmonary surfactant which is needed throughout the alveolar surface to keep the alveoli open. In addion, Type II cells can divide to replace damaged Type I cells. Make up roughly 5% of alveolar epithelial cells. a. Type I form the very thin simple squamous epithelium of the alveoli in junction with capillaries. Make up roughly 95% of alveolar epithelial cells. b. Type II produce and secrete pulmonary surfactant which is needed throughout the alveolar surface to keep the alveoli open. In addition, Type II cells can divide to replace damaged Type I cells. Make up roughly 5% of alveolar epithelial cells. Question 7 2 / 2 pts True/False: Positive pressure is used to move air into the lungs. True Correct! False (Negative pressure) Question 8 2 / 2 pts True/False: During inhalation the diaphragm contracts to pull the lungs open. Correct! True False Question 9 2 / 2 pts True/False: During inhalation the rib cage lifts in an upward motion to open and expand the lungs. Correct! True False Question 10 2 / 2 pts True/False: As the thoracic cavity expands and lung volume increases, the density of the gases filling the lungs decreases. Correct! True False Question 11 2 / 2 pts True/False: When the diaphragm rises, thoracic pressure increases and air naturally flows out of the lungs. Correct! True (air naturally flows out of the lungs because of the pressure difference) False Question 12 2 / 2 pts Boyle's law states that gas volume is: A. Directly proportional to temperature B. Inversely proportional to temperature C. Directly proportional to pressure Correct! D. Inversely proportional to pressure E. Both A and B Question 13 2 / 2 pts Which one of the following tracheal cartilages are paired? Thyroid Cricoid Correct! Arytenoid Epiglottal Hyaline Question 14 2 / 2 pts Which one of the following is not true of the pleurae? The pleurae are membranes that cover surfaces Parietal pleurae cover the surfaces surrounding the lungs Correct! Visceral pleurae cover the diaphragm A healthy pleural cavity is nearly empty of air or fluid Question 15 2 / 2 pts Which one of the following is not true of the respiratory physiology? Correct! Tidal volume is the maximum amount of air able to be inhaled beyond normal inhalation Tidal volume is the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in one cycle of quiet breathing Inspiratory reserve volume is the maximum amount of air able to be inhaled beyond normal inhalation Expiratory reserve volume is the maximum amount of air able to be exhaled beyond normal exhalation Question 16 2 / 2 pts Which one of the following is true of the respiratory physiology calculations? (You may find it helpful to draw the respiratory physiology diagram on a piece of scratch paper.) Vital Capacity (VC) = ERV+TV Correct! Total Lung Capacity (TLC) = VC +RV Inspiratory Capacity (IC) = TV+RV Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) = IRV + TV Question 17 2 / 2 pts True/False: The gas-exchange region in the lungs must be dry, thin and large. True Correct! False requires moisture Question 18 2 / 2 pts True/False: The vestibule is the most external portion of the nasal cavity. Correct! True False Question 19 2 / 2 pts True/False: The vestibule is lined with typical respiratory epithelium. True Correct! False stratified squamous epithelium is found in the vestibule Question 20 0 / 2 pts True/False: Because of diffusion, oxygen naturally moves out of the blood and into the lungs. You Answered True Correct Answer False Question 21 2 / 2 pts True/False: The bronchioles are surrounded by capillaries for gas exchange. True Correct! False Question 22 10 / 10 pts Matching: The pleural space fills with air, pus or blood. A. Emphysema This condition results from fluid-filled alveoli. B. Cystic Fibrosis This condition results in a loss of alveoli. C. Pulmonary edema This hereditary illness results in excess mucus. D. Pleurisy Correct! The pleural space fills with air, pus or blood. Correct! This condition results from fluid-filled alveoli. Correct! This condition results in a loss of alveoli. Correct! This hereditary illness results in excess mucus. Question 23 4 / 4 pts The pressure of three gases equals 1 atmosphere. What is the partial pressure of oxygen (in mmHG) if nitrogen is 300 mmHg and carbon dioxide is 350 mmHg? To receive full credit you must show your work. D. Pleurisy C. Pulmonary edema A. Emphysema B. Cystic Fibrosis Your Answer: 1 atm = 760 mmHg 300 mmHg+350 mmHg + X = 760 mmHg X = 110 mmHg 110 mmHG 1atm= 760 mmHg 300 mmHg + 350 mmHG + X = 760 mmHg OR: 760 - 300-350= 110 mmHG Question 24 3 / 3 pts Why would warming air be beneficial to gas exchange? Your Answer: The higher temperature the greater gas volume, or the lower temperature the lower gas volume. That's mean is Charles's Law. According to Charles's Law, the volume of a given quantity of gas is directly proportional to its temperature. Therefore the weather when be warm, gas volume greater. Warm air helps keep our lungs expanded in alveoli full and open and gas exchange can take place. It would expand the air to make it more available for gas exchange [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 20, 2022
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 20, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
138