*NURSING > EXAM > ACLS Final Comprehensive Test Bank Solution Guide Answered | Distinction Level Guide Has everything (All)
ACLS Final Comprehensive Test Bank Solution Guide Answered | Distinction Level Guide Has everything
Document Content and Description Below
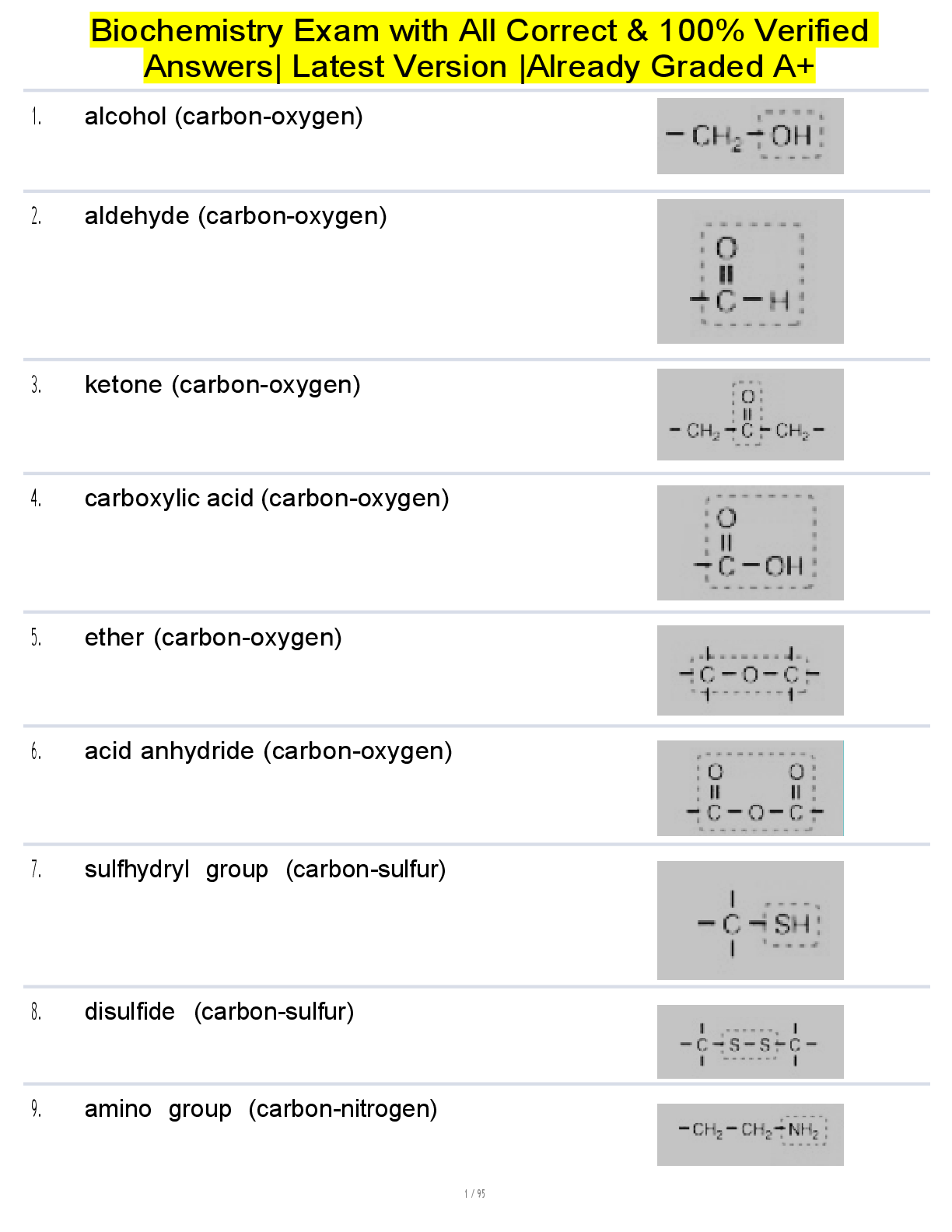
ACLS Final Comprehensive Test Bank Solution Guide updated 20255/2026 BLS & Chocking Relief of Adults, Children, Infants; Opioid Overdose; EKG interpretation; Cardiac anatomy; Team dynamics; BLS/Pri ... mary/Secondary Assessment; H's & T's; Airway Management; Bradycardia ACLS Algorithm; ACS ACLS Algorithm; Stroke ACLS Algorithm; Tachycardia ACLS Algorithm; Immediate Post-Cardiac Arrest Care ACLS Algorithm; Phamacology What is the most common cause of cardiac arrest in children? Correct Ans- respiratory failure or shock What is cardiac arrest? Correct Ans- occurs when the heart develops an abnormal rhythm and stops beating or beats too ineffectively to circulate blood to the brain and other vital organs What is heart attack? Correct Ans- A blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle. List the eight components of high quality CPR. Correct Ans- 1. Start compressions within 10 seconds of recognition of cardiac arrest. 2. Compress at a rate of 100-120/min with a depth of at least 2 inches in adults/children and 1 1/2 inches in infants. 3. Allow complete chest recoil after each compression. 4. Minimize interruptions in compressions (limit to <10 seconds). 5. Give effective breaths that make the chest visibly rise. 6. Switch compressors about every 2 minutes or earlier if fatigued. 7. Continue delivering chest compressions while the AED is charging. 8. Avoid prolonged rhythm analysis, frequent or inappropriate pulse checks, taking too long to give breaths to the patient, excessive ventilation, or unnecessarily moving the patient. What is the recommended compression depth for adults and children? Correct Ans- 2 inches What is the recommended compression depth for infants? Correct Ans- 1 1/2 inches What can result if a patient is ventilated too quickly? Correct Ans- hyperventilation -> excessive intrathoracic pressure and gastric inflation -> decreased venous return -> decreased coronary and cerebral perfusion pressures -> diminished cardiac output -> decreased rates of survival What memory aid may be used when evaluating a patient's level of consciousness? Correct Ans- AVPU Alert, responds to Verbal stimuli, responds to Painful stimuli, Unresponsive Upon finding an unresponsive adult patient, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- simultaneously look for breathing and feel for a carotid pulse for no more than 10 seconds Upon finding an unresponsive child, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- simultaneously look for breathing and feel for a carotid or femoral pulse for no more than 10 seconds Upon finding an unresponsive infant, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- simultaneously look for breathing and feel for a brachial pulse for no more than 10 seconds Upon finding an unresponsive adult patient, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient has no pulse and is not breathing normally. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- begin chest compressions; remove clothing; use AED as soon as it arrives Upon finding an unresponsive adult patient, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient is breathing normally and a pulse is present. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- continue to monitor until additional help arrives. Upon finding an unresponsive infant or child, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient has no pulse and is not breathing normally. The arrest was not sudden and not witnessed. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- begin chest compressions 30:2 (1 rescuer), 15:2 (2 rescuer); if 2 rescuers are present, one rescuer begins CPR and the other activates the ERS; use the AED as soon as it arrives; after about 2 min of CPR, if you are still alone, activate the ERS and get the AED if not already done Upon finding an unresponsive infant or child, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient has no pulse and is not breathing normally. The arrest was sudden and witnessed. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- activate the emergency response system and retrieve the AED; begin chest compressions 30:2 (1 rescuer), 15:2 (2 rescuer) Upon finding an unresponsive infant or child, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient is breathing normally and a pulse is present. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- activate ERS, return to victim and monitor until emergency responders arrive Upon finding an unresponsive adult patient, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient is not breathing normally but a pulse is present. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- provide rescue breathing (one breath every 5-6 seconds) and recheck for a pulse every 2 minutes; be ready to perform high quality CPR if you do not feel a pulse; if opioid use is suspected, consider administering naloxone Upon finding an unresponsive infant or child, you verified that the scene is safe, called for help and asked that someone get an AED or defibrillator. You check for breathing and a carotid pulse simultaneously. The patient is not breathing normally but a pulse is present. Your next action should be to: Correct Ans- provide rescue breathing (one every 3-5 seconds); add compressions if pulse remains <60/min with signs of poor perfusion; activate ERS after 2 min; continue rescue breathing and check pulse about every 2 min (if no pulse begin CPR) What is the purpose of the primary survey? Correct Ans- to detect the presence of life-threatening problems that require rapid interventions What two cardiac arrest rhythms are shockable? Correct Ans- VF and pVT What two cardiac arrest rhythms are not shockable? Correct Ans- asystole and PEA During the primary survey, for what length of time should you assess for the presence of a pulse? Correct Ans- at least 5 seconds but no more than 10 seconds What is the importance of measuring coronary perfusion pressure during CPR? Correct Ans- represents myocardial blood flow during chest compressions and is a key determinant of the success of resuscitation What is an adequate coronary perfusion pressure (CPP)? Correct Ans- 15 mm Hg What is the importance of measuring waveform capnography (PETCO2) during CPR? Correct Ans- allows for evaluation of CPR quality, optimize chest compressions, detection of ROSC during chest compressions or when a rhythm check reveals an organized rhythm, ET tube placement What is an adequate waveform capnogrpahy (PETCO2) range? Correct Ans- 10-20 mm Hg When ROSC occurs, what happens to waveform capnography? Correct Ans- There will be a significant increase in the ETCO2. (35-45 mmHg) This increase represents a drastic improvement in blood flow (more CO2 being dumped in the lungs by the circulation) which indicates circulation. What is chest compression fraction? Correct Ans- the proportion of time that chest compressions are performed during a cardiac arrest What is the target goal of chest compression fraction during CPR? Correct Ans- 60-80% What is the appropriate tidal volume for adult cardiac arrest patients? Correct Ans- 500-600 mL (half a squeeze of an adult ventilation bag; enough to see visible chest rise) Single rescuers should use the compression-to-ventilation ratio of ____ compressions to ____ breaths when giving CPR to victims of any age. Correct Ans- 30:2 At what rate should compressions occur? Correct Ans- 100-120/min Interruptions in chest compressions should be limited to how many seconds? Correct Ans- <10 Rescuers should switch compressors how often? Correct Ans- every 5 cycles (2 min) or sooner if fatigued What method should be utilized when opening the airway of a patient who is suspected of having a head or neck injury? Correct Ans- jaw thrust When communicating with a team member, the team leader communicates by taking these steps: 1. The team leader gives a message, order, or assignment to a team member. 2. By receiving a clear response and eye contact, the team leader confirms that the team member heard and understood the message. 3. The team leader listens for confirmation of task performance from the team member before assigning another task. What type of communication do these steps represent? Correct Ans- closed-loop communication Which pulse is palpated when performing a BLS assessment on an adult? Correct Ans- carotid What do agonal gasps represent? Correct Ans- not normal breathing; is a sign of cardiac arrest How does one palpate a carotid pulse? Correct Ans- locate the trachea; slide 2-3 fingers into the groove between the trachea and the muscles at the side of the neck; feel for at least 5 seconds but no more than 10 seconds When should the victim be moved during chest compressions? Correct Ans- never unless the victim is in a dangerous environment (such as a burning building) or if you believe you cannot perform CPR effectively in the victim's present position or location How does one properly perform chest compressions on an adult during resuscitation efforts? Correct Ans- 1. Make sure the victim is lying face-up on a firm surface. 2. Put the heel of one hand in the center of the victim's chest, on the lower half of the sternum. 3. Put the heel of your hand on top of the first hand. 4. Straighten your arms and position your shoulders directly over your hands. 5. Rate of 100-120/min. 6. Press down at least 2 in with each compression. 7. Allow for complete chest recoil. 8. Minimize interruptions in chest compressions. How does one properly perform the head tilt-chin lift technique? Correct Ans- 1. Place one hand on the victim's forehead and push with your palm to tilt the head back. 2. Place the fingers of the other hand under the bony part of the lower jaw near the chin. 3. Lift the jaw to bring the chin forward. How does one properly perform the jaw thrust maneuver? Correct Ans- 1. Place one hand on each side of the victim's head. You may rest your elbows on the surface on which the victim is lying. 2. Place your fingers under the angles of the victim's lower jaw and lift with both hands, displacing the jaw forward. 3. If the lips close, push the lower lip with your thumb to open the lips. How does one properly use a pocket mask to deliver breaths using the head tilt-chin lift technique? Correct Ans- 1. Position yourself at the victim's side. 2. Place the pocket mask on the victim's face, using the bridge of the nose as a guide for correct position. 3. Seal the pocket mask against the face. Using the hand that is closer to the top of the victim's head, place the index finger and thumb along the edge of the mask. Place the thumb of your other hand along the edge of the mask. 4. Place the remaining fingers of your second hand along the bony margin of the jaw and lift the jaw. Perform a head tilt-chin lift to open the airway. 5. While you lift the jaw, press firmly and completely around the outside edge of the mask to seal the pocket mask against the face. 6. Deliver each breath over 1 second, enough to make the victim's chest rise. How does one properly use a bag mask device to deliver breaths? Correct Ans- 1. Position yourself directly above the victim's head. 2. Place the mask on the victim's face, using the bridge of the nose as a guide for correct position. 3. Use the E-C clamp technique to hold the mask in place while you lift the jaw to hold the airway open. 4. Squeeze the bag to give breaths (1 second each) while watching for chest rise. A 53-year-old man suddenly collapses and becomes unresponsive. You witness him collapse and are the first rescuer to arrive at the scene. You find him lying motionless on the floor. What is the first action you should take in this situation? Correct Ans- verify that the scene is safe for you and the victim A 53-year-old man suddenly collapses and becomes unresponsive. You witness him collapse and are the first rescuer to arrive at the scene. You find him lying motionless on the floor. The man doesn't respond when you touch his shoulder and shout, "Are you OK?" What is your best next action? Correct Ans- check for breathing and carotid pulse; shout for nearby help A 53-year-old man suddenly collapses and becomes unresponsive. You witness him collapse and are the first rescuer to arrive at the scene. You find him lying motionless on the floor. Several rescuers respond, and you ask them to activate the emergency response and retrieve the AED and emergency equipment. As you check for a pulse and breathing, you notice that the man is gasping for air and making "snorting" sounds. You do not feel a pulse. What is your best next action? Correct Ans- start high-quality CPR, beginning with chest compressions How does one properly use an AED? Correct Ans- 1. Open the carrying case and power on the AED. 2. Attach AED pads to the victim's bare chest. 3. When the AED prompts you, clear the victim and allow the AED to analyze the rhythm. 4. Resume chest compressions while the AED is charging. 5. Clear the victim when delivering a shock; resume compressions after the shock has been delivered. 6. If no shock is needed, immediately resume CPR starting with chest compressions. What are the two correct methods for placement of AED pads? Correct Ans- Method 1. AKA Anterolateral Placement. Place one AED pad directly below the right collarbone. Place the other pad to the right side of the left nipple, with the top edge of the pad a few inches below the arm pit. Method 2. AKA Anteroposterior Placement. Place one AED pad on the left side of the chest, between the victim's left side of the breastbone and left nipple. Place the other pad on the left side of the victim's back, next to the spine. When placing AED pads on a patient with an implanted defibrillator or pacemaker, what precautions should be taken? Correct Ans- avoid placing AED pad directly over the implanted device What is the most appropriate first step to take as soon as the AED arrives at the victim's side? Correct Ans- power on the AED What action should you take when the AED is analyzing the heart rhythm? Correct Ans- stand clear of the victim How does one properly palpate a brachial pulse on an infant? Correct Ans- 1. Place 2-3 fingers on the inside of the upper arm, midway between the elbow and the shoulder. 2. Then press the fingers to attempt to feel the pulse for at least 5 seconds but no more than 10 seconds. How does one properly palpate a femoral pulse on a child? Correct Ans- 1. Place 2 fingers in the inner thigh, midway between the hipbone and the pubic bone and just below the crease where the leg meets the torso. 2. Feel for a pulse for at least 5 but no more than 10 seconds. What pulse location should be palpated when assessing an unresponsive infant? Correct Ans- brachial What pulse location should be palpated when assessing an unresponsive child? Correct Ans- femoral or carotid What is the correct hand placement for performing high-quality chest compressions on a child? Correct Ans- 2 hands or 1 hand (optional for small child) on the lower half of the sternum What is the correct hand placement for performing high-quality chest compressions on an infant? Correct Ans- 1 rescuer: 2 fingers in the center of the chest, just below the nipple line 2 or more rescuers: 2 thumb-encircling hands in the center of the chest, just below the nipple line What are some signs of poor perfusion? Correct Ans- cool extremities, altered mental status, weak pulses, pale skin, mottling, cyanosis What is the correct compression ratio for children and infants when two rescuers are present? Correct Ans- 15:2 How does one properly perform 2 finger compression technique on an infant? Correct Ans- 1. Place the infant on a firm, flat surface. 2. Place 2 fingers in the center of the infant's chest, just below the nipple line, on the lower half of the breastbone. 3. Give compressions at a rate of 100-120/min. 4. Compress at least one third the AP diameter of the infant's chest (about 1 1/2 in). 5. Allow for complete chest recoil. Minimize interruptions to less than 10 seconds. 6. After every 30 compressions, open the airway using head tilt-chin lift method and deliver two breaths. 7. After about 5 cycles (2 min) of CPR, if you are alone and the ERS has not been activated, leave the infant (or carry the infant with you) and activate the ERS and retrieve the AED. 8. Continue compressions and breaths at 30:2 ratio and use the AED as soon as it arrives. Continue until advanced providers take over or the infant begins breathing or moving. How does one properly perform 2 thumb-encircling hands technique on an infant? Correct Ans- 1. Place the infant on a firm, flat surface. 2. Place both thumbs side by side in the center of the infant's chest, on the lower half of the breastbone. Thumbs may overlap in small infants. 3. With your hands encircling the chest, use both thumbs to depress the breastbone at a rate of 100-120/min. 4. Compress at least one third the AP diameter of the infant's chest (about 1 1/2 in). 5. After each compression, completely release the pressure on the breastbone and allow the chest to recoil completely. 6. After every 15 compressions, pause briefly for the second rescuer to open the airway with a head tilt-chin lift and give 2 breaths, each over 1 sec. 7. Continue compressions and breaths in a ratio of 15:2 (2 rescuer). The rescuer providing chest compressions should switch roles with another provider about every 5 cycles (2 min). Continue CPR until the AED arrives, advanced providers take over, or the infant begins to breath/move. Why is it important to ensure that the infant's head is kept in the neutral position? Correct Ans- if you tilt (extend) an infant's head beyond the neutral (sniffling) position, the infant's airway may become blocked; you should ensure the infant's neck is in a neutral position so that the external ear canal is level with the top of the infant's shoulder What is the correct compression-to-ventilation ratio for a single rescuer of a 3-year-old child? Correct Ans- 30:2 What is the correct compression-to-ventilation ratio for a 7-year-old child when 2 rescuers or more are present? Correct Ans- 15:2 Adult pads should be used on what age victim? Correct Ans- 8 years and older; may use them on infants if you do not have child pads What are two ways to open the victim's airway? Correct Ans- head tilt-chin lift and jaw thrust If the chest does not rise when you give a breath, what should you do? Correct Ans- reposition the head and try again >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>CONTUES.........................................Purchase for a complete solution guide. [Show More]
Last updated: 9 months ago
Preview 5 out of 47 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 21, 2022
Number of pages
47
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 21, 2022
Downloads
4
Views
838





.png)