
NursingExam3StudyGuide
$ 9

SEC 572 Week 8 Final Exam - Latest 2019/20 complete solution guide, Devry
$ 10

MGT 6311 FINAL EXAM LATEST UPDATE WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 7

NCLEX RN LATEST TESTBANK
$ 65

C785 Unit 2 Quiz 2022
$ 13

NRS 430V Topic 2 Assignment, Contemporary Nursing Practice
$ 12

NURS 329 Final Exam.NURSING INFORMATICS FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
$ 35
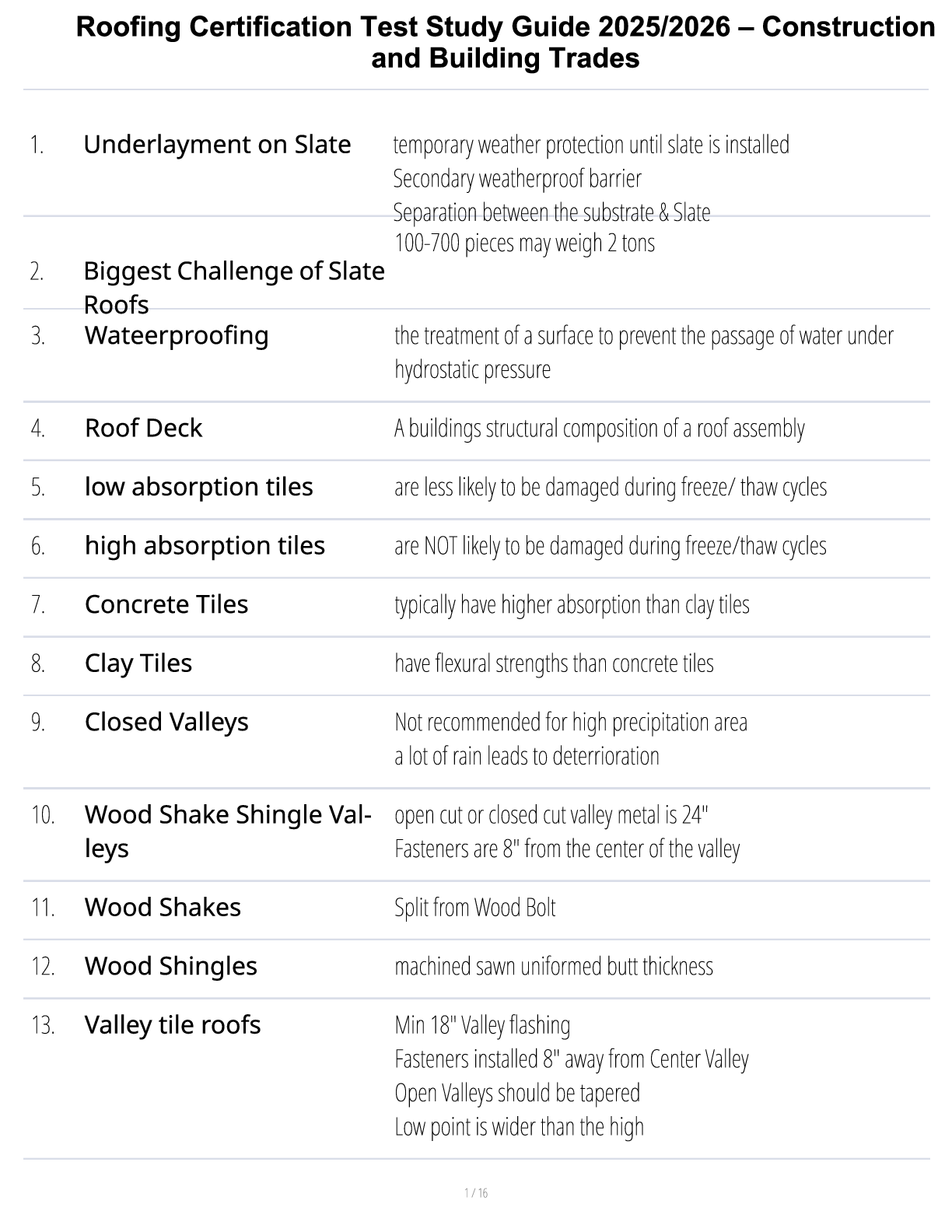
Roofing Certification Test Study Guide 2025/2026 – Construction and Building Trades
$ 12.5

HESI MED-SURG II LATEST UPDATE 2024-2025 COMPLETE 150 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS
$ 10

SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS, EXERCISES, AND PROBLEMS


























