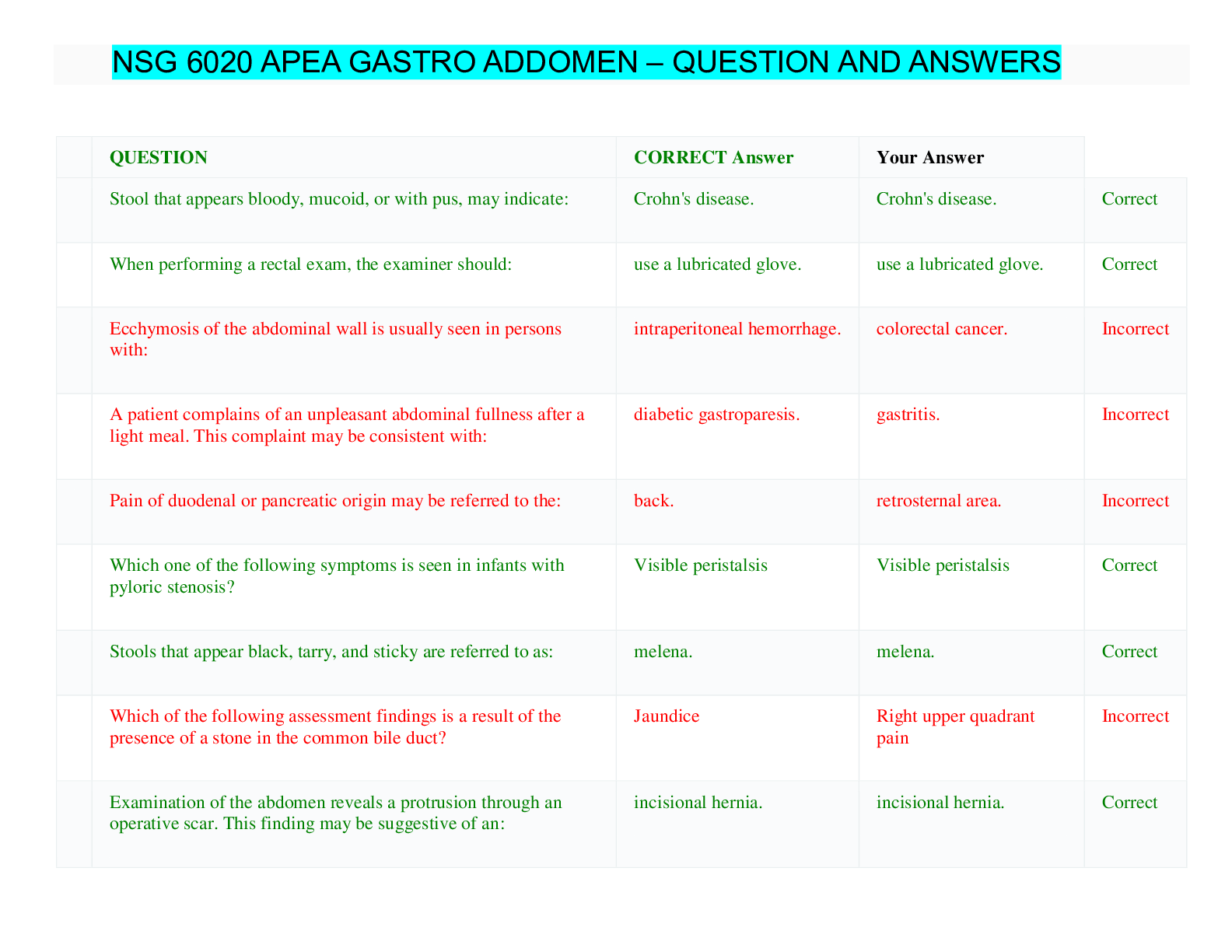
*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NSG 6020 Weeks 7-8-9 (answered) South University. (All)
NSG 6020 Weeks 7-8-9 (answered) South University.
Document Content and Description Below
NSG 6020 week 7-8-9. A 22-year-old architecture major comes to your office, complaining of severe burning with urination, a fever of 101 degrees, and aching all over. She denies any upper respiratory... , gastrointestinal, cardiac, or pulmonary symptoms. Her past medical history consists of severe acne. She is currently on an oral contraceptive. She has had no pregnancies or surgeries. She reports one new partner within the last month. She does not smoke but does drink occasionally. Her parents are both in good health. On examination you see a young woman appearing slightly ill. Her temperature is 100.3 and her pulse and blood pressure are unremarkable. Her head, ears, eyes, nose, throat, cardiac, pulmonary, and abdominal examinations are unremarkable. Palpation of the inguinal nodes shows lymphadenopathy bilaterally. On visualization of the perineum there are more than 10 shallow ulcers along each side of the vulva. Speculum and bimanual examination are unremarkable for findings, although she is very tender at the introitus. Urine analysis has some white blood cells but no red blood cells or bacteria. Her urine pregnancy test is negative. Which disorder of the vulva is most likely in this case? A) Genital herpes B) Condylomata acuminata C) Syphilitic chancre D) Epidermoid cyst A 42-year-old realtor comes to your clinic, complaining of "growths" in her vulvar area. She is currently undergoing a divorce and is convinced she has a sexually transmitted disease. She denies any vaginal discharge or pain with urination. She has had no fever, malaise, or night sweats. Her past medical history consists of depression and hypothyroidism. She has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries and one cesarean section. She has had no other surgeries. She denies smoking or drug use. She has two to three drinks weekly. Her mother also has hypothyroidism and her father has high blood pressure and hypercholesterolemia. On examination you see a woman who is anxious but appears otherwise healthy. Her blood pressure, pulse, and temperature are unremarkable. On visualization of the perineum you see two 2- to 3-mm, round, yellow nodules on the left labia. On palpation they are nontender and quite firm. What diagnosis best fits this description of her examination? A) Genital herpes B) Condylomata acuminata C) Syphilitic chancre D) Epidermoid cyst A 30-year-old paralegal analyst comes to your clinic, complaining of a bad-smelling vaginal discharge with some mild itching, present for about 3 weeks. She tried douching but it did not help. She has had no pain with urination or with sexual intercourse. She has noticed the smell increased after intercourse and during her period last week. She denies any upper respiratory, gastrointestinal, cardiac, or pulmonary symptoms. Her past medical history consists of one spontaneous vaginal delivery. She is married and has one child. She denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. Her mother has high blood pressure and her father died from a heart disease. On examination she appears healthy and has unremarkable vital signs. On examination of the perineum there are no lesions noted. On palpation of the inguinal nodes there is no lymphadenopathy. On speculum examination a thin gray-white discharge is seen in the vault. The pH of the discharge is over 4.5 and there is a fishy odor when potassium hydroxide (KOH) is applied to the vaginal secretions on the slide. Wet prep shows epithelial cells with stippled borders (clue cells). What type of vaginitis best describes her findings? A) Trichomonas vaginitis B) Candida vaginitis C) Bacterial vaginosis D) Atrophic vaginitis A 48-year-old high school librarian comes to your clinic, complaining of 1 week of heavy discharge causing severe itching. She is not presently sexually active and has had no burning with urination. The symptoms started several days after her last period. She just finished a course of antibiotics for a sinus infection. Her past medical history consists of type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure. She is widowed and has three children. She denies tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. Her mother has high blood pressure and her father died of diabetes complications. On examination you see a healthy-appearing woman. Her blood pressure is 130/80 and her pulse is 70. Her head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are unremarkable. Palpation of the inguinal lymph nodes is unremarkable. On visualization of the vulva, a thick, white, curdy discharge is seen at the introitus. On speculum examination there is a copious amount of this discharge. The pH of the discharge is 4.1 and the KOH whiff test is negative, with no unusual smell. Wet prep shows budding hyphae. What vaginitis does this patient most likely have? A) Trichomonas vaginitis B) Candida vaginitis C) Bacterial vaginosis D) Atrophic vaginitis A 55-year-old married homemaker comes to your clinic, complaining of 6 months of vaginal itching and discomfort with intercourse. She has not had a discharge and has had no pain with urination. She has not had a period in over 2 years. She has no other symptoms. Her past medical history consists of removal of her gallbladder. She denies use of tobacco, alcohol, and illegal drugs. Her mother has breast cancer and her father has coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and Alzheimer's disease. On examination she appears healthy and has unremarkable vital signs. There is no lymphadenopathy with palpation of the inguinal nodes. Visualization of the vulva shows dry skin but no lesions or masses. The labia are somewhat smaller than usual. Speculum examination reveals scant discharge and the vaginal walls are red, dry, and bleed easily. Bimanual examination is unremarkable. The KOH whiff test produces no unusual odor and there are no clue cells on the wet prep. What form of vaginitis is this patient most likely to have? A) Trichomonas vaginitis B) Candida vaginitis C) Bacterial vaginosis D) Atrophic vaginitis A 28-year-old married clothing sales clerk comes to your clinic for her annual examination. She requests a refill on her birth control pills. Her only complaint is painless bleeding after intercourse. She denies any other symptoms. Her past medical history consists of two spontaneous vaginal deliveries. Her past six Pap smears have all been normal. She is married and has two children. Her mother is in good health and her father has high blood pressure. On examination you see a young woman appearing healthy and relaxed. Her vital signs are unremarkable and her head, eyes, ears, throat, neck, cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. Visualization of the perineum shows no lesions or masses. Speculum examination shows a red mass at the os. On taking a Pap smear the mass bleeds easily. Bimanual examination shows no cervical motion tenderness and both ovaries are palpated and nontender. What is the most likely diagnosis for the abnormality of her cervix? A) Carcinoma of the cervix B) Mucopurulent cervicitis C) Cervical polyp D) Retention cyst An 18-year-old college freshman comes to your clinic, complaining of severe left-sided lower abdominal pain and a foul yellow discharge. The pain began last night while she was having intercourse with her boyfriend. Afterward the pain became more severe and the discharge started. By this morning she had a fever of 101 degrees and walking was making the pain worse. Only lying very still makes the pain better. She has tried ibuprofen and acetaminophen without any improvement. She denies any nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She has had two past sexual partners. She uses the birth control patch instead of condoms. She smokes a half pack of cigarettes a day and drinks four to five beers per weekend night. She denies any illegal drug use. Her parents are both healthy. On examination you find a young woman who appears ill. Her temperature is 102 degrees and her pulse is elevated at 110. She is tender in the left lower quadrant but has no guarding or rebound. Speculum examination reveals yellow purulent drainage from the os. On palpation there is cervical motion tenderness and the left adnexa is swollen and tender. A urine analysis is unremarkable and the urine pregnancy test is pending. What is the best choice of diagnosis for this adnexal swelling? A) Ovarian cyst B) Tubal pregnancy C) Pelvic inflammatory disease A 34-year-old married daycare worker comes to your office, complaining of severe pelvic pain for the last 6 hours. She states that the pain was at first cramp-like but is now sharp. Nothing makes the pain better or worse. She has had no vaginal bleeding or discharge. She has had no pain with urination. She has had some nausea for the last few days but denies vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea. She states she feels so bad that when she stands up she has fainted. Her past medical history consists of two prior cesarean sections and an appendectomy. She is married and has two children. She denies any tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. Her parents are both healthy. On examination you find a pale young woman who is obviously in a great deal of pain. She is lying on her right side with her eyes closed. Her blood pressure is 90/60 and her pulse is 110. She is afebrile. She has bowel sounds and her abdomen is soft. The speculum examination reveals a bluish cervix but no blood or purulent discharge at the os. There is a mild amount of tenderness with palpation of the cervix. The uterus is nongravid but the right adnexal area is swollen and very tender. Urine analysis is normal and the urine pregnancy test is pending. What type of adnexal disorder is causing her pain? A) Ovarian cysts B) Tubal pregnancy C) Pelvic inflammatory disease A 23-year-old waitress comes to your clinic complaining of severe pelvic pain radiating to her right side. The pain began yesterday and is getting much worse. She has had no burning with urination and denies any recent sexual activity. She has no nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, fever, or vaginal discharge. Her last period was 3 to 4 weeks ago. Her past medical history consists of severe acne, depression, and mild obesity. She has had no surgeries. She broke up with her boyfriend 6 months ago and denies dating anyone else. She smokes one pack of cigarettes a day, drinks three to four beers two to three times a week, and denies any illegal drug use. Her mother is diabetic and her father has coronary artery disease. On examination you see a mildly obese female in moderate distress. Her blood pressure is 130/80 and her pulse is 90. She is afebrile. On auscultation she has active bowel sounds. She has no rebound or guarding in any abdominal quadrant. Speculum examination shows no lesions on the cervix and no discharge or bleeding from the os. During the bimanual examination she has no cervical motion tenderness, but her right adnexal area is swollen and tender. A urine analysis is normal and the urine pregnancy test is pending. What disorder of the adnexa is most likely the diagnosis? A) Ovarian cyst B) Tubal pregnancy C) Pelvic inflammatory disease A 24-year-old travel agent comes to your clinic, complaining of pain and swelling in her vulvar area. She states that 2 days earlier she could feel a small tender spot on the left side of her vagina but now it is larger and extremely tender. Her last period was 1 year ago and she is sexually active. She uses the Depo-Provera shot for contraception. She denies any nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, pain with urination, or fever. Her past medical history is significant for ankle surgery. Her mother is healthy and her father has type 2 diabetes. On examination she appears her stated age and is standing up. She states she cannot sit down without excruciating pain. Her blood pressure, temperature, and pulse are unremarkable. On visualization of her perineum, a large, red, tense swelling is seen to the left of her introitus. Palpation of the mass causes a great deal of pain. What disorder of the vulva is most likely causing her problems? A) Bartholin's gland infection B) Vulvar carcinoma C) Secondary syphilis D) Condylomata acuminata Which of the following represents metrorrhagia? A) Fewer than 21 days between menses B) Excessive flow C) Infrequent bleeding D) Bleeding between periods Jean has just given birth 6 months ago and is breast-feeding her child. She has not had a period since giving birth. What does this most likely represent? A) Primary amenorrhea B) Secondary amenorrhea C) Oligomenorrhea D) Dysmenorrhea Mrs. Jaeger is a 67-year-old who went through menopause at age 55. She has now had some vaginal bleeding. Which of the following should be considered? A) Endometrial cancer B) Hormone replacement therapy C) Uterine or cervical polyps D) All of the above Abby is a newly married woman who is unable to have intercourse because of vaginismus. Which of the following is true? A) This is most likely due to lack of lubrication. B) This is most likely due to atrophic vaginitis. C) This is most likely due to pressure on an ovary. D) Psychosocial reasons may cause this condition. Which of the following is true of human papilloma virus (HPV) infection? A) Pap smear is a relatively ineffective screening method. B) It commonly resolves spontaneously in 1-2 years. C) It is the second most common STI in the United States. D) HPV infections cause a small but important number of cervical cancers. Which of the following is true of the HPV vaccine? A) Ideally it should be administered within 3 years of first intercourse. B) It covers against almost every HPV type. C) It can be used as adjuvant therapy in cervical cancer. D) It can protect against anogenital lesions. Patients who are diagnosed with gonorrhea should also be treated for which of the following infections - Chlamydia Week 8 A 32-year-old white male comes to your clinic, complaining of aching on the right side of his testicle. He has felt this aching for several months. He states that as the day progresses the aching increases, but when he wakes up in the morning he is pain-free. He denies any pain with urination and states that the pain doesn't change with sexual activity. He denies any fatigue, weight gain, weight loss, fever, or night sweats. His past medical history is unremarkable. He is a married hospital administrator with two children. He notes that he and his wife have been trying to have another baby this year but have so far been unsuccessful despite frequent intercourse. He denies using tobacco, alcohol, or illegal drugs. His father has high blood pressure but his mother is healthy. On examination you see a young man appearing his stated age with unremarkable vital signs. On visualization of his penis, he is circumcised with no lesions. He has no scars along his inguinal area, and palpation of the area shows no lymphadenopathy. On palpation of his scrotum you feel testes with no discrete masses. Upon placing your finger through the right inguinal ring you feel what seems like a bunch of spaghetti. Asking him to bear down, you feel no bulges. The left inguinal ring is unremarkable, with no bulges on bearing down. His prostate examination is unremarkable. What abnormality of the scrotum does he most likely have? A 48-year-old policeman comes to your clinic, complaining of a swollen scrotum. He states it began a couple of weeks ago and has steadily worsened. He says the longer he stands up the worse it gets, but when he lies down it improves. He denies any pain with urination. Because he is impotent he doesn't know if intercourse would hurt. He states he has become more tired lately and has also gained 10 pounds in the last month. He denies any fever or weight loss. He has had some shortness of breath with exertion. His past medical history consists of type 2 diabetes for 20 years, high blood pressure, and coronary artery disease. He is on insulin, three high blood pressure pills, and a water pill. He has had his gallbladder removed. He is married and has five children. He is currently on disability because of his health problems. Both of his parents died of complications of diabetes. On examination you see a pleasant male appearing chronically ill. He is afebrile but his blood pressure is 160/100 and his pulse is 90. His head, eyes, ears, nose, throat, and neck examinations are normal. There are some crackles in the bases of each lung. During his cardiac examination there is an extra heart sound. Visualization of his penis shows an uncircumcised prepuce but no lesions or masses. Palpation of his scrotum shows generalized swelling, with no discrete masses. A gloved finger is placed through each inguinal ring, and with bearing down there are no bulges. The prostate is smooth and nontender. What abnormality of the scrotum is most likely the diagnosis? Scrotal edema is a generalized swelling of the scrotum due to a systemic illness. No discrete masses are palpated. In this case, with the history of diabetes, hypertension, and coronary artery disease, the symptom of weight gain, and the signs of crackles in the lungs and an extra heart sound, the patient is probably suffering from congestive heart failure. A 36-year-old security officer comes to your clinic, complaining of a painless mass in his scrotum. He found it 3 days ago during a testicular self-examination. He has had no burning with urination and no pain during sexual intercourse. He denies any weight loss, weight gain, fever, or night sweats. His past medical history is notable for high blood pressure. He is married and has three healthy children. He denies using illegal drugs, smokes two to three cigars a week, and drinks six to eight alcoholic beverages per week. His mother is in good health and his father had high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. On physical examination he appears anxious but in no pain. His vital signs are unremarkable. On visualization of his penis, he is circumcised and has no lesions. His inguinal region has no lymphadenopathy. Palpation of his scrotum shows a soft cystic-like lesion measuring 2 cm over his right testicle. There is no difficulty getting a gloved finger through either inguinal ring. With weight bearing there are no bulges. His prostate examination is unremarkable. What disorder of the scrotum does he most likely have? A 22-year-old unemployed roofer presents to your clinic, complaining of pain in his testicle and penis. He states the pain began last night and has steadily become worse. He states it hurts when he urinates and he has not attempted intercourse since the pain began. He has tried Tylenol and ibuprofen without improvement. He denies any fever or night sweats. His past medical history is unremarkable. He has had four previous sexual partners and has had a new partner for the last month. She is on oral contraceptives so he has not used condoms. His parents are both in good health. On examination you see a young man lying on his side. He appears mildly ill. His temperature is 100.2 and his blood pressure, respirations, and pulse are normal. On visualization of the penis he is circumcised, with no lesions or discharge from the meatus. Visualization of the scrotal skin appears unremarkable. Palpation of the testes shows severe tenderness at the superior pole of the normal-sized left testicle. He also has tenderness when you palpate the structures superior to the testicle through the scrotal wall. The right testicle is unremarkable. An examining finger is placed through each inguinal ring without bulges being noted with bearing down. His prostate examination is unremarkable. Urine analysis shows white blood cells and bacteria. A 15-year-old high school football player is brought to your office by his mother. He is complaining of severe testicular pain since exactly 8:00 this morning. He denies any sexual activity and states that he hurts so bad he can't even urinate. He is nauseated and is throwing up. He denies any recent illness or fever. His past medical history is unremarkable. He denies any tobacco, alcohol, or drug use. His parents are both in good health. On examination you see a young teenager lying on the bed with an emesis basin. He is very uncomfortable and keeps shifting his position. His blood pressure is 150/100, his pulse is 110, and his respirations are 24. On visualization of the penis he is circumcised and there are no lesions and no discharge from the meatus. His scrotal skin is tense and red. Palpation of the left testicle causes severe pain and the patient begins to cry. His prostate examination is unremarkable. His cremasteric reflex is absent on the left but is normal on the right. By catheter you get a urine sample and the analysis is unremarkable. You send the boy with his mother to the emergency room for further workup. What is the most likely diagnosis for this young man's symptoms? A 16-year-old high school junior is brought to your clinic by his father. The teenager was taught in his health class at school to do monthly testicular self-examinations. Yesterday when he felt his left testicle it was enlarged and tender. He isn't sure if he has had burning with urination and he says he has never had sexual intercourse. He has had a sore throat, cough, and runny nose for the last 3 days. His past medical history is significant for a tonsillectomy as a small child. His father has high blood pressure and his mother is healthy. On examination you see a teenager in no acute distress. His temperature is 100.8 and his blood pressure and pulse are unremarkable. On visualization of his penis, he is uncircumcised and has no lesions or discharge. His scrotum is red and tense on the left and normal appearing on the right. Palpating his left testicle reveals a mildly sore swollen testicle. The right testicle is unremarkable. An examining finger is put through both inguinal rings, and there are no bulges with bearing down. His prostate examination is unremarkable. Urine analysis is also unremarkable. What abnormality of the testes does this teenager most likely have? Acute orchitis causes an inflamed, tender testicle. The scrotum will be red and tense. Orchitis is usually unilateral and often associated with viral infections such as mumps. Upgrade to remove ads Only $1/month A 45-year-old electrical engineer presents to your clinic, complaining of spots on his scrotum. He first noticed the spots several months ago, and they have gotten bigger. He denies any pain with urination or with sexual intercourse. He has had no fever, night sweats, weight gain, or weight loss. His past medical history consists of a vasectomy 10 years ago and mild obesity. He is on medication for hyperlipidemia. He denies any tobacco or illegal drug use and drinks alcohol socially. His mother has Alzheimer's disease and his father died of leukemia. On examination he appears relaxed and has unremarkable vital signs. On visualization of his penis, he is circumcised and has no lesions on his penis. Visualization of his scrotum shows three yellow nodules 2-3 millimeters in diameter. During palpation they are firm and nontender. What abnormality of the male genitalia is this most likely to be? (basically big pimples on his balls) Jim is a 47-year-old man who is having difficulties with sexual function. He is recently separated from his wife of 20 years. He notes that he has early morning erections but otherwise cannot function. Which of the following is a likely cause for his problem? Induration along the ventral surface of the penis suggests which of the following? Urethral stricture A tender, painful swelling of the scrotum should suggest which of the following? Acute epididymitis, Strangulated inguinal hernia, Torsion of the spermatic cord Bascically its a medical emergency A young man feels something in his scrotum and comes to you for clarification. On your examination, you note what feels like a "bag of worms" in the left scrotum, superior to the testicles. Which of the following is most likely? Which of the following would lead you to suspect a hydrocele versus other causes of scrotal swelling? You are examining a newborn and note that the right testicle is not in the scrotum. What should you do next? Francis is a middle-aged man who noted right-sided lower abdominal pain after straining with yard work. Which of the following would make a hernia more likely? Absence of symmetry of the inguinal areas with straining Frank is a 24-year-old man who presents with multiple burning erosions on the shaft of his penis and some tender inguinal adenopathy. Which of the following is most likely? Herpes simplex Which of the following is true of human papilloma virus (HPV) infection? It commonly resolves spontaneously in 1-2 years. A 36-year-old married bank teller comes to your office, complaining of pain with defecation and occasional blood on the toilet paper. She states that last week she had food poisoning with nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. She had runny stools but no black or bloody stools. Ever since her illness, she has continued to have severe pain with bowel movements. She now tries to put off defecation as long as possible. Although she is having constipation she denies any further diarrhea or leakage of stool. She has a past medical history of hypothyroidism and two spontaneous vaginal deliveries. She has had no other chronic illnesses or surgeries. She does not smoke and rarely drinks. She has two children. There is no family history of breast or colon cancer. She has had no weight gain, weight loss, fever, or night sweats. On examination she is afebrile, with a blood pressure of 115/70 and a pulse of 80. On abdominal examination she has active bowel sounds, is nontender in all quadrants, and has no hepatosplenomegaly. Inspection of the anus reveals inflammation on the posterior side with erythema. Digital rectal examination is painful for the patient but no abnormalities are palpated. Anoscopic examination reveals no inflammation or bleeding. What is the anal disorder that best describes her symptoms? A 42-year-old house painter comes to your clinic, complaining of pain with defecation and profuse bleeding in the toilet after a bowel movement. He was in his usual state of health until 2 weeks ago, when he was injured in a car accident. After the accident he began taking prescription narcotics for the pain in his shoulder. Since then he has had very few bowel movements. His stool is hard and pebble-like. He states he has always been "regular" in the past, with easy bowel movements. His diet has not changed but he states that he is exercising less since the accident. His past medical history includes hypertension and he is on a low-dose diuretic. He has had no other chronic illnesses or surgeries. He has a family history of hypertension, coronary heart disease, and diabetes but no cancer. He is divorced and has three children. He smokes two packs of cigarettes per day and quit drinking more than 10 years ago. He has had no recent weight loss, weight gain, fever, or night sweats. On examination he appears muscular and healthy; he is afebrile. His blood pressure is 135/90 with a pulse of 80. His cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. He is wearing a sling on his left arm. On observation of his anus you find a swollen bluish ovoid mass that appears to contain a blood clot. Digital rectal examination is extremely painful for the patient. No other mass is palpated within the anus or rectum. What disorder of the anus is this patient likely to have? A 75-year-old retired construction worker comes to your clinic, complaining of bright red blood in the toilet for the last several months. He has no pain with defecation but has occasional constipation. He states he eats a healthy diet with fruits and vegetables and walks 2 miles a day. He has had a 10-pound weight loss over the last 3 months. He denies fever or night sweats. His medical history includes high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and arthritis. He has also had an appendectomy. He smoked for 40 years, two packs a day, but quit 15 years ago. He used to drink alcohol but doesn't now. His father died in his 60s of a heart attack and his mother had breast cancer in her 70s. On examination he appears his stated age and sits comfortably on the examining table. His blood pressure is 150/85 and his pulse is 88. He is afebrile. His cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. Visualization of the anus shows no erythema, masses, or inflammation. Digital rectal examination elicits an irregular, firm mass on the posterior side of the rectum. After you remove your finger you notice frank blood on your glove. What anal or rectal disorder is this patient most likely to have? A 60-year-old coach comes to your clinic, complaining of difficulty starting to urinate for the last several months. He believes the problem is steadily getting worse. When asked he says he has a very weak stream and it feels like it takes 10 minutes to empty his bladder. He also has the urge to go to the bathroom more often than he used to. He denies any blood or sediment in his urine and any pain with urination. He has had no fever, weight gain, weight loss, or night sweats. His medical history includes type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure treated with medications. He does not smoke but drinks a six pack of beer weekly. He has been married for 35 years. His mother died of a myocardial infarction in her 70s and his father is currently in his 80s with high blood pressure and arthritis. On examination you see a mildly obese male who is alert and cooperative. His blood pressure is 130/70 with a heart rate of 80. He is afebrile and his cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. On visualization of the anus you see no inflammation, masses, or fissures. Digital rectal examination reveals a smooth, enlarged prostate. No discrete masses are felt. There is no blood on the glove or on guaiac testing. An analysis of the urine shows no red blood cells, white blood cells, or bacteria. What disorder of the anus, rectum, or prostate is this most likely to be? A 24-year-old graduate student comes to your clinic, complaining of burning during urination and increased urinary frequency. He has had a low-grade fever (100.5 degrees) and does not feel very well. He is very worried about sexually transmitted diseases because he had a drunken encounter 2 weeks ago and did not use a condom. He has had no recent weight loss, weight gain, or night sweats. His past medical history includes knee surgery in high school and genital warts in college. He does not smoke but drinks six beers every Friday and Saturday night. He denies using any IV drugs but has tried marijuana in the past. His father has high cholesterol but his mother is healthy. On examination he appears tired. His temperature is 99.5 degrees and his blood pressure is 110/70. His abdominal examination is normal. Visualization of the anus shows no masses, inflammation, or fissures. Digital rectal examination reveals a warm, boggy, tender prostate. No discrete masses are felt and there is no blood on the glove. The scrotum and penis appear normal. Urinalysis shows moderate amounts of white blood cells and bacteria. What disorder of the anus, prostate, or rectum best describes this situation? A 45-year-old African-American minister comes to your clinic for a general physical examination. He has not been feeling very well for about 3 months, including night sweats and a chronic low-grade fever of 100 to 101 degrees. He denies any upper respiratory symptoms, chest pain, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, blood in his stool, or urinary tract symptoms. He has had some lower back pain. He has a past history of difficult-to-control high blood pressure and high cholesterol. He has had no surgeries in the past. His mother has diabetes and high blood pressure. He knows very little about his father because his parents divorced when he was young. He knows his father died in his 50s, but he is unsure of the exact cause. The patient denies smoking, drinking, or drug use. He is married and has three children. On examination he appears his stated age and is generally fit. His temperature is 99.9 degrees and his blood pressure is 160/90. His head, ears, nose, throat, and neck examinations are normal. His cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are also normal. On visualization of the anus there is no inflammation, masses, or fissures. Digital rectal examination elicits an irregular, asymmetric, hard nodule on the otherwise normal posterior surface of the prostate. Examination of the scrotum and penis are normal. Laboratory results are pending. What disorder of the anus, rectum, or prostate is mostly likely in this case? A 26-year-old woman comes to your clinic, complaining of leakage of stool despite generally normal, pain-free bowel movements. She denies any blood in her stool or on the toilet paper. She has had no recent episodes of diarrhea. Her past medical history includes a spontaneous vaginal delivery 3 months ago. She had a fourth-degree tear of the perineal area (from the vagina through the rectum) that was surgically repaired after delivery. A few days later the patient developed an abscess in the anal area that had to be incised and drained. She denies using any tobacco, alcohol, or illegal drugs. Her mother and father are both in good health. She denies any weight gain, weight loss, fever, or night sweats. She is still breast-feeding without any problems. On examination you visualize a small opening anterior to the anus with some surrounding erythema. There is not a mass or other inflammation on inspection. Digital rectal examination reveals smooth rectal walls with no blood. She has no pain during the rectal examination. Bimanual vaginal examination is also normal. What anal or rectal disorder is the most likely cause of her symptom? A 22-year-old nurse comes to your clinic, complaining of severe constipation and pain during defecation. She has also seen blood on the toilet paper. She states that she eats a healthy diet and does some light exercising. She is currently at the beginning of her third trimester of an unremarkable pregnancy. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Her mother has high cholesterol but her father is in good health. She does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illegal drugs. She is married and expecting her first child. On examination she appears healthy and is afebrile, with a blood pressure of 110/60. Her abdominal examination reveals a gravid uterus but is otherwise unremarkable. On visualization of the anus there is a slight red, moist-appearing protrusion from the anus. As you have her bear down, the protrusion grows larger. On digital rectal examination you can feel an enlarged tender area on the posterior side. There is some blood on the glove after the examination. What disorder of the anus or rectum best fits this presentation? A 55-year-old retired property manager comes to your clinic, concerned that she may have a tumor in her rectum. When asked why, she states that after straining at a bowel movement she felt a mass around her rectum. She denies any blood in her stool, black stools, or pain with defecation. She admits to having had chronic constipation for 30 years. She often uses laxatives to be able to have a bowel movement. She denies any recent weight gain, weight loss, fever, or night sweats. Her past medical history consists of hypothyroidism, and she has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries. Her mother died recently of colon cancer and her father has high blood pressure but is otherwise healthy. She denies any smoking and only occasionally drinks alcohol. On examination she seems nervous. Her blood pressure is 140/90 and her pulse is 100. Her cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. On visualization of her anus, no inflammation, masses, or fissures are noted. When she is asked to bear down, you see a rosette of red mucosa prolapsing from the anus. On digital rectal examination there are no masses and no blood is found on the glove. What disorder of the anus or rectum is this likely to be? A 50-year-old truck driver comes to your clinic for a work physical. He has had no upper respiratory, cardiac, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, urinary, or musculoskeletal system complaints. His past medical history is significant for mild arthritis and prior knee surgery in college. He is married and just changed jobs, working for a different trucking company. He smokes one pack of cigarettes a day, drinks less than six beers a week, and denies using any illegal drugs. His mother has high blood pressure and arthritis and his father died of lung cancer in his 60s. On examination, his blood pressure is 130/80 and his pulse is 80. His cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal. He has no inguinal hernia, but on his digital rectal examination you palpate a soft, smooth, nontender pedunculated mass on the posterior wall of the rectum. What anal, rectal, or prostate disorder best fits his presentation? Which is a sign of benign prostatic hyperplasia? Nocturia Which is true of prostate cancer? Ethnicity is a risk factor The rate of prostate cancer is almost double in African-American men, which is one of the reasons to begin screening at 40 years of age rather than the standard recommendation of 50. Dawn is a 55-year-old woman who comes in today for her yearly wellness examination. You carefully perform the rectal examination in the lithotomy position and feel a mass against the bowel wall which is firm and immobile. Which of the following is most likely? Mr. Jackson is a 50-year-old African-American who has had discomfort between his scrotum and anus. He also has had some fevers and dysuria. Your rectal examination is halted by tenderness anteriorly, but no frank mass is palpable. What is your most likely diagnosis? An elderly woman with dementia is brought in by her daughter for a "rectal mass." On examination you notice a moist pink mass protruding from the anus, which is nontender. It is soft and does not have any associated bleeding. Which of the following is most likely? Rectal prolapse A 56-year-old homosexual man presents with itching, anorectal pain, and tenesmus of 1 week's duration. Rectal examination reveals generalized tenderness without frank prostate abnormalities. Which of the following is most likely? Which of the following conditions involves a tight prepuce which one retracted cannot be returned Which of the most common cause of cancer deaths in males induration along the ventral surface of the penis suggest which of the following A 28 year old male presents with a painless solitary chancre on the shaft of his penis A 29 year old married computer programmer comes to the clinic complaining of something strange going on in his scrotum. Last month while he was doing his self testicular exams he felt a lump in his left testis. He waited a month and felt the area again but the lymp was still there. He has had some aching in his left testis but denies any pain with urination or sexual intercourse. Palpation of scrotum is unremarkable on the right and has a large mass on the left. While placing a finger through the inguinal ring on the right, the examiner asks the client to bear down. Nothing is felt. The examiner attempts to place a finger through the left inhuinal ring but cannot get above the mass. On the rectal exam the clients prostate is unremarkable. What disorder of the tested is most likely. Which of the following is the most important action when taking a rectal temp using a clinical glass thermometer A 20 year old part time college student comes to your clinic complaining of growths on his penile shaft. They have been there for about 6 weeks and haven’t gone away. In fact he thinks there may be more now. He denies any pain with intercourse or urination. He has had three former partners and has been with his current girlfriend for siz month. He says that because she is on the pill they don’t use condoms. He denies any fever, weight loss, or night sweats. His past history is unremarkable. On visualization of his penis you see several moist papules along all sides of his penile shaft and even two on the corona. A 21-year-old engineering student comes to your office, complaining of leg and back pain and of tripping when he walks. He states this started 3 months ago with back and buttock pain but has since progressed to feeling weak in his left leg. He denies any bowel or bladder symptoms. He can think of no specific traumatic incidences but he was a defensive lineman in high school and junior college. His past medical history is unremarkable. He denies tobacco use or alcohol or drug abuse. His parents are both healthy. On examination he is tender over the lumbar spine and he has a positive straight-leg raise on the left. His Achilles tendon deep reflex is decreased on the left. While watching his gait you notice he has to pick his left foot up high in order not to trip. What abnormality of gait does he most likely have? This gait is associated with foot drop, usually secondary to a lower motor neuron disease. This is often seen with a herniated disc, such as in this patient. A 17-year-old high school student is brought in to your emergency room in a comatose state. His friends have accompanied him and tell you that they have been shooting up heroin tonight and they think their friend may have had too much. The patient is unconscious and cannot protect his airway, so he is intubated. His heart rate is 60 and he is breathing through the ventilator. He is not posturing and he does not respond to a sternal rub. Preparing to finish the neurologic examination, you get a penlight. What size pupils do you expect to see in this comatose patient? Narcotics and cholinergics cause very small (1 mm) pupils. A 37-year-old woman is brought into your emergency room comatose. The paramedics say her husband found her unconscious in her home. Her past medical history consists of type 1 diabetes and she is on insulin. In the ambulance the paramedics obtained a glucose check and her sugar was 15 (normal is 70 to 105). They began a dextrose saline infusion and intubated her to protect her airway. Despite their efforts, she is posturing in the emergency room with her arms straight at her side and her jaw clenched. Her legs are also straight and her feet are plantar flexed. What type of posturing is she showing? Abnormal posturing is an involuntary flexion or extension of the arms and legs, indicating severe brain injury. Decorticate rigidity A patient presents with a left-sided facial droop. On further testing, you note that he is unable to wrinkle his forehead on the left and has decreased taste. Which of the following is true? This may be related to travel. Because the forehead is also involved, this represents a peripheral nerve lesion of CN VII and does not represent a classic middle cerebral artery stroke. The latter would spare the upper face but include speech difficulties as well as upper extremity weakness on the ipsilateral side. One cause of this type of lesion is Lyme disease and relates to travel to endemic areas, so a careful travel history should be sought. Which is true of examination of the olfactory nerve? Steve has had a stroke and comes to you for follow-up today. On examination you find that he has increased muscle tone, some involuntary movements, an abnormal gait, and a slowness of response in movements. He most likely has involvement of which of the following? You are conducting a mental status examination and note impairment of speech and judgement, but the rest of your examination is intact. Where is the most likely location of the problem? A patient presents with a daily headache which has worsened over the past several months. On funduscopic examination, you notice that the disk edge is indistinct and the veins do not pulsate. Which is most likely? Increased intracranial pressure A patient with a history of seizure disorder and on several seizure medications says a friend noted "jumping eye movements." The patient describes a sensation of movement at rest since his medications were adjusted upward following a breakthrough seizure several weeks ago. On examination you note that the eyes both slowly move to the right and then quickly jump to the left. Which of the following is true? Nystagmus is named for the fast component, in this case, toward the left. Nystagmus is common with several seizure medications and in this case is likely due to the recent increase in medications rather than a more ominous cause. You are testing the biceps strength in a young man following a spinal trauma from a motor vehicle accident. He cannot lift his hand upward, but if the arm is abducted to 90 degrees, he can then move his forearm side to side. This would represent which muscle strength grading? You ask a patient to hold her arms up, with her palms up, and then to close her eyes. The right arm begins to move downward after a few seconds and her thumb rotates upward. This is most likely a problem with which part of the nervous system? You are examining a child with severe cerebral palsy. When you suddenly move his foot dorsally, a sustained "beating" of the foot against your hand ensues. What does this represent? Clonus Jim is an HIV-positive patient who complains about back pain in addition to several other problems. On percussion, there is slight tenderness over the T7 vertebrae, and when you flex his thigh to 90 degrees and extend his lower legs, you meet strong resistance at about 45 degrees of extension. What are likely causes of this constellation of symptoms? Infection (Kernig's sign) of the meninges A patient with alcoholism is brought in with confusion. You ask him to "stop traffic" with his palms and notice that every few seconds his palms suddenly move toward the floor. What does this indicate? (asterixis-also called the flapping tremor, or liver flap) You examine a "sleepy" patient. You note that she will open her eyes and look at you but responds slowly and is confused. She does not appear interested in her surroundings. How would you describe her level of consciousness? Obtunded A patient opens her eyes to verbal cues and may respond appropriately but promptly falls back patient responds only to painful stimuli, and when the stimulus is withdrawn lapses into unconsciousness again Stupor patient has no obvious response to external stimuli. Coma A woman experiences syncope after hearing that her son was severely injured. She becomes pale and collapses to the ground without injuring herself. On waking, she states that she feels very warm. She denies any other symptoms. There are no findings on examination. What caused her loss of consciousness? A 7-year-old boy is performing poorly in school. His teacher is frustrated because he is frequently seen "staring off into space" and not paying attention. If this is a seizure, it most likely represents which type? A young woman comes in with brief, rapid, jerky, irregular movements. They can occur at rest or during other intentional movements and involve mostly her face, head, lower arms, and hands. How would you describe these movements? [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 23, 2020
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 23, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
125