
Nurses Touch: Nursing informatics and technology- Informatics
$ 10
PHTLS Review 2022 With complete solution .
$ 8.5

Character Analysis of a Nurse
$ 4
AQA 2022// GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Higher Tier Physics Paper 1H
$ 7

Army Explosive Safety Familiarization updated 2023
$ 9

NR599 Nursing Informatics Final Exam Study Guide 2023
$ 6.5
.png)
> Interchange A Level GCE Physics B H557/01;Practical skills in physics Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for Autumn 2021.
$ 13.5

Using Sage 50 Accounting 2022 1st Edition By Mary Purbhoo | SOLUTIONS MANUAL
$ 25
(WGU C968) ITSW 3215 Software I - C# Latest Complete OA Guide 2024
$ 13

AERM Assembly & Rigging Unit 1 Test Guide Questions And Answers
$ 8
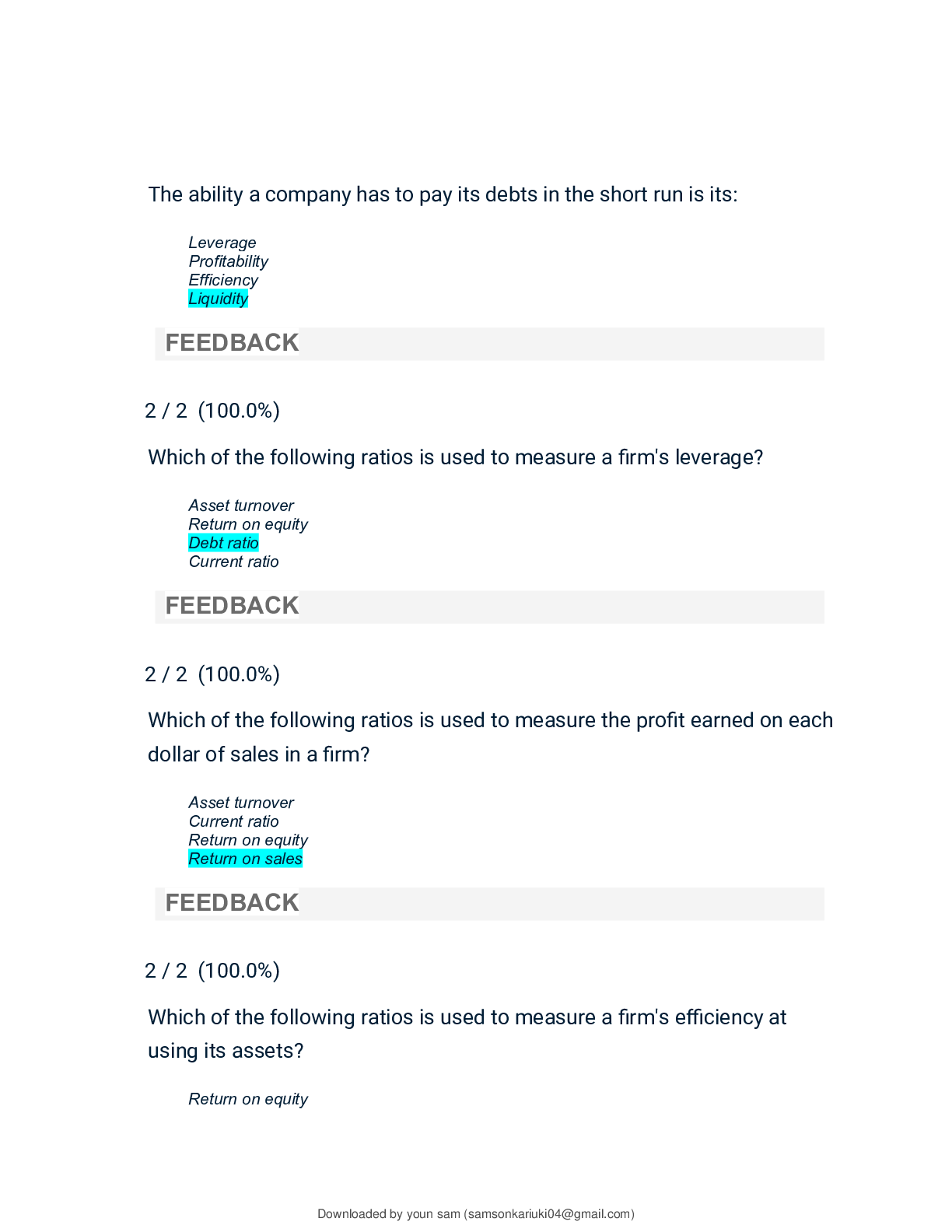
Principles Of Accounting I (ACC 290) | Topic 7: Widely Used Financial Ratios Quick Check | Answered.
$ 6

Cell Structure GIZMOS 2021/2022
$ 8

AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS 8300/1H Higher Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculator Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 6
 ansswers.png)
2017-2020 History 410 Final Exam practice questions and answers solution docs
$ 9

HM 441- RM- Final JMU 45 Questions with Answers 2023,100% CORRECT
$ 8.5

Pearson Edexcel GCE As Level 8BI0/02 Biology B Advanced Subsidiary PAPER 2: Core Physiology and Ecology QP June 2022
$ 4

Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach 4th Edition by Marjorie Kelly Cowan, Heidi Smith and Jennifer Lusk. All Chapters 1-22. TEST BANK
$ 22

Police Theory and Practices Quiz 1
$ 7

ATI TEASE 6 Science Quiz Bank. Includes over 300 Questions and Answers.
$ 9

MICR 221 Module 1: All the Content for module 1. Includes pictorials graphics in an easy to read layout.
$ 8.5

ATI RN NUTRITION 2025 - PROCTORED EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (Question 1 to 70 with correct answers and rationales)
$ 35.5

WGU C464 Intro To Communication pre assess Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 15

eBook The Power Platform Playbook for Digital Transformation Implement Strategy, Automation, and AI for Scalable Digital Transformation 1st Edition By Victor Dantas, Chris Huntingford
$ 29

NASM CPT 7TH EDITION - PRACTICE EXAM MISSED QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
$ 13.5

Pearson Edexcel International GCSE_English Language A_4EA1/01 Mark Scheme Oct 2021 | Non-fiction Texts and Transactional Writing
$ 7

final exam study guide Advanced Pathophysiology (NURS-6501N)
$ 10

(WGU C624) CHEM 3501 - Biochemistry - FA Review 20242025
$ 10

OCR A Level Biology A PAPER 2 H420/02: Biological diversity Mark Scheme for June 2024
$ 8

OCR A Level Computer Science H446/01 Computer Systems Monday 13 June 2022 – Afternoon
$ 9

Solution Manual For Business Accounting & Finance, 6th Edition by Catherine Gowthorpe Chapter 1-20
$ 20

2024 Advanced Pathophysiology HESI RN Exam 3 Guaranteed A+ Actual Questions and Answers, Complete 100%
$ 13

eBook [PDF] Sustainable Construction Green Building Design and Delivery 5th Edition By Charles J. Kibert
$ 20

AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS 8300/1H Higher Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculator Mark scheme June 2022 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 7

HESI RN MENTAL HEALTH 2018 V1 V2 V3 38 PAGES OF QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS FROM TEST
$ 7

HIEU 201 Chapter 11 Quiz Liberty University | Complete Answers All Answers Correct
$ 6

ATI COMPREHENSIVE NURSING – NUTRITION & BIOCHEM - NEW VERSION SUMMARY 2023-2024
$ 8.5

Digital License Key for Windows 10 Professional: Life Time Activation with Digital Key from Microsoft Windows 10 Pro: 5 Users: 5 Keys
$ 40

Radiology Guideline Quiz Latest
$ 7

PMHNP Exam Reported Questions and Answers Latest 2022 Test with complete solutions
$ 15

MATH 321 Vector and Complex Calculus for the Physical Sciences by Fabian Wale
e
$ 10

DAD 220 6-1 Project One Creating a Database and Querying Data
$ 3

Arts (Fine arts, Performing arts) Essay
$ 4

ATI RN Critical Care Dosage Calculation 3.1 Exam with Explained Answers
$ 17.5

FLETC BOP Final Exam 2022 with complete solution
$ 9

St. Petersburg College-POLI 330N Week 6 Discussion: Presidential Advisor-Already_verified_Solutions_100%
$ 6.5

NR 328 – Pediatric Nursing MIDTERM EXAM 2 Questions and correct Answers (Verified Answers) 2025
$ 15

AQA A-LEVEL PHYSICS 7408/2 Paper 2 Mark scheme June 2022
$ 8

A-level HISTORY Component 2R The Cold War, c1945–1991
$ 9

SOLAS Quiz 5 Latest 2023 with complete solution
$ 9

eBook [PDF] The Changing World of a Bombay Muslim Community 1870 - 1945 1st Edition By Salima Tyabji
$ 29

NR601 _week 5 case study _ DeLost.
$ 10

Stutts - ANSC 4395 Animal Breeding & Genetics - Test 2 QUESTIONS WITH COMPLETE ANSWERS
$ 5

>_AS Level Physics A_H156/02 Mark Scheme Oct 2021 | Depth in Physics
$ 5

Pearson Edexcel A Level 3 GCE (9RU0/01) Russian Advanced Paper 1: Listening, Reading and Translation Question paper+ mark scheme MAY 2024
$ 7

Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Mathematics Advanced Subsidiary Paper 2A: Statistics
$ 6

Accounting Final Review Questions With Correct Answers From CH7 to CH12
$ 10

SAFe 5 Scrum Master Questions & Answers (attempt score 95%)
$ 11.5

Pearson Edexcel GCE Question Booklet + Mark Scheme Additional Assessment Materials Summer 2021 Pearson Edexcel GCE in History 9HI0 2H.1 Resource Set 1: The USA, c1920-55: boom, bust and recovery Set 1
$ 8.5

MATH 225N Week 1 Assignment Sampling Methods – Questions and Answers
$ 13

PHY 114 Lab Report 4: Physics of a Light Bulb. Arizona State University
$ 7
.png)
AQA GCSE PHYSICS 8463/2H Paper 2 Higher Tier Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final Mark Scheme
$ 10

2024 AHIP Module 5 Questions and Correct Solutions.pdf'
$ 17

2024 KSU CSE 1321 FINAL EXAM ACTUAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALREADY GRADED A+
$ 19.5

NURS 6050 Agenda Comparison Grid Immigrant Healthcare
$ 7

Introduction to Econometrics, 3rd Edition James H. Stock, and Mark W. Watson. CHAPTER 1-18.
$ 16

Edexcel as level english literature question paper 2 june 2023 + mark scheme
$ 10

eBook [PDF] Safety Rebels Real World Transformations in Health and Safety 1st Edition By Selma Pirić
$ 20

PHY 122 University Physics ! Mechanics Lab - Lab 10 Rotational Motion Report- Arizona State University
$ 8.5

MN 551 Advanced Pathophysiology Final Exam
$ 14

Mastering Search Engine Optimization
$ 2

World of Turf Exam 3 | 100% Correct Answers | Verified | Latest 2024 Version
$ 7

AQA AS PHYSICS Paper 2 QUESTIONS PAPER JUNE 2022










 all correct_2022.png)













