ATI NURSING STUDY GUIDE:ASSISTING WITH POSITIONING PATIENTS IN BED
ALERT
Use lifting and transfer devices when available.1
•To prevent further injury in patients suffering a spinal cord injury or recovering from nec
...
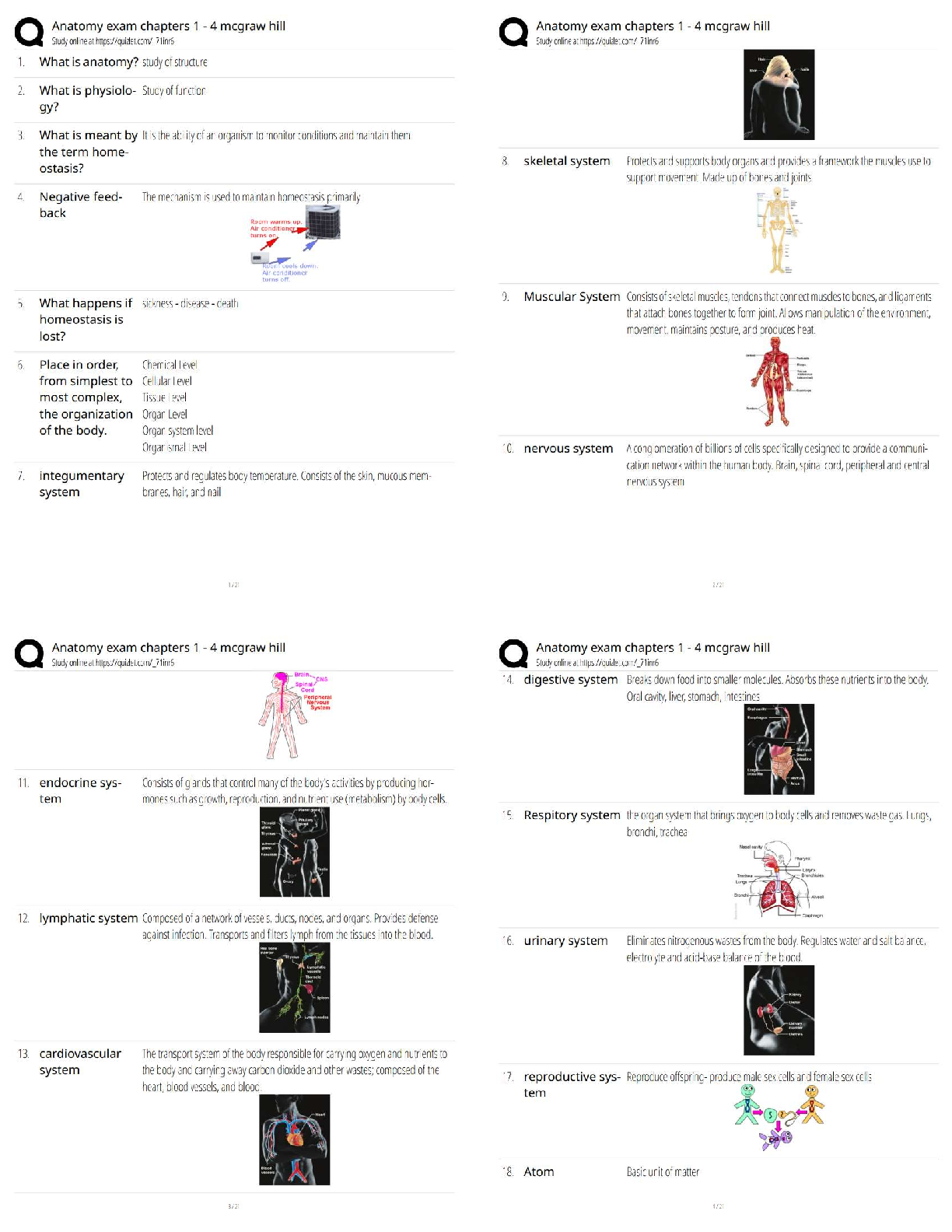
ATI NURSING STUDY GUIDE:ASSISTING WITH POSITIONING PATIENTS IN BED
ALERT
Use lifting and transfer devices when available.1
•To prevent further injury in patients suffering a spinal cord injury or recovering from neck, back, or spinal surgery, keep the spinal column in alignment.
•Avoid pulling or sliding the patient; this can result in shear or friction injury to the patient.
OVERVIEW
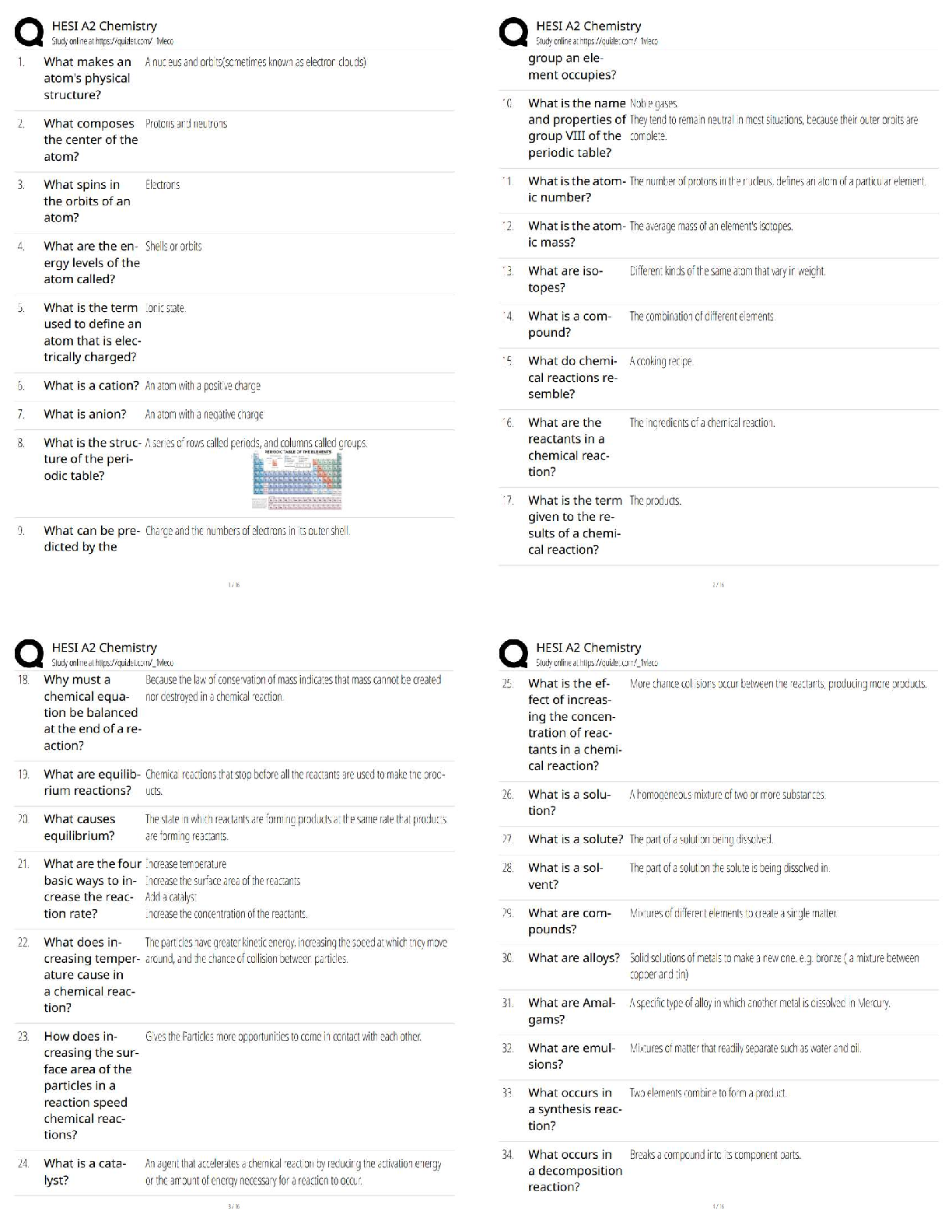
Correctly positioning patients is crucial for maintaining body alignment and comfort; preventing injury to the musculoskeletal, neurologic, and integumentary systems.
A patient with diabetes, vascular disease, impaired mobility, decreased sensation, impaired circulation, or lack of voluntary muscle control is at greater risk for sustaining musculoskeletal, neurologic, and integumentary damage while in the supine or modified supine position.
You must minimize this risk by maintaining unrestricted circulation and correct body alignment while moving, turning, or positioning a patient. When the joints, tendons, ligaments and muscles of the body are properly aligned in any position, no excessive strain is placed on these structures.
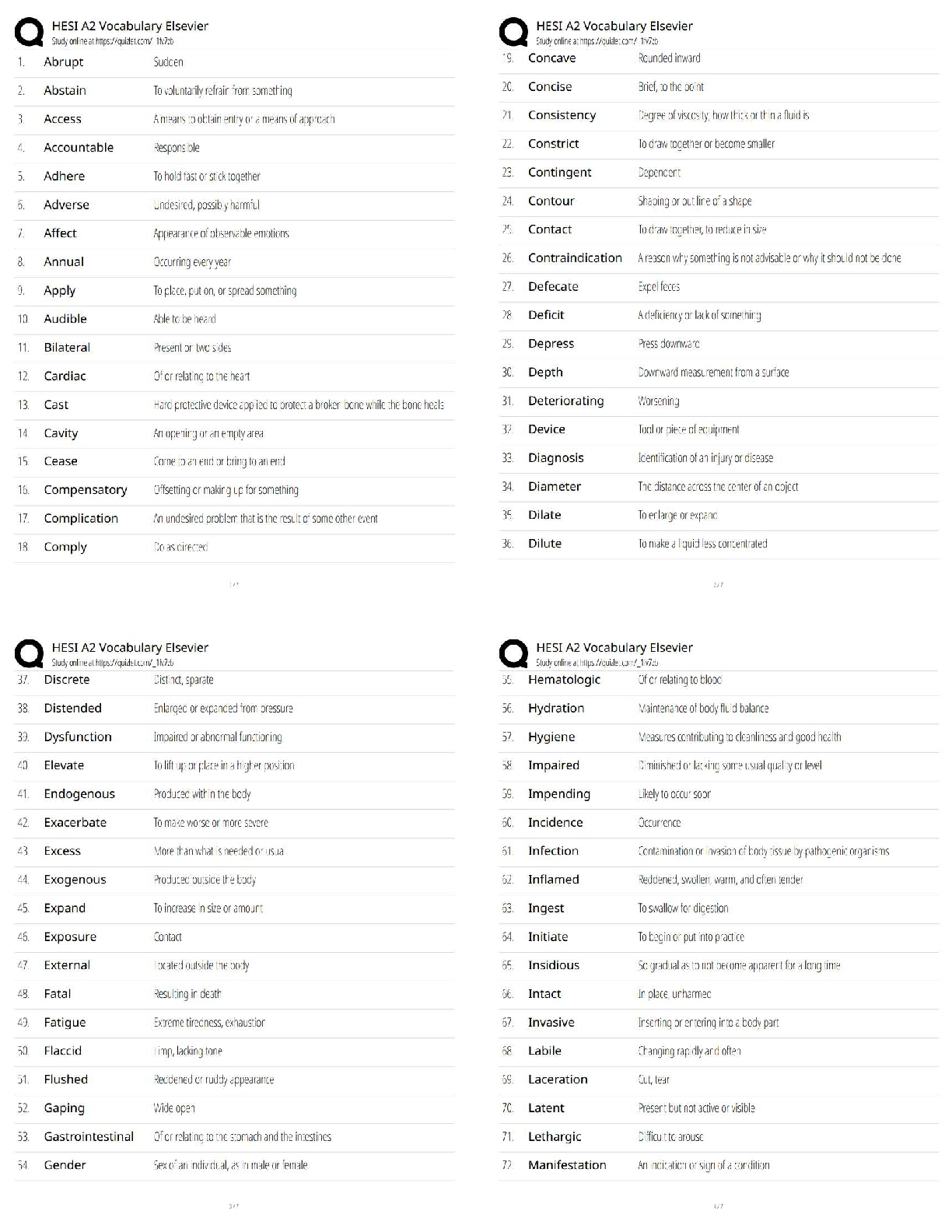
Body alignment means that the body is in line with the pull of gravity and contributes to body balance. Without this balance the center of gravity is displaced, which increases the force of gravity and predisposes a person to falls and injuries.
Body balance is achieved when a wide base of support exists, the center of gravity falls within the base of support, and a vertical line can be drawn from the center of gravity through the base of support.
Manual lifting is a high-risk task that can contribute to musculoskeletal disorders. Principles of ergonomics should be applied to reduce the risk of occupational injury. Safe patient handling programs can reduce injuries, increase worker satisfaction, and contribute to better care of the patient.2
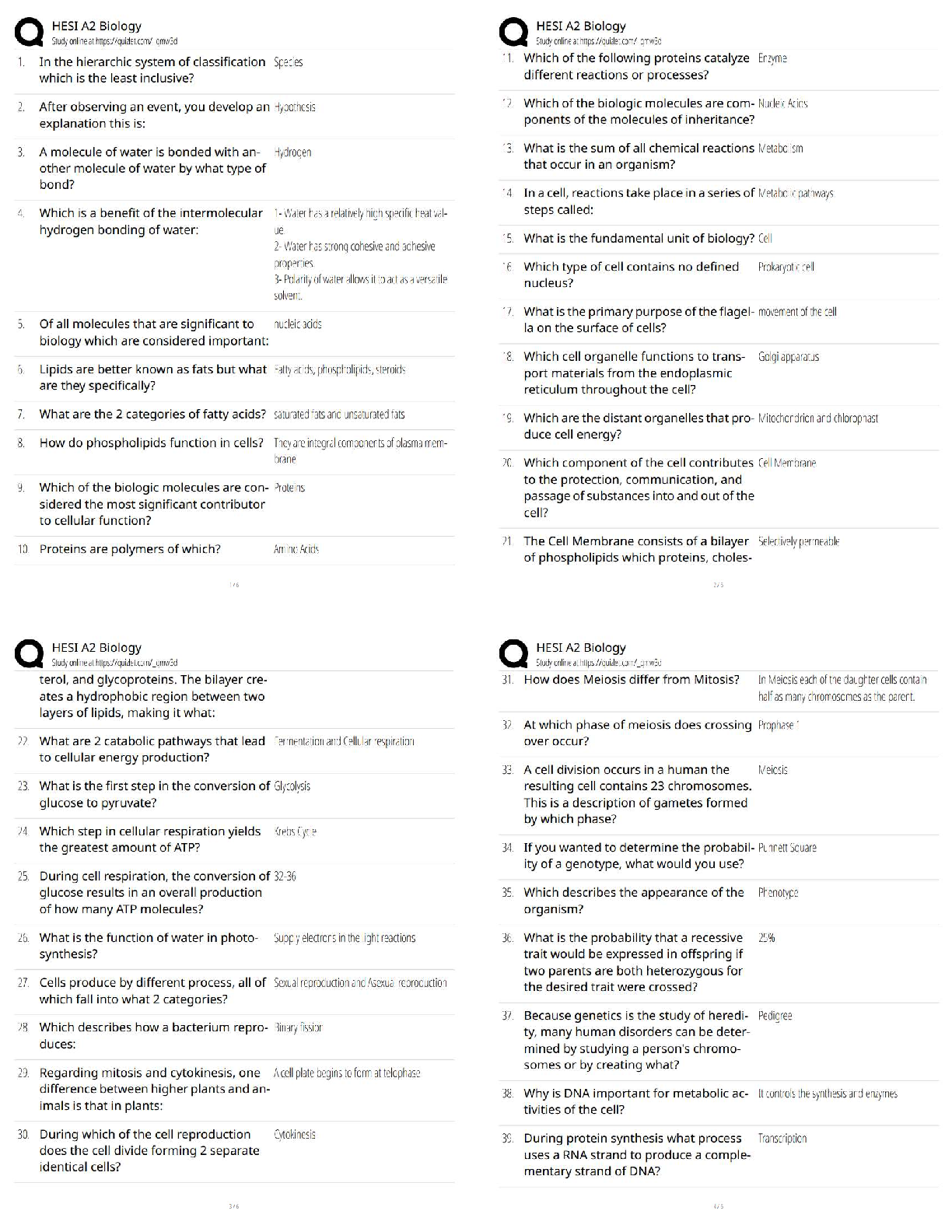
Assistive devices minimize the risk to both nurse and patient and should be used when indicated. Assistive devices for moving the patient up in bed include
1.friction-reducing sheets,
2.bed repositioning devices,
3.mechanical patient lifts, and
4.over-bed trapezes. The patient should be assessed before and after the procedure for signs of complications.
[Show More]








.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)