*NURSING > QUESTIONS and ANSWERS > Medical Surgical Nursing Notes (All)
Medical Surgical Nursing Notes
Document Content and Description Below
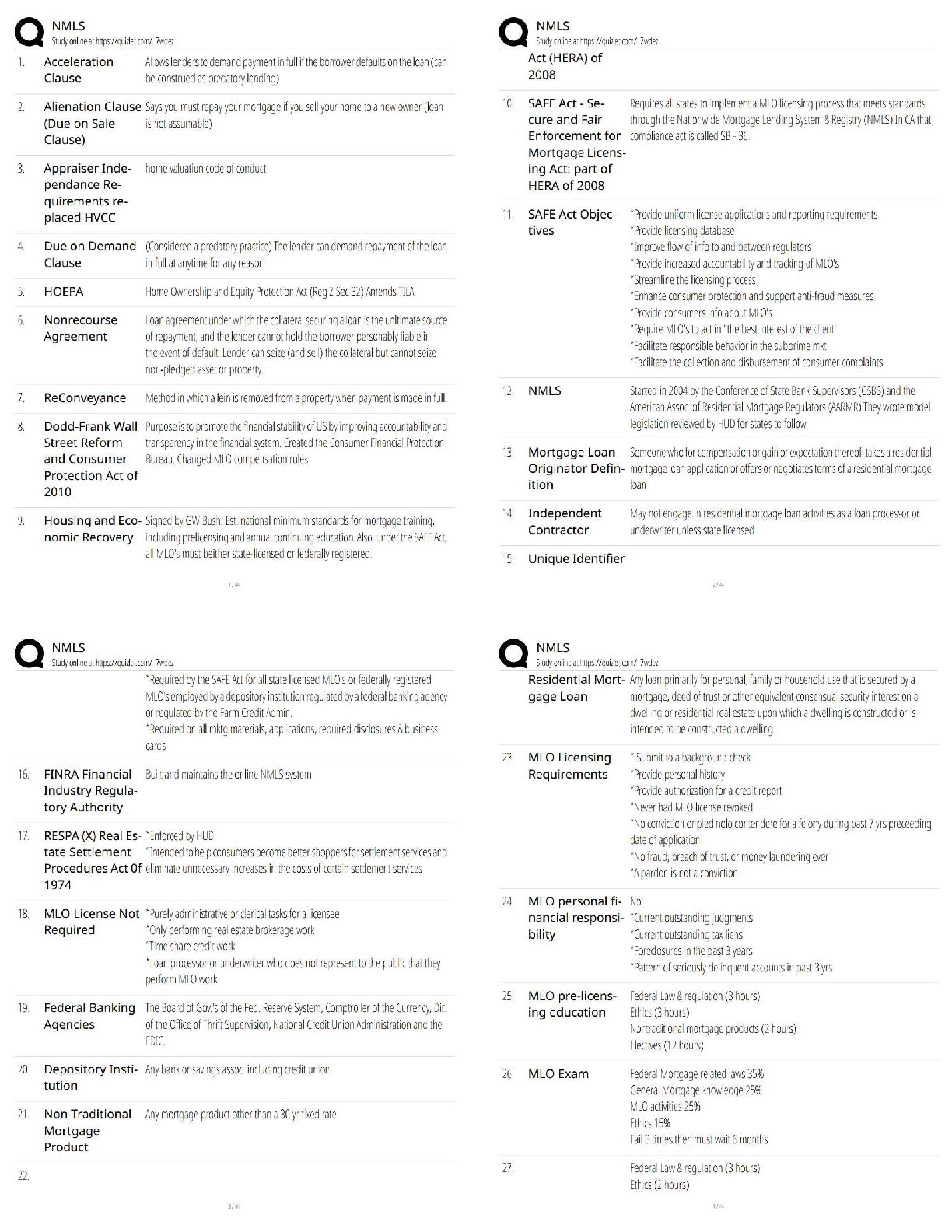
MEDICAL SURGICAL Overview of the Structures & Functions of Nervous System Central NS PNS ANS Brain & spinal cord 31 spinal & cranial sympathetic NS Parasypathatic NS Somatic NS C- 8 T- 12 L- 5 ... S- 5 C- 1 ANS (or adrenergic of parasympatholitic response) SNS involved in fight or aggression response Effects of SNS (anti-cholinergic/adrenergic) 1. Dilate pupil – to aware of surroundings Release of norepinephrine (adrenaline – cathecolamine) - medriasis Adrenal medulla (potent vasoconstrictor) 2. Dry mouth Increases body activities VS = Increase 3. BP & HR= increased Except GIT – decrease GITmotility bronchioles dilated to take more oxygen 4. RR increased * Why GIT is not increased = GIT is not important! 5. Constipation & urinary retention Increase blood flow to skeletal muscles, brain & heart. I. Adrenergic Agents – Epinephrine (adrenaline) SE: SNS effect II. PNS: Beta adrenergic blocking agents (opposite of adrenergic agents) (all end in –‘lol’) - Blocks release of norepinephrine. - Decrease body activities except GIT (diarrhea) Ex. Propanolol, Metopanolol SE: B – broncho spasm (bronchoconstriction) E – elicits a decrease in myocardial contraction T – treats HPN A – AV conduction slows down Given to angina & MI – beta-blockers to rest heart Anti HPN agents: 1. Beta blockers (-lol) 2. Ace inhibitors (-pril) ex ENALAPRIL, CAPTOPRIL 3. Calcium antagonist ex CALCIBLOC or NEFEDIPINE Peripheral nervous system: cholinergic/ vagal or sympatholitic response Effect of PNS: (cholinergic) - Involved in fly or withdrawal response 1. Meiosis – contraction of pupils - Release of acetylcholine (ACTH) 2. Increase salivation - Decrease all bodily activities except GIT (diarrhea) 3. BP & HR decreased 4. RR decrease – broncho constriction I Cholinergic agents 5. Diarrhea – increased GI motility ex 1. Mestinon 6. Urinary frequency Antidote – anti cholinergic agents Atropine Sulfate – S/E – SNS S/E- of anti-hpn drugs: 1. orthostatic hpn 2. transient headache & dizziness. -Mgt. Rise slowly. Assist in ambulation. CNS (brain & spinal cord) I. Cells – A. neurons Properties and characteristics a. Excitability – ability of neuron to be affected in external environment. b. Conductivity – ability of neuron to transmit a wave of excitation from one cell to another c. Permanent cells – once destroyed, cant regenerate (ex. heart, retina, brain, osteocytes) Regenerative capacity A. Labile – once destroyed cant regenerate - Epidermal cells, GIT cells, resp (lung cells). GUT B. Stable – capable of regeneration BUT limited time only ex salivary gland, pancreas cells cell of liver, kidney cells C. Permanent cells – retina, brain, heart, osteocytes can’t regenerate. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 75 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 02, 2022
Number of pages
75
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 02, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
176