A 13-year-old obese (body mass index [BMI] above the 95th percentile) boy reports low-grade left knee pain for the past 2 months. He denies antecedent trauma but admits to frequent “horseplay” with his friends. The pain
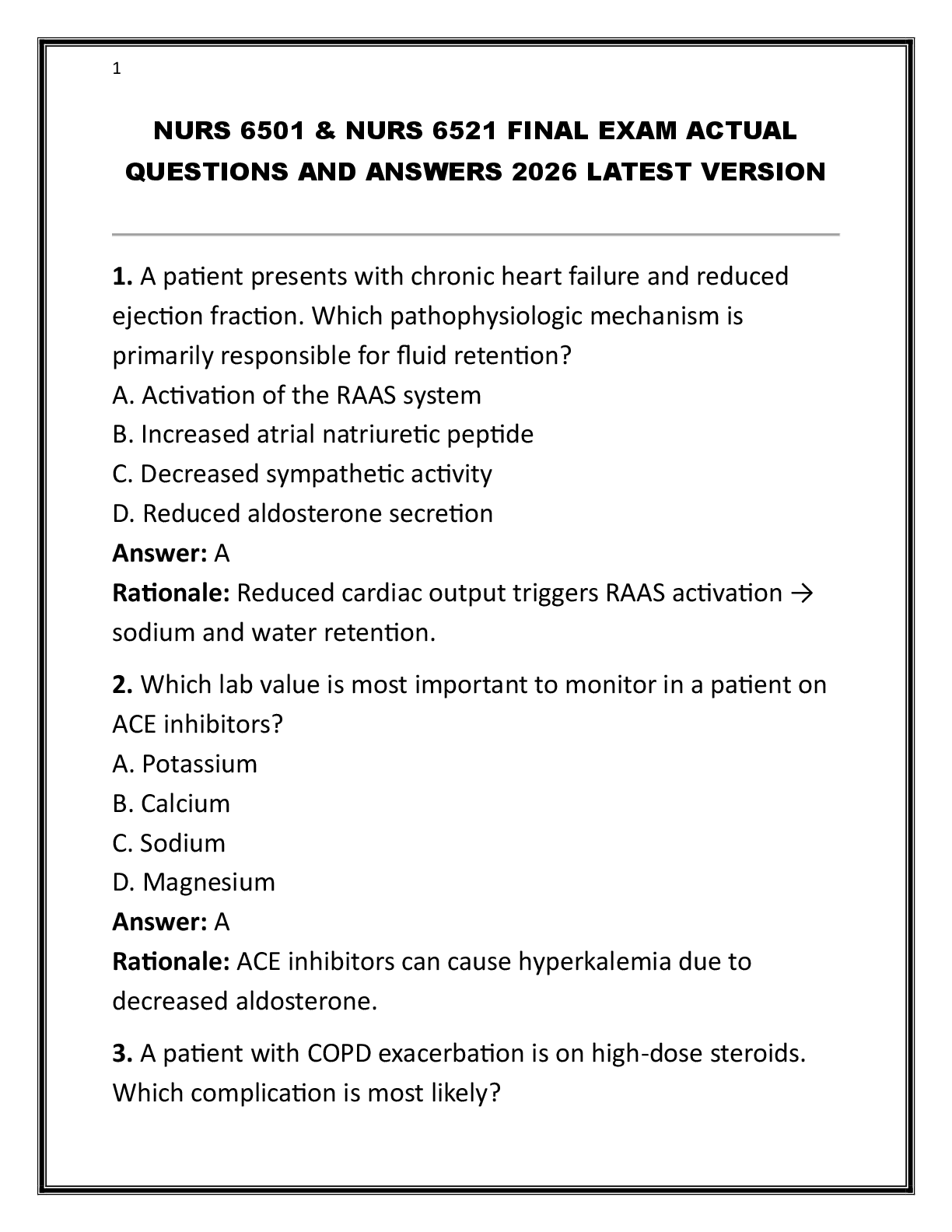
...
A 13-year-old obese (body mass index [BMI] above the 95th percentile) boy reports low-grade left knee pain for the past 2 months. He denies antecedent trauma but admits to frequent “horseplay” with his friends. The pain has progressively worsened, and he is now unable to bear weight at all on his left leg. His current complaints include left groin, thigh, and medial knee pain and tenderness. His examination demonstrates negative drawer, Lachman, and McMurray tests; left hip with decreased internal rotation and abduction; and external hip rotation with knee flexion. Based on the above scenario, the clinician should suspect which of the following?
Osgood-Schlatter disease.
A left anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear.
A slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).
A left meniscal tear.
SCFE is a displacement of the femoral head relative to the femoral neck that occurs through the physis (growth plate) of the femur. The vast majority of clients with this condition are obese, as the added weight increases shear stress across the physis. The mean age at diagnosis is 12 years for females and 13.5 years for males. Surgery is often required via in situ pin fixation (single screw) to stabilize the growth plate to prevent further slippage and avoid complications.
A 16-year-old male patient presents to the clinic after sustaining a football injury to his right knee. The clinician elicits a positive anterior/posterior drawer sign. This test indicates an injury to the ?
Collateral ligament.
Medial meniscus.
Lateral meniscus.
Cruciate ligament.
Positive anterior and posterior drawer signs indicate injury to the anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament, respectively. The drawer and Lachman tests are utilized to assess for cruciate ligament injury.
A conservative approach is recommended in the initial approach to the management of low back pain. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment plan for a 32-year-old obese male (BMI 33) diagnosed with an acute lumbar strain?
[Show More]