Biology > GIZMOS > Cell Types Gizmos.pdf. Gizmos, questions and answers. 100% proven pass rate,. Graded A+ (All)
Cell Types Gizmos.pdf. Gizmos, questions and answers. 100% proven pass rate,. Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
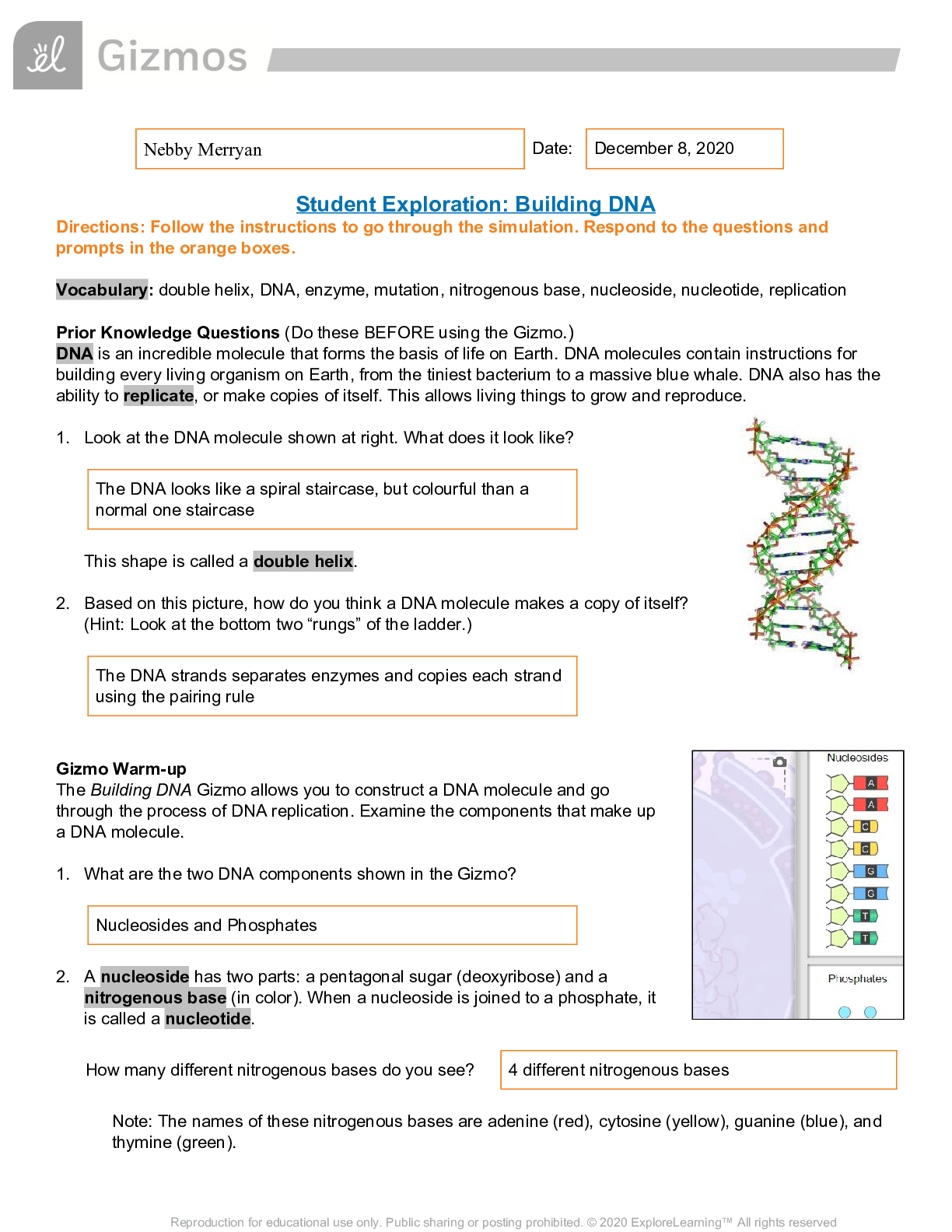
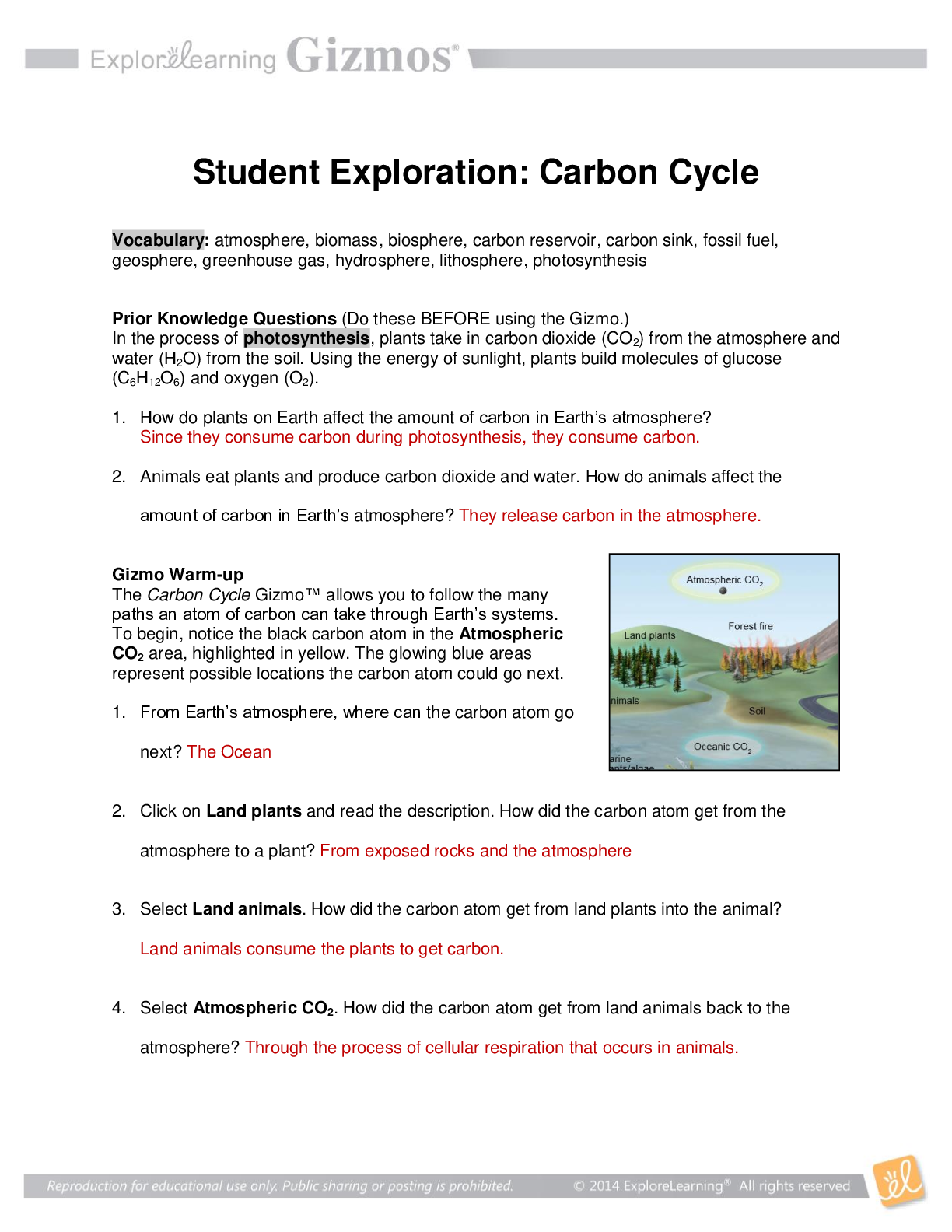
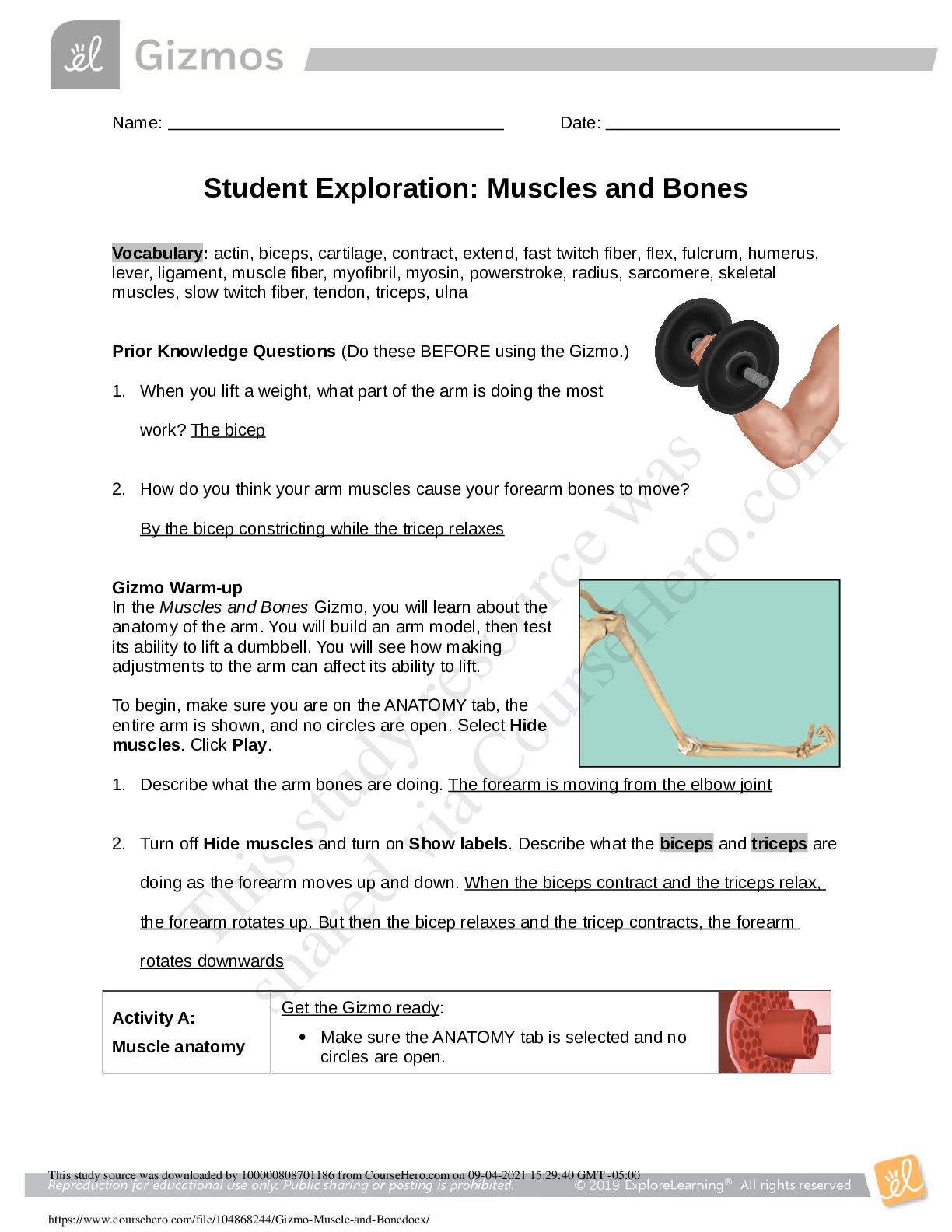
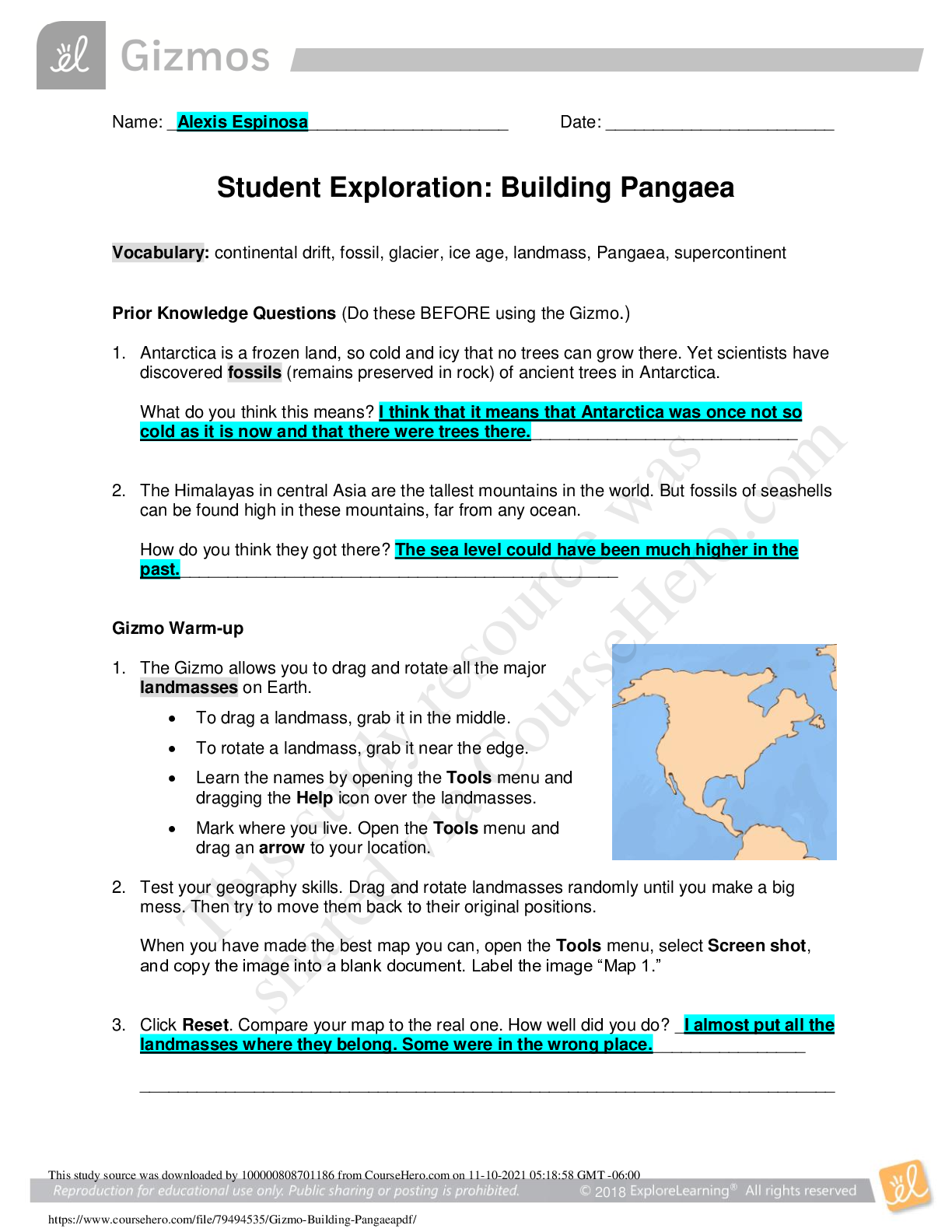
Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle, photosynthesis, prokaryote, protist ... , red blood cell, root hair cell, tissue, unicellular, white blood cell Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. How do you know if something is alive? Describe some of the characteristics of living things. Composed of one or more cells, growth and development, ability to reproduce, responsiveness to the environment, and using food to provide energy to their cells, and maintaining homeostasis. 2. Humans, plants and mushrooms are all alive. What do these organisms have in common? They all share the characteristics of life. Gizmo Warm-up In the Cell Types Gizmo, you will use a light microscope to compare and contrast different samples. On the LANDSCAPE tab, click on the Elodea leaf. (Turn on Show all samples if you can’t find it.) Switch to the MICROSCOPE tab to observe the sample as it would appear under the microscope. By default, this microscope is using 40x magnification. 1. Drag the Coarse focus slider until the sample is focused as well as possible. Then, improve the focus with the Fine focus slider. What do you see? I see a pattern of cells. 2. Select the 400x magnification. If necessary, adjust the fine focus. Now, what do you see? I see the individual chloroplasts, the cell walls, nuclei, the cytoplasms (the part outside of the nuclei), and the vacuoles. Reproduction for educational use only. Public sharing or posting prohibited. © 2020 ExploreLearning™ All rights reserved The individual chambers you see are cells, the smallest functional unit of an organism. Reproduction for educational use only. Public sharing or posting prohibited. © 2020 ExploreLearning™ All rights reserved Activity A: Observing cells Get the Gizmo ready: ● On the LANDSCAPE tab, click on the woman’s right arm to choose the Human skin sample. ● Select the MICROSCOPE tab. Introduction: Complex organisms are made up of smaller units, called cells. Most cells are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopes are used to magnify small objects, so here you will use a compound light microscope to observe the cells of different organisms. Question: What are similarities and differences between cells from different organisms? 1. Match: Read about each microscope part. Match the description to the part on the diagram. B Stage: Platform where a slide is placed. A Eye piece: Lens at the top of the microscope that the user looks through. This lens most commonly magnifies a sample by 10x. C Coarse focus knob: Large knob that moves the stage up and down to focus the sample. D Fine focus knob: Small knob that moves the stage over a short distance to refine the focus. E Objective lens: A second lens that further magnifies the sample. Microscopes usually have several objective lenses with different magnifications. The total magnification is the product of the eyepiece magnification and the objective lens magnification. F Slide: A rectangular piece of glass upon which a sample is mounted for viewing under a microscope. 2. Manipulate: With 40x selected, use the Coarse and Fine focus sliders to focus on the sample. Then, choose 400x and focus on the sample using the Fine focus slider. A. Which focus knob is easier to use at 40x? 400x? 40x was Coarse Focus 400x was Fine Focus B. Turn on Show labels. What structures can you see in human skin cells? Cytoplasm, Nuclei, and Cell Membranes C. Turn off Show labels and turn on Show scale bars. The scale bar has a width of 20 micrometers, or 20 μm. (There are 1,000 micrometers in a millimeter.) Using the scale bar, about how wide is a human skin cell? 30 micrometers Reproduction for educational use only. Public sharing or posting prohibited. © 2020 ExploreLearning™ All rights reserved 3. Observe: An organelle is a cell structure that performs a specific function. Observe the samples below under the highest magnification. Click the Show labels checkbox to label the organelles. List the organelles and approximate size of the cells in each sample. Sample Organelles Estimated size (μm) Mouse skin Nuclei, cell membranes, mitochondria, golgi bodies, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, nucleolus and cytoplasm. 25 μm Fly muscle Striation, cell membranes, mitochondria, golgi bodies, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, nucleolus, nuclei, and cytoplasm. 6 μm Maple leaf Chloroplasts, mitochondria, golgi bodies, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, cell membranes, cell wall, nuclei, large vacuole, and cytoplasm [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$5.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 12, 2022
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 12, 2022
Downloads
2
Views
1800