Student Exploration: Carbon Cycle
Vocabulary (refer to vocab file located on the Gizmo site for definitions):
Atmosphere: the gases that surround a planet
Biomass: the total mass of a group of living things.
Biospher
...
Student Exploration: Carbon Cycle
Vocabulary (refer to vocab file located on the Gizmo site for definitions):
Atmosphere: the gases that surround a planet
Biomass: the total mass of a group of living things.
Biosphere: living things on a planet.
Carbon reservoir: a part of Earth that stores carbon
Carbon sink: a carbon reservoir that absorbs carbon from the atmosphere and
stores it for a long period of time
fossil fuel: a fuel formed over thousands or millions of years from the remains of
living organisms
Geosphere: the rocky, non-living parts of a planet.
Greenhouse gas: a gas in Earth’s atmosphere that absorbs and then re-radiates
heat.
Hydrosphere: – the water on a planet.
Lithosphere: the rigid upper layer of the Earth
Photosynthesis: – a process in which plants use energy from light to change
carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
In the process of photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) from the
atmosphere and water (H2O) from the soil. Using the energy of sunlight, plants build
molecules of glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
1. How do plants on Earth affect the amount of carbon in Earth’s atmosphere?
The plants take in carbon from the air for photosynthesis. It decreases the
amounts of carbon levels in the air.
2. Animals eat plants and produce carbon dioxide and water. How do animals affect
the amount of carbon in Earth’s atmosphere?
Animals affect the amount of carbon on the Earth because they release carbon
into the air, increasing the levels.
Gizmo Warm-up
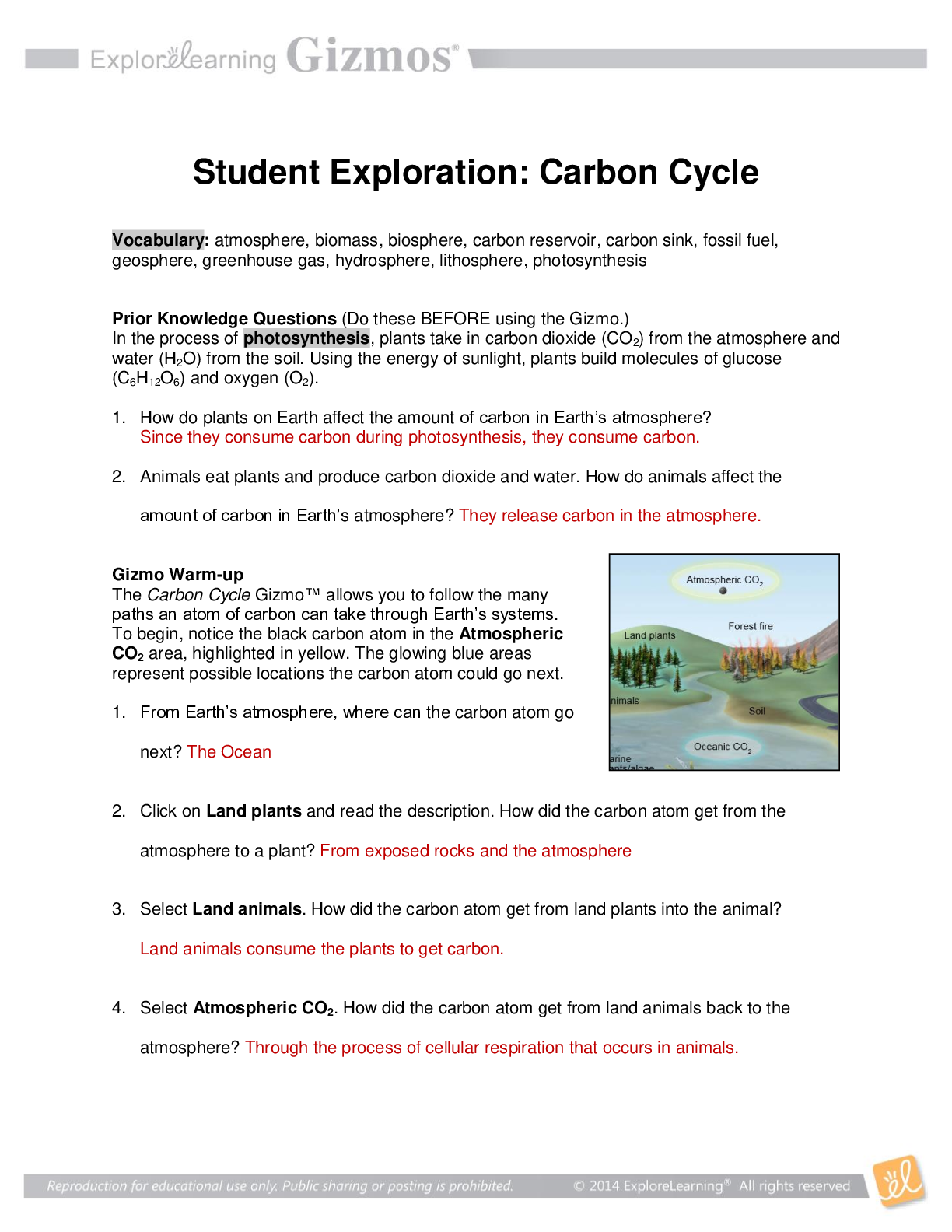
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo™ allows you to follow the
many paths an atom of carbon can take through Earth’s
systems. To begin, notice the black carbon atom in the
Atmospheric CO2 area, highlighted in yellow. The
glowing blue areas represent possible locations the
carbon atom could go next.1. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon
atom go next?
The carbon atom can go to the plants next.
2. Click on Land plants and read the description. How did the carbon atom get from
the atmosphere to a plant?
The carbon atom got from the atmosphere to a plant from photosynthesis.
3. Select Land animals. How did the carbon atom get from land plants into the
animal?
The carbon atom would get from the plant to the animal from the animal eating
the plant.
4. Select Atmospheric CO2. How did the carbon atom get from land animals back to
the atmosphere?
The animals release the carbon back into the air by the process of cellular
respiration.
Activity A:
Carbon
pathways
Get the Gizmo ready:
• Click Reset.
Introduction: Earth can be divided into four systems. The atmosphere is the air above
Earth’s surface. The hydrosphere is composed of all of Earth’s water. The geosphere
is the rocky, non-living part of Earth. The biosphere consists of all living things,
including people. Some scientists use the term “anthroposphere” to describe everything
made or modified by humans.
Question: How does carbon move between the atmosphere, hydrosphere,
biosphere, and geosphere?
1. Explore: Use the Gizmo to create a path for carbon that begins and ends in the
atmosphere. Fill in the steps in the path below. Then, label each location with the
system it represents. Finally, summarize very briefly how the carbon atom got to that
location.
Carbon path System How it got there
Atmospheric CO2 Atmosphere Atmospheric CO2 comes from
volcanoes, burning fossil fuels, and
other sources.
Oceanic CO2 Hydrosphere
CO2 dissolves in the cold water of the
ocean, and the colder the
temperature, the more it dissolves.
Large amounts of dissolved CO2
remain in the bottom of the ocea
[Show More]




.png)
.png)