Heap-leach extraction removes gold from ore by
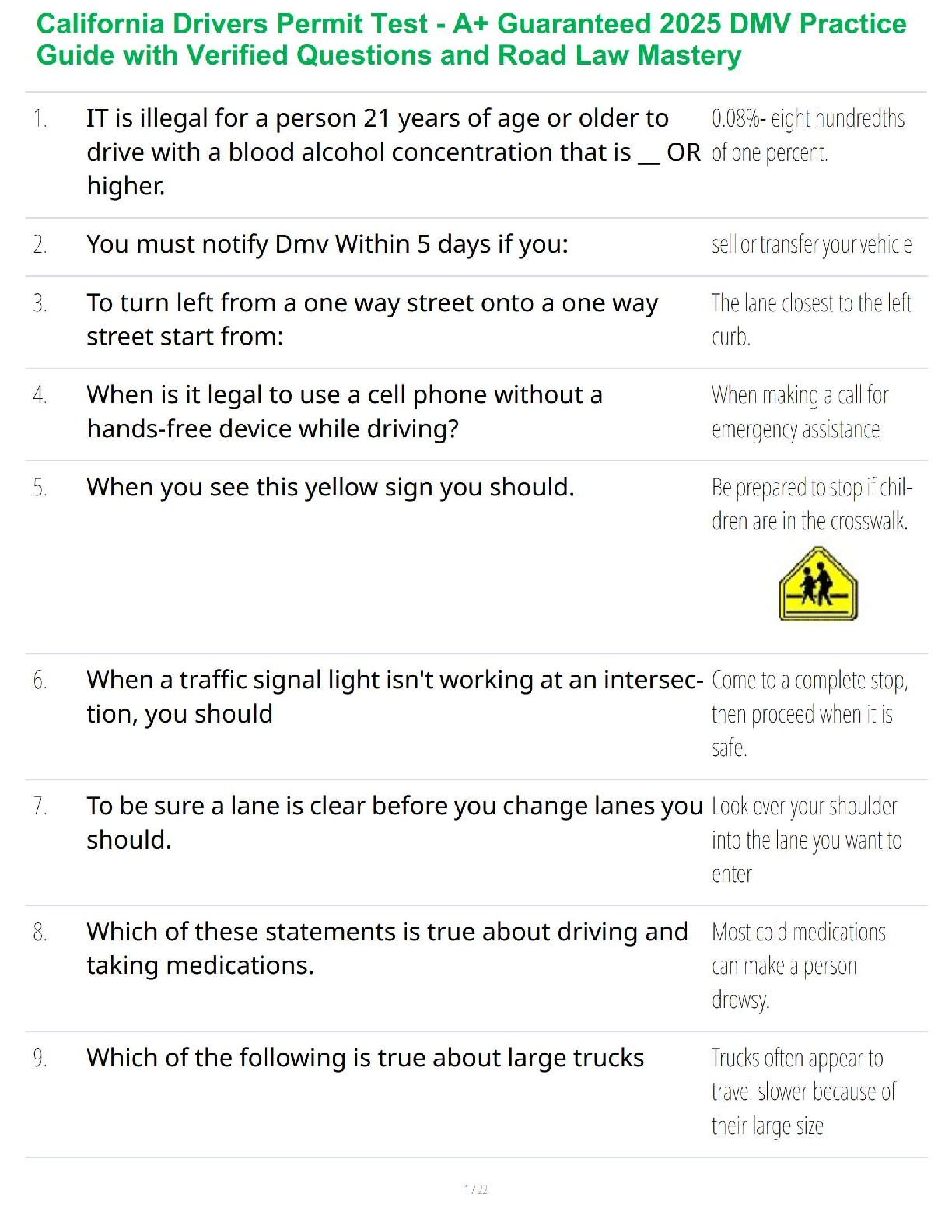
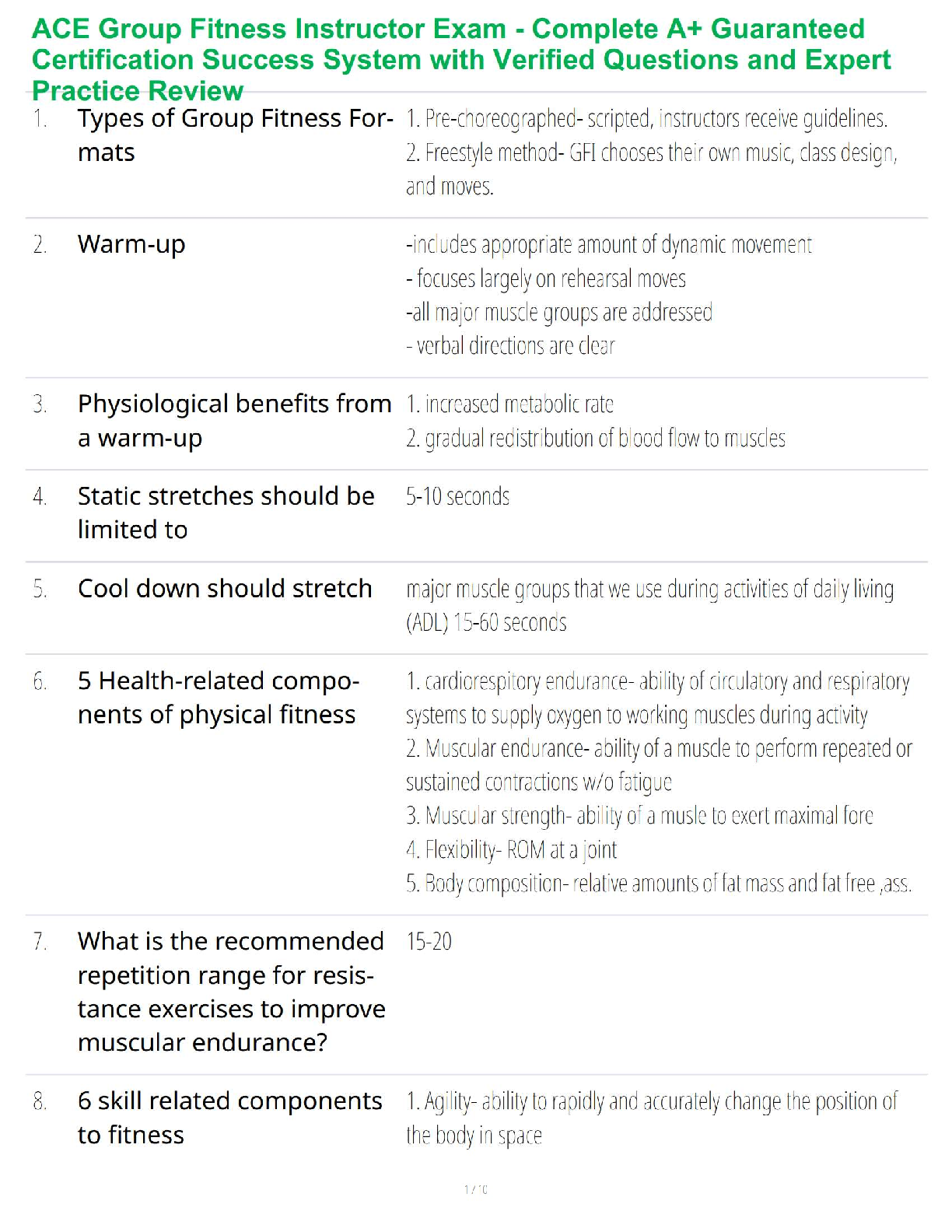
A. Pouring gravel into holding tanks
B. Spraying cyanide on a pile of ore gravel
C. Roasting ore to release the gold
D. High-pressure spraying of ore
E. Digging the
...
Heap-leach extraction removes gold from ore by
A. Pouring gravel into holding tanks
B. Spraying cyanide on a pile of ore gravel
C. Roasting ore to release the gold
D. High-pressure spraying of ore
E. Digging the gold out of the mountains
2. In the diagram, the mantle is labeled
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
3. In the diagram, the semisolid part of the Earth is labeled
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
4. In the diagram, the densest part of the Earth is labeled
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
5. Which of the following statements regarding tectonics is true?
A. Because of tectonic movements, Europe and Africa are drifting slowly toward the Americas
B. When continental plates collide with continental plates, both plates usually subside
C. When oceanic plates collide with continental plates, the continent usually rides up over the seafloor
D. Because of tectonic movements, California is slowly increasing in size
E. When oceanic plates collide with continental plates, the oceanic plate usually rides up over the continental plate
6. Subduction is the process of a tectonic plate
A. Falling freely into the mantle
B. Being forced below another plate
C. Melting without moving
D. Sliding alongside another plate
E. Being sucked into the outer core
7. The "ring of fire" is the source of more earthquakes and volcanic activity than any other place on earth.
What causes the ring of fire?
A. The subduction of Pacific plates under continental plates
B. The drift of Europe and Africa away from the Americas
C. The collision of two continental plates
D. Mid-oceanic ridges
E. The conduction currents in the hot magma
8. A mineral is composed of
A. Other minerals
B. Noncrystalline elements
C. Inorganic elements
D. A metal and a crystal
E. Organic material
9. The basic material of rocks is a cohesive group of
A. One or more minerals
B. Any noncrystalline elements
C. One or more inorganic elements
D. A metal and a crystal
E. One or more organic elements
10. Rock formed from magma extruded to the surface through volcanic vents is classified as
A. Sedimentary
B. Igneous
C. Metamorphic
D. Weathered rock
E. Lava
11. Water, wind and glaciers are examples of forces that cause
A. Chemical weathering
B. Mechanical weathering
C. Abrasion
D. Sedimentation
E. Metamorphosis in rocks
12. The physical breakdown of a rock into smaller pieces is called
A. The rock cycle
B. Sedimentation
C. Chemical weathering
D. Mechanical weathering
E. Abrasion
13. Metamorphic rocks are produced when rocks are
A. Chemically weathered
B. Recrystallized by heat and pressure
C. Physically broken down
D. Melted in the mantle and recrystallized
E. Recrystallized through chemical processes
14. Under the 1872 U.S. General Mining Law, mining companies are required to pay what percentage of their profits in taxes?
A. 2 percent
B. 8 percent
C. 12.5 percent
D. 15 percent
E. No taxes are paid on mining profits
15. According to the 1872 General Mining Law, miners can stake claim anywhere on public land, but must pay __________ per acre to take the minerals they find.
A. Less than US $5.00
B. US $50.00
C. US $500.00
D. US $5000.00
E. None of these, miners do not have to pay anything, they just have to lay claim to the land
16. Reclamation of strip-mined land is difficult chiefly because
A. Nobody can afford it because the minimum reclamation costs about $1000 per acre
B. Topsoil is mixed up and buried so topsoil must take time to develop again for plants to grow
C. There is no legal enforcement
D. No plants will grow in the spoil banks because of the heavy load of dangerous chemicals
E. There are no subsidies that exist for mining, unlike other resource-based industries
17. Smelting ore, as in Ducktown, Tennessee, releases toxic chemicals in the form of
A. Gases, from baked ore
B. Liquids, from leaching processes
C. Dust, from grinding ore gravel
D. Solids, in the form of toxic waste
E. All of these are correct
18. It takes _______________ energy to recycle waste aluminum (e.g., beverage cans) compared to the energy of extracting new aluminum from bauxite.
A. About half as much
B. About twice as much
C. About one-twentieth as much
D. About the same
E. Slightly more
19. On average, it takes ______________ energy to produce steel from scrap metal compared to the energy of producing steel from raw ore.
A. About half as much
B. About twice as much
C. About one-twentieth as much
D. About the same
E. Slightly more
20. In terms of mineral resources, recycling is ________ as raw materials become more _______ and ________ are more plentiful.
A. Slowly increasing; scarce; wastes
B. Slowly decreasing; scarce; environmental laws
C. Quickly increasing; expensive; environmental laws
D. Quickly decreasing; scarce; wastes
E. Staying about the same; expensive; environmental laws
21. ______________ can lead to mass wasting.
A. Clearcutting on steep slopes
B. Building on the flood plain
C. Building flood walls for flood control
D. The overuse of our natural resources
E. All of these are practices that can lead to mass wasting
22. Placer mining involves washing metals, minerals and the gemstones from streambeds with a water cannon.
True False
Chapter 15: Air Weather and Climate
23. Climate is a description of ________ weather conditions.
A. Long-term, regional
B. Stable and unchanging
C. Temporary
D. Temporary, local
E. Annual
24. The two main gases making up the lower atmosphere are
A. Helium and hydrogen
B. Carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide
C. Oxygen and methane
D. Nitrogen and oxygen
E. Oxygen and carbon dioxide
25. Aerosols are
A. Gases produced by industry
B. Tiny particles and droplets suspended in the air
C. The principal gas involved in the greenhouse effect
D. Tiny droplets of a very specific chemical composition
E. The principal gas involved in global warming
26. The "ozone hole" that causes concern among scientists and the public is an ozone depletion in the
A. Troposphere
B. Stratosphere
C. Thermosphere
D. Mesosphere
E. Tropopause
27. Much of the ultraviolet light from the sun is absorbed by _______ as it passes through the atmosphere.
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Water vapor
C. Nitrogen gas
D. Ozone
E. Green house gases
28. Albedo is a term describing the Earth's
A. Reflection of solar radiation
B. Refraction of energy
C. Production of radiant heat
D. Use of energy in biomass production
E. Outgoing infrared energy
29. Which of the following would have the highest albedo?
A. A field of black soil
B. A snowfield
C. A dark forest
D. An asphalt parking lot
E. A grass field
30. The greenhouse effect in the atmosphere occurs because
A. Clouds reflect sunlight back into space
B. Oceans absorb heat and then release it slowly at night
C. Stratospheric ozone absorbs UV radiation
D. CO2, water vapor, methanol and other gases absorb infrared radiation
E. All of these are correct
31. The phenomenon causing the greenhouse effect is that ________ in the lower atmosphere selectively absorbs reradiated ________ radiation.
A. Ozone; visible light
B. Carbon dioxide, methane and other gases; infrared (heat)
C. Hydrocarbons; very short wavelength
D. Carbon dioxide; ultraviolet
E. Carbon dioxide, methane and other gases; insolation
32. Why don't storms over land have as much energy as storms over oceans?
A. Convection currents are intensified by the latent energy of condensation
B. Convection currents are intensified by the latent energy of warm dry air
C. High pressure cells are more common over oceans
D. There aren't as many low-pressure systems over land
E. None of these, storms over land have as much energy as those over oceans
33. Milankovitch cycles involve the periodic ___________ and could be responsible for ________ weather changes.
A. Convection currents in the lower atmosphere; drastic
B. Summer/winter seasonality on the Earth; gradual
C. Wobbling of the earth's axis and orbital shifts; cyclic
D. Tidal cycles from month to month; seasonal
E. Seasons; daily
34. When El Ni–o occurs every three to five years, a mass of warm Pacific water that is usually pushed westward by trade winds
A. Surges back eastward toward South America
B. Becomes much warmer than usual, strengthening trade winds
C. Cools dramatically
D. Sinks and therefore cools substantially
E. Surges northward toward Japan
35. Proponents of climate change say that given what we know about the probability of the greenhouse effect the best thing to do is
A. Immediately cease all industrial activity
B. Wait and see how much temperatures change before we change our habits
C. Severely cut back on production of greenhouse gases
D. Not worry about greenhouse gas production
E. Focus on the development of technological advances to help decrease the effects of climate change
36. Most of the excessive carbon dioxide that is expected to cause global warming is generated by green plants.
True False
37. Since biodiversity is usually higher in warmer, milder climates, biodiversity will probably be increased with global warming.
True False
38. What does the acronym ENSO stand for? Describe the weather patterns in the U.S. as a result of ENSO.
El Nino/Southern Oscillations
The northern jet stream (which is normally over Canada) splits and is drawn over the US. This pulls warm moist air from the pacific and gulf of mexico inland, bringing intense storms and heavy rains from CA across the Midwestern states
39. What is the Kyoto Protocol? Discuss the role of the U.S. government, the role of big business in the U.S. and the role of individual citizens in meeting the standards set by the Kyoto.
Called for a 5% reduction in carbon emissions
Chapter 16: Air Pollution
40. Primary pollutants are those that are
A. Released directly in dangerous forms
B. Produced in the greatest quantities
C. The most dangerous
D. The most threatening to people
E. Classified by the EPA as the most dangerous and abundant
41. Secondary pollutants
A. Harm only vulnerable members of a population
B. Become dangerous after reacting in the atmosphere
C. Are produced in lesser quantities than primary pollutants
D. Are less dangerous than other pollutants
E. Classified by the EPA as the second most dangerous and abundant
42. Fugitive emissions are produced by
A. Smokestacks
B. Power plants and other heating equipment
C. Reactions between pollutants and atmospheric gases
D. Strip mining, rock crushing and other dust-producing activities
E. Industry and must go through a smokestack for filtration
43. Criteria pollutants are those that
A. Contribute the most to air quality degradation
B. Are most highly toxic even in small quantities
C. Are easiest to get rid of
D. Cause the most damage to buildings
E. Set the standards for other pollutants
44. The brown haze in smog is caused by
A. Sulfuric acid
B. NO2
C. Carbon monoxide
D. Chlorofluorocarbons
E. Particulates
45. An aerosol is
A. A chemical propellant
B. A rigidly defined chemical composition
C. Any liquid droplet or solid particle suspended in air
D. Not considered as hazardous to human health as other air pollutants
E. Not as apparent in the air as other air pollutants
46. The most dangerous airborne particulates are those
A. Large enough to damage skin and eyes
B. Small enough to be drawn into the lungs
C. That are anthropogenic
D. That are liquid
E. Produced in industrial settings
47. Anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are
A. Increasing at the rate of about 0.5 percent per year
B. Easily determined with recent technological advances
C. Measured with a great deal of precision
D. All offset by carbon storage in northern forests
E. All of these are correct
48. Many fish contain high levels of _____________ and should either not be eaten or their consumption should be limited.
A. Lead
B. Mercury
C. Chloroform
D. Ozone
E. Chlorophyll
49. Which of the following statements is true?
A. Most carbon monoxide produced in the United States comes from internal combustion engines (cars)
B. Nearly all emissions of sulfur compounds are anthropogenic
C. Overall, in the past twenty years air pollution conditions have steadily decreased in most North American and Western European cities
D. Volatile organic compounds are produced exclusively by human activity
E. None of these is correct
50. Ozone is produced by
A. Incomplete burning of fuels
B. Combustion of sulfur containing fuel
C. Decaying organic matter
D. Photochemical oxidation
E. The burning of coal
51. Aesthetic degradation is a term that describes
A. Health risks associated with pollution
B. Primarily the brown color of smoggy air
C. Noises, odors and light pollution
D. The discomfort of knowing the air is dirty
E. The apparent form of air pollution because they leave dirty residues
52. Radon in houses comes from
A. Building materials in walls
B. Emissions from furnaces
C. Radioactive decay in the Earth below a house
D. Solar radiation coming through the roof
E. Home furnishing such as carpets, curtains and furniture
53. Native peoples living in the Canadian Arctic have some of the highest recorded PCB concentrations in their bodies because of
A. Unusually high susceptibility to contamination
B. Concentrated natural occurrence of PCBs in that region
C. Local production of PCBs
D. Long-range transport of airborne pollutants
E. An industrial accident that left the persistent PCBs in the environment
54. ___________ ozone is harmful, damaging plants and human health while ozone at the _________ level screens out mutagenic ultraviolet radiation.
A. Stratospheric; troposphere
B. Thermospheric; mesosphere
C. Tropospheric; stratosphere
D. Mesospheric; thermosphere
E. Stratospheric; mesosphere
55. Pollutants such as chlorofluorocarbons deplete atmospheric ozone
A. When nitrogen combines with O3 to form NOx
B. When chlorine-containing molecules are oxidized at the expense of O3
C. Because chlorine is most stable as ClO3
D. When carbon reacts with O3 to form CO3
E. None of these is correct
56. The most common human health response to air pollution is
A. Inflammatory responses in sensitive tissues
B. Lung cancer
C. Blindness caused by deteriorating eye tissues
D. Skin cancer
E. Heart disease
57. Which of the following is the best example of synergistic effects?
A. The disappearance of plant life around Sudbury, Ontario
B. The prevalence of cancer among smokers exposed to asbestos fibers
C. The appearance of PCBs in residents of remote Arctic villages
D. Cancer caused by fibrosis in the lungs
E. Chlorosis in plant leaves
58. Worldwide, air pollution control efforts are least advanced or least successful in
A. Major cities of leading industrialized countries
B. Major cities of developing countries
C. Small towns in developing countries
D. Rural areas in industrialized countries
E. Small towns of leading industrialized countries
59. Norilsk, Russia has been notable in recent years for its
A. Widespread and terrible pollution conditions
B. Severe acid deposition
C. Complete lack of industrial pollution
D. Steady and successful cleanup accomplishments
E. None of these is correct
60. Human-produced pollutants are different from natural particulates and gases because they are almost always chemically more dangerous.
True False
61. Synergistic effects occur when there is more damage of exposure when two factors are together.
True False
Chapter 17: Water Use and Management
62. Which of the following is not a factor in determining how much or how little precipitation a region receives?
A. Topography
B. Global atmospheric circulation patterns
C. Vegetation
D. Proximity to water
E. All of these are important factors
63. Transpiration is the way plants
A. Return large amounts of water to the atmosphere
B. Absorb water from the atmosphere
C. Absorb water from the ground
D. Return large amounts of water from the atmosphere to the ground
E. Respire using water
64. Evaporation is
A. The way plants absorb water
B. Liquid water turning to vapor well below boiling temperature
C. Liquid water boiling to produce water vapor
D. The way water seeps into the ground
E. The process of water becoming a liquid at a lower temperature
65. The rainiest or snowiest zone on the mountain in the diagram would be in the area marked
A. From A to B
B. From B to C
C. From C to D
D. At A and at D
E. At C and at D
66. Air moving in the direction indicated in the diagram will become dryer as it moves from
A. B to D
B. A to B
C. C to A
D. D to A
E. None of these is correct
67. Residence time of water in oceans is a measure of the
A. Age of the oceans
B. Average amount of time a water molecule spends in the ocean
C. Average amount of time needed for the entire ocean to be replaced by rainfall
D. Time an average water molecule spends in one region before it circulates to another
E. Average time it takes for a water molecule to make its way back to the ocean
68. The hydrologic compartment that contains the greatest amount of fresh water is
A. Groundwater
B. The Great Lakes
C. Living organisms and biomass
D. Ice and snow
E. Clouds in the atmosphere
69. Water enters groundwater by
A. Infiltration
B. Entering the runoff stream
C. Transpiration
D. Interception
E. Sublimation
70. The place where aquifers are most likely to be contaminated is at
A. Artesian springs
B. Seeps and other outlets
C. Recharge zones
D. All discharge and recharge areas
E. The zone of aeration
71. The amount of water in aquifers in the United States is
A. Nearly as great as the amount of surface water in the United States
B. Higher than all the Great Lakes together
C. Only a small portion of surface water in the United States
D. Over thirty times greater than all surface water in the United States
E. About the same amount as all surface water in the United States
72. The largest river in the world is the
A. Orinoco
B. Amazon
C. Mississippi
D. Nile
E. Congo
73. Which of the following factors is the most important factor in determining whether a country is "water rich" or "water poor"?
A. Population density
B. Country size
C. Humid climate
D. Rivers running through the country
E. Renewable water supplies
74. The United States has a drought cycle that brings dry periods about every ____ years.
A. 100
B. 60
C. 30
D. 10
E. 5
75. Technically speaking, when water is consumed it
A. Has been used
B. Is no longer suitable for any other purpose
C. Is no longer available for other purposes
D. Is lost to evaporation or leakage
E. Is available for other uses
76. Human water withdrawals have been increasing at about ___________ rate as worldwide population growth.
A. The same
B. Half the
C. One third the
D. Three times the
E. Twice the
77. In general, water use worldwide is dominated by
A. Agricultural use
B. Domestic needs
C. Industrial activities
D. Use as drinking water
E. All of these are sectors that use water about equally
78. The activity that uses the greatest share of U.S. household water is
A. Bathing
B. Drinking and cooking
C. Flushing the toilet
D. Washing clothes and dishes
E. Watering lawns
79. On the graph of domestic water use per person, each letter represents a country. Which of the following is most likely?
A. A is the United States; B is China
B. B is the United States; A is China
C. A is the United States; B is Canada
D. B is India; A is China
E. A is India; B is China
80. One of the major reasons for the removal of dams in the United States is
A. Buildup of silt behind the dams
B. Danger of earthquakes beneath the reservoir
C. To satisfy conservation groups
D. To restore fish populations
E. To make the region look more natural
81. The Ogallala Aquifer supplies water to ___________ and once held more water than all of the surface water __________.
A. California's Central Valley; in the world
B. The Rocky Mountain states; in the United States
C. The central Plains states; in the world
D. Most of New England; in the United States
E. Arizona and Las Vegas; in the United States
82. Withdrawal of groundwater often causes subsidence, a situation where
A. Aquifer volume decreases sharply
B. Withdrawals exceed recharge rates
C. Water quality and water tables fall
D. Porous rocks settle and ground level falls
E. Wells dry up
83. A method of increasing water supplies that has been successful, but expensive is
A. Desalination
B. Cloud seeding
C. Towing icebergs by ship from polar regions
D. Altering the climate's convection currents
E. None of these is correct
84. Many experts think that in the future, water conflicts will be a major cause of international conflict. Currently, however, there are no international conflicts over water.
True False
85. Charging a higher proportion of real costs rather than subsidies has led to water conservation.
True False
Chapter 18: Water Pollution
86. Which of the following would not help to improve water quality?
A. Composting yard waste
B. Stop using fertilizers
C. Not using jet skis
D. Changing your car oil on the driveway rather than in the grass
E. Keeping your car well maintained
87. _________ sources of water pollution are relatively easy to monitor and regulate while _____________ sources of water pollution are difficult to monitor and clean up.
A. Domestic; industrial
B. Primary; tertiary pollutant
C. Nonpoint; point
D. Tertiary pollutant; primary
E. Point; nonpoint
88. The discharge from a nonpoint source of pollution is
A. Usually constant throughout the year
B. Generally easier to regulate than a point source
C. Usually less polluting than point sources
D. Highly seasonal in quantity
E. Less damaging than other sources of pollution
89. ____________ is to point source of water pollution as _____________ is to nonpoint source of water pollution.
A. Golf course runoff; atmospheric deposition
B. Golf course runoff; power plant effluent
C. Power plant effluent; golf course runoff
D. Atmospheric deposition; golf course runoff
E. Power plant effluent; an underground coal mine drain
90. The water pollutant that most commonly threatens human health is
A. Pathogenic organisms
B. Dissolved plant matter
C. Toxic and hazardous chemicals
D. Thermal pollution
E. Oxygen-demanding wastes
91. On the graph of clean drinking water per person, each letter represents a country. Which of the following is most likely?
A. A is the United States; B is India
B. B is the United States; A is India
C. A is the United States; B is Canada
D. B is India; A is China
E. A is India; B is Canada
92. When natural waters are overloaded with plant nutrients, such as nitrate and phosphate ions, they become
A. Oligotrophic
B. Dystrophic
C. Eutrophic
D. Metatrophic
E. Megatrophic
93. Cultural eutrophication results from
A. Natural sediment and nutrient levels
B. A change in animal life as well as plants
C. The disappearance of tributary streams
D. Human activity
E. Natural topography
94. Tertiary treatment of sewage produces water that is typically used for
A. Agriculture
B. Drinking
C. Industrial activities
D. Watering livestock
E. Dumping into freshwater systems
95. Dioxins, pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls are all types of
A. Inorganic toxic substances
B. Heavy metals
C. Suspended solids and BODs
D. Acidifying agents
E. Toxic organic compounds
96. Best practical technology (BPT) is legally required for all
A. Point source polluters
B. Priority toxic pollutants
C. Pollution and polluters
D. Common toxic pollutants
E. Municipal planning officers to control urban runoff
97. The main reason that surface water pollution has largely decreased in the United States since 1950 is
A. The Clean Water Act
B. A series of epidemics that inspired action
C. The discovery of newer technology that makes it cheaper not to pollute
D. Decreases in water withdrawal for industrial uses
E. The emphasis in 1950 of watershed management
98. In 1998, a change in the approach to water quality was initiated by _________ with an emphasis on _________.
A. The EPA; cost-benefit analysis
B. A series of epidemics that inspired action; watershed management
C. Industry; cost-benefit analysis
D. Decreases in water withdrawal for industrial uses; cost-benefit analysis
E. The EPA; watershed management
99. Feedlots are a major cause of _________ in water.
A. Viruses
B. Coliform bacteria
C. Nitrates
D. Phosphates
E. All of these are correct
100. __________ should never be allowed down a drain when a septic tank and drain field system is being used for
sewage disposal.
A. Kitchen wastes from cooking
B. Dog or cat urinary or fecal matter
C. Chlorine and antimicrobial cleansers
D. Oils and greases
E. Solid materials
ENV 101 Chapters 14, 15, 16, 17, 18
Key Terms and Concepts
core
mantle
crust
tectonic plates
magma
subducted
mineral
rock
rock cycle
igneous rock
metamorphic rock
weathering
sedimentary rock
mining effects
smelting
geological hazards
mass wasting
weather
climate
troposphere
stratosphere
ozone
albedo
greenhouse effect
latent heat
Coriolis effect
monsoons
Milankovitch cycles
El Nino
La Nina
IPCC
climate change
global warming
Kyoto Protocol
carbon neutral
carbon management
air pollution
primary pollutants
secondary pollutants
fugitive pollutants
ambient air
conventional/criteria pollutants
sulfur compounds
nitrogen compounds
carbon oxides
carbon monoxide
aerosol
particulate material
VOCs
photochemical oxidants
HAPs
TRI
aesthetic degradation
stratospheric ozone
chlorofluorocarbons
Montreal Protocol
synergistic effects
acid precipitation
hydrologic cycle
transpiration
evaporation
rain shadow
groundwater
infiltration
water table
artesian well
recharge zones
discharge
water compartments
renewable water supplies
withdrawal
consumption
degraded water
water use categories
freshwater shortages
subsidence
desalination
water pollution
point sources
nonpoint sources
atmospheric deposition
BOD
DO
oligotrophic
eutrophic
red tide
inorganic pollutants
organic pollutants
1972 Clean Water Act
TMDL
water quality problems
primary treatment
secondary treatment
tertiary treatment
effluent sewerage
BPT
BAT
[Show More]

.png)







.png)