BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BioChem C785 unit 2 Questions with all the correct answers latest update (All)
BioChem C785 unit 2 Questions with all the correct answers latest update
Document Content and Description Below
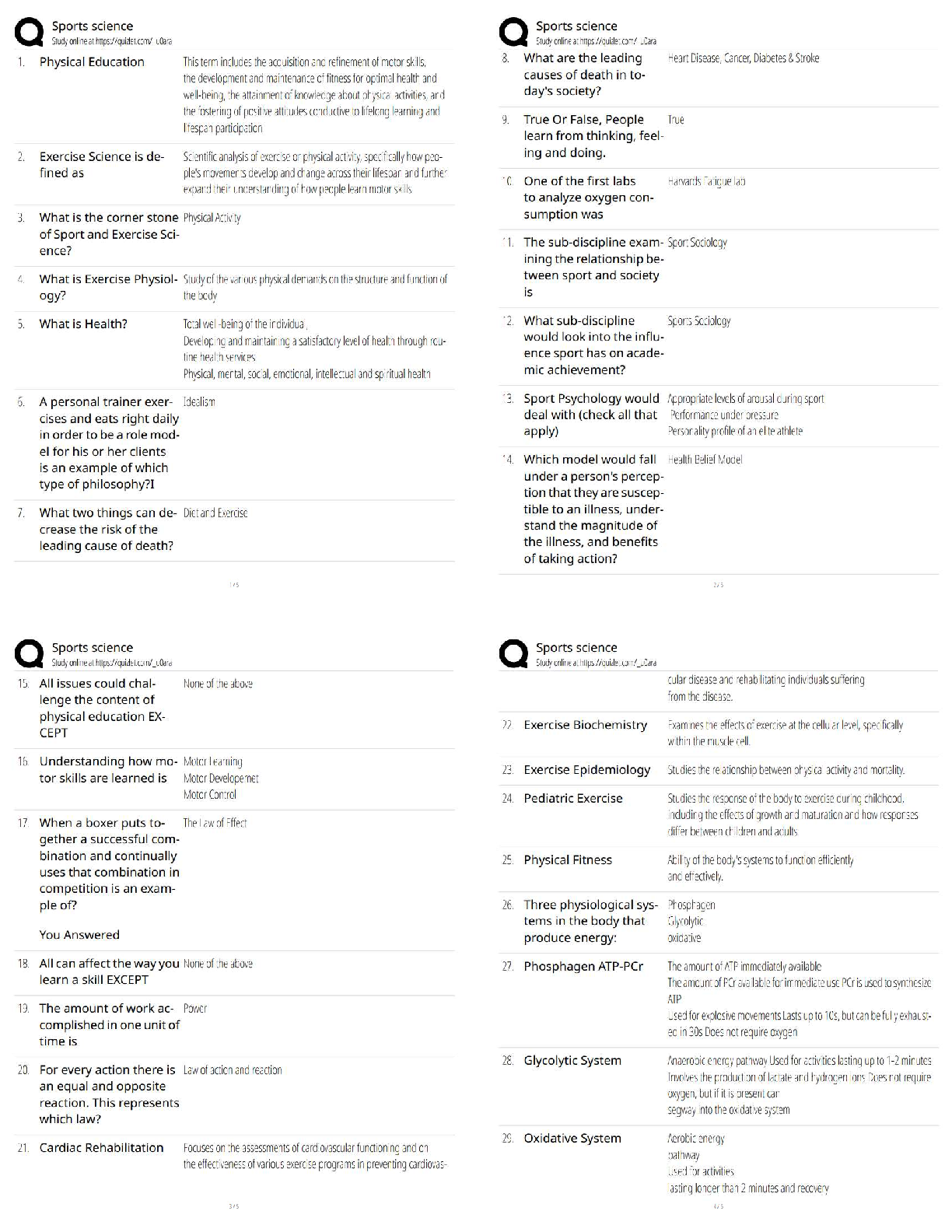
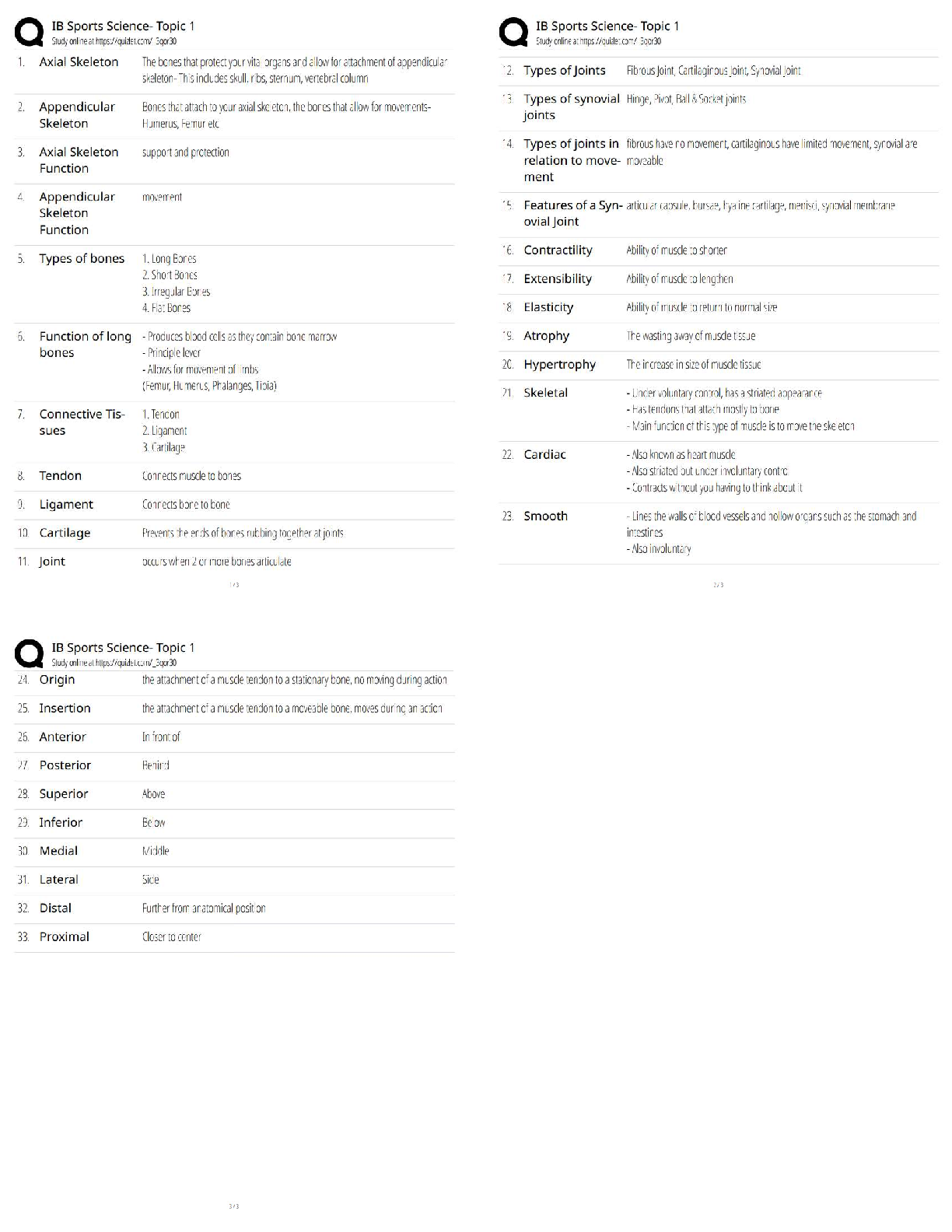
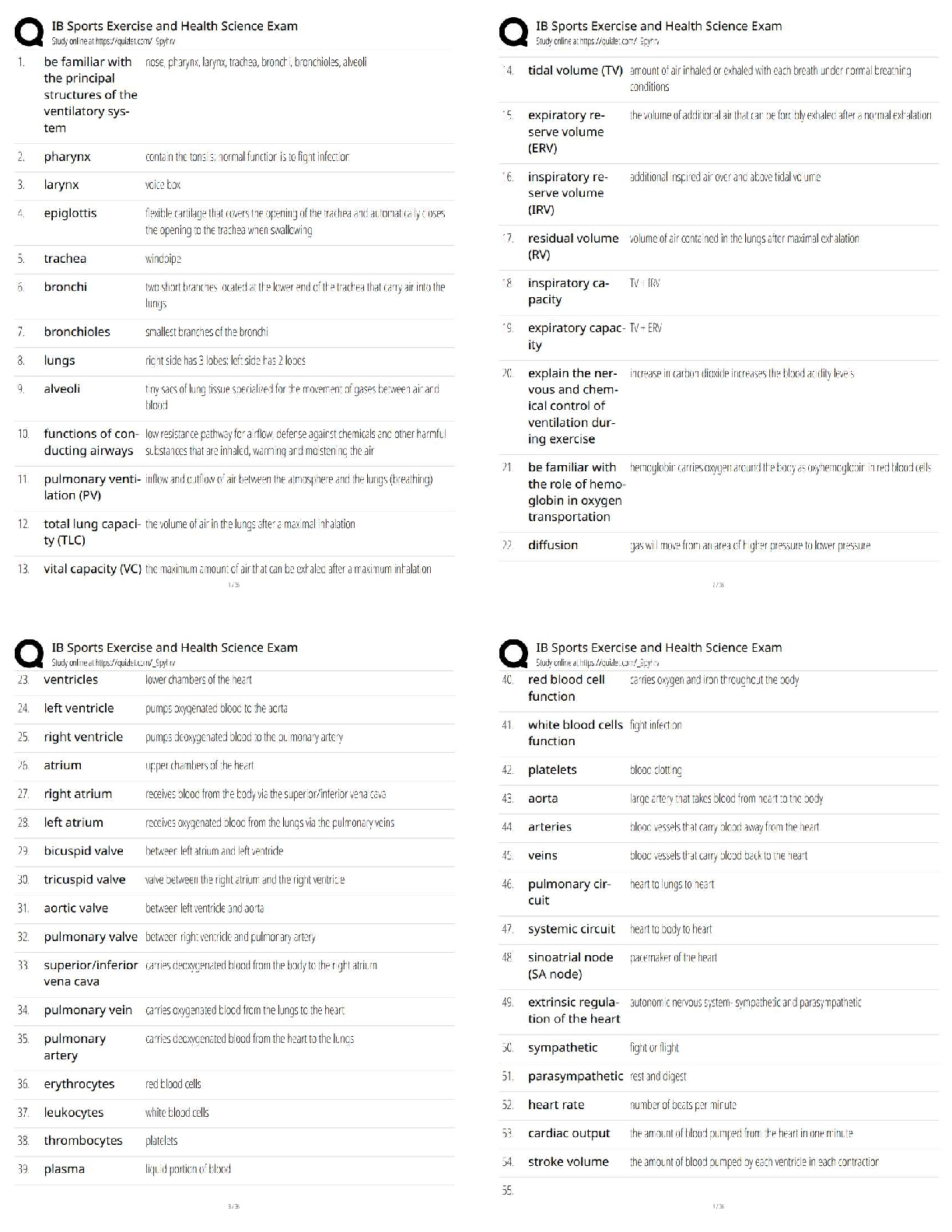
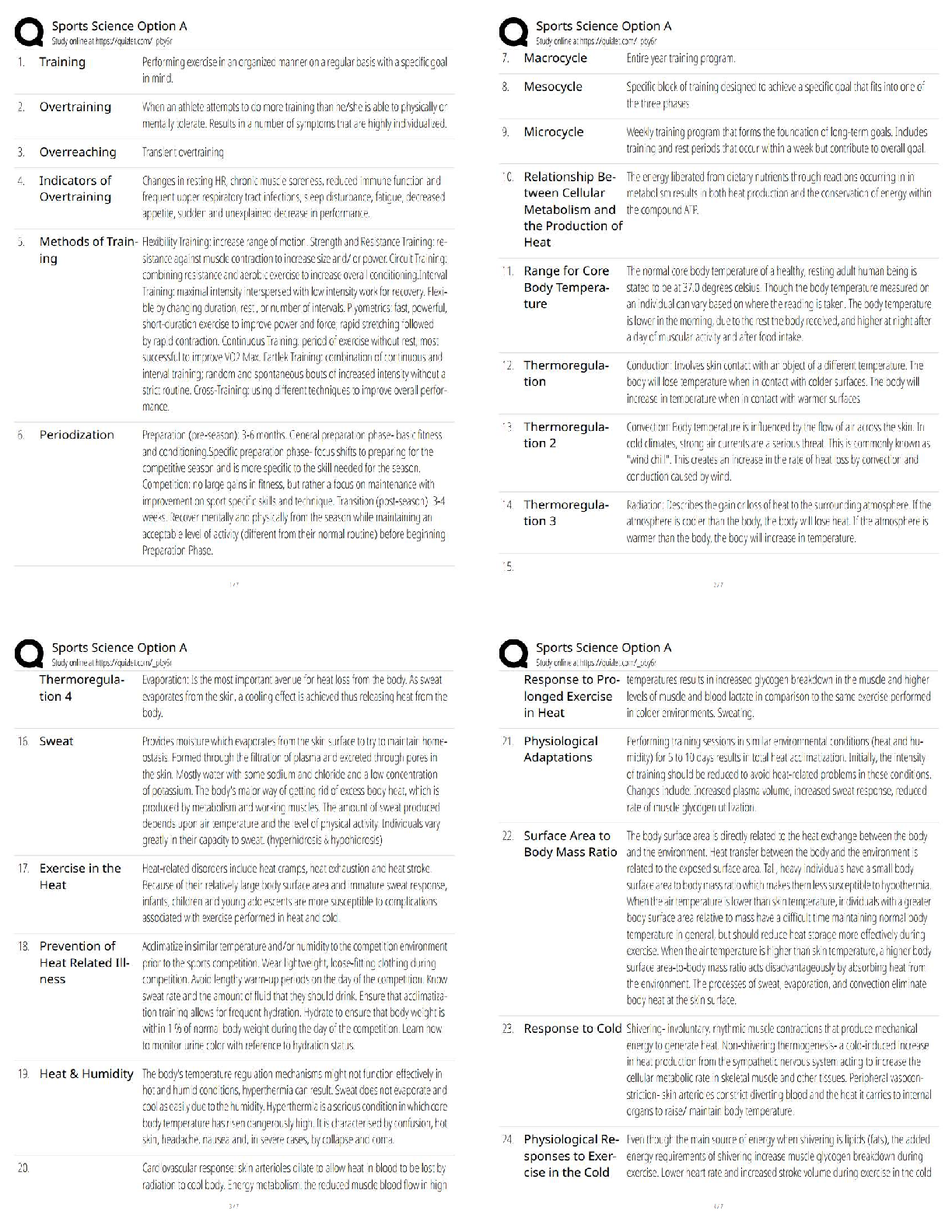
ioChem C785 unit 2 Questions with all the correct answers Hydrogen bond Correct Answer- Weak bond interaction Between two molecules Amino group Correct Answer- Consists of hydrogen and nitrogen atom ... s (-NH3+) Macromolecules Correct Answer- A giant molecule in a living organism formed by the joining of smaller molecules: a protein, carbohydrate, or nucleic acid. polymer Correct Answer- a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds Amino acid Correct Answer- Amino group + Carboxylic acid + R group = Amino acid carboxyl group Correct Answer- A -COOH group, found in organic acids. Coo-, O=C-O- Four classes of biological macromolecules Correct Answer- Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids SPONCH Correct Answer- Sulfur phosphorous oxygen nitrogen carbon hydrogen polymer Correct Answer- a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together by covalent bonds. R group Correct Answer- a functional group that defines a particular amino acid that makes it a specific protein (20 amino acids) aka side chain Catalyst Correct Answer- Speed up chemical reactions but remain unchanged by the reaction. Monomers Correct Answer- repeating units that serve as the building blocks of a polymer enzymes Correct Answer- specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions in cells alpha carbon Correct Answer- the central carbon atom of each amino acid Atomic number Correct Answer- number of protons atomic mass Correct Answer- number of protons plus number of neutrons dehydration synthesis Correct Answer- a chemical reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule. amino acid backbone Correct Answer- The structure comprised of the amino group, carboxyl group with a central alpha carbon atom. dehydration reaction Correct Answer- A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule. Ionic bond Correct Answer- formed when two oppositely charged ions attract Hydrophobic Correct Answer- non polar, afraid of water Disulfide bond Correct Answer- double (di) bond between two Sulfur (sulfide) atoms in cysteine side chains. They stabilize tertiary and quaternary structures of a protein. carbohydrates Correct Answer- Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one carbon atom to two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom. They exist as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. protein Correct Answer- a macromolecule consisting of one or more polypeptides chains made up amino acids folded and coiled into a specific three-dimensional structure. polar Correct Answer- Amino acid Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water. covalent bond Correct Answer- formed when the difference in electronegativity between A atoms is equal they then share electrons Polar covalent bond Correct Answer- when electrons are unequally shared between Atoms because they have different electronegativities Functions of proteins Correct Answer- structural support, catalyst, transport, defense, movement, regulation charged Correct Answer- Amino acid has a positive or negative charge hydrophobic effect Correct Answer- (Water Fearing). Tendency of nonpolar (non charged) substances to aggregate (clump together) in water and exclude the water molecules. amino acid Correct Answer- an organic molecule possessing both a carboxyl and an amino group. The monomers of polypeptides. There are 20 different forms. Distinguished by side chains. hydrophobic interactions Correct Answer- Interaction between nonpolar molecules in water. Polypeptide Correct Answer- A single protein chain formed by amino acids bonded together peptide bond Correct Answer- the linkage between amino acids forming a covalent bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on another, formed by a dehydration reaction. denaturation Correct Answer- loss of a proteins normal 3D structure; can possibly be caused by pH and temperature changes which affect the ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds & hydrophilic interactions Hydrolysis Correct Answer- Peptide bonds can be broken by this...A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water. ( this happened frequently in the stomach when proteins begin to bee digested into their amino acids) enzyme Correct Answer- a macromolecule serving as a catalyst, a chemical agent that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. most of them are proteins. Primary Structure Correct Answer- Sequence of amino acids forming a protein or polypeptide chain, the most basic element of its structure. What are the functions of carbohydrates Correct Answer- function as energy source & structure support; examples: simple sugars, and complex polysacchrides, structural suppport examples: cell wall in pant cells, chitin in insects. cellulose Correct Answer- a structural polysaccharide of plant cell walls, consisting of glucose monomers joined by β glycosidic linkages. Quaternary structure Correct Answer- Spatial arrangement of two or more individual polypeptide chains. primary structure Correct Answer- sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide aka amino acid chain [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

WGU Biochemistry 785 Full Solution Pack(Bundled exams 100% verified)
BioChem C785 module 2 quiz with complete solution WGU Biochemistry Final Review WGU 785 Final Exam With Complete Solution WGU BioChem OA Review with complete solution C785 Biochemistry preassessment w...
By Nutmegs 3 years ago
$22
21
Reviews( 0 )
$9.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 10, 2022
Number of pages
11
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 10, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
184








.png)