Religious Studies > EXAMs > RELI 367 YOGA Exam 2. Scored 100%. (All)
RELI 367 YOGA Exam 2. Scored 100%.
Document Content and Description Below
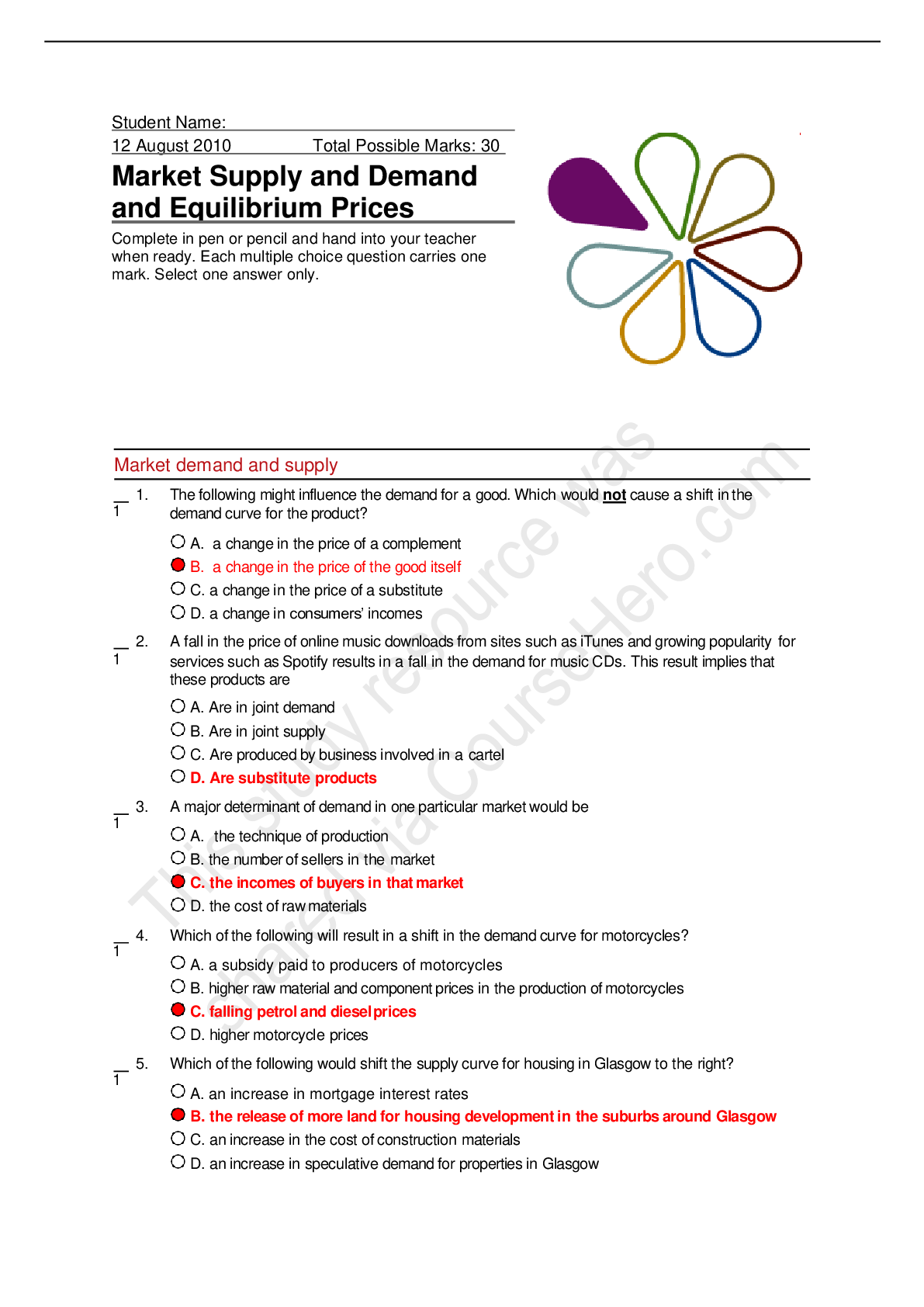
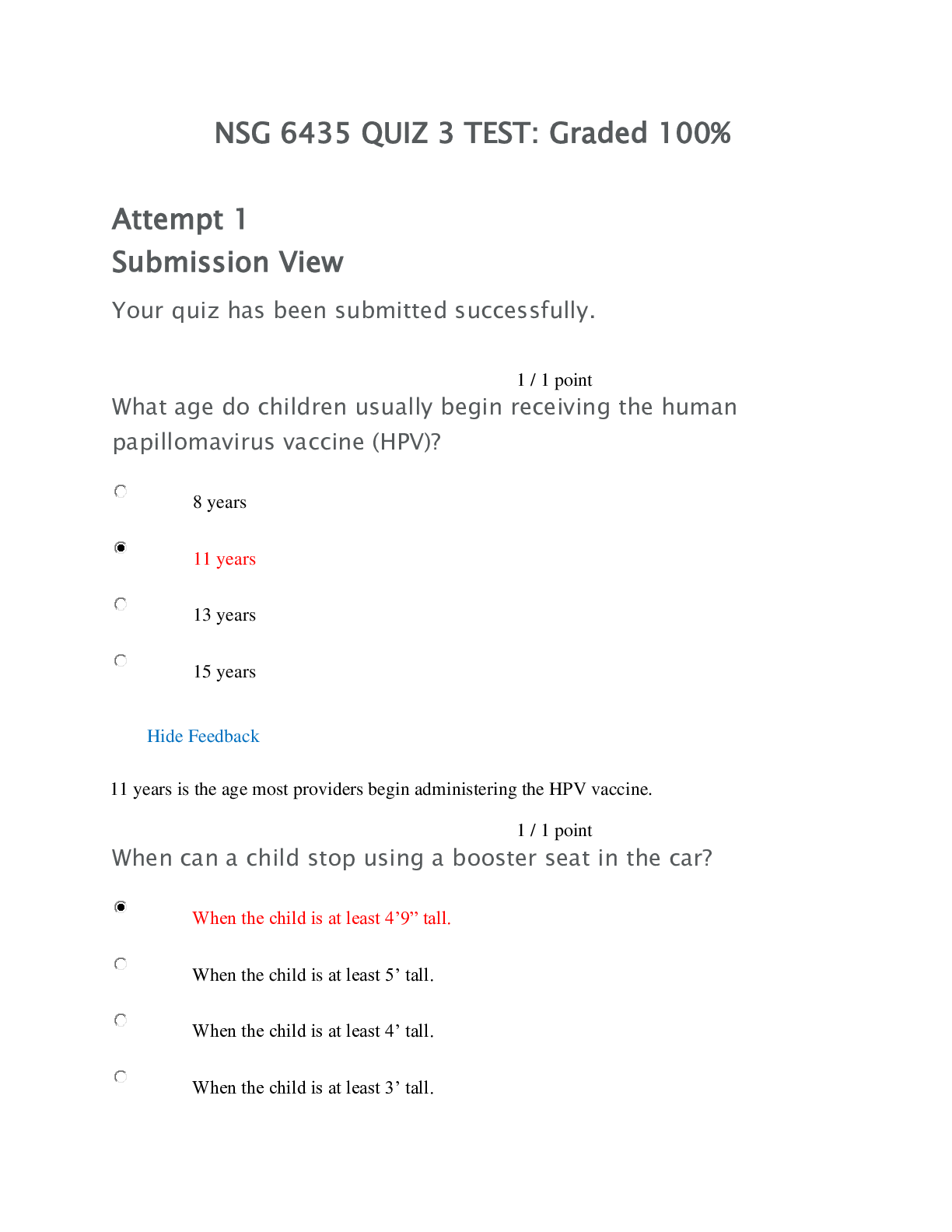
RELI 367: YOGA Fall 2020 Question 1 (1 point) Saved “There is no right to [practice] yoga without initiation.” According to this verse in the Mālinīvijayottara, which of the following is ... necessary for yoga practice? Question 1 options: deity manual guru mantra Question 2 (1 point) Saved “Enthusiasm, boldness, patience, knowledge of the levels of reality, resoluteness and renunciation of contact with people” In the Haṭhayogapradīpikā, these are considered hindrances to yoga practice. Question 2 options: True False Question 3 (1 point) Saved “The afflictions are ignorance, egoism, passion, aversion, and clinging to life” This passage from Patañjalayogaśāstra is similar to Kṛṣṇa’s description of the causes of saṃsāra in the Gītā. Question 3 options: True False Question 4 (1 point) Saved Classical yoga texts are female-centric. Question 4 options: True False Question 5 (1 point) Saved “One should shun those who wear religious garb. These people are always obstacles to your yoga practice.” According to the Dattatreyayogaśāstra, institutional religion is a good thing for yoga practice. Question 5 options: True False Question 1 (1 point) Saved In early yoga texts, āsanas (postures) were ________________. Question 1 options: Complex Simple and seated Question 2 (1 point) Saved Postural yogic sequences were first associated with which of the following groups when encountered by Europeans? Question 2 options: priests Americans street performers holy people Question 3 (1 point) Saved What major change can be associated with Hemacandra? Question 3 options: Banning yoga in temples Naming postures Associating yoga with god Introducing yoga to non-ascetics Question 4 (1 point) Saved Postural yoga has been part of which of the following religious traditions? Question 4 options: Hinduism Jainism Buddhism All of the above Question 5 (1 point) Saved There are no examples of early yoga outside of yoga texts. Question 5 options: True False Question 1 (1 point) Saved Prāṇāyāma seems to have always been central in yoga practice, especially haṭha yoga. Question 1 options: True False Question 2 (1 point) Saved Some texts argue that breath control leads to liberation. Question 2 options: True False Question 3 (1 point) Saved There is no relationship between the mind and breath. Question 3 options: True False Question 4 (1 point) Saved What is prāṇāyāma? Question 4 options: lotus position devotion Krishna's true form breath control Question 5 (1 point) Saved Prāṇāyāma is said to be a purifying process. Question 5 options: True False Question 1 (1 point) Saved What is a nāḍī? Question 1 options: conduit of energy rounded pot means of perfection form of purification Question 2 (1 point) Saved What is a cakra in the yogic body? Question 2 options: difficult posture left big toe mental awakening hub of different energy conduits Question 3 (1 point) Saved What does Kuṇḍalinī literally mean? Question 3 options: she who gives awakening through meditation movement of vital energy true liberation she who is coiled Question 4 (1 point) Saved Modern yoga emphasizes the __________ body, but classical yoga emphasized the _______body. Question 4 options: beautiful; smart flexible; strong anatomical; metaphysical metaphysical; anatomical Question 5 (1 point) Saved Where does bindu reside in the yogic body? Question 5 options: genitals left big toe heart head Question 1 (1 point) Saved What is a mudra in the context of classical yoga? Question 1 options: seal hand gesture monkey pose amulet Question 2 (1 point) Saved What is the purpose of a mudra in classical yoga? Question 2 options: to mimic the gods to speak without using verbal language to gain greater flexibility to lock in vital energy Question 3 (1 point) Saved In which context are mudras most common? Question 3 options: Shakta Shaiva Tantric Vaishnava Question 4 (1 point) Saved During which period were mudras incorporated into asana (postural) practice? Question 4 options: They were never incorporated into asana practice. ancient modern medieval Question 5 (1 point) Saved What is pictured above Question 5 options: lotus position mahamudra/great seal monkey pose sun salutation Question 1 (1 point) Saved What is the literal meaning of the word "mantra?" Question 1 options: instrument of thought word to live by You only live once magic Question 2 (1 point) Saved __________ is often called "mantra marga" or the "path of mantras." Question 2 options: Shaktism Vaishnavism Shaivism Tantra Question 3 (1 point) Saved The chant "OM" is an example of which of the following? Question 3 options: mudra prana asana mantra Question 4 (1 point) Saved Mantra has never been associated with breath control Question 4 options: True False Question 5 (1 point) Saved Hathayoga traditionally dismisses mantras as a lower form of practice. Question 5 options: True False Question 1 (1 point) Saved What is the pivotal practice between inner and outer yogic practice? Question 1 options: pratyāhāra intellect śramaṇa praṇāyama Question 2 (1 point) Saved What is the practice of dhāraṇā? Question 2 options: cultivation of advanced mental and ontological states wanting something really badly concentration and placement of the mind retraction of the mind from phenomenal objects Question 3 (1 point) Saved What is the practice of pratyāhāra? Question 3 options: concentration and placement of the mind retraction of the mind from phenomenal objects wanting something really badly cultivation of advanced mental and ontological states Question 4 (1 point) Saved What is the practice of dhyāna? Question 4 options: retraction of the mind from phenomenal objects cultivation of advanced mental and ontological states concentration and placement of the mind wanting something really badly Question 5 (1 point) Saved What is the meaning of dhyāna? Question 5 options: withdrawal cognition fixation meditation Question 1 (1 point) Saved What is the last limb of the 8-limbs of yoga? Question 1 options: samadhi dharana dhyana asana Question 2 (1 point) Saved Yogic powers or siddhis are accepted by all classical yoga traditions. Question 2 options: True False Question 3 (1 point) Saved What is the literal meaning of samadhi? Question 3 options: some idea joining/combining difficult posture enlightenment Question 4 (1 point) Saved What is the ultimate goal of classical yoga? Question 4 options: Ripped body Making friends Flexibility Liberation Question 5 (1 point) Saved The ultimate goal in classical yoga was always theistic. Question 5 options: True False [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 09, 2020
Number of pages
17
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 09, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
336