TNCC 8th edition
Document Content and Description Below
TNCC 8th edition
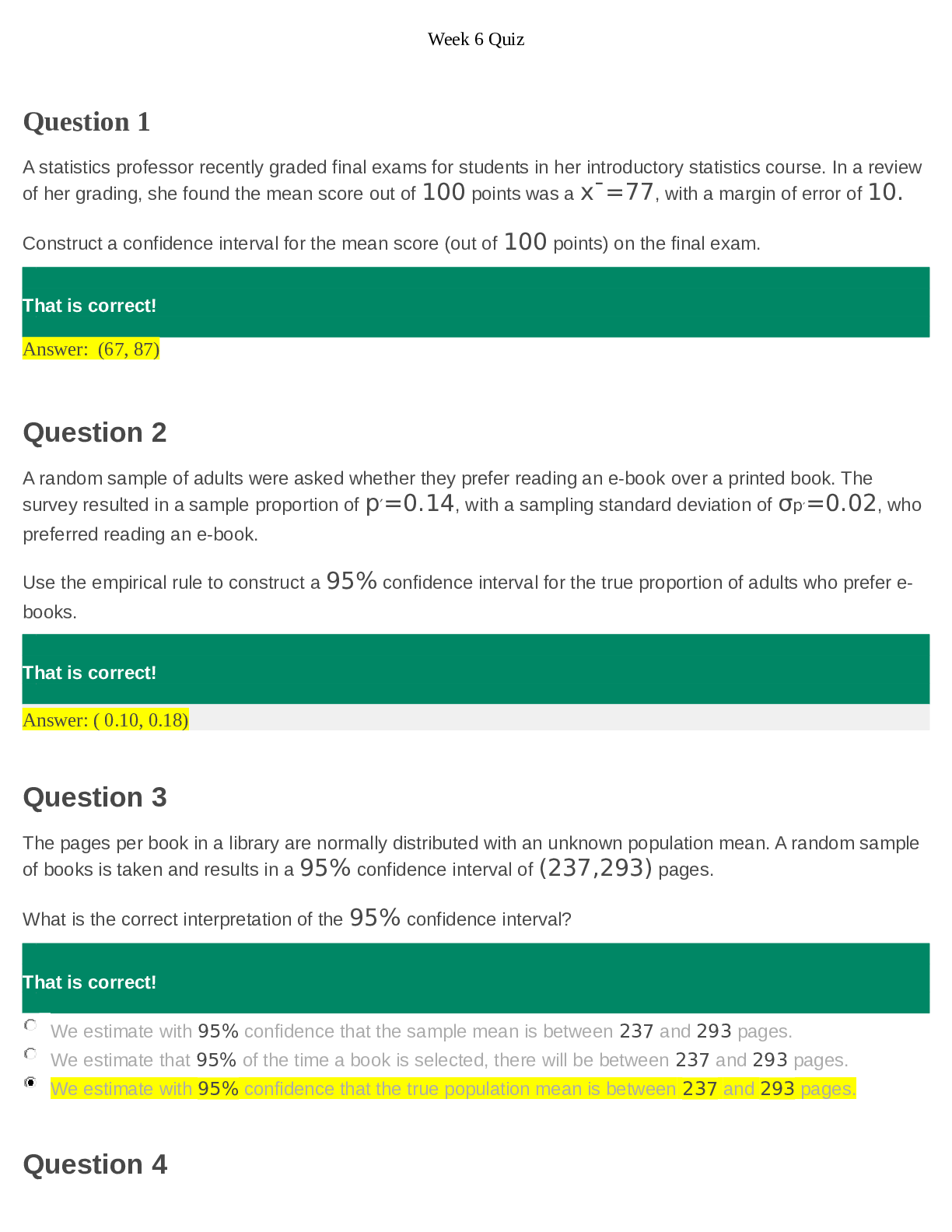
The major cause of preventable death after injury ans: Uncontrolled hemorrhage
The best measure of the adequacy of cellular perfusion and helps to predict the outcome of resusci
...
tation ans: Base deficit
Examples of primary blast injuries ans: Blast lung, ruptured tympanic membrane, TBI, abdominal hemorrhage
Examples of secondary blast injuries ans: Wounds from debris and bomb fragments
Examples of tertiary blast injuries ans: Blunt or penetrating trauma from the body being thrown by the blast
Examples of quaternary blast injuries ans: Injuries or illness related to explosion: burns, toxic injury from chemicals
Examples of quinary blast injuries ans: Injuries associated with exposure to hazardous materials from the components of the blast
Questions to ask for airway assessment (need 4) ans: Is the tongue obstructing?
Are there any foreign objects?
Is there any edema?
Are there loose or missing teeth?
Is there snoring, gurgling, or stridor?
Is there bony deformity?
Is there blood, vomit, or secretions?
Questions to ask during breathing assessment. (Need 4) ans: Is there symmetrical chest rise?
Is there spontaneous breathing?
Is there tracheal deviation or JVD?
What is their skin color?
Are there open wounds or deformities in the chest?
What's the depth, pattern, and rate of respirations?
Is there increased work of breathing?
Are breath sounds present and equal?
3 ways to assess ETT placement ans: 1. Apply end tidal, assess CO2 after 5-6 breaths
2. Assess for symmetrical chest wall rise and fall
3. Auscultation over the epigastrium for gurgling and bilateral breath sounds.
What do you document after placing an ETT? ans: ETT placement at teeth or gums
Situations that require a definitive airway ans: GCS 8 or less
Apnea
Inhalation injury
Increased risk of aspiration
Anticipate decreased neuro status
Severe maxo fractures
Laryngeal/tracheal injury
Where do you listen for breath sounds? ans: 2nd intercostal space at midclavicular line and
5th intercostal space at anterior axillary line
King airway ans: A multidimensional esophageal airway that traps the glottis opening between an esophageal cuff and an oropharyngeal cuff
3 things to assess for circulation ans: Palpate central pulse
Assess (again) for external hemorrhage
Inspect and palpate skin for color, temp, and moisture.
When do you establish IV access? ans: Right after the circulatory assessment
At what point to you evaluate need for transfer or definitive care? ans: After the primary survey
How do you palpate the iliac crests? ans: Downward and medially
The 3 components of the pediatric assessment triangle ans: Skin circulation, work of breathing, general appearance
What type of fluids should you give kids with normal blood glucose? ans: Fluids with dextrose to prevent hypoglycemia
How much fluid do you give a kid? ans: 20mL/kg
What assessment finding gives concern for severe brain injury? ans: Bulging fontanels
Parkland formula ans: 3mL x the weight in kg x % TBSA = the fluid to go over 24 hours
How do you give the fluid over 24 hours in parkland formula? ans: First half over 8 hours and second half over 16 hours
Normal baseline FHR ans: 120-160
What does Kleihaver-Betke test for? ans: Tests for fetal RBCs I. Maternal circulation, which is abnormal and could indicate fetomaternal hemorrhage has occurred
Symptoms of abruptly placentae ans: Dark red bleeding, sudden sharp abdominal pain, "board-like" uterus, increased FHR
Symptoms of uterine rupture ans: Sudden sharp abdominal or suprapibic pain, asymmetry of uterus, decreased FHR
What degree to you tilt the supine pregnant patient to prevent supine hypotension? ans: 15 degrees
3 parts of the trauma triad of death ans: Hypothermia, coagulopathy, metabolic acidosise
Examples of obstructive shock ans: Tension pneumo, cardiac tamponade, pulmonary artery embolism
Symptoms of stage 1 of shock ans: Change in neuro status, increased DBP, decreased UO, tachycardia
Symptoms of stage 2 of shock ans: Declining neuro status, tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure, weak thready pulse, cool skin, abnormal base deficit, increased lactate
symptoms of epidural hematoma ans: Transient LOC with a lucid period, HA, N/V, rapidly declining neuro status
For what reasons would you not give mannitol? ans: An active bleed or hypotension
What is Beck triad for cardiac tamponade? ans: Hypotension, distended neck veins, muffled heart sounds
Solid abdominal organs and what are they prone to? ans: Liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas, prone to lacerations
Hollow abdominal organs and what are they prone to ans: Stomach, bowels, uterus, bladder, prone to rupture
Big symptom of splenic injury ans: Left shoulder pain
Where do you secure a pelvic binder? ans: At the level of the greater trochanter and symphysis pubis
What is Turners sign? ans: Ecchymosis over the flank at the 11th and 12th ribs, in renal injury
What organs do you ultrasound in a FAST exam? ans: Bladder, liver, spleen
What kind of dressing do you apply to an open pneumo? ans: Nonporous dressing (petroleum gauze or plastic wrap) and tape on 3 sides
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages






 (1).png)