Counseling > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Encyclopedia of Counseling the purple book Exam Solved for counseling Exam NCE And CPCE (All)
Encyclopedia of Counseling the purple book Exam Solved for counseling Exam NCE And CPCE
Document Content and Description Below
Encyclopedia of Counseling the purple book Exam Solved for counseling Exam NCE And CPCE Ch. 3 - Human Growth & Development (100) 1. Freud’s stages are psychosexual while Erik Erikson’s stages ar... e a. Psychometric. b. Psychodiagnostic. c. Psychopharmacological. d. psychosocial. 2. In Freud’s psychodynamic theory instincts are emphasized. Erik Erikson is an ego psychologist. Ego psychologists a. emphasize id processes. b. refute the concept of the superego. c. believe in man’s powers of reasoning to control behavior. d. are sometimes known as radical behaviorists. 3. The only psychoanalyst who created a developmental theory which encompasses the entire life span was a. Erik Erikson. b. Milton H. Erickson. c. A. A. Brill. d. Jean Piaget, who created the four stage theory. 4. The statement “the ego is dependent on the id” would most likely reflect the work of a. Erik Erikson. b. Sigmund Freud, who created psychodynamic theory. c. Jay Haley. d. Arnold Lazarus, William Perry, and Robert Kegan. 5. .Jean Piaget’s idiographic approach created his theory with four stages. The correct order from stage 1 to stage 4 is a. formal operations, concrete operations, preoperations, sensorimotor. b. formal operations, preoperations, concrete operations, sensorimotor. c. sensorimotor, preoperations, concrete operations, formal operations. d. concrete operations, sensorimotor, preoperations, formal operations. 6. Some behavioral scientists have been critical of Swiss child psychologist Jean Piaget’s developmental research inasmuch as a. he utilized the t test too frequently. b. he failed to check for Type I or alpha errors. c. he worked primarily with minority children. d. his findings were often derived from observing his own children. 7. A tall skinny pitcher of water is emptied into a small squatty pitcher. A child indicates that she feels the small pitcher has less water. The child has not yet mastered a. symbolic schema. b. Conservation. c. androgynous psychosocial issues. d. trust versus mistrust. 8. In Piagetian literature, conservation would most likely refer to a. volume or mass. b. defenses of the ego. c. the sensorimotor intelligence stage. d. a specific psychosexual stage of life. 9. A child masters conservation in the Piagetian stage known as a. formal operations—12 years and older. b. concrete operations—ages 7–11 years. c. preoperations—ages 2–7 years. d. sensorimotor intelligence—birth to 2 years. 10. ________ expanded on Piaget’s conceptualization of moral development. a. Erik Erikson b. Lev Vygotsky c. Lawrence Kohlberg d. John B. Watson 11. According to Jean Piaget, a child masters the concept of reversibility in the third stage, known as concrete operations or concrete operational thought. This notion suggests a. that heavier objects are more difficult for a child to lift. b. the child is ambidextrous. c. the child is more cognizant of mass than weight. d. one can undo an action, hence an object (say a glass of water) can return to its initial shape. 12. During a thunderstorm, a 6-year-old child in Piaget’s stage of preoperational thought (stage 2) says, “The rain is following me.” This is an example of a. Egocentrism. b. Conservation. c. Centration. d. abstract thought. 13. Lawrence Kohlberg suggested a. a single level of morality. b. two levels of morality. c. three levels of morality. d. preoperational thought as the basis for all morality. 14. The Heinz dilemma is to Kohlberg’s theory as a. a brick is to a house. b. Freud is to Jung. c. the Menninger Clinic is to biofeedback. d. a typing test is to the level of typing skill mastered. 15. The term identity crisis comes from the work of a. counselors who stress RS involvement issues with clients. b. Erikson. c. Adler. d. Jung. 16. Kohlberg’s three levels of morality are a. preconventional, conventional, postconventional. b. formal, preformal, self-accepted. c. self-accepted, other directed, authority directed. d. preconventional, formal, authority directed. 17. Trust versus mistrust is a. an Adlerian notion of morality. b. Erikson’s first stage of psychosocial development. c. essentially equivalent to Piaget’s concept of egocentrism. d. the basis of morality according to Kohlberg. 18. A person who has successfully mastered Erikson’s first seven stages would be ready to enter Erikson’s final or eighth stage, a. generativity versus stagnation. b. initiative versus guilt. c. identity crisis of the later years. d. integrity versus despair. 19. In Kohlberg’s first or preconventional level, the individual’s moral behavior is guided by a. psychosexual urges. b. consequences. c. periodic fugue states. d. Counterconditioning. 20. Kohlberg’s second level of morality is known as conventional morality. This level is characterized by a. psychosexual urges. b. a desire to live up to society’s expectations. c. a desire to conform. d. b and c. 21. Kohlberg’s highest level of morality is termed postconventional morality. Here the individual a. must truly contend with psychosexual urges. b. has the so-called “good boy/good girl” orientation. c. has self-imposed morals and ethics. d. a and b. 22. According to Lawrence Kohlberg, level 3, which is postconventional or self-accepted moral principles, a. refers to the naive hedonism stage. b. operates on the premise that rewards guide morals. c. a and b. d. is the highest level of morality. However, some people never reach this level. 23. The zone of proximal development a. was pioneered by Lev Vygotsky. b. was pioneered by Jean Piaget and Lawrence Kohlberg. c. emphasized organ inferiority. d. a, b, and c. 24. Freud and Erikson a. could be classified as behaviorists. b. could be classified as maturationists. c. agreed that developmental stages are psychosexual. d. were prime movers in the dialectical behavior therapy or DBT movement. 25. John Bowlby, the British psychiatrist, is most closely associated with a. the work of psychologist and pediatrician, Arnold Gesell, a maturationist. b. developmental stage theories. c. bonding and attachment. d. the unconscious mind. 26. In which Eriksonian stage does the midlife crisis occur? a. Generativity versus stagnation. b. Integrity versus despair. c. a and b. d. Erikson’s stages do not address midlife issues. 27. The researcher who is well known for his work with maternal deprivation and isolation in rhesus monkeys is a. Harry Harlow. b. John Bowlby. c. Lawrence Kohlberg. d. all of the above. 28. The statement: “Males are better than females when performing mathematical calculations” is a. false. b. true due to genetics. c. true only in middle-aged men. d. true according to research by Eleanor Maccoby and Carol Jacklin. 29. The Eriksonian stage that focuses heavily on sharing your life with another person is a. actually the major theme in all of Erikson’s eight stages. b. generativity versus stagnation—ages 35–60 years. c. intimacy versus isolation—ages 23–34 years. d. a critical factor which Erikson fails to mention. 30. We often refer to individuals as conformists. Which of these individuals would most likely conform to his or her peers? a. A 19-year-old male college student. b. A 23-year-old male drummer in a rock band. c. A 57-year-old female stockbroker. d. A 13-year-old male middle school student. 31. In Harry Harlow’s experiments with baby monkeys a. a wire surrogate mother was favored by most young monkeys over a terry-cloth version. b. the baby monkey was more likely to cling to a terry-cloth surrogate mother than a wire surrogate mother. c. female monkeys had a tendency to drink large quantities of alcohol. d. male monkeys had a tendency to drink large quantities of alcohol. 32. Freud postulated the psychosexual stages: a. id, ego, and superego. b. oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital. c. eros, thanatos, regression, and superego. d. manifest, latent, oral, and phallic. 33. In adolescence a. females commit suicide more than males. b. suicide is a concern but statistically very rare. c. the teens who talk about suicide are not serious. d. males commit suicide more often than females, but females attempt suicide more often. 34. In the general U.S. population a. the suicide rate is 2/100,000. b. suicide occurs at the beginning of a depressive episode, but rarely after the depression lifts. c. suicide rates tend to increase with age. d. suicide occurs at the beginning of a depressive episode, but rarely after the depression lifts, and suicide rates tend to increase with age. 35. The fear of death a. is greatest during middle age. b. is an almost exclusively male phenomenon. c. is the number one psychiatric problem in the geriatric years. d. surprisingly enough occurs in the teen years. 36. In Freudian theory, attachment is a major factor a. in the preconscious mind. b. in the mind of the child in latency. c. which evolves primarily during the oral age. d. a and b. 37. When comparing girls to boys, it could be noted that, in general a. girls grow up to smile more. b. girls are using more feeling words by age 2. c. girls are better able to read people without verbal cues at any age. d. all of the above 38. The Freudian developmental stage which “least” emphasizes sexuality is a. oral. b. anal. c. phallic. d. Latency. 39. In terms of parenting young children a. boys are punished more than girls. b. girls are punished more than boys. c. boys and girls are treated in a similar fashion. d. boys show more empathy toward others. 40. When developmental theorists speak of nature or nurture they really mean a. how much heredity or environment interact to influence development. b. that the focus is skewed in favor of biological attributes. c. a and b. d. a theory proposed by B. F. Skinner’s colleagues. 41. Stage theorists assume a. qualitative changes between stages occur. b. differences surely exist but usually can’t be measured. c. that humanistic psychology is the only model which truly supports the stage viewpoint. d. b and c. 42. Development a. begins at birth. b. begins during the first trimester of pregnancy. c. is a continuous process which begins at conception. d. a and c. 43. Development is cephalocaudal, which means a. foot to head. b. head to foot. c. limbs receive the highest level of nourishment. d. b and c. 44. Heredity is the transmission of traits from parents to their offspring and a. assumes the normal person has 23 pairs of chromosomes. b. assumes that heredity characteristics are transmitted by chromosomes. c. assumes that genes composed of DNA hold a genetic code. d. all of the above. 45. Piaget’s final stage is known as the formal operational stage. In this stage a. abstract thinking emerges. b. problems can be solved using deduction. c. a and b. d. the child has mastered abstract thinking but still feels helpless. 46. Kohlberg lists ________ stages of moral development which fall into ________ levels. a. 6; 3 b. 6; 6 c. 3; 6 d. 3; 3 47. A person who lives by his or her individual conscience and universal ethical principles a. has, according to Kohlberg, reached the highest stage of moral development. b. is in the preconventional level. c. is in the postconventional level of self-accepted moral principles. d. a and c. 48. Freud’s Oedipus complex (or Oedipus stage) a. is the stage in which fantasies of sexual relations with the opposite-sex parent occur. b. occurs during the phallic stage. c. a and b. d. is a concept Freud ultimately eliminated from his theory. 49. In girls the Oedipus complex may be referred to as a. systematic desensitization. b. covert desensitization. c. in vivo desensitization. d. the Electra complex. 50. The correct order of the Freudian psychosexual or libidinal stages is: a. oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital. b. oral, anal, genital, phallic, and latency. c. oral, phallic, latency, genital, and anal. d. phallic, genital, latency, oral, and anal. 51. Eleanor Gibson researched the matter of depth perception in children by utilizing a. Piaget’s concept of conservation. b. Erikson’s trust versus mistrust paradigm. c. Piaget’s formal operations. d. an apparatus known as a visual cliff. 52. Theorists who believe that development merely consists of quantitative changes are referred to as a. organismic theorists. b. statistical developmentalists. c. empiricists. d. all of the above. 53. An empiricist view of development would be a. psychometric. b. behavioristic. c. against the use of formal statistical testing. d. a and c. 54. In the famous experiment by Harry Harlow, frightened monkeys raised via cloth and wire mothers a. showed marked borderline personality traits. b. surprisingly enough became quite friendly. c. demonstrated a distinct lack of emotion. d. ran over and clung to the cloth and wire surrogate mothers. 55. A theorist who views developmental changes as quantitative is said to be an empiricist. The antithesis of this position holds that developmental strides are qualitative. What is the name given to this position? a. Behaviorism. b. Organicism. c. Statistical developmentalism. d. all of the above. 56. In Piaget’s developmental theory, reflexes play the greatest role in the a. sensorimotor stage. b. formal operational stage. c. preoperational stage. d. acquisition of conservation. 57. A mother hides a toy behind her back and a young child does not believe the toy exists anymore. The child has not mastered a. object permanence. b. reflexive response. c. representational thought. d. a and c. 58. The schema (i.e., a mental representation of the real world) of permanency and constancy of objects occurs in the a. sensorimotor stage—birth to 2 years. b. preoperational stage—ages 2–7 years. c. concrete operational stage—ages 7–12 years. d. formal operational stage—12 years and beyond. 59. John Bowlby has asserted that a. attachment is not instinctual. b. attachment is best explained via the Skinnerian principle. c. a and b. d. conduct disorders and other forms of psychopathology can result from inadequate attachment and bonding in early childhood. 60. The Harlow experiments utilizing monkeys demonstrated that animals placed in isolation during the first few months of life a. still developed in a normal fashion. b. still related very well with animals reared normally. c. appeared to be autistic. d. were fixated in concrete operational thought patterns. 61. According to the Freudians, if a child is severely traumatized, he or she may ________ a given psychosexual stage. a. skip b. become fixated at c. ignore d. a and c 62. An expert who has reviewed the literature on videos and violence would conclude that a. watching violence tends to make children more aggressive. b. watching violence tends to make children less aggressive. c. reality TV shows or videos have no impact on a child’s behavior. d. what adults see as violent, children perceive as caring. 63. A counselor who utilizes the term instinctual technically means a. behavior results from unconscious aggression. b. women will show the behavior to a higher degree than men. c. a and b. d. behavior that manifests itself in all normal members of a given species. 64. The word ethology, which is often associated with the work of Konrad Lorenz, refers to a. Piaget’s famous case study methodology. b. the study of animals’ behavior in their natural environment. c. studies on monkeys raised in Skinnerian air cribs. d. all of the above. 65. A child who focuses exclusively on a clown’s red nose but ignores the clown’s other features would be illustrating the Piagetian concept of a. egocentrism. b. centration. c. formal abstract reasoning. d. deductive processes. 66. Piaget felt a. that homework depresses the elementary child’s IQ. b. strongly that the implementation of Glasser’s concepts in Schools Without Failure should be made mandatory in all elementary settings. c. that teachers should lecture a minimum of four hours daily. d. that teachers should lecture less, as children in concrete operations learn best via their own actions and experimentation. 67. Piaget’s preoperational stage a. is the final stage, which includes abstract reasoning. b. includes mastering conservation. c. includes the acquisition of a symbolic schema. d. all of the above. 68. Sigmund Freud and Erik Erikson agreed that a. each developmental stage needed to be resolved before an individual could move on to the next stage. b. developmental stages are primarily psychosexual. c. developmental stages are primarily psychosocial. d. a person can proceed to a higher stage even if a lower stage is unsolved. 69. The tendency for adult females in the United States to wear high heels is best explained by a. the principle of negative reinforcement. b. sex-role socialization. c. Lorenz’s studies on imprinting. d. ethological data. 70. The sequence of object loss, which goes from protest to despair to detachment, best describes the work of a. Freud. b. Adler on birth order. c. Erikson. d. Bowlby. 71. A counselor who is seeing a 15-year-old boy who is not doing well in public speaking class would need to keep in mind that a. in general, boys possess better verbal skills than girls. b. in general, girls possess better verbal skills than boys. c. in general, boys have better visual–perceptual skills and are more active and aggressive than girls. d. b and c. 72. Two brothers begin screaming at each other during a family counseling session. The term that best describes the phenomenon is a. the primal scene. b. preconscious psychic processes. c. sibling rivalry. d. BASIC-ID. 73. A preschool child’s concept of causality is said to be animistic. This means the child attributes human characteristics to inanimate objects. Thus, the child may fantasize that an automobile or a rock is talking to him. This concept is best related to a. Jung’s concepts of anima, animus. b. Freud’s wish fulfillment. c. Piaget’s preoperational period, ages 2–7 years. d. ego identity. 74. Elementary school counseling and guidance services a. have been popular since the early 1900s. b. became popular during World War II. c. are a fairly new development which did not begin to gain momentum until the 1960s. d. none of the above. 75. Research related to elementary school counselors indicates that a. counselors of this ilk work hard, but just don’t seem to have an impact on youngsters’ lives. b. these counselors are effective, do make a difference in children’s lives, and more counselors should be employed. c. counselors of this ilk could be helpful if they would engage in more consultation work. d. these counselors should be used primarily as disciplinarians, but this is not happening in most districts. 76. According to the Yale research by Daniel J. Levinson a. Erikson’s generativity versus stagnation stage simply doesn’t exist. b. 80% of the men in the study experienced moderate to severe midlife crises. c. an “age 30 crisis” occurs in men when they feel it will soon be too late to make later changes. d. b and c. 77. Erikson’s middle-age stage (ages 35–60) is known as generativity versus stagnation. Generativity refers to a. he ability to do creative work or raise a family. b. the opposite of stagnation. c. the productive ability to create a career, family, and leisure time. d. all of the above. 78. A person who can look back on his or her life with few regrets feels a. the burden of senile psychosis. b. ego-integrity in Erikson’s integrity versus despair stage. c. despair, which is the sense that he or she has wasted life’s precious opportunities. d. the burden of generalized anxiety disorder as described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). 79. Sensorimotor is to Piaget as oral is to Freud, and as ________ is to Erikson. a. integrity versus despair b. Kohlberg c. trust versus mistrust d. play therapy 80. Which theorist was most concerned with maternal deprivation? a. A. Lazarus. b. H. Harlow. c. J. Wolpe. d. A. Ellis. 81. When development comes to a halt, counselors say that the client a. has “learned helplessness” syndrome. b. suffers from a phobia. c. suffers from fixation. d. is displaying the risky shift phenomenon. 82. Kohlberg proposed three levels of morality. Freud, on the other hand, felt morality developed from the a. superego. b. ego. c. id. d. Eros. 83. Which theorist would be most likely to say that aggression is an inborn tendency? a. Carl Rogers. b. B. F. Skinner. c. Frank Parsons, the father of guidance. d. Konrad Lorenz. 84. The statement “bad behavior is punished, good behavior is not” is most closely associated with a. Kohlberg’s premoral stage at the preconventional level. b. Kohlberg’s conventional level. c. the work of Carl Jung. d. Piaget’s autonomous stage, which begins at about age 8. 85. A critical period a. makes imprinting possible. b. emphasizes manifest dream content. c. signifies a special time when a behavior must be learned or the behavior won’t be learned at all. d. a and c. 86. Imprinting—rapid learning during a critical period of development—is an instinct in which a newborn will follow a moving object. The primary work in this area was done by a. Erik Erikson. b. Milton H. Erickson. c. Konrad Lorenz. d. Harry Harlow. 87. Marital satisfaction a. is usually highest when a child is old enough to leave home. b. often decreases with parenthood and often improves after a child leaves home. c. correlates high with performance IQ. d. is highest among couples who have seven or more college-educated children. 88. Maslow, a humanistic psychologist, is famous for his “hierarchy of needs,” which postulates a. wer-order physiological and safety needs and higher-order needs, such as self-actualization. b. that psychopathology rests within the id. c. that unconscious drives control self-actualization. d. that stimulus-response (S-R) psychology dictates behavioral attributes. 89. To research the dilemma of self-actualization, Maslow a. used goslings as did Konrad Lorenz. b. psychoanalyzed over 400 neurotics. c. worked exclusively with schizophrenics in residential settings. d. interviewed the best people he could find who escaped “the psychology of the average.” 90. Piaget is a. a maturationist. b. a behaviorist. c. a structuralist who believes stage changes are qualitative. d. Cognitive-behavioral. 91. ________ factors cause Down syndrome, the most common type known as trisomy 21. a. Environmental b. Genetic (conditions passed through genes) c. Chemical dependency d. Unconscious 92. Piaget referred to the act of taking in new information as assimilation. This results in accommodation, which is a modification of the child’s cognitive structures (schemas) to deal with the new information. In Piagetian nomenclature, the balance between assimilation and accommodation is called a. counterbalancing. b. equilibration. c. balance theory. d. ABA design. 93. There are behavioral, structural, and maturational theories of development. The maturational viewpoint utilizes the plant growth analogy, in which the mind is seen as being driven by instincts while the environment provides nourishment, thus placing limits on development. Counselors who are maturationists a. conduct therapy in the here and now. b. focus primarily on nonverbal behavior. c. believe group work is most effective. d. allow clients to work through early conflicts. 94. Ritualistic behaviors, which are common to all members of a species, are known as a. hysteria. b. pica. c. fixed-action patterns elicited by sign stimuli. d. dysfunctional repetition. 95. Robert Kegan speaks of a “holding environment” in counseling in which a. the client is urged to relive a traumatic experience in an encounter group. b. biofeedback training is highly recommended. c. the client can make meaning in the face of a crisis and can find new direction. d. the activity of meaning making is discouraged. 96. Most experts in the field of counseling agree that a. no one theory completely explains developmental processes; thus, counselors ought to be familiar with all the major theories. b. Eriksonian theory should be used by counselors practicing virtually any modality. c. a counselor who incorporates Piaget’s stages into his or her thinking would not necessarily need knowledge of rival therapeutic viewpoints. d. a realistic counselor needs to pick one developmental theory in the same manner that he or she picks a psychotherapeutic persuasion. 97. Equilibration is a. a term which emphasizes the equality between the sexes. b. performed via the id according to the Freudians. c. a synonym for concrete operational thought. d. the balance between what one takes in (assimilation) and that which is changed (accommodation). 98. A counselor is working with a family who just lost everything in a fire. The counselor will ideally focus on a. Maslow’s higher-order needs, such as self-actualization. b. building accurate empathy of family members. c. Maslow’s lower-order needs, such as physiological and safety needs. d. the identified patient. 99. The anal retentive personality is a. charitable. b. stingy. c. kind. d. thinks very little about money matters. 100. From a Freudian perspective, a client who has a problem with alcoholism and excessive smoking would be a. considered an oral character. b. considered an anal character. c. considered a genital character. d. fixated at the latency stage. Ch. 4 - Social and Cultural Diversity (100) 101. America has been called the most diverse country on the face of our planet. Counseling a client from a different social and/or cultural background is known as a. cross-cultural counseling. b. multicultural counseling. c. intercultural counseling. d. all of the above. 102. Culture refers to a. customs shared by a group which distinguish it from other groups. b. values shared by a group that are learned from others in the group. c. attitudes, beliefs, art, and language which characterize members of a group often passed from generation to generation. d. all of the above. 103. Our culture is more diverse than in the past. Multicultural counselors often work with persons who are culturally different. This means the client a. is culturally biased. b. suffers from the diagnosis of cultural relativity. c. belongs to a different culture from the helper. d. presents problems which deal only with culturally charged issues. 104. In order to diagnose clients from a different culture a. the counselor ideally will need some information regarding the specifics of the culture. b. the counselor will find the DSM useless. c. the counselor should rely heavily on cultural epoch theory. d. NBCC ethics prohibit the use of DSM diagnosis. 105. In the United States, each socioeconomic group represents a. a separate race. b. a separate culture. c. the concept of color blindness. d. a separate national culture. 106. Which therapist was not instrumental in the early years of the social psychology movement? a. Freud. b. Durkheim. c. McDougall. d. Berne. 107. ________ and ________ would say that regardless of culture, humans have an instinct to fight. a. Maslow; Rogers b. Ellis; Harper c. Freud; Lorenz d. Glasser; Rogers 108. ________ believe that aggression is learned. Thus, a child who witnesses aggressive behavior in adults may imitate the aggressive behavior. a. Instinct theorists b. Innate aggression theorists c. Social learning theorists d. Followers of Erik Erikson 109. The APGA, which became the AACD until 1992 and is now the ACA, contributed to the growth of cross-cultural counseling by a. the 1972 formation of the Association for Non-White Concerns in Personnel and Guidance, later known as the Association for Multicultural Counseling and Development. b. the 1972 ethic which made it unethical to see culturally different clients without three hours of relevant graduate work in this area. c. the 1972 ethic which required a 3,000-hour practicum in order to work with culturally different clients. d. urging nonwhites to take graduate counseling courses. 110. Daniel Levinson proposed a controversial stage-crisis view theory with several major life transitions. He a. is the father of multicultural counseling. b. wrote the 1978 classic Seasons of a Man’s Life and the 1997 sequel Seasons of a Woman’s Life. c. postulated a midlife crisis for men between ages 40 and 45 and for women approximately five years earlier. d. B and c. 111. The three factors which enhance interpersonal attraction are: a. assertiveness, anxiety, ego strength. b. close proximity, physical attraction, similar beliefs. c. culture, race, assertiveness. d. ego strength, anxiety, race. 112. The term contextualism implies that a. multicultural counseling is the oldest subspecialty in the profession. b. behavior must be assessed in the context of the culture in which the behavior occurs. c. the notion of worldview is highly inaccurate. d. projective tests are more accurate than objective measures when performing cross-cultural counseling. 113. Carol Gilligan, although she was an assistant to Lawrence Kohlberg, was critical of his theory of moral development a. as she felt it was too psychoanalytic. b. as she felt it was too behavioristic. c. as she felt it was not applicable to African Americans. d. as she felt it was more applicable to males than females. 114. ________ helped to popularize the multicultural counseling movement. a. Arthur Jensen’s views on IQ testing (also known as Jensenism) b. The civil rights movement c. Jung’s feeling that all men and women from all cultures possess a collective unconscious d. The Tarasoff duty 115. When a counselor speaks of a probable outcome in a case, he or she is technically referring to a. the prognosis. b. the diagnosis. c. the intervention. d. attending behavior. 116. When a counselor speaks of what he or she believes must transpire from a psychotherapeutic standpoint, he or she technically is referring to a. Recommendations. b. the diagnosis. c. the prognosis. d. the notion of transference. 117. The 1971 famous Stanford Prison experiment conducted by Philip Zimbardo demonstrated that a. passivity is the norm for most individuals. b. assertive behavior is clearly the healthiest behavioral alternative. c. it takes people several weeks to change their behavior. d. people conform to social roles. 118. A wealth of research demonstrates that a. surprisingly enough, African Americans generally request Asian American counselors. b. surprisingly enough, Asian Americans generally request African American counselors. c. in most instances, clients prefer a counselor of the same race and a similar cultural background. d. in most instances, clients prefer a counselor of the same race, yet a different culture. 119. The frustration-aggression theory is associated with 92 a. Albert Ellis. b. Robert Havinghurst, who created the idea of the developmental task concept. c. Eric Berne, the creator of transactional analysis (TA). d. John Dollard and Neal Miller. 120. A popular cognitive consistency or balance theory in social psychology is ________ cognitive dissonance theory. a. Dollard and Miller’s b. Crites and Roe’s c. Festinger’s d. Holland and Super’s 121. Culture is really a set of rules, procedures, ideas, and values shared by members of a society. Culture is said to be normative. This implies that a. one culture will have norms which differ only slightly from another. b. culture excludes customs. c. culture provides individuals with standards of conduct. d. culture is never socially learned. 122. A statistical norm measures actual conduct, while a cultural norm a. describes how people are supposed to act. b. has little to do with expectations. c. is irrelevant when counseling a client. d. all of the above. 123. Mores are beliefs and social customs a. regarding the rightness or wrongness of behavior. b. which should be the central focus in multicultural counseling. c. that are conscious decisions made by persons in power. d. that are identical with the folkways in the culture. 124. ________ was the first pioneer to focus heavily on sociocultural issues. a. Mark Savickas, a major figure in career construction theory relying on narrative therapy, b. Alfred Adler, the father of individual psychology, c. Maxie Maultsby, the father of rational behavior therapy (RBT), d. Frank Parsons, the father of guidance, 125. A counselor who is part of a research study will be counseling clients in the polar regions and then at a point near the equator. Her primary concern will be a. universal culture. b. national culture. c. ecological culture. d. B and c. 126. Biological similarities and sameness are indicated by a. ecological culture. b. mores. c. regional and national culture. d. universal culture. 127. Early vocalization infants a. Is more complex in African American babies. b. Is more complex in white babies. c. Is nearly identical in all cultures around the globe. d. Is the finest indicator of elementary school performance. 128. In the 1920s, Emory Bogardus developed a social distance scale, which evaluated a. Socioeconomic trends b. How an individual felt toward other ethnic groups c. Disadvantaged youth d. Language barriers between African American and Asian Americans. 129. According to the foot-in-the-door compliance technique, which has two distinct steps, a counselor who needs to make a home visit to a resistant client’s home a. Should conduct the interview from the porch b. Should double-bind the client c. Should ask to come in the home d. Should exude accurate empathy, but never ask to enter the home. 130. Most countries have an official language, a stated viewpoint, and a central government. This is reflected mainly by a. National culture b. Human culture c. Regional culture d. Ecological culture 131. Whereas a culture is defined primarily via norms and values, a society differs from a culture in that a society a. Is defined as a set of more b. Has a distinct lack of norms c. Is a self-perpetuating independent group which occupies a definitive territory. d. None of the above 132. Ethnocentrism a. Uses one’s own cultures as a yardstick to measure all others b. Means race c. Is a genetic term d. All of the above. 133. All of these statements are ethnocentric except a. You can’t trust anyone over the age of 40. b. American are generous c. Blue-collar workers are mean and selfish d. The Gross Domestic Product in the United States exceeds the figure in Mexico 134. Ethnocentrism a. Is not universal b. Promotes a sense of patriotism and national sovereignty c. Promotes stability and pride, yet danger in the nuclear age. d. B and C. 135. Regardless of culture, the popular individual a. Has good social skills b. Values race over ethnicity c. Dresses in the latest styles d. Never possesses a modal personality 136. Social exchange theory postulates that a. a relationship will endure if both parties are assertive. b. a relationship will endure if the rewards are greater than the costs. c. A a relationship will endure if the rewards are greater than the costs. d. men work harder to keep a relationship strong. 137. Balance theory postulates a. A move from cognitive consistency to inconsistency b. A move from cognitive inconsistency to consistency c. A tendency to achieve a balanced cognitive state d. B and c. 138. Most individuals believe that people whom they perceive as attractive a. Are nonassertive b. Are aggressive c. Have other positive traits d. are social adept but not very intelligent. 139. A counselor who works primarily with older adults needs to be aware that a. too many counselors choose gerontology as their specialty. b. individuals over 65 tend to overuse hotline and helpline crisis counseling services. c. surprisingly, attractiveness is a fine predictor of retirement adjustment. d. surprisingly, financial security and health are the best predictors of retirement adjustment. 140. Most experts would agree that a multicultural counselor’s diagnosis a. Must be performed without regard to cultural issues. b. Must be done within a cultural context c. A and b. d. None of the above. 141. A counselor who is seeing a client from a different culture would most likely expect ________ social conformity than he or she would from a client from his or her own culture. a. Less b. More c. The same d. More realistic 142. In terms of diagnosis a. a client’s behavior could be sane and appropriate in one culture, yet disturbed and bizarre in another. b. culture is irrelevant in children under 14. c. culture is an issue with males, but not with females. d. culture is an issue with females, but not with males. 143. In the United States, a frequent practice is to see a perfect stranger for therapy. a. This trend seems to be true in any area of the world. b. This is true for Licensed Professional Counselors (LPCs) but not true for Licensed Clinical Social Workers (LCSWs). c. This is true for LPCs and LCSWs but not licensed clinical psychologists. d. In other cultures it would not be the norm to see a stranger and receive pay for providing help. 144. According to the cognitive dissonance theory of Leon Festinger, a woman has an approach–approach conflict. She has her choice of a beautiful silver watch and an equally stunning gold watch. Both are different brands. She feels the silver model will be perfect for some of her jewelry and outfits while the gold is ideal for other jewelry and modes of dress. She chooses the silver watch. a. She will feel intense guilt. b. She will read positive reviews on the silver watch—and possibly negative reviews about the gold model—after the purchase to justify her behavior and reduce post-decisional dissonance. c. According to the theory she will remain a tad ambivalent about her choice. d. She will be angry because in reality she wanted both watches, but could not afford them. 145. A woman who being robbed a. would probably get the most assistance in a crowd with a large number of bystanders. b. would find that the number of people who would respond to her distress actually decreases as the number of bystanders increases. c. would rarely have a bystander from a different race try to help her. d. none of the above. 146. A counselor reading this book says, “I couldn’t care less about passing my comprehensive exam.” This a. is displacement. b. is an attempt to reduce dissonance via consistent cognitions. c. is an attempt to reduce dissonance by denial, thus minimizing tension. d. is projection. 147. The statement “Even though my car is old and doesn’t run well, it sure keeps my insurance payments low” a. is displacement. b. is an attempt to reduce dissonance via consistent cognitions. c. is projection. d. would never reduce dissonance in an individual. 148. In the case of an individual who purchased a $50,000 watch, cognitive dissonance theory postulates that a. he or she might ignore positive information regarding other models and secure a lot of information regarding the $50,000 platinum model. b. he or she might sell the $50,000 watch immediately following the purchase. c. he or she might focus heavily on negative information regarding rival models. d. a and c. 149. In the United States, middle- and upper-class citizens seem to want a counselor who a. will give them “a good talking to.” b. gives a specific and steady stream of advice. c. helps them work it out on their own. d. is highly authoritarian and autocratic. 150. In a traditional culture which places a high premium on authority figures, a. passivity on the part of the counselor would be viewed in a negative manner. b. a client would be disappointed if he or she did not receive advice. c. assigning homework and teaching on the part of the counselor would be appropriate. d. all of the above. 151. Cognitive dissonance research deals mainly with a. attraction. b. cognition and attitude formation. c. cognitions and emotion. d. none of the above. 152. Parents who do not tolerate or use aggression when raising children produce a. less-aggressive children. b. more-aggressive children. c. passive-aggressive children. d. passive-dependent children. 153. Overall, Rogerian person-centered counseling a. is rarely utilized in cross-cultural counseling. b. is too nondirective for intercultural counseling. c. a and b. d. has been used more than other models to help promote understanding between cultures and races. 154. In intercultural/multicultural counseling the term therapeutic surrender means a. nothing—it is not a valid term. b. most therapists will give up in 16 sessions or less if progress is not evident. c. the client psychologically surrenders himself or herself to a counselor from a different culture and becomes open with feelings and thoughts. d. the therapist assumes a passive therapeutic stance. 155. The literature suggests these factors as helpful in promoting therapeutic surrender: a. an analysis of cognitive dissonance. b. rapport, trust, listening, conquering client resistance, and self-disclosure. c. paradoxing the client. d. analyzing flight-to-health defense mechanism variables. 156. In terms of trust and therapeutic surrender, a. it is easier to trust people from one’s own culture. b. lower-income people often don’t trust others from a higher social class. c. lower-income clients may feel that they will end up as losers dealing with a counselor from a higher social class. d. all of the above. 157. A(n) ________ client would most likely have the most difficulty with self-disclosure when speaking to a white counselor. a. white female b. African American female c. African American male d. upper-class white male 158. According to assimilation-contrast theory, a client will perceive a counselor’s statement that is somewhat like his or her own beliefs as even more similar (i.e., an assimilation error). He or she would perceive any dissimilar attitudes as a. even more dissimilar (i.e., a contrast error). b. standardization. c. similar to his or her own. d. paraphrasing. 159. When counseling a client from a different culture, a common error is made when negative transference a. Is interpreted as positive transference b. Is interpreted as therapeutic resistance c. Is interpreted as white privilege d. None of the above 160. Counselors who have good listening skills a. facilitate therapeutic surrender. b. hinder therapeutic surrender. c. often have a monolithic perspective. d. are too nondirective to promote therapeutic surrender. 161. Counselors can more easily advise a. clients from their own culture. b. clients from a different culture. c. clients of a different race. d. clients utilizing ethnocentric statements. 162. It’s easiest to empathize with a. a client who is similar to you. b. a client who is dissimilar to you. c. Latino/a clients. d. Asian American male clients. 163. In cross-cultural counseling, structuring is very important. This concept asserts that counseling is most effective a. when structured exercises are utilized. b. when a counselor takes an active–directive stance. c. when nondirective procedures are emphasized. d. when the nature and structure of the counseling situation is described during the initial session. 164. A client from another culture will a. talk to the counselor the same as he or she would to a peer. b. speak to the counselor differently from the way he or she would when speaking to someone of his or her own background. c. generally use slang on purpose to confuse the counselor. d. generally play dumb to receive the counselor’s sympathy. 165. An African American client tells a white counselor that the dance she went to last night was “bad,” though she literally means it was good. The counselor’s misunderstanding could best be described as a a. client of color error. b. cognitive dissonance error. c. connotative error. d. confounding variable. 166. A monolingual U.S. counselor a. speaks only English. b. speaks English and Spanish. c. works as a counseling interpreter. d. fits the definition of bilingual. 167. ________ was a prime factor in the history of multicultural counseling. a. Frankl’s experience in a concentration camp b. Perl’s use of the German concept of gestalt c. Freud’s visits to the United States d. The 1954 Supreme Court decision, Brown v. the Board of Education, which outlawed public school segregation 168. Multicultural counseling promotes a. eclecticism. b. rigidity. c. psychodynamic models. d. neurolinguistic programming (NLP). 169. Multicultural counselors often adhere to the emic viewpoint. The word emic a. is associated with the Supreme Court decision of 1954 outlawing segregation. b. suggests that all clients are alike regardless of culture. c. is associated with rational behavior therapy (RBT). d. is a “culture-specific” perspective, from the word phonemic meaning sounds in a particular language. 170. A practicum supervisor who says to his or her supervisee “You can deal with your Asian American clients the same as you deal with anybody else” is espousing the a. emic viewpoint. b. alloplastic viewpoint. c. etic viewpoint, derived from the term phonetic referring to sounds that remain the same in any language. d. autoplastic viewpoint. 171. The statement “All humans, from all cultures, all races, and all nations, are more alike than different” is based on the a. emic viewpoint. b. alloplastic viewpoint. c. etic viewpoint. d. autoplastic viewpoint. 172. A counselor is confronted with his or her first Native American client. Native Americans (also called American Indians on some exams) are descendants of the original inhabitants of North America. After the initial session, the counselor secures several books which delineate the cultural aspects of Native American life. She discovers that there are over 560 federally recognized tribes in the United States. This counselor most likely believes in the a. emic viewpoint. b. alloplastic viewpoint. c. etic viewpoint. d. autoplastic viewpoint. 173. An Asian American counselor says to an African American client, “If you’re unhappy with the system, get out there and rebel. You can change the system.” This is the ________ viewpoint for coping with the environment. a. emic b. alloplastic c. etic d. autoplastic 174. A young Latino male is the victim of discrimination. His counselor remarks, “I hear what you are saying and I will help you change your thinking so this will not have such a profound impact on you.” In this case the counselor had suggested a. an alloplastic method of coping. b. an autoplastic method of coping. c. the emic–etic distinction. d. the emic viewpoint. 175. You are counseling a client from a different culture. She cannot move her right arm, but has been examined by some of the finest physicians and they cannot find any physical reason for her condition. The irony is that she is there to work on some personal issues but states forthrightly that the total lack of mobility in her arm does not bother her and thus is not an issue to deal with in the counseling sessions. The most likely explanation would be a. she is displaying malingering. b. she was severely abused as a young child. c. she is suicidal. d. she has a conversion disorder with la belle indifference. 176. Positive transference is to love or affection, as negative transference is to hostility, and as ambivalent transference is to a. anger. b. hate. c. uncertainty. d. admiration. 177. The word personalism in the context of multicultural counseling means a. all people must adjust to environmental and geological demands. b. the counselor must adjust to the client’s cultural mores. c. a counselor who personalizes the treatment is most effective. d. biologically speaking, there is no reason why humans must adjust to environmental demands. 178. A client whose counselor pushes the alloplastic viewpoint may believe his counselor is simply a. too Rogerian. b. attacking the system. c. too Freudian. d. too cognitive. 179. Good multicultural counselors are a. flexible. b. rigid. c. utilize Eric Berne’s transactional analysis (TA), Fritz Perl’s gestalt therapy, and/or William Glasser’s reality therapy in nearly every case. d. generally behavioristic. 180. A client remarks, “Hey, I’m African American and it’s nearly impossible to hide it.” This is illustrative of the fact that a. race is not the same as ethnicity. b. race and ethnicity are virtually identical. c. a connotative impediment exists. d. severe ambivalent transference exists. 181. Experts in the field of multicultural counseling feel that the counselor’s training a. must come from an APA-approved graduate program. b. must come from a supervisor who is from a different culture than the graduate student. c. should be broad and interdisciplinary. d. need not include rational-emotive behavior therapy (REBT). 182. Doing cross-cultural counseling a. makes counselors increasingly aware of cultural differences. b. allows counselors to see that culture is merely a matter of semantics. c. is different since clients are more likely to return for help after the first session. d. allows counselors to ignore the concept of pluralism. 183. Floyd Henry Allport created the concept of social facilitation. According to this theory, an individual who is given the task of memorizing a list of numbers will a. perform better if he or she is alone. b. perform better if he or she is part of a group. c. perform better if he or she has undergone psychotherapy. d. perform better if he or she is an auditory learner. 184. In social psychology, the sleeper effect asserts that a. sleep learning facilitates social skills. b. after a period of time, one forgets the communicator but remembers the message. c. after a period of time, one remembers the communicator but forgets the message. d. REM sleep facilitates insight. 185. In 1908, books by ________ helped to introduce social psychology in America. a. Moreno and Yalom b. Holland and Roe c. Barber and Salter d. McDougall and Ross 186. ________ is associated with obedience and authority. a. Stanley Milgram, a noted psychologist, b. Arthur Janov, who created primal scream therapy, c. A. T. Beck, a cognitive therapy pioneer, d. Robert Harper, a pioneer in the REBT bibliotherapy movement, 187. Milgram discovered that normal people would administer seemingly fatal electric shocks to others when instructions to do so were given by a person perceived as a. a peer. b. an equal. c. an individual from another culture. d. an authority figure. 188. The tendency to affiliate with others a. is highest in the middle child. b. is highest in children with DSM diagnoses. c. is highest in firstborns and only children. d. is based on hormonal output. 189. A client tells his counselor that he has a choice of entering one of two prestigious PhD counseling programs. Kurt Lewin would call this an a. approach–avoidance conflict. b. approach–approach conflict. c. avoidance–avoidance conflict. d. avoidance vector. 190. When a person has two negative alternatives, it is called an a. approach–approach conflict. b. approach vector. c. avoidance–avoidance conflict. d. Avoidance cohesiveness. 191. A male client tells his counselor that he is attracted to “a gorgeous woman who is violent and chemically dependent.” This creates an a. approach–avoidance conflict. b. avoidance–avoidance conflict. c. avoidance of life space. d. approach affiliation. 192. According to Charles Osgood and Percy Tannenbaum’s congruity theory, a client will accept a. suggestions more readily if b. the client likes the counselor. c. the client dislikes the counselor. d. the client distrusts the counselor. e. the counselor is in a higher economic bracket. 193. An adept multicultural counselor a. generally believes in the melting pot concept. b. has a strong ethnocentric worldview. c. will not ask the client for information related to religion or level of faith development. d. usually supports the salad bowl model of diversity. 194. A classic experiment in social psychology was conducted by the social psychologist Muzafer Sherif et al. at a boys’ summer camp near Robbers’ Cave, Oklahoma. The important finding in this study was that a. most people cooperate in a social setting. b. competition plays a small role in most of our lives. c. a and b. d. a cooperative, or so-called superordinate, goal attained only by working in a joint manner, can bring two hostile groups together, thus reducing competition and enhancing cooperation. 195. Sex-role stereotyping would imply that a. a counselor would only consider traditional feminine careers for his female client. b. a male counselor would rate a female client’s emotional status differently than he would a male client’s. c. female clients are treated the same as male clients. d. choices a and b. 196. The statement “whites are better than African Americans” illustrates a. a weakening of the caste system in the U.S. b. racism. c. sexism. d. codependency. 197. In terms of research related to affiliation a. misery loves miserable company. b. firstborns are more likely to affiliate than other children born later. c. people affiliate in an attempt to lower fear. d. all of the above. 198. Six persons attend a counseling group. After the group, five members praise the merits of a group activity assigned by the group leader. The sixth person, who has heard the opinion of the other five people, felt the activity was useless and boring. According to studies on social behavior, about one third of the time the sixth individual would most likely tell the other five that a. he totally disagreed with their assessment. b. he too felt the group activity was very helpful. c. he really wasn’t certain how he felt about the activity. d. a and c. 199. The client who would most likely engage in introspection would be a a. 52-year-old, single, African American male school administrator. b. 49-year-old, white homeless male. c. 40-year-old, divorced white female who is out of work and has three children. d. 19-year-old Latina mother on welfare with two children. 200. A Japanese client who was reluctant to look you in the eye during her counseling session would most likely be displaying a. severe negative transference. b. positive transference. c. normal behavior within the context of her culture. d. ambivalent transference. Ch. 5 - Counseling and Helping Relationships (200) 201. Sigmund Freud is the father of psychoanalysis, which is both a form of treatment and a very comprehensive personality theory. According to Freud’s theory, inborn drives (mainly sexual) help form the personality. ________ and ________, who originally worked with Freud, created individual psychology and analytic psychology, respectively. a. Carl Jung; Alfred Adler b. Alfred Adler; Carl Jung c. Josef Breuer; A. A. Brill d. Alfred Adler; Rollo May 202. Eric Berne’s transactional analysis (TA) posits three ego states: the Child, the Adult, and the Parent. These roughly correspond to Freud’s structural theory that includes a. oral, anal, and phallic. b. unconscious, preconscious, and conscious. c. a and b. d. id, ego, and superego 203. In transactional analysis (TA), the ________ is the conscience, or ego state concerned with moral behavior, while in Freudian theory it is the ________. a. Adult, unconscious b. Parent, ego c. Parent, superego d. Parent, id 204. Freud felt that successful resolution of the Oedipus complex led to the development of the superego. This is accomplished by a. identification with the aggressor, the parent of the same sex. b. analysis during the childhood years. c. identification with the parent of the opposite sex, the aggressor. d. transference. 205. Freudians refer to the ego as a. the executive administrator of the personality and the reality principle. b. the guardian angel of the mind. c. the pleasure principle. d. the seat of libido. 206. Freud’s theory speaks of Eros and Thanatos. A client who threatens a self-destructive act is being ruled primarily by a. Eros. b. Eros and the id. c. Thanatos. d. both Eros and Thanatos. 207. The id is present at birth and never matures. It operates mainly out of awareness to satisfy instinctual needs according to the a. reality principle. b. notion of transference. c. Eros principle. d. pleasure principle, suggesting humans desire instinct gratification such for libido, sex, or the elimination of hunger or thirst. 208. If you think of the mind as a seesaw, then the fulcrum or balancing apparatus would be the a. id, which has no concept of rationality or time. b. ego. c. superego, which judges behavior as right or wrong. d. BASIC-ID. 209. A therapist who says to a patient “Say whatever comes to mind” is practicing a. directive counseling. b. transactional analysis. c. paraphrasing. d. free association. 210. The superego contains the ego ideal. The superego strives for ________, rather than ________ like the id. a. perfection; pleasure b. pleasure; perfection c. morals; ethics d. logic; reality 211. All of these theorists could be associated with the analytic movement except: a. Freud. b. Jung. c. Adler. d. Wolpe. 212. Most scholars would assert that Freud’s 1900 work entitled The Interpretation of Dreams was his most influential. Dreams have a. manifest and latent content. b. preconscious and unconscious factors. c. id and ego. d. superego and id. 213. When a client projects unconscious feelings toward the therapist that he or she originally had toward a significant other, it is called a. free association. b. insight. c. transference. d. resistance. 214. Which case is not associated with the psychodynamic movement? a. Little Hans. b. Little Albert. c. Anna O. d. Daniel Paul Schreber. 215. In contrast with classical psychoanalysis, psychodynamic counseling or therapy a. utilizes fewer sessions per week. b. does not utilize the couch. c. is performed face to face. d. all of the above. 216. Talking about difficulties in order to purge emotions and feelings is a curative process known as a. catharsis and/or abreaction. b. resistance. c. accurate empathy. d. reflection of emotional content. 217. Id, ego, superego is to structural theory as ________ is to topographical theory. a. Child, Adult, Parent b. abreaction, catharsis, introspection c. ego ideal d. unconscious, preconscious, conscious 218. The most controversial aspect of Freud’s theory is a. catharsis. b. the Oedipus complex. c. the notion of the preconscious mind. d. the interpretation of dreams. 219. Evidence for the unconscious mind comes from all of these except: a. Hypnosis. b. Slips of the tongue and humor. c. Dreams. d. Subjective units of distress scale. 220. In a counseling session, a counselor asked a patient to recall what transpired three months ago to trigger her depression. There was silence for about two and one-half minutes. The client then began to remember. This exchange most likely illustrates the function of the a. preconscious mind. b. ego ideal. c. conscious mind. d. unconscious mind. 221. Unconscious processes, which serve to minimize anxiety and protect the self from severe id or superego demands, are called a. slips of the tongue. b. ego defense mechanisms. c. id defense processes. d. latent dream material. 222. Most therapists agree that ego defense mechanisms are unconscious and deny or distort reality. Rationalization, compensation, repression, projection, reaction formation, identification, introjection, denial, and displacement are ego defense mechanisms. According to Freudians, the most important defense mechanism is a. repression. b. reaction formation c. denial. d. sublimation 223. Suppression differs from repression in that a. suppression is stronger. b. repression only occurs in children. c. repression is automatic or involuntary. d. all of the above. 224. An aggressive person who becomes a professional boxer because he or she is sadistic is displaying a. suppression. b. rationalization. c. sublimation. d. displacement. 225. An advertising agency secretly imbeds the word SEX into newspaper ads intended to advertise the center’s chemical dependency program. This is the practice of a. sublimation. b. repression. c. introjection. d. none of the above. 226. A man receives a nickel an hour pay raise. He was expecting a 1 dollar per hour raise. He is furious but nonassertive. He thus smiles and thanks his boss. That night he yells at his wife for no apparent reason. This is an example of a. displacement. b. denial. c. identification. d. a Type II error. 227. A student tells a college counselor that he is not upset by a grade of “F” in physical education that marred his fourth-year perfect 4.0 average, inasmuch as “straight A students are eggheads.” This demonstrates a. introjection. b. reaction formation. c. sour grapes rationalization. d. sweet lemon rationalization. 228. A master’s level counselor lands an entry-level counseling job in an agency in a warm climate. Her office is not air conditioned, but the counselor insists she likes this because sweating really helps to keep her weight in check. This illuminates a. sour grapes rationalization. b. sweet lemon rationalization. c. repression. d. sublimation. 229. A teenager who had his heart set on winning a tennis match broke his arm in an auto accident. He sends in an entry form to play in the competition which begins just days after the accident. His behavior a. is influenced by a. denial. b. displacement of anger. c. sublimation. d. organ inferiority. 230. ________ is like looking in a mirror but thinking you are looking out a window. a. Repression b. Sour grapes rationalization c. Projection d. Denial 231. Mark is obsessed with stamping out pornography. He is unconsciously involved in this cause so that he can view the material. This is a. reaction formation. b. introjection. c. projection. d. rationalization. 232. Ted has always felt inferior intellectually. He currently works out at the gym at least four hours daily and is taking massive doses of dangerous steroids to build his muscles. The ego defense mechanism in action here is a. reaction formation. b. compensation. c. projection. d. Rationalization. 233. Jane feels very inferior. She is now president of the board at a shelter for the homeless. She seems to be obsessed with her work for the agency and spends every spare minute trying to help the cause. When asked to introduce herself in virtually any social situation, Jane invariably responds with, “I’m the president of the board for the homeless shelter.” Jane is engaging in a. projection. b. displacement. c. introjection. d. identification. 234. A client who has incorporated his father’s values into his thought patterns is a product of a. introjection. b. repression. c. rationalization. d. displacement. 235. The client’s tendency to inhibit or fight against the therapeutic process is known as a. resistance. b. sublimation. c. projection. d. individuation. 236. Freud has been called the most significant theorist in the entire history of psychology. His greatest contribution was his conceptualization of the unconscious mind. Critics, however, contend that a. he was too concerned with the totem and the taboo. b. he failed to emphasize sex. c. many aspects of his theory are difficult to test from a scientific standpoint. d. he was pro female. 237. The purpose of interpretation in counseling is to a. help the therapist appear genuine. b. make the clients aware of their unconscious processes. c. make clients aware of nonverbal behaviors. d. help clients understand feelings and behaviors related to childhood. 238. Organ inferiority relates mainly to the work of a. C. G. Jung’s analytical psychology. b. Alfred Adler’s individual psychology. c. Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory. d. Josef Breuer’s work on hysteria. 239. When a client becomes aware of a factor in his or her life that was heretofore unknown, counselors refer to it as a. individual psychology. b. confrontation. c. transference neurosis. d. insight. 240. C. G. Jung, the founder of analytic psychology, said men operate on logic or the ________ principle, while women are intuitive, operating on the ________ principle. a. Eros; Thanatos b. Logos; Eros c. reality; pleasure d. transference; countertransference 241. Jung used drawings balanced around a center point to analyze himself, his clients, and dreams. He called them a. mandalas. b. projective drawings. c. unconscious automatic writing. d. eidetic imagery. 242. ________ emphasized the drive for superiority. a. Jung b. Adler c. Constructivist therapists d. Freud and Jung 243. The statement “Sibling interaction may have more impact than parent–child interaction” describes a. Sigmund Freud’s theory. b. Alfred Adler’s theory. c. insight. d. Carl Jung’s theory. 244. In contrast with Freud, the neo-Freudians emphasized a. baseline measures. b. social factors. c. unconditional positive regard. d. insight. 245. The terms introversion and extroversion are associated with a. psychoanalysis. b. Freud. c. Adler. d. Jung. 246. The personality types of the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) are associated with the work of a. psychoanalysis. b. Sigmund Freud. c. Afred Adler. d. Carl G. Jung. 247. One of Adler’s students, Rudolph Dreikurs, a. created the TAT. b. was the first to discuss the use of group therapy in private practice c. was a noted Freud hater. d. created the hierarchy of needs. 248. Adler emphasized that people wish to belong. This is known as a. superiority. b. social connectedness. c. the collective unconscious. d. animus. 249. Adler was one of the first therapists who relied on paradox. Using this strategy, a client (who was a student in a counselor preparation program) who was afraid to give a presentation in front of his counseling class for fear he might shake and embarrass himself would be instructed to a. exaggerate the behavior and really do a thorough job shaking in front of the class. b. practice relaxation techniques for 10–20 minutes before the speech. c. practice rational self-talk. d. practice rational thinking. 250. C. J. Jung felt that society caused men to deny their feminine side known as ________ and women to deny their masculine side known as ________. a. Eros; Thanatos b. animus; anima c. anima; animus d. yin; yang 251. Jung spoke of a collective unconscious common to all men and women. The material that makes up the collective unconscious, which is passed from generation to generation, is known as a. a hierarchy of needs. b. instinctual. c. paradox. d. archetypes. 252. Common archetypes include a. the persona—the mask or role we present to others to hide our true self. b. animus, anima, and self. c. shadow—the mask behind the persona, which contains id-like material, denied, yet desired. d. all of the above. 253. A client is demonstrating inconsistent behavior. She is smiling but says that she is very sad about what she did. When her counselor points this out to her, the counselor’s verbal response is known as a. active listening. b. confrontation. c. accurate empathy. d. summarization. 254. During a professional staff meeting, a counselor says he is worried that if techniques are implemented to stop a 6-year-old boy from sucking his thumb, then he will begin biting his nails or stuttering. The counselor a. is using ACT or acceptance and commitment therapy, a mindfulness-based behavior therapy. b. is using Donald Meichenbaum’s cognitive behavior modification. c. is most likely a behaviorist concerned with symptom substitution. d. is most likely an analytically trained counselor concerned with symptom substitution. 255. An eclectic counselor a. is analytic. b. is behavioristic. c. attempts to choose the best theoretical approach based on the client’s attributes, resources, and situation. d. insists on including all family members in the treatment. 256. The word eclectic is most closely associated with a. Frederick C. Thorne. b. Sigmund Freud. c. Jean Piaget. d. Burrhus Frederic Skinner. 257. A counselor who is obsessed with the fact that a client missed his or her session is the victim of a. cognitive dissonance. b. transference. c. countertransference. d. positive transference. 258. Lifestyle, birth order, and family constellation are emphasized by a. Freud. b. Jung. c. Adler. d. Thorne and Lazarus. 259. A counselor who remarks that firstborn children are usually conservative but display leadership qualities is most likely a. a Freudian who believes in the unconscious mind. b. an Adlerian who believes behavior must be studied in a social context; never in isolation. c. a Rogerian who stresses the importance of the therapeutic relationship. d. a behavior modifier using a behavioral contract. 260. Existentialism is to logotherapy as ________ is to behaviorism. a. operants b. associationism c. Skinner d. Socrates 261. B. F. Skinner’s reinforcement theory elaborated on a. Edward Thorndike’s law of effect. b. Alfred Adler’s concept of lifestyle. c. Arnold Lazarus’s concept of the BASIC-ID used in the multimodal therapeutic approach that is eclectic and holistic. d. symptom substitution. 262. Classical conditioning relates to the work of a. E. G. Williamson. b. B. F. Skinner. c. Viktor Frankl, who created logotherapy. d. Ivan Pavlov. 263. An association that naturally exists, such as an animal salivating (an unconditioned response known as a UR or UCR) when food is presented, is called a. an operant. b. a conditioned stimulus (CS). c. an unconditioned stimulus (UCS). d. an acquisition period. 264. Skinner’s operant conditioning is also referred to as a. instrumental learning. b. classical conditioning. c. cognitive learning. d. learning via insight. 265. Respondent behavior refers to a. reflexes. b. operants. c. a type of phobia. d. punishment. 266. All reinforcers a. are plastic tokens. b. tend to increase the probability that a behavior will occur. c. are secondary. d. do not raise behavior since negative reinforcement lowers behavior. 267. Negative reinforcement requires the withdrawal of an aversive (negative) stimulus to increase the likelihood that a behavior will occur. Negative reinforcement is not used as often as positive reinforcement and a. is really the same as punishment. b. effectively lowers the frequency of behavior in young children. c. is not the same thing as punishment. d. is a psychodynamic conceptualization. 268. Punishment a. is the same as negative reinforcement. b. is much more effective than reinforcement. c. decreases the probability that a behavior will occur. d. is used extensively in reality therapy. 269. In Pavlov’s famous experiment using dogs, the bell was the ________ and the meat was the ________. a. CS; UCS b. UCS; CS c. CR; UCS d. UCS; CR 270. The most effective time interval (temporal relation) between the CS and the US a. is irrelevant—it does not influence the learning process. b. is 5 seconds. c. is the .05 level according to social scientists. d. is .5 or half a second. 271. Many researchers have tried putting the UCS (the meat) before the CS (the bell). This usually results in a. increased learning. b. anger on the part of the dog. c. experimental neurosis. d. no conditioning. 272. Several graduate students in counseling trained a poodle to salivate to a child’s toy horn using Pavlov’s classical conditioning paradigm. One day the department chairman was driving across campus and honked his horn. Much to the chagrin of the students, the poodle elicited a salivation response. What had happened? a. experimental neurosis had obviously set in. b. extinction. c. stimulus generalization or what Pavlov termed irradiation. d. stimulus discrimination 273. The department chairman found the poodle’s response (see question 272) to his automobile horn humorous. He thus instructed the graduate students to train the dog to salivate only to his car horn and not the original toy bell. Indeed the graduate students were able to perform this task. The poodle was now demonstrating a. experimental neurosis. b. irradiation. c. pica. d. stimulus discrimination. 274. The department chair was further amused by the poodle’s tendency to be able to discriminate one CS from another (see question 273). He thus told the students to teach the dog to salivate only to the horn on his Ford but not one on a graduate student’s Chevrolet truck. In reality, the horns on the two vehicles sounded nearly identical. The training was seemingly unsuccessful inasmuch as the dog merely took to very loud barking. In this case a. experimental neurosis set in. b. irradiation became a reality. c. borderline personality traits no doubt played a role. d. a covert process confounded the experiment. 275. In one experiment, a dog was conditioned to salivate to a bell paired with a fast-food cheeseburger. The researcher then kept ringing the bell without giving the dog the cheeseburger. This is known as a. instrumental learning via shaping. b. positive reinforcement. c. extinction, and the salivation will disappear. d. negative reinforcement. 276. John B. Watson’s name is associated with a. Little Hans. b. Anna O. c. Little Albert. d. B and c. 277. During a family counseling session, a 6-year-old girl repeatedly sticks her tongue out at the counselor, who is obviously ignoring the behavior. The counselor is practicing a. negative reinforcement, b. chaining. c. reciprocal inhibition d. Extinction 278. In general, behavior modification strategies are based heavily on ________, while behavior therapy emphasizes ________. a. instrumental conditioning; classical conditioning b. Pavlovian principles; Skinnerian principles c. Skinnerian principles; Pavlovian principles d. a and c 279. A behavioristic counselor decides upon aversive conditioning as the treatment of choice for a gentleman who wishes to give up smoking. The counselor begins by taking a baseline. This is accomplished a. using hypnosis. b. by charting the occurrence of the behavior prior to any therapeutic intervention. c. using a biofeedback device. d. by counterconditioning. 280. The first studies, which demonstrated that animals could indeed be conditioned to control autonomic processes, were conducted by a. Edward Thorndike. b. Joseph Wolpe. c. Neal Miller. d. Ivan Pavlov. 281. The significance of the Little Albert experiment by John B. Watson and Rosalie Rayner was that a. a phobia could be a learned behavior. b. it provided concrete proof that Skinner’s model was correct. c. it provided concrete proof that Pavlov’s model was correct. d. none of the above. 282. John B. Watson is to cause as Mary Cover Jones is to a. cure. b. Skinner. c. Piaget. d. NLP. 283. In the famous Little Albert experiment, a child was conditioned to fear a harmless white furry animal. Historical accounts indicate that the child also began to fear a Santa Claus mask. This would demonstrate a. two DSM diagnoses which often co-occur: panic disorder and agoraphobia. b. stimulus generalization. c. an adjustment reaction. d. stimulus discrimination. 284. A counselor who says he or she practices depth psychology technically bases his or her treatment on a. Pavlov’s dogs. b. Mary Cover Jones. c. John B. Watson. d. Freud’s topographic hypothesis. 285. When a counselor refers to a counseling paradigm, she really means a. she is nondirective. b. she is very directive. c. a treatment model. d. she is not a depth psychologist. 286. A man says, “My life has been lousy for the past six months.” The counselor replies, “Can you tell me specifically what has made life so bad for the last six months?” The counselor is a. using interpretation. b. using summarization. c. using concreteness. d. using a depth psychology paradigm. 287. A client who is having panic attacks is told to practice relaxing his jaw muscle for three minutes per day. The counselor here is using a. concreteness. b. a directive. c. interpretation. d. parroting. 288. ________ is a biofeedback device. a. A bathroom scale b. A DVD player c. A digital clock d. An analyst’s couch 289. Johnny just loves M&Ms but doesn’t do his homework. The school counselor thus instructs Johnny’s mom to give the child a bag of M&Ms every night after he finishes his homework. This is an example of a. punishment. b. biofeedback. c. a Pavlovian strategy. d. positive reinforcement. 290. Genuineness, or congruence, is really a. identical to concreteness. b. selective empathy. c. the counselor’s ability to be himself or herself. d. an archaic Freudian notion. 291. Empathy is a. the ability to understand the client’s world and to communicate this to the client. b. behavioristic. c. A and b. d. the same as sympathy. 292. When something is added following an operant, it is known as a ________, and when something is taken away it is called a ________. a. negative reinforcer; positive reinforcer b. positive reinforcer; negative reinforcer c. extinction; shaping d. classical conditioning; operant conditioning 293. After a dog is conditioned using the well-known experiment of Pavlov, a light is paired with the bell (the CS). In a short period of time the light alone would elicit the salivation. This is called a. extinction. b. token reinforcement. c. biofeedback. d. higher-order conditioning. 294. A to ward off migraines. He would utilize counselor decides to use biofeedback training to help a client raise the temperature in his right hand a. a temperature trainer. b. EMG feedback. c. EEG neurofeedback. d. EKG feedback. 295. A counselor discovered that a client became nervous and often experienced panic attacks when she would tense her frontalis muscle over her eyes. The counselor wanted direct muscle feedback and thus would rely on a. the Jacobson relaxation method. b. GSR feedback. c. EMG feedback. d. a simple yet effective mood ring. 296. According to the Premack principle, an efficient reinforcer is what the client himself or herself likes to do. Thus, in this procedure a. a lower-probability behavior is reinforced by a higher-probability behavior. b. a higher-probability behavior is reinforced by a lower-probability behavior. c. a and b are paradoxically both effective. d. none of the above. 297. A counselor who wanted to teach a client to produce alpha waves for relaxation would utilize a. EMG feedback. b. GSR feedback. c. EEG feedback. d. EKG feedback. 298. A reinforcement schedule gives the guidelines or rules for reinforcement. If a reinforcer is given every time a desired response occurs, it is known as a. an intermittent schedule. b. an extinction schedule. c. continuous reinforcement. b. thinning. 299. The two basic classes of intermittent reinforcement schedules are the ________, based on the number of responses and the ________, based on the time elapsed. a. ratio; interval b. interval; ratio c. continuous; ratio d. interval; continuous 300. The most difficult intermittent schedule to extinguish is the a. fixed ratio, for example giving a child an M&M for each five math problems she completes. b. fixed interval, which describes the way most agency counselors are paid (e.g., one time per month, c. although the amount of work may vary from month to month). d. variable interval. e. variable ratio. 301. Ch. 6 - Group Counseling and Group Work (100) Ch. 7 - Career Development (100) Ch. 8 - Assessment and Testing (100) 302. A short answer test is a(n) ________ test. a. Objective b. culture-free c. forced choice d. free choice 303. The NCE and the CPCE would be examples of a(n) ________ test. a. free choice b. forced choice c. projective d. intelligence 304. The ________ index indicates the percentage of individuals who answered each item correctly. a. difficulty b. critical c. intelligence d. personal 305. Short answer tests and projective measures utilize free response items. The NCE and the CPCE uses forced choice or so-called ________ items. a. Vague b. B. subjective c. C. recognition d. D. numerical 306. A true/false test has ________ recognition items. a. similar b. free choice c. dichotomous d. No 307. A test format could be normative or ipsative. In the normative format a. each item depends on the item before it. b. each item depends on the item after it. c. the client must possess an IQ within the normal range. d. each item is independent of all other items. 308. A client who takes a normative test a. cannot legitimately be compared to others who have taken the test. b. can legitimately be compared to others who have taken the test. c. could not have taken an IQ test. d. could not have taken a personality test. 309. In an ipsative measure the person taking the test must compare items to one another. The result is that a. an ipsative measure cannot be utilized for career guidance. b. you cannot legitimately compare two or more people who have taken an ipsative test. c. an ipsative measure is never a forced choice format. d. an ipsative measure is never reliable. 310. Tests are often classified as speed tests versus power tests. A timed typing test used to hire secretaries would be a. a power test. b. neither a speed test nor a power test. c. a speed test. d. a fine example of an ipsative measure. 311. A counseling test consists of 300 forced response items. The person taking the test can take as long as he or she wants to answer the questions. a. This is most likely a projective measure. b. This is most likely a speed test. c. This is most likely a power test. d. This is most likely an invalid measure. 312. An achievement test measures maximum performance or present level of skill. Tests of this nature are also called attainment tests, while a personality test or interest inventory measures a. typical performance. b. minimum performance. c. unconscious traits. d. self-esteem by always relying on a Q-Sort design. 313. In a spiral test a. the items get progressively easier. b. the difficulty of the items remains constant. c. the client must answer each question in a specified period of time. d. the items get progressively more difficult. 314. In a cyclical test a. The items get progressively easier b. The difficulty of the items remains constant c. You have several sections which are spiral in nature. d. The client must answer each question in a specified period of time. 315. A test battery is considered a. a horizontal test. b. a vertical test. c. valid test. d. a reliable test. 316. In a counseling research study, two groups of subjects took a test with the same name. However, when they talked with each other they discovered that the questions were different. The researcher assured both groups that they were given the same test. How is this possible? a. The researcher is not telling the truth. The groups could not possibly have taken the same test. b. The test was horizontal. c. The test was not a power test. d. The researcher gave parallel forms of the same test. 317. The most critical factors in test selection are a. the length of the test and the number of people who took the test in the norming process. b. horizontal versus vertical. c. validity and reliability. d. spiral versus cyclical format. 318. Which is more important, validity or reliability? a. Reliability. b. They are equally important. c. Validity. d. It depends on the test in question. 319. In the field of testing, validity refers to a. whether the test really measures what it purports to measure. b. whether the same test gives consistent measurement. c. the degree of cultural bias in a test. d. the fact that numerous tests measure the same traits. 320. A counselor peruses a testing catalog in search of a test which will repeatedly give consistent results. The counselor a. is interested in reliability. b. is interested in validity. c. is looking for information which is not available. d. is magnifying an unimportant issue. 321. Which measure would yield the highest level of reliability? a. A TAT, projective test popular with psychodynamic helpers. b. The WAIS-IV, a popular IQ test. c. The MMPI-2, a popular personality test. d. A very accurate postage scale. 322. Construct validity refers to the extent that a test measures an abstract trait or psychological notion. An example would be a. Height. b. weight. c. ego strength. d. the ability to name all men who have served as U.S. presidents. 323. Face validity refers to the extent that a test a. looks or appears to measure the intended attribute. b. measures a theoretical construct. c. appears to be constructed in an artistic fashion. d. can be compared to job performance. 324. A job test which predicted future performance on a job very well would a. have high criterion/predictive validity. b. have excellent face validity. c. have excellent construct validity. d. not have incremental validity or synthetic validity. 325. A new IQ test which yielded results nearly identical to other standardized measures would be said to have a. good concurrent validity. b. good face validity. c. superb internal consistency. d. all of the above. 326. When a counselor tells a client that the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) will predict her ability to handle graduate work, the counselor is referring to a. good concurrent validity. b. construct validity. c. face validity. d. predictive validity. 327. A reliable test is ________ valid. a. always b. 90% c. not always d. 80% 328. A valid test is ________ reliable. a. not always b. always c. never d. 80% 329. One method of testing reliability is to give the same test to the same group of people two times and then correlate the scores. This is called a. test–retest reliability. b. equivalent forms reliability. c. alternate forms reliability. d. the split-half method. 330. One method of testing reliability is to give the same population alternate forms of the identical test. Each form will have the same psychometric/statistical properties as the original instrument. This is known as a. test–retest reliability. b. equivalent or alternate forms reliability. c. the split-half method. d. internal consistency. 331. A counselor doing research decided to split a standardized test in half by using the even items as one test and the odd items as a second test and then correlating them. The counselor a. used an invalid procedure to test reliability. b. was testing reliability via the split-half correlation method. c. was testing reliability via the equivalent forms method. d. was testing reliability via the inter-rater method. 332. Which method of reliability testing would be useful with an essay test but not with a test of algebra problems? a. Test–retest. b. Alternate forms. c. Split-half. d. Inter-rater/inter-observer. 333. A reliability coefficient of 1.00 indicates a. a lot of variance in the test. b. a score with a high level of error. c. a perfect score which has no error. d. a typical correlation on most psychological and counseling tests. 334. 636. An excellent psychological or counseling test would have a reliability coefficient of a. 50. b. 90. c. 1.00. d. –.90. 335. A researcher working with a personality test discovers that the test has a reliability coefficient of .70 which is somewhat typical. This indicates that a. 70% of the score is accurate while 30% is inaccurate. b. 30% of the people who are tested will receive accurate scores. c. 70% of the people who are tested will receive accurate scores. d. 30% of the score is accurate while 70% is inaccurate. 336. A career counselor is using a test for job selection purposes. An acceptable reliability coefficient would be ________ or higher. a. .20 b. .55 c. .80 d. .70 337. The same test is given to the same group of people using the test–retest reliability method. The correlation between the first and second administration is .70. The true variance (i.e., the percentage of shared variance or the level of the same thing measured in both) is a. 70%. b. 100%. c. 50%. d. 49%. 338. IQ means a. a query of intelligence. b. indication of intelligence. c. intelligence quotient. d. intelligence questions for test construction. 339. ________ did research and concluded that intelligence was normally distributed like height or weight and that it was primarily genetic. a. Spearman b. Guilford c. Williamson d. Galton 340. Francis Galton felt intelligence was a. a unitary faculty. b. best explained via a two factor theory. c. best explained via the person’s environment. d. fluid and crystallized in nature. 341. J. P. Guilford isolated 120 factors which added up to intelligence. He also is remembered for his a. thoughts on convergent and divergent thinking. b. work on cognitive therapy. c. work on behavior therapy. d. work to create the first standardized IQ test. 342. A counselor is told by his supervisor to measure the internal consistency reliability (i.e., homogeneity) of a test but not to divide the test in halves. The counselor would need to utilize a. the split-half method. b. the test–retest method. c. the Kuder–Richardson coefficients of equivalence. d. Cross-validation. 343. The first intelligence test was created by a. David Wechsler. b. J. P. Guilford. c. Francis Galton. d. Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon. 344. Today, the Stanford–Binet IQ test is a. a nonstandardized measure. b. a standardized measure. c. a projective measure. d. b and c. 345. IQ stands for intelligence quotient, which is expressed by a. CA/MA × 100. b. CA/MA × 100. c. MA/CA × 50. d. MA/CA × 100. 346. The Binet stressed age-related tasks. Utilizing this method, a 9-year-old task would be one which a. only a 10-year-old child could answer. b. only an 8-year-old child could answer. c. 50% of the 9-year-olds could answer correctly. d. 75% of the 9-year-olds could answer correctly. 347. Simon and Binet pioneered the first IQ test around 1905. The test was created to a. assess high school seniors in America. b. assess U.S. military recruits. c. discriminate children without an intellectual disability from children with an intellectual disability. d. measure genius in the college population. 348. Today the Stanford–Binet is used from age 2 to adulthood. The IQ formula has been replaced by the a. SAS. b. SUDS. c. Entropy. d. KR-20 formula. 349. Most experts would agree that the Wechsler IQ tests gained popularity, as the Binet a. must be administered in a group. b. favored the geriatric population. c. didn’t seem to be the best test for adults. d. was biased toward women. 350. The best IQ test for a 22-year-old single male would be the a. WPPSI-III. b. WAIS-IV. c. WISC-IV. d. any computer-based IQ test. 351. The best intelligence test for a sixth-grade girl would be the a. WPPSI-IV. b. WAIS-IV. c. WISC-IV. d. Merrill–Palmer. 352. The best intelligence test for a kindergartner would be the a. WPPSI-IV. b. WAIS-IV. c. WISC-IV. d. Myers–Briggs Type Indicator. 353. The mean on the Wechsler and the Stanford–Binet Intelligence scales (SB5) is ________ and the standard deviation is ________. a. 100; 100 b. 100; 15 Wechsler, 16 Stanford–Binet c. 100; 20 d. 100; 1 354. Group IQ tests like the Otis–Lennon, the Lorge–Thorndike, and the California Test of Mental Abilities are popular in school settings. The advantage is that a. group tests are quicker to administer. b. group tests are superior in terms of predicting school performance. c. group tests always have a higher degree of reliability. d. individual IQ tests are not appropriate for school children. 355. The group IQ test movement began a. in 1905. b. with the work of Binet. c. with the Army Alpha and Army Beta in World War I. d. with Freudian psychoanalysis and the psychodynamic movement. 356. In a culture-fair test a. items are known to the subject regardless of his or her culture. b. the test is not standardized. c. culture-free items cannot be utilized. d. African Americans generally score higher than whites. 357. The black versus white IQ controversy was sparked mainly by a 1969 article written by ________. a. John Ertl b. Raymond B. Cattell c. Arthur Jensen d. Robert Williams 358. The MMPI-2 is a. an IQ test. b. a neurological test. c. a projective personality test. d. a standardized personality test. 359. The word psychometric means a. a form of measurement used by a neurologist. b. any form of mental testing. c. a mental trait which cannot be measured. d. the test relies on a summated or linear rating scale. 360. In a projective test the client is shown a. something which is highly reinforcing. b. something which is highly charged from an emotional standpoint. c. a and b. d. neutral stimuli. 361. The 16 PF reflects the work of a. Raymond B. Cattell. b. Carl Jung. c. James McKeen Cattell. d. Oscar K. Buros. 362. The Myers–Briggs Type Indicator reflects the work of a. Raymond B. Cattell. b. Carl Jung. c. William Glasser. d. Oscar K. Buros. 363. The counselor who favors projective measures would most likely be a a. Rogerian. b. strict behaviorist. c. TA therapist. d. psychodynamic clinician. 364. An aptitude test is to ________ as an achievement test is to ________. a. what has been learned; potential b. potential; what has been learned c. profit from learning; potential d. a measurement of current skills; potential 365. Both the Rorschach and the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) are projective tests. The Rorschach uses 10 inkblot cards while the TAT uses a. a dozen inkblot cards. b. verbal and performance IQ scales. c. Pictures. d. incomplete sentences. 366. Test bias primarily results from a. a test being normed solely on white middle-class clients. b. the use of projective measures. c. using whites to score the test. d. using IQ rather than personality tests. 367. A counselor who fears the client has an organic, neurological, or motoric difficulty would most likely use the a. Bender Gestalt II. b. Rorschach. c. Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory-2. d. Thematic Apperception Test. 368. An interest inventory would be least valid when used with a. a first-year college student majoring in philosophy. b. a third-year college student majoring in physics. c. an eighth-grade male with an IQ of 136. d. a 46-year-old white male construction worker. 369. One major criticism of interest inventories is that a. they have far too many questions. b. they are most appropriate for very young children. c. they emphasize professional positions and minimize blue-collar jobs. d. they favor jobs that will require a bachelor’s degree or higher. 370. Interest inventories are positive in the sense that a. they are reliable and not threatening to the test taker. b. they are always graded by the test taker. c. they require little or no reading skills. d. they have high validity in nearly all age brackets. 371. A counselor who had an interest primarily in testing would most likely be a member of a. HS-BCP. b. AARC. c. NASW. d. ACES. 372. The NCE is a. an intelligence test. b. an aptitude test. c. a personality test. d. an achievement test. 373. The ________ are examples of aptitude tests. a. O*NET Ability Profiler and the MCAT b. GZTS and the MMPI-2 c. CPI and the MMPI-2 d. Strong and the LSAT 374. One problem with interest inventories is that the person often tries to answer the questions in a socially acceptable manner. Psychometricians call this response style phenomenon a. standard error. b. social desirability (the right way to feel in society). c. cultural bias. d. Acquiescence. 375. An aptitude test predicts future behavior while an achievement test measures what you have mastered or learned. In the case of a test like the ________ the distinction is unclear. a. Binet b. Wechsler c. GRE d. Bender 376. Your supervisor wants you to find a new personality test for your counseling agency. You should read a. professional journals. b. the Buros Mental Measurements Yearbook. c. classic textbooks in the field as well as test materials produced by the testing company. d. all of the above. 377. The standard error of measurement tells you a. how accurate or inaccurate a test score is. b. what population responds best to the test. c. something about social loafing. d. the number of people used in norming the test. 378. A new IQ test has a standard error of measurement (SEM) of 3. Tom scores 106 on the test. If he takes the test a lot, we can predict that about 68% of the time a. Tom will score between 100 and 103. b. Tom will score between 100 and 106. c. Tom will score between 103 and 109. d. Tom will score higher than Betty who scored 139. 379. A counselor created an achievement test with a reliability coefficient of .82. The test is shortened since many clients felt it was too long. The counselor shortened the test but logically assumed that the reliability coefficient would now a. be approximately .88. b. remain at .82. c. be at least 10 points higher or lower. d. be lower than .82. 380. A counselor can utilize psychological tests to help secure a ________ diagnosis if third-party payments are necessary. a. CPT b. DSM or ICD c. Percentile d. standard error 381. A colleague of yours invents a new projective test. Seventeen counselors rated the same client using the measure and came up with nearly identical assessments. This would indicate a. high validity. b. high reliability. c. excellent norming studies. d. culture fairness. 382. Counselors often shy away from self-reports since a. clients often give inaccurate answers. b. ACA ethics do not allow them. c. clients need a very high IQ to understand them. d. they are generally very lengthy. 383. In most instances, who would be the best qualified to give the Rorschach Inkblot Test? a. A counselor with NCC after his or her name. b. A clinical psychologist. c. A D.O. psychiatrist. d. A social worker with LCSW after his or her name. 384. Your client, who is in an outpatient hospital program, is keeping a journal of irrational thoughts. This would be a. an unethical practice based on NBCC ethical guidelines. b. considered a standardized test. c. an informal assessment technique. d. an aptitude measure. 385. You are uncertain whether a test is intended for the population served by your not-for-profit agency. The best method of researching this dilemma would be to a. contact a local APA clinical psychology graduate program. b. e-mail the person who created the test. c. read the test manual included with the test. d. give the test to six or more clients at random. 386. Clients should know that a. validity is more important than reliability. b. projective tests favor psychodynamic theory. c. face validity is not that important. d. a test is merely a single source of data and not infallible. 387. One major testing trend is a. computer-assisted testing and computer interpretations. b. more paper and pencil measures. c. to give school children more standardized tests. d. to train pastoral counselors to do projective testing. 388. One future trend which seems contradictory is that some experts are pushing for a. a greater reliance on tests while others want to rely on them less. b. social workers to do most of the testing. c. psychiatrists to do most of the testing. d. counselors to ban all computer-assisted tests. 389. Most counselors would agree that a. more preschool IQ testing is necessary. b. teachers need to give more personality tests. c. more public education is needed in the area of testing. d. the testing mystique has been beneficial to the general public. 390. ________ would be an informal method of appraisal. a. IQ testing b. Standardized personality testing c. GRE scores d. A checklist 391. The WAIS-IV is given to 100,000 individuals in the United States who are picked at random. A counselor would expect that a. approximately 68% would score between 85 and 115. b. approximately 68% would score between 70 and 130. c. the mean IQ would be 112. d. 50% of those tested would score 112 or above. 392. A word association test would be an example of a. a neuropsychological test. b. a motoric test. c. an achievement test. d. a projective test. 393. Infant IQ tests are a. more reliable than those given later in life. b. more unreliable than those given later in life. c. not related to learning experiences. d. never used. 394. A good practice for counselors is to a. always test the client yourself rather than referring the client for testing. b. never generalize on the basis of a single test score. c. stay away from culture-free tests. d. stay away from scoring the test yourself. 395. You want to admit only 25% of all counselors to an advanced training program in psychodynamic group therapy. The item difficulty on the entrance exam for applicants would be best set at a. 0.0. b. .5 regardless of the admission requirement. c. 1.0. d. .25. 396. According to Public Law 93–380, also known as the Buckley Amendment, a 19-year-old college student attending college a. could view her record, which included test data. b. could view her daughter’s infant IQ test given at preschool. c. could demand a correction she discovered while reading a file. d. all of the above. 397. Lewis Terman a. constructed the Wechsler tests. b. constructed the initial Binet prior to 1910. c. constructed the Rorschach. d. Americanized the Binet. 398. In constructing a test you notice that all 75 people correctly answered item number 12. This gives you an item difficulty of a. 1.2. b. .75. c. 1.0. d. 0.0. Ch. 9 - Research and Program Evaluation (100) Ch. 10 - Professional Orientation and Ethical Practice (100) Ch. 11 - Counseling Families, Diagnosis, Neurocounseling, and Advanced Concepts (200) 399. A married couple brings their two children to counseling for behavioral problems. The 14-year-old daughter stays out late and their 17-year-old son is using drugs. According to most marriage and family therapists the identified patient would be a. the 17-year-old son. b. the 14-year-old daughter. c. the family. d. both children. 400. You are seeing a husband and wife for marriage counseling. During one of the sessions you decide to see them separately. The husband tells you he has seen an attorney because he is filing for divorce. He has not told his wife and indicates that he will not do so. You feel the wife has a right to know this because it will help her plan for the future. You should only tell his wife if he gives you permission. a. communicate his intent to his wife since ethics guidelines state you may do so when a member of the couple is contemplating divorce. b. not tell the wife since research indicates that women respond more positively to divorce when they have less time to think about it. c. terminate the husband unless he tells her. 401. You are supervising a licensing candidate who is primarily interested in marriage and family counseling. You are very attracted to her and have sex with her. According to ethics guidelines this is perfectly ethical, since this is a student and not a client. this is unethical. this is perfectly ethical, since this is a supervisee and not a client. a and c are both correct. 402. The fastest growing clientele for professional counselors are persons experiencing bipolar disorder. experiencing suicidal ideation. experiencing marriage and family problems. who abuse their children. 403. Family counselors generally believe in circular/reciprocal causality (e.g., dynamics of family members). linear causality. random causality. dream analysis. 404. Cybernetics is a concept used by family therapists. It is usually associated with the work of Sigmund Freud and Albert Ellis. Norbert Wiener. Virginia Satir. behavioral family therapists and cognitive family therapists. 405. A family that is stable and reaches an equilibrium is in a state of adaptability. enmeshment. nonsummativity. homeostasis. 406. Adaptability is the ability of the family to balance ego strength. stability and change. morphostasis and morphogenesis. b and c. 407. A family wants to see you for counseling; however, they have a very limited income and can’t afford to pay. You therefore agree to see the family for free (i.e., pro bono). The term that best describes your actions would be aspirational ethics. mandatory ethics. empathy. all of the above. 408. Experiential conjoint family therapy is closely related to the work of Virginia Satir. Albert Ellis. Jay Haley. Salvador Minuchin. 409. Virginia Satir felt that a major goal of therapy was to improve intrafamily communication (i.e., communication between family members). According to Satir, four basic patterns prevented good communication under stress. These defensive postures or stress positions are: placating, blaming, being overly reasonable, and being irrelevant. Placating means you disagree with all the other family members. you pick a favorite family member and agree with him or her. you ignore the other family members. you try to please everybody out of a fear of rejection. 410. The placater is a people pleaser under stress while the blamer will sacrifice others to feel good about himself. will often say “if it weren’t for you….” will point the finger at others to avoid dealing with his or her own issues. all of the above are typical behaviors of the blamer. 411. The person who becomes overly reasonable practices excitation. cries a lot during therapy sessions. is likely to engage in the defense mechanism of intellectualization. has a high degree of emotion. 412. According to Virginia Satir, the individual displaying an irrelevant style will distract the family from the problem via constantly talking about irrelevant topics. will become a people pleaser. will analyze the situation more than most. all of the above. 413. Virginia Satir is considered a leading figure in experiential family therapy. ________ is sometimes called the dean of experiential family therapy. Ludwig von Bertalanffy Gregory Bateson Carl Whitaker Murray Bowen 414. Carl Whitaker’s interaction with the family could best be described as quiet and empathic. joining the family and experiencing it as if he were a family member. a reality therapist. a cognitive behavior therapist. 415. According to Carl Whitaker, a co-therapist is helpful. a co-therapist should never be used. a co-therapist should be used only with blended families. all of the above could be true. 416. Psychotherapy of the absurd is primarily related to the work of Virginia Satir. Carl Whitaker. Maxie C. Maultsby, Jr. William Glasser. 417. A behavioristic marriage and family therapist is counseling the entire family together. She turns to the 18-year-old son who is attending community college and says, “You must complete your sociology essay before you can use the family car and go out with your friends.”Which theorist is primarily guiding her intervention strategy? David Premack’s principle or law. Ivan Pavlov and John B. Watson. B. F. Skinner. all of the above. 418. A behavioristic marriage and family counselor is counseling the entire family together. She turns to the 18-year-old son who is attending community college and says, “I know you like to play golf. Therefore, every time you cut the grass your father will take you to play golf. I am going to have you and your dad sign a contract confirming that you agree with this policy.” Which principle is primarily guiding her strategy? Negative reinforcement. Thought stopping. Shaping with successive approximations. Quid pro quo. 419. A male is supervising a female counselor for state licensing. He tells her that he will continue to supervise her as long as she has sex with him. This is an example of quid pro quo. a legal but not an ethical violation. a and b. none of the above. 420. A behavioristic family counselor suggests that the family chart the number of times that 6-year-old Billy says “no” when he is told to do something. The baseline of the chart would refer to the period when positive reinforcement is being implemented. when negative reinforcement is being implemented. when quid pro quo is being implemented. before the behavior modification begins. 421. The family counselor explains to Mrs. Smith that the next time that 9-year-old Sally hits her little brother she must sit in the family room by herself. The counselor is using shaping. shaping with successive approximations. reciprocity. time-out, a procedure that most behaviorists feel is a form of extinction. 422. Mrs. Chance tells a family therapist that she pays all the bills, does all the cleaning, and brings in 90% of the family’s income. Moreover, Mrs. Chance is convinced that her husband does not appreciate her or show her affection. According to the behavioristic principle of family therapy known as reciprocity there is a good chance that Mrs. Chance will consider leaving the marriage. it may seem paradoxical; nevertheless, Mrs. Chance will be more committed to making the marriage work. it may seem paradoxical; nevertheless, there is a good chance Mr. Chance will consider leaving the marriage. this situation will have virtually no impact on this couple’s marriage. 423. A couple is having sexual problems that stem from anxiety. A marriage counselor who is a strict behaviorist would most likely dispute the couple’s irrational thinking. prescribe thought stopping. rely on systematic desensitization procedures. rely primarily on paraphrasing and reflection. 424. A family counselor notices that the husband in a blended family is having obsessive sexual thoughts about a woman living down the street. A strict behaviorist would most likely analyze the man’s dreams. have him chart the incidence of the behavior, but do little else. practice thought stopping. rely primarily on Wolpe’s systematic desensitization. 425. You secure a job as the executive director of a family counseling agency. As you go through your files you discover that five years before you took the job the agency selected 100 families and counseled them using a strict behaviorist model. The agency took the next group of 100 families and counseled them using Satir’s experiential conjoint family therapy model. Each family received 12 sessions of therapy and each family took a before and after assessment that accurately depicted how well the family was functioning. You decide to run a t test to examine whether or not a statistically significant difference is evident between the two approaches. This is an ex post facto (i.e., after the fact) correlation study. causal comparative or ex post facto (i.e., after the fact) research. a true experiment. simple survey research. 426. All of the techniques listed below would be used by a behavioristic family therapist except: Family sculpting. A functional analysis of behavior followed by operant conditioning. Modeling. Chaining and extinction. 427. Which statement is true of families? The divorce rate has decreased markedly in the last several years. Remarriage today is uncommon. Remarriage today is common. The divorce rate in the United States hovers at about 10%. 428. Which statement is true? Single life is short-lived for divorced persons. About 30% of all divorced persons are remarried within 12 months of being divorced. Most persons who are divorced do not remarry. Most persons who are divorced wait a minimum of five years to remarry. Women remarry quickly, however, men do not. 429. The theory of psychodynamic family counseling is primarily associated with William Glasser. Sigmund Freud. Virginia Satir and Carl Whitaker. Nathan Ackerman. 430. In psychoanalytic family therapy the word object means a dream. a significant other with whom a child wishes to bond. transference. Countertransference. 431. In psychoanalytic family therapy the term introjects really means that the client unconsciously internalizes the positive and negative characteristics of the objects within themselves. possesses internal verbalizations. possesses a finite number of problem-solving options. possesses the internal motivation to solve his or her own difficulties. 432. Pick the best example(s) of the psychoanalytic concept of splitting. A client who realistically perceives her therapist as a very empathic person. A client who realistically perceives her therapist as only having good qualities. A client who sees her therapist as all bad. b and c. 433. A 72-year-old woman you are counseling in a family reminds you of your mother and this is bringing up unresolved childhood issues for you as the counselor. This is an example of positive transference. negative transference. countertransference. ambivalent transference. 434. A family actually changes the structure of their family system. According to Watzlawick, Weakland, and Fisch the family has achieved second-order change that is more desirable than first-order change. first-order change that is more desirable than second-order change. mediation. a Greek chorus. 435. A woman sees her husband as all good sometimes and all bad at others. An analytically trained family therapist who believes in object relations would see this as ambivalent transference. splitting. persistent depressive disorder. psychotic behavior. 436. Nathan Ackerman is considered a famous psychoanalytic family therapist; so are Carl Rogers and Albert Ellis. Arnold Lazarus and Joseph Wolpe. William Glasser and Robert Wubbolding. James Framo and Robin Skynner. 437. Cloe Madanes and Jay Haley are associated with the ________ school of family counseling. strategic behavioral psychodynamic object relations 438. When Jay Haley began investigating psychotherapy he was already trained as a Freudian analyst like so many other pioneers in the field. was already trained as a behaviorist. had studied REBT with Albert Ellis. had a degree in the arts and communication rather than the helping professions. 439. Jay Haley believes in giving clients directives. You are counseling a family and during the session the 14-year-old daughter exclaims that she is suicidal. The best example of a directive would be you turn to the 14-year-old daughter and say, “You seem to be saying that living is too painful.” you turn to the 14-year-old daughter and say, “Could it be that you want to hurt yourself because your boyfriend no longer wishes to see you?” you turn to the family and say, “If your daughter threatens suicide this week I want the entire family—including your daughter—to stay home and nobody leaves for the day.” you turn to the family and say, “Could this be a family problem rather than a difficulty for your daughter?” 440. Which of these responses is the best example of the double-bind concept used in Haley’s strategic therapy? You are trying to help a client stop smoking: You hypnotize her and tell her she will never smoke another cigarette again. After you awaken her you admonish her to smoke as many cigarettes as she can for the first three days. You recommend that the client chart the number of cigarettes she smokes. You tell her to mentally visualize herself as a nonsmoker whenever she has the desire to smoke. All of the above. 441. The directive or prescription given to the smoker in the previous question could best be described as a paradoxical intervention. a cognitive intervention. an object relations intervention. a behavioristic intervention. 442. A couple tells a therapist using strategic family therapy that they have a quarrel at least once every evening. The therapist says, “Between now and the next time I see you I want you to have a serious quarrel at least twice every evening.” This is an example of relabeling, which is commonly used in this form of therapy. reframing, which is commonly used in this form of therapy. prescribing the symptom. a directive that is not paradoxical or a double bind. 443. Strategic family counselors often rely on relabeling or reframing. A client says his girlfriend yells at him every time he engages in a certain behavior. The best example of reframing or relabeling would be a counselor who remarks, “Research seems to show that when she yells at you it is because she loves you so much. A woman often feels foolish if she hugs or kisses you in a situation like that.” a counselor who remarks, “Can you tell me about it in the present moment, as if she is yelling at you this very minute?” a counselor who remarks, “You are upset by her verbal assaults.” a counselor who remarks, “Are you really hurt by your girlfriend’s remarks or is it the fact that you are telling yourself how catastrophic it is that she said these things?” 444. In strategic family counseling the person with the power in the family has the authority to make rules and enforce them. is usually extremely aggressive. is usually not willing to follow a family therapist’s prescriptions or directives. is the one who talks the most. 445. Psychoanalytic practitioners do not attack symptoms directly. Strategic therapy does not attack the symptoms directly either. is pragmatic and often focuses on abating symptoms. does not take a position on whether a counselor should attempt to ameliorate symptoms or not. takes the position that if you can change each family member’s unconscious, then symptoms will gradually disappear. 446. Cloe Madanes insisted that symptoms serve a function. A child, for example, sees that her mother is depressed. The daughter throws a glass cup to the floor to break it. This brings her mother out of the depressed state and makes her mother angry and powerful. This is known as symptom substitution. the perverse triangle. incongruous hierarchy. Latency. 447. Madanes advocated pretend techniques that are somewhat paradoxical. An example might be a child who has panic attacks pretends he has a mental bullhorn in his head and shouts “stop.” a child who has panic attacks pretends in his mind that a therapist is counseling him. a child who has panic attacks pretends his dad is a therapist during the actual family therapy session. a child who has panic attacks pretends to have one during the session and the parents pretend to help him. 448. A strategic family therapist says to a family, “I don’t know what else you can do to stop the bickering and fighting in your house.” This is an example of restraining. quid pro quo. pretending. Interpretation. 449. A client remarks that her depression is extremely intense. Her strategic counselor remarks, “It is very possible your depression is hopeless. It is possible you will never get over it.” Her comment is an example of a blatant ethical violation. positioning. cohesion. behavioral disputation. 450. A family counselor treats an Asian American family exactly like he treats the Arab American families in his caseload. He also imposes values from his own culture on them. This counselor has been described in the literature as culturally sensitive. lacking cultural sensitivity. culturally encapsulated. b and c. 451. Which statement is true of African American families? They are the largest minority in the United States. Fewer African Americans are getting married. African Americans are less likely to be concerned about gender roles (e.g., men and women can cook meals or work outside of the home). b and c. 452. When working with an African American family, the best approach would probably be Bowen’s family therapy; Minuchin’s structural family therapy; or Haley’s strategic family therapy. cognitive family therapy. Ackerman’s psychoanalytic approach to family therapy. a strict reality therapy approach based on the work of psychiatrist William Glasser. 453. When counseling Asian American families the best approach would most likely be a. Ackerman’s psychoanalytic approach. behavioral family therapy. solution-focused/problem-focused modalities. a, b, and c. 454. Which statement is true of Latino/a families? They have a high unemployment rate, often live in poverty, and rarely earn high school diplomas or college degrees. They have higher than average incomes but usually don’t finish high school or college. They have college degrees, but still generally live in poverty. They prefer long-term treatment in therapy. 455. A model by Olson, Sprenkle, and Russell suggests that family functioning can be described in two dimensions—cohesion and adaptability. The family therapy term cohesion refers to the level of emotional bonding between family members. Adaptability refers to a family’s level of enmeshment or disengagement. a family’s ability to adapt to the therapist’s personality. a family’s ability to adapt to the theoretical persuasion of the therapist. how rigid, structured, flexible, or chaotic the family is. 456. Which statement is true regarding Native American families? a. They are a very diverse group as they belong to over 550 state-recognized tribes, with over 220 in Alaska. Extended family and the tribe are very significant. A high percentage of children have been placed in foster care homes, residential facilities, or adoption homes that are non-Native American. All of the above are true. 457. The statement “Native Americans, also called American Indians in some of the literature, have a problem with alcoholism and suicide” is false. true as far as alcoholism is concerned, however, false where suicide is concerned. true. true regarding the suicide rate, however, false regarding their use of alcoholic beverages. 458. Murray Bowen is known for his work in intergenerational family therapy. When Bowen refers to triangulation he means that most people have three ego states (i.e., the Parent, the Adult, and the Child) in their personality. that most people have a personality structure composed of the id, the ego, and the superego. when a dyad (i.e., two individuals) is under stress a third person is recruited to help stabilize the difficulty between the original dyad. This could even be a child placed in the middle of the conflict. therapy has three distinct phases. 459. One of the primary goals of Bowen’s intergenerational family therapy is differentiation. Differentiation is a. the extent that one can separate one’s intellect from one’s emotional self. the extent that one is different from one’s peers. the extent that one is different from one’s childhood. the same as fusion. 460. Bowen popularized a three-generational pictorial diagram as a therapy tool. This is known as an histogram. a sociogram. a genogram. family sculpting. 461. An intergenerational family therapist says she is concerned with the nuclear family emotional system. She is referring to the fact that although the current family in therapy has an emotional system, this emotional system is influenced by previous generations whether they are alive or dead. the fact that a genogram should depict a single generation. the fact that emotional discord is a function of the unconscious mind. the miracle question. 462. Albert Ellis is to REBT as Salvador Minuchin is to a. the MRI model. structural family therapy. intergenerational family counseling. behavioral family counseling. 463. An important technique in structural family therapy is joining. Which statement most accurately depicts this intervention? The therapist meets, greets, and attempts to bond with the family. The therapist will use language similar to that of the family and mimesis which means that he or she will mimic communication patterns. The therapist is professional but distant. The therapist joins the family and sympathizes with their difficulties. Joining is used during the final session of therapy. 464. A family is seeing a structural family therapist because there is a huge argument every time the subject of the 16-year-old daughter’s boyfriend comes up. The therapist says, “Okay, I want you to play like you are at home and act out precisely what transpires when the subject of your daughter’s boyfriend is mentioned.” The structural family therapist is using a technique called joining. reframing. enactment. cognitive disputation. 465. When a structural therapist uses the term boundaries he or she really means a. the limits of the human mind. b. the limits of behavior in the family. the separation of the family members from their family of origin. the physical and psychological entities that separate individuals and subsystems from others in the family. 466. In Minuchin’s structural approach, clear boundaries are pathological. rigid. also called diffuse boundaries. ideal—firm yet flexible. 467. A woman is having difficulties at her place of employment. Her husband turns to her in a session and says, “You’re on your own, I’ve got my own problems.” A structural family therapist would assert that the boundaries between this couple are rigid. clear. diffuse. a combination of a and c. 468. A mother insists on accompanying her 20-year-old daughter on a date. A structural therapist would assume that the family has clear boundaries. has rigid boundaries. has diffuse boundaries. supports individuation. 469. Minuchin would often mimic the family’s style. This is known as cognitive disputation. the structural map. permeable boundaries. none of the above. 470. Ackerman is psychodynamic. Haley is strategic. Minuchin is structural. Bowen is intergenerational. Another well-known intergenerational family therapist would be Alfred Adler. Ivan Boszormenyi-Nagy (enunciated Naahge). Andrew Salter. Mara Selvini-Palazzoli. 471. A family member who is emotionally distant is disengaged. enmeshed. an example of equifinality. a placater. 472. During the course of a family session you discover that the man and his 14-year-old son are putting pressure on mom to quit her job. Mom very much likes her work. In Haley’s theory this set of dynamics would be called reframing. equifinality. the perverse triangle. Paradox. 473. ________ was a pioneer in the early history of family therapy. Carl Jung David Wechsler Alfred Adler Franz Anton Mesmer 474. Which therapist could best be described as atheoretical? Jay Haley. Carl Whitaker. Alfred Adler. Nathan Ackerman. 475. Solution-oriented therapy as practiced by William O’Hanlon, Insoo Kim Berg, Steve de Shazer, and Michelle Weiner Davis focuses primarily on the past. the present. the future. dream analysis. 476. Narrative therapy (NT), which highlights stories in counseling, is associated with the work of William O’Hanlon. William Glasser. Milton H. Erickson. Michael White, his wife Cheryl White, and David Epston. 477. Postmodernist Tom Anderson, a psychiatrist from Norway, became disenchanted with traditional family therapy. He began using a radical approach based primarily on a one-way mirror and a reflecting treatment team. three therapists. the gestalt empty chair technique. homework assignments. 478. Feminist therapy criticizes traditional therapies a. because they are androcentric (i.e., they use male views to analyze the personality). because they are gendercentric (i.e., they assume that there are two separate psychological developmental patterns—one for men and one for women). because they emphasize heterosexism and debase same-sex relationships. all of the above. 479. The term skeleton keys as used in Steve de Shazer’s brief solution-focused therapy (BSFT) indicates a standard or stock intervention that will work for numerous problems. a technique where the client goes home to see his or her family of origin. a technique that works for one specific problem, but usually will not work with other difficulties. a technique in which the therapist hands the client or clients a sheet of paper with a compliment on it. 480. One criticism of using cognitive-behavioral methods like REBT with families or individuals in multicultural counseling would be that the theory is not intended to be used with diverse populations. the theory suggests that the therapist must have ethnic or racial ties with the client in order for efficacious treatment to occur. that it ignores present moment problems. that the cognitive disputation could go against cultural messages. 481. Most experts predict that in the twenty-first century, theories of counseling and psychotherapy will become more integrative, since about 30–50% of all therapists say they are eclectic. become more behavioristic, since this is the approach that uses statistical outcomes. become more Rogerian, since the world as a whole is becoming more humanistic. not tolerate eclecticism, since it is not scientific. 482. Pick the most accurate statement. Brief solution-oriented therapy requires the use of a one-way mirror with a treatment team behind the mirror. Brief solution-oriented therapy does not utilize a treatment team behind a one-way mirror. Brief solution-oriented therapy sometimes uses a treatment team behind a one-way mirror, nevertheless, it is not required. Brief solution-oriented therapy does not utilize paradoxical interventions. 483. A researcher takes a group of clients and gives them a depression inventory. He then provides each client with two sessions of brief solution-oriented therapy and gives them the same depression inventory. A t test is used to compare the two sets of scores on the same people (i.e., the before and after measures of depression). This would be a between-groups design. a correlation coefficient. a related measures within-subject design. survey research. 484. A question on the NCE or CPCE regarding a pre-experimental design uses the letters XO. The letters stand for treatment (X) and observation, measurement, or score (O). the mean (X) and no treatment was given (O). the median (X) and other group (O). treatment (X) and the number of observations taken (O). 485. Another type of pre-experimental design is the one-group only posttest design. This is best depicted by a. OXO. XO. OX. XX. 486. A time-series design is a quasi-experimental design that utilizes two randomly chosen groups; a control group and an experimental group. without randomly chosen control and experimental groups, which relies on multiple observations of the dependent variable (i.e., the thing you are measuring) before and after the treatment occurs. a and b. is not depicted by any of the answers above. 487. The Solomon four-group is considered a true experimental design since each group is chosen via a random sample. When using this design all groups receive a pretest. there is no pretest. one control group receives a pretest and one experimental group receives a pretest; the other control group and experimental group do not. there is no posttest. 488. John Gottman is known for a. setting the level for intoxication driving while under the influence (DUI) or driving while intoxicated (DWI) at .08 or higher in most states. creating a paradigm to predict which marriages would likely end in divorce. demonstrating that physical biomarkers of older adults can be reversed if they are placed in an environment from the past and told to act like they are living in the past. popularizing the notion of propinquity. 489. The newest career theory would be constructivist and cognitive approaches. the trait-and-factor approach. the developmental and psychoanalytic approaches. the transactional analysis approach. 490. A popular TWA career counseling model by René V. Dawis and Lloyd Lofquist uses the abbreviation PEC. This stands for a. person emotion consequence. person education consequence. person environment correspondence. person environment consequence. 491. Most experts believe that the number of multigenerational families with a child, a parent, and a grandparent living together will decrease. increase. remain static. will continue to go up and down on a fairly regular basis. 492. A researcher wants to prove that structural family therapy is the most effective modality. She conducted a study a year ago using a significance level of .05. Several colleagues felt her significance level needed to come down. She thus ran the same basic experiment again with new people using a significance level of .01. Her chances of making a Type I error or so-called alpha error reduced. Now assume you compare her new research to her old research. What could you say about the possibility that her results will indicate that structural family therapy was not significantly different when in reality it truly is significant? Statistically, nothing. The chance of this occurring will go down when compared to the first experiment. The chance of this occurring increases when compared to the first experiment. It would totally depend on the sample size. 493. A question on your comprehensive exam asks you to compute the coefficient of determination. You are given a correlation coefficient of .70. How would you mathematically accomplish this task? You would subtract .70 from a perfect correlation of 1.00. You would multiply the mean of the population by .70. You would add .70 to a perfect correlation of 1.00. You would square the .70. 494. A correlation coefficient between variables X and Y is .60. If we square this figure we now have the coefficient of determination or true common variance of 36%. What is the coefficient of nondetermination that shows unique rather than common variance? There is no such concept. You would subtract 36 from 100. It would still be 36%. It would be 64%. 495. John Krumboltz proposes a ________ model of career development. social learning behavioristic trait-and-factor developmental psychoanalytic 496. Krumboltz’s social learning theory is sometimes referred to as a cognitive theory because it emphasizes beliefs that clients have about themselves as well as the world of work. When Krumboltz speaks of self-observation generalizations he really means a. generalizations regarding a given occupation and how successful the client would be in the occupation. Pavlov’s principle of stimulus generalization. Skinner’s principle of operant conditioning. in career counseling your primary concern is the manner in which people view themselves and their ability to perform in an occupation. 497. SCCT stands for social cognitive career theory. social cognitive family therapy. self-control career theory. self-contained career therapy. 498. Career counselors refer to job shadowing and volunteering as ________ activities, while reading the job hunting book What Color Is Your Parachute? is ________. noninteractive; interactive interactive; noninteractive interactive; interactive noninteractive; noninteractive 499. Urie Bronfenbrenner is one of the codevelopers of the National Head Start Program. He proposed a theory of development that is a. essentially the same as Piaget’s constructivism. b. almost identical to Watson’s behaviorism. c. an ecological systems theory. d. based on 12 discrete stages 500. Before ________ child psychologists studied the child, sociologists studied the family, anthropologists studied society, economists analyzed the economic framework, and political scientists investigated the political structure. a. James W. Fowler b. Daniel Levinson c. Urie Bronfenbrenner d. Nancy Chodorow 501. The school psychometrician refers Katie to you for individual counseling. She indicates that Katie’s IQ is at the 50th percentile. Katie’s IQ a. indicates she has an intellectual disability. b. cannot be estimated based on this statistic. c. is approximately 100. d. is well above the norm for children her age. 502. The psychometrician calls you to tell you that she has another student, who has an IQ that falls near the 84th percentile. This student’s IQ a. is somewhere in the gifted range, say 140. b. is most likely near 105. c. is approximately 115. d. is between 75 and 80. 503. An exam has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 20. Phil has a score of 90. His score would fall a. at the 40th percentile. b. at the 5th stanine. c. near the 98th percentile and the 9th stanine. d. in the 6th stanine. 504. Mrs. Kim wanted her daughter to attend a private school for gifted children who have very high intelligence. Mrs. Kim’s daughter took the Otis–Lennon IQ test. Her t-score was 80. Kim’s counselor knew that a. Mrs. Kim would be very upset because her daughter’s low score would not allow her to be admitted. b. Mrs. Kim would be elated because her daughter scored exceptionally high and would be admitted. c. she could not give Kim’s mother any feedback since a t-score tells you nothing about one’s actual IQ score. d. a t-score of 80 is very average. 505. The mean score on a new counseling exam is 65. The standard deviation is 15. Tanja scored a 35. This tells us that a. she had a z-score of +1. b. she had a z-score of -1. c. she had a t-score of 40. d. she had a z-score of -2. 506. Kia was given a new client with a morbid fear of heights. Her supervisor emphasized that he wanted her to use the most high-tech form of treatment available. Kia should use a. VRT. b. William Glasser’s new reality therapy with choice theory. c. Joseph Wolpe’s systematic desensitization (also known as reciprocal inhibition), a form of behavior therapy that works well with fears d. REBT, created by Albert Ellis, which was once called RET. 507. The DSM-5 provides diagnostic criteria for intellectual disability (ID), formerly billed as mental retardation. It states that a. the client must have an IQ score of 70 or below on an individually administered IQ test and the onset of the condition must be prior to age 18. The client’s ability to adapt to normal life in school, work, or family at home must also be impaired. b. the client must have an IQ score below 70 on any group administered IQ test. T c. he client must have an IQ score on an individually administered IQ test and the onset of the condition must be prior to age 21. d. the client must have an IQ score of 70 or below on an individually administered IQ test. 508. Measures of central tendency are used to summarize data. A counseling researcher wants to use a measure of central tendency which reacts to every score in the distribution. He will thus a. use the median, or middle score when the data are ranked from lowest to highest. The median divides the distribution in half since half the scores will fall above the median, while half the scores will fall below the median. b. use the mode, which is the most frequently occurring score or category. c. use the mean, which has been termed the arithmetic average. d. use the median or the mode. 509. Which theorist would most likely assert that EQ is more important than IQ? a. David Wechsler b. Alfred Binet c. Charles Spearman d. Daniel Goleman 510. A counseling agency decides to pay their employees once a week. The agency is using a a. fixed interval (FI) schedule of reinforcement. b. a variable interval (VI) schedule of reinforcement. c. a fixed ratio (FR) schedule of reinforcement. d. a variable ratio (VR) schedule of reinforcement. 511. As a gambling addiction counselor Laura is well aware that slot machines operate on a a. variable ratio schedule of reinforcement. b. variable interval schedule of reinforcement. c. fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement. d. reinforcement system that counselors truly cannot explain. 512. Pick the most accurate statement. a. Behavior therapies based on classical conditioning are used primarily with clients who have bipolar disorder. Lithium is no longer used. b. Behavior therapies based on classical conditioning are much more effective than CBT when treating mood disorders. c. Behavior therapies based on classical conditioning are commonly used to treat phobias, but are also utilized for clients with obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD). d. Behavior therapy is never based on classical conditioning. 513. Ken’s supervisor told Ken to do a meta-analysis related to treating children with sleep disorders. a. Ken can use a correlation coefficient. b. Ken can set up a true experiment with a control group and an experimental group. c. Ken can use a single subject N = 1 intensive design. d. Ken will use statistics based on numerous studies to investigate the issue. 514. You gave your client, Ester, a personality test and then shared your interpretation of the test with her. Your client was amazed at how accurate the test results were in terms of depicting her personality. She readily accepted the interpretation. The next day you discovered that you had interpreted the wrong test! The test you were analyzing was not Ester’s but rather belonged to another client! Ester’s behavior could best be explained by a. the obvious fact that she is psychotic, which means that she is not in touch with reality. b. the Barnum effect. c. negative transference. d. the placebo effect. 515. Approximately 40% of all elementary schools have shortened recess or student playtime. Counselors a. are excited about this change because U.S. children are behind other countries academically and thus need more study time. b. believe the change will actually have little or no impact on the children. c. are concerned because some research indicates that recess can have a positive impact since children are less fidgety on days when they have recess; especially if they are hyperactive. d. are not concerned as boys have better concentration on days when they do not have recess. 516. Neuroscience supports a. the analytic notion that focusing on negative emotions is helpful. b. the medical model, and thus it is not truly relevant to counselors. c. the notion that the concept of neuroplasticity is merely a myth. d. the notion that empathy and exercise could benefit depressed individuals. 517. Neuroscience seems to show that a. cognitive therapy does not impact one’s brain. b. cognitive therapy could raise serotonin, the feel good chemical in the brain, just like antidepressant pharmaceuticals. c. cognitive therapy raises cortisol to an extremely high level. d. cognitive therapy has virtually no impact on the frontal cortex. 518. Which statement best reflects the position of neurogenesis? a. A 76-year-old man signs up for a course in chess and generates more neurons. b. A 9-year-old girl falls off her bicycle and now has a learning disability. c. A 32-year-old man uses temperature/thermal biofeedback to help ward off headaches. d. A 32-year-old man uses EMG biofeedback to help ward off headaches. 519. __________ seemingly is related to serotonin in the brain. Deficits of serotonin are thought to cause depression. a. Vitamin B5, also known as pantothenic b. acid, L-Arginine, an amino acid, c. Tryptophan, an amino acid, d. Omega 3 from sources such as fish oil, krill oil, or algae, 520. At the last count, approximately 43,000 U.S. citizens committed suicide during a single year making suicide the tenth leading cause of death. Worldwide the figure is an alarming 800,000 per year. Suicide often checks in as the second- or third-leading killer of young people in the 15–24-year-old age bracket. Men commit suicide more frequently than women, however, women attempt suicide far more often than men. It is accurate to say that a. 10–15% of all claims handled by the ACA liability insurance programs are related to suicide. b. nearly 100% of the claims handled by the ACA liability insurance programs are related to suicide. c. ACA liability insurance will not cover you if a client commits suicide. d. African American females have an extremely high rate of suicide. 521. Statistically speaking, males typically use ________________ and females use _________ to commit suicide. a. poison; firearms b. heroin; alcohol c. firearms; poison d. heroin; jumping off a building or bridge 522. Neurocounseling research indicates that the _______________ is dominant ___________. a. left hemisphere; in most people b. right hemisphere; in most people c. left hemisphere; in right-handed people d. left hemisphere; in 50% of the population 523. Matt was diagnosed with a somatic symptom disorder (SSD), with predominant pain. It is safe to say that a. Matt is at least 40 years of age. b. Matt has never had a physical exam in regard to his pain. c. no physiological basis or medical condition can be found to explain his reaction. d. Matt’s pain can be carefully traced to a precise physical cause. 524. Millie has a panic attack whenever she drives across a bridge. She has a. situationally bound panic attacks. b. cued panic attacks. c. a and b. d. predisposed panic attacks. 525. Sybil was a famous client who had 15 personalities. At the time Sybil was said to suffer from multiple personality disorder (MPD). Today her diagnosis would be a. dissociative identity disorder. b. a mood disorder. c. related to RS issues. d. a personality disorder. 526. Bulimia is classified as a. an eating disorder which occurs equally in both men and women. b. an eating disorder that occurs primarily in women. c. an anxiety disorder. d. a narcissistic personality disorder. 527. Binge-eating disorder (BED) a. is not a valid DSM diagnosis. b. occurs mainly in men. c. results in vomiting and extreme bouts of exercise. d. is the most common type of eating disorder. 528. A counselor can assume that, in general a. women make less money than men for the same job. b. most complaints against counselors for exploitation come from women complaining about male counselors. c. women are not as comfortable as men when they are involved in competitive situations d. all of the above. 529. Intersexuality a. describes an individual with male and female sexual characteristics and possibly male and female internal or external sex organs. b. describes a person who is always gay. c. describes a person who is always heterosexual. d. describes a person who is a cross-dresser. 530. Gay men and women a. primarily live the gay or lesbian lifestyle. b. basically have the same range of gender-role behaviors as do male and female heterosexuals. c. cannot be characterized in terms of lifestyle due to a distinct lack of research. d. are always transgender. 531. Warren needs to conduct a study. His supervisor wants him to use a parametric inferential statistic. This means that a. he will need to use random sampling and the distribution is normal. b. he will need to use a convenience sample or a volunteer sample. c. his distribution will be positively skewed. d. his distribution will be bimodal. 532. A counselor has an answering machine in her office. Which statement most accurately depicts the ethical guidelines related to this situation? a. Ethical guidelines forbid the use of answering machines. b. Ethical guidelines allow answering machines, but forbid speaking with clients via a cell phone. c. Ethical guidelines allow answering machines, but experts insist that unauthorized staff should not be allowed to listen or retrieve such messages. d. Ethical guidelines are clear that a pager should be used rather than an answering machine. 533. The law requires clinicians to a. keep process notes. b. keep progress notes. c. keep process and progress notes. d. keep the client’s name and address, but no other information. 534. A client wants to read her record. Pick the statement which is not accurate. a. You should allow her to read the record or a summary of it because she has an ethical right to do so. b. You should allow her to read it, however, you should go back and change things you don’t want her to see; for example, the fact that you said she was schizophrenic. c. You should allow her to read the record realizing that it is best if you enter the information as soon as possible after the session and then sign and date the entry. d. Since your agency inputs the client’s record on a computer, each entry will be dated and have a time on it. You could then print the document for her perusal. 535. A counselor is seeing a client on a managed care plan. Unfortunately, the client has used up her maximum number of sessions for the year. The counselor is convinced that the client is in need of additional counseling, however, the counselor’s agency will not allow him to see her for any additional sessions. The best plan of action would be for the counselor to a. refer the client for continued counseling to a practitioner who will see the client whether or not she has managed care benefits. b. empathize with the client, but be sure to explain that she is catastrophizing (an irrational thought pattern delineated by Albert Ellis) and use REBT, a cognitive therapy, to help her cope with the fact that she cannot be seen again until next year. c. threaten to sue the managed care company, since this the company’s policy would be in violation of ethical care for the client. d. see the client, but don’t tell your supervisor. This is both legal and ethical. 536. A career counselor who relies on the constructivist viewpoint would emphasize that a. unconscious conflicts influence career decisions. b. an individual’s career choice is influenced by his or her personal story and attempt to construct meaning out of the world of work. c. most career counselors do not give enough career inventories. d. SCCT is the best theory. 537. A gay male protests that he is unhappy with his sexual preference and wants to lead a heterosexual lifestyle. He tells you that he wants a family and children. You should a. refer him to a psychiatrist as medicine is necessary. b. use dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). c. bring in other members of his family since homosexuality has its roots in the family system. d. explain that homosexuality is not a mental disorder that needs to be changed. 538. Conversion or reparative therapy is intended to change sexual orientation and behaviors from gay to straight. a. The literature in scientific and peer-reviewed journals does not indicate that a person’s sexual orientation can be altered from same-sex attraction to opposite-sex attraction. b. ACA prohibits counselors from practicing conversion or reparative therapies although no studies exist in this area. c. Longitudinal studies with clients who have been through reparative or conversion therapy indicate that the treatment is effective, but it still remains unethical. d. ACA ethics indicate that a counselor trained in conversion or reparative therapy can practice these modalities if the client insists on the treatment. 539. A lesbian client wants to become heterosexual and asks for conversion or reparative therapy. You explain that you ethically do not believe in this form of intervention. She asks you to refer her to a practitioner who will perform this type of therapy. You should a. comply, since ethical counselors provide an appropriate referral. b. comply, but you must provide her with at least three referrals. c. tell the client you prefer not to refer her to a therapist who engages in this form of treatment. Discuss the potential harm and risks with the client emphasizing that this is an unproven form of treatment. d. tell her to secure a consultation with a licensed physician prior to making a referral. 540. The ethical requirement to have a transfer plan in writing would apply to a. a situation in which a counselor became disabled. b. a situation in which a counselor died. c. a situation where a counselor moved to another state. d. all of the above. 541. You are counseling a 29-year-old man in your private practice who is seeing a primary care physician (PCP) for severe headaches. a. You are required to contact the PCP. b. You are not required to contact the PCP; however, attempting to secure permission to do so from your client would be considered the ideal course of action. c. The answer would be no for headaches, but yes if the client had visited the PCP regarding a mental health complaint. d. Yes, but only if the client is abusing a child or a senior citizen. 542. As a private practice counselor your ________ would be most important in terms of filing claims. a. graduate transcript b. undergraduate and graduate transcript c. NCC provider number d. NPI number 543. A counselor is treating a woman for a mood disorder. The counselor has sex with the woman’s daughter. This is considered a. unethical. b. ethical. c. ethical only after the counselor terminates the client’s sessions and then waits two years. d. debatable since ACA guidelines fail to deal with sexual issues of this nature. 544. You have impeccable training and experience as a counseling supervisor. One of your supervisees comes in for her session and she is crying uncontrollably because her boyfriend told her he was breaking up with her. It is clear counseling would be beneficial and she asks you for counseling. You should a. provide appropriate crisis counseling and then assist her in finding an appropriate counselor. b. begin counseling her immediately as she needs it, but refer her to another supervisor. c. assist her in finding an appropriate counselor. d. begin counseling her immediately as she needs it, but make her sign a statement saying there could be issues and if she begins to feel the sessions are exploitative in any way, you will refer her to another colleague. 545. ACA ethical guidelines stipulate that a counselor can refrain from making a diagnosis if the counselor believes the diagnosis could harm the client or others. a. Therefore, a counselor could ethically diagnose all clients as having an adjustment disorder to secure insurance since this diagnosis is somewhat benign and not likely to harm the client. b. A counselor could refrain from making a diagnosis if it is in the best interest of the client. c. A decision to refrain from making a diagnosis is ideally made in collaboration with the client, although the counselor has the final say. d. Choices “b” and “c” are both correct. 546. The agency you work for insists that you diagnose every client. Since this is in violation of the newer ACA ethics this would qualify as “negative conditions.” You could handle this by a. meeting with your supervisor and executive director of the agency and discussing other ways to secure funding that go beyond DSM reimbursement. b. advocate for the client by explaining to the insurance company asking for the diagnosis that in some cases it is best that a diagnosis not be given. You could even teach the client to advocate for herself by having her inform the insurance company that a diagnosis might not be in her best interest. c. show your supervisor, executive director, or insurance company/managed care firm the actual ACA Code of Ethics so they can see it in writing that the Code stipulates that “Counselors may refrain from making and/or reporting a diagnosis if they believe it would cause harm.” d. All of the above. 547. You leave your practice to study mental health treatment in another country. Dr. Kline, another licensed counselor, is now the custodian of your records. This was clearly explained in your informed consent brochure given to the client during the first visit. The clients have Dr. Kline’s contact information. Ethically a. Dr. Kline should contact each client when he receives the record. b. you should contact each client even though you are residing in another country. c. the client is totally responsible for contacting Dr. Kline since he or she was given an informed consent document. d. neither you nor Dr. Kline would be obligated to contact the client. 548. In terms of the previous question: a. A certified public accountant (CPA) would be preferable to a mental health professional such as Dr. Kline to use as a custodian for the records. b. An attorney would make the best custodian for the records. c. Using a mental health professional on staff or at another facility is preferable to using a lawyer or a CPA. d. A CPA, an attorney, or a mental health professional would be an excellent choice. 549. During a counseling session Mrs. Sander’s 13-year-old daughter Jamie tries to speak. Mrs. Sanders says, “I told you not to say anything.” Her daughter wants to know why she cannot talk. Mrs. Sanders replies, “Because I’m the parent, end of discussion young lady.” According to the parenting typology of Diana Baumrind, Mrs. Sanders is a. an authoritative parent. b. an authoritarian parent. c. a permissive parent. d. a nonpunitive parent. 550. A counselor identifies herself as an ABA practitioner. The technique she would be least likely to use would be a. VR reinforcement. b. FR reinforcement. c. asking the client to talk about his dreams as if the dream is occurring in the present. d. Thinning. 551. A counselor is working with a client suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Which counselor would be most concerned about inducing REM/EM during the sessions? a. A counselor who is performing systematic desensitization as set forth by Joseph Wolpe. b. A counselor who is using Francine Shapiro’s EMDR. c. A counselor who is using existential strategies popularized by Irvin Yalom. d. A counselor who relies on brief strategic therapy (BST). 552. A counselor is using the memory device: IS PATH WARM? He is most likely working with a. a client with bipolar disorder. b. a client with test anxiety. c. a client diagnosed on the autism spectrum disorder. d. a client whom he feels could be suicidal. 553. Child-centered play therapy (CCPT) is experiencing rapid growth in popularity and spawning research. This modality was created by a. Virginia Mae Axline, an associate of Carl R. Rogers who penned Dibs In Search of Self. b. Carl R. Rogers, who created client-centered/person-centered counseling. c. Gerard Egan, author of the well-known text, the Skilled Helper. d. Anna Freud, daughter of Sigmund Freud. 554. In a children’s career counseling group, the group will help the children a. have a sense of belonging. b. share feelings and ideas. c. engage in desirable peer interaction. d. in all the ways listed above. 555. In terms of adolescents and career group counseling a. the literature indicates such groups just don’t work. b. such groups are cost effective and promote peer identification. c. textbook authors such as Dr. Samuel T. Gladding insist that adolescents can only be assisted in individual sessions. d. it may be true that such groups work, but they do not help adolescents with other aspects of their lives. 556. The concept of universality (also called mutuality) applies to group treatment. In career groups we can safely say a. the group allows the members to see that others can be struggling with similar issues related to work, vocation, and career. b. these terms are rarely, if ever, utilized. c. other members of the group are in similar situations. d. choices a and c are both correct. 557. If you compare group career counseling to noncounselor interventions a. you will discover that group career counseling is more effective. b. you should know this is not a valid question. Because there is no counselor in noncounselor interventions, career counseling cannot take place! The question defies common sense. c. you will find out that no studies exist in this area. d. you will find that they are equal in terms of helping persons who are wrestling with career and vocational issues. 558. When you conduct group career counseling a. unstructured groups work best. b. structured groups work best. c. gestalt groups work best. d. the group must be based on the concepts set forth by motivational interviewing. 559. Special career counseling groups can be set up. Some examples include a group with displaced homemakers or persons receiving public assistance. Groups of this nature a. are discriminatory and are not recommended. b. have been used, but are rarely desirable. c. can be very helpful. d. are never a good choice if individual sessions are available. 560. Group career counseling a. is an international phenomenon. It is used in China with college students. b. is not used in any other country except the U.S. We are clearly the world leader in this area. c. is more expensive to conduct than providing individual sessions. d. is rarely used in the U.S. for college students; however, it is used with K-12 students. 561. The main purpose of a career group is a. to promote insight. b. to provide catharsis related to job and career issues. c. to release pent up emotions related to frustrations surrounding work-related issues. d. to provide information to participants. 562. According to expert John Krumboltz a. career groups with a psychodynamic slant are the most effective. b. group career counseling is important, but will not have an impact on your happiness. c. career decision issues are crucial in terms of one’s happiness. d. career groups should focus primarily on developmental issues. 563. An advantage of group career counseling over individual career counseling is a. other clients in the group can help you to rev up your motivation. b. you get to help other clients and they get to help you. c. participants can role-play situations such as how to answer questions during a job interview. d. All of the above statements are correct. 564. Richard Nelson Bolles penned the bestselling job hunting manual in history titled What Color Is Your Parachute? The book, updated yearly, has sold over 10 million copies and is published in over 20 languages. a. Bolles champions the idea of securing a network of persons who can help you with your job search. b. Bolles likes groups if the group uses the trait-and-factor theory. c. Bolles likes groups if the group uses Donald Super’s theory. d. Bolles likes groups if the group uses the concepts set forth by Nathan Azrin. 565. Nathan Azrin studied with B. F. Skinner. His job club groups are based on a. REBT. b. narrative therapy. c. behaviorism based somewhat on positive reinforcement. d. DBT. 566. Career groups are often considered a theme group. The best intervention in a structured career group would be a. promoting psychodynamic insight. b. paraphrasing as often as possible. c. using activities such as a game. d. changing the client’s internal verbalizations as stressed by REBT, the model created by Albert Ellis. 567. You create a career group to examine the clients’ roles in life as a child, student, citizen, homemaker/parent, worker, citizen, and time spend participating in leisure activities (leisurite). You should use the a. MBTI based on the work of psychiatrist Carl Jung. b. Nathan Azrin’s job club model, based on behaviorism. c. John Holland’s SDS or so-called Self-Directed Search. d. Donald Super’s life career rainbow. 568. According to the fetal origins hypothesis, adult heart disease, some emotional disorders, and type 2 diabetes could be related to a. lack of stimulation (i.e., nurture) during the first year of life. b. nature. c. in utero malnutrition d. undiscovered factors related to the human genome. 569. According to the human growth and development notion of plasticity every client you see a. can alter his or her traits at any point in the life span. b. has his or her behavior governed by critical periods. c. must be aware of the fact that change is not an ongoing process. d. must be aware that most processes of change are merely random. 570. Two 18-year-olds are given the exact same dosage of an antidepressant medication. One indicates that the medicine makes her feel “great” while the other insists the intervention makes her “very tired.” This can most likely be attributed to a. differential sensitivity. b. the fact that medical practitioners, including psychiatrists, overmedicate and should use smaller doses of antidepressants. c. the fact that both clients are impacted by the placebo effect. d. the fact that antidepressants are intended to make clients extremely tired, but do help with mood disorders. 571. You are conducting a program evaluation (PE) for your 501(c)(3) nonprofit counseling agency. You should begin by a. getting the support of the staff, administration, and clients. b. writing a grant to fund the study. c. asking United Way for help. d. taking the steps in choices b and c. 572. Program evaluation (PE) helps agencies, organizations, and centers make wiser decisions. PE takes place in a natural, rather than a laboratory or controlled, setting and helps _________ answer questions posed via __________. a. researchers; staff b. programs; researchers c. programs; staff d. staff; researchers 573. A cost–benefit analysis (CBA) answers the question: a. Should the counseling organization become a private practice or a 501(c)(3) nonprofit? b. Should a counseling center opt to do brief strategic therapy? c. Was the money wisely spent or does the counseling center need a new program? d. Which clients should receive pro bono services? 574. You are the owner of a counseling practice. You make the sole decision which counselor receives the new referrals. According to new ACA ethics on fee splitting a. you can charge counselors 50% of the agency counseling fee for office space. b. you can charge counselors one third of the agency counseling fee for office space, but it must never exceed one third. c. fee splitting is totally ethical and the director could set the fee split at any cost he or she feels is appropriate. d. although many counselors believe this is controversial, it is unethical based on the fact that charging a percentage of the payment rate per client appears to be a kickback scheme similar to accepting a referral fee. 575. You are supervising a counselor-in-training and focusing on the OARS core skills. You are teaching her how to perform a. psychodynamic group therapy. b. gestalt therapy created by Fritz Perls. c. motivational interviewing (MI) created mainly by William Miller and Stephen Rollnick. d. career counseling using directive techniques. 576. The order of the four processes that MI uses is a. engaging, focusing, evoking, and planning. b. engaging, evoking, focusing, and planning. c. evoking, focusing, engaging, and planning. d. planning, engaging, focusing, and evoking. 577. According to existential therapist Irvin D. Yalom a. most therapists do a superb job of interacting with clients who bring up the topic of death. b. most therapists are afraid of their own mortality and avoid the topic of death. c. discussing dreams related to death is not very therapeutic. d. helping the client put death out of one’s mind aids the client’s growth. 578. Pick the most accurate statement regarding patients diagnosed with cancer. a. Since January 1, 2015 there is official recognition that a diagnosis of cancer will affect a patient’s mental health. b. Physicians are required by law to give all cancer patients a referral for counseling or psychotherapy. c. Paradoxically, although a diagnosis of cancer is often very serious there is virtually no evidence that cancer patients have any more mental health issues than prior to the diagnosis. d. Counselors have always been the primary workers in the medical system when compared to social workers and psychologists and thus traditionally have counseled most patients diagnosed with cancer. 579. Transgender individuals have an attempted suicide rate which is approximately 25 times higher than the rate for the general population. A high percentage of transgender youth experience oppression and are physically assaulted. A transgender does not identify with the gender they were given at birth or the person’s expression differs from societal expectations. What is cisgender? a. All females. b. All males. c. The same as genderfluid. d. A person who identifies with the gender they were assigned at birth and hence by definition this person is not a transgender individual. 580. A correlation/association between variables x and y is .50. According to the notion of effect size (ES) a. the correlation is medium. b. the correlation is small. c. the correlation is large. d. the correlation would not be applicable to this statistic. 581. You conduct a true experiment. The results between the several groups are statistically significant. You have rejected the null hypothesis. a. You should still provide an effect size (ES) statistic. b. You would not need to provide the effect size (ES) since the data indicate there is a statistical significance. c. You would not need to provide the effect size (ES) since the ES only applies to correlations and this is a true experiment. d. You could provide the effect size (ES), but since it is a true experiment this information could be very misleading. 582. A major meta-analysis (a term coined by researcher Gene V. Glass) of 375 outcome studies using effect size (ES) by Mary Lee Smith, Gene V. Glass, and Thomas I. Miller revealed that a. psychotherapy is approximately as effective as antidepressants, about .31. b. psychotherapy is less effective than antidepressants, about .22. c. psychotherapy was too hard to define to come up with an ES statistic. d. psychotherapy had a strong or so-called big effect, checking in at a .85. 583. According to the DSM-5 a. pathological gambling is not a disorder. b. pathological gambling is a disorder and is listed with Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders just like trichotillomania (now called hair pulling). c. pathological gambling is a disorder and is listed with Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders. d. pathological gambling is a conduct disorder. 584. All of the statements below are true about bullying except: a. More girls are bullied than boys. b. More whites are bullied than minorities. c. Fewer students claim they are being bullied in recent years. d. More students are harassed in the hallways than on social media. 585. Wilderness therapy falls under the auspices of adventure-based therapy. There is no one set model for wilderness therapy. All of the statements below are true about wilderness therapy except: a. Effective wilderness therapy occurs when a boot camp model is used in the wilderness. b. Most counselors believe stricter regulations should be put in place to avoid abuses. c. Effective wilderness therapy settings use little or no force, confrontation, or point level systems. d. Reports of abuse and even death of youth have surfaced. 586. The 1974 Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) could be called the Buckley Amendment on your exam since Senator James K. Buckley was a strong supporter. All of these facts are true regarding FERPA except: a. Parents have access to a minor child’s educational records. Children over age 18 can view their own records. b. A parent is able to have the educational record amended. c. A counselor working in a private educational institution which does not receive federal funding would still be required to follow FERPA guidelines. d. In situations involving imminent danger, a counselor could release information to protect the client, others, or ward off harm. 587. Mr. Donald is seeing you for a gambling addiction problem. Several years ago he won a huge amount of money at the casino from a slot machine. As soon as he pulled the handle he snapped his fingers. Now he always snaps his fingers after he pulls a slot machine handle. His superstition can best be explained by a. accidental reinforcement. b. contingent reinforcement. c. shaping with successive approximations. d. the fact that he has savant tendencies. 588. Pick the incorrect statement. a. Men commit suicide more than women. b. Women suffer from depression more than men. c. Alcoholism occurs more in women than men. d. Autism occurs more in men than women. 589. You are supervising a graduate student. The client she is discussing was raped and robbed several days prior to your session with this student. When you ask your supervisee for more information she says, “Well, I’m certain the fact that she was carrying a very expensive handbag and wearing tight clothes was an issue.” Based on gestalt psychologist Fritz Heider’s concept of attribution theory a. your supervisee is relying on situational attributions. b. your supervisee is relying on dispositional attributions. c. paradoxically, the expensive handbag and tight clothes would ward off crime. d. the tight clothes were an issue, but not the expensive handbag. 590. Based on the information in the previous question, the best example of a fundamental attribution error (also called a fundamental attribution bias) would be: a. The graduate student blames the woman for carrying an expensive handbag and wearing tight clothes. b. The graduate student blames the man who committed the rape and the robbery. c. The graduate student blames the police force for not patrolling the area better. d. The graduate student becomes so emotional, she cannot discuss the incident with you as her supervisor. 591. According to attribution theory and the self-serving bias, if you pass your exam _________ and if you fail your exam ___________. a. it is because of external issues; it is because of internal issues b. it is because of situational issues; it is because of dispositional issues c. it is because of dispositional issues; it is because of situational issues d. you lucked out; the authors of the exam chose poor exam questions 592. You are performing career counseling with a client. This client is extremely depressed. The client goes on a job interview and doesn’t get the job. Based on research related to attribution theory a. in most instances this client will begin having suicidal ideation within 24 hours. b. the client’s view of reality will be swayed due to his depression and thus he will insist that the interviewer was a total jerk. c. he will blame himself for his poor performance during the interview. d. he will make a joke out of the fact that he did not get the job. 593. A counselor is using telephone coaching with a client. The counselor is most likely to base her treatment on a. William Glasser’s reality therapy with choice theory. b. REBT as set forth by Albert Ellis. c. DBT as set forth by Marsha M. Linehan. d. systematic desensitization. 594. A counselor is utilizing a thought log—also known as a thought record—with an anxious client. She is practicing a. psychodynamic therapy. b. career counseling based on the work of Donald Super. c. cognitive behavior therapy (CBT). d. the transtheoretical model which draws from all of the available theories to help the client change. 595. You are conducting a session using CBT; however, you are incorporating mindfulness as well as ACT into the session. Strictly speaking you are a. performing second wave CBT. b. third wave CBT. c. first wave CBT. d. operant conditioning. 596. A counselor is performing CBT. He believes his client is not dealing with the real or core issue causing the difficulty. The most effective ploy would be to a. change his approach to narrative therapy. b. give the client a projective personality test. c. use the downward arrow technique, created by David D. Burns, M.D. d. prescribe rational imagery (RI), often advocated by Albert Ellis. 597. Classical conditioning is based on paired learning, whereas operant conditioning is predicated on rewards or punishment. In a classical conditioning experiment a dog was trained to salivate to a bell which was originally presented about 0.5 second before the meat. The bell is a. a CS or conditioned stimulus. b. an NS or neutral stimulus. c. a UR or unconditioned response. d. a CR or conditioned response. 598. Your supervisor insists you rely on a teleological approach with a client. Pick the correct statement. a. You would simply talk to the client about her childhood. b. You would prescribe a homework assignment related to her childhood. c. You would focus exclusively on the here and now. d. You would focus on the client’s goal to become a stock broker in four years when she finishes her business degree. 599. A short answer test is a(n) ________ test. a. Objective b. culture-free c. forced choice d. free choice [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 86 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 21, 2022
Number of pages
86
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 21, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
261










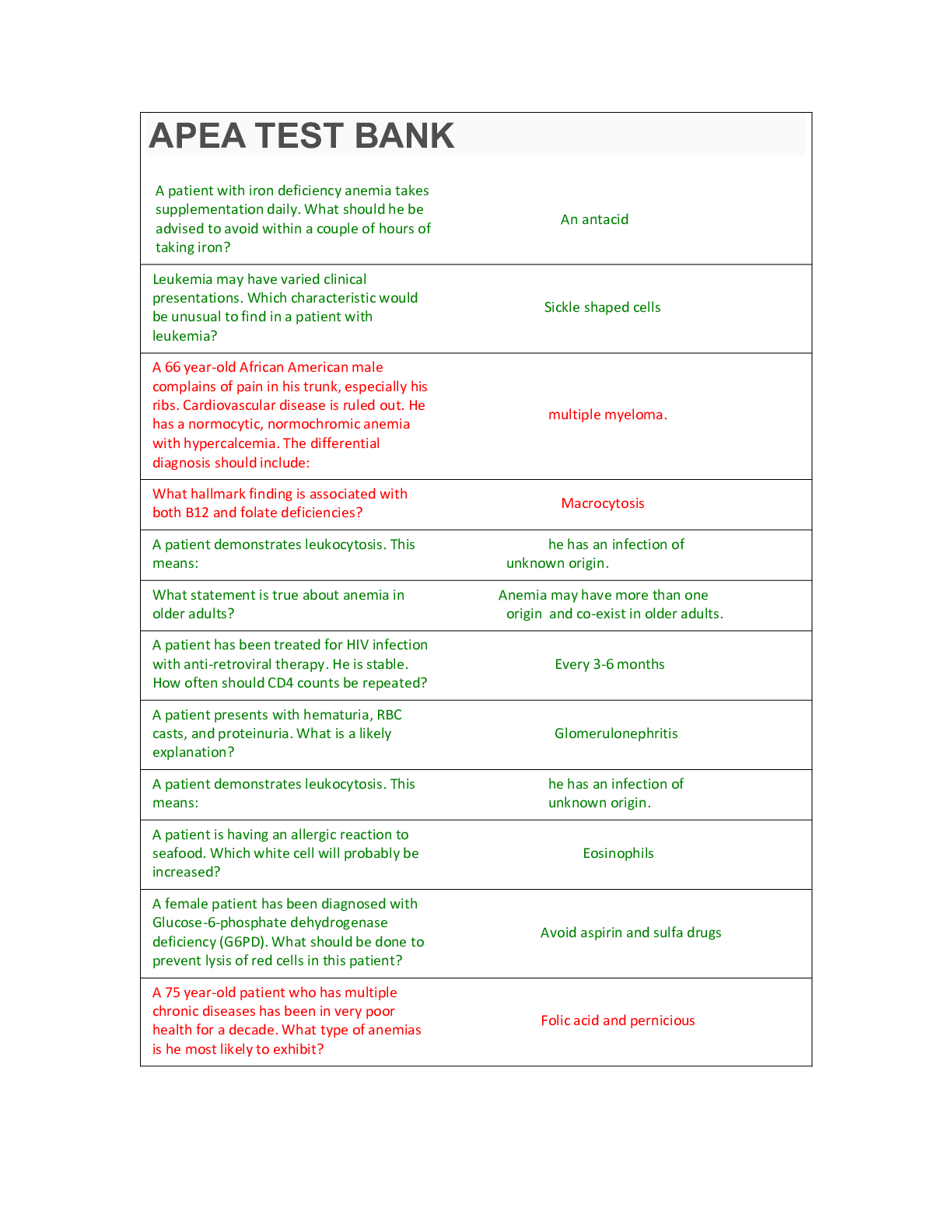


.png)





.png)
.png)

