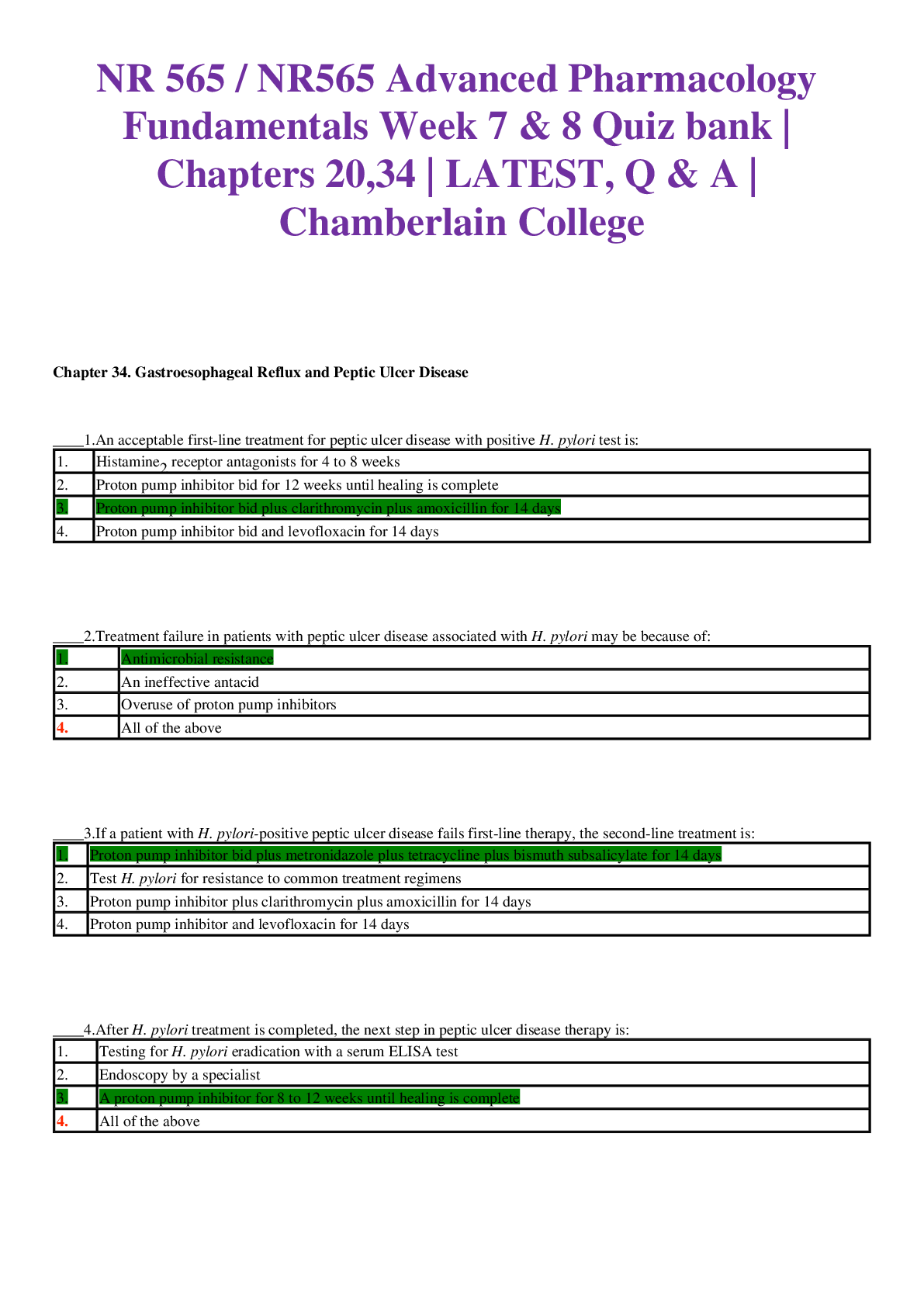
*NURSING > EXAM > NR 565 / NR565 Advanced Pharmacology Fundamentals Week 5 Study Guide | Chapters 26 and 47 | 20202/20 (All)
NR 565 / NR565 Advanced Pharmacology Fundamentals Week 5 Study Guide | Chapters 26 and 47 | 20202/2021| Complete Guide |Chamberlain College
Document Content and Description Below
NR 565 / NR565 Advanced Pharmacology Fundamentals Week 5 Study Guide | Chapters 26 and 47 | 20202/2021| Complete Guide |Chamberlain College Chapter 26: Drugs used in treating eye & ear disorders ... Contraindications for topical beta blockers Beta blockers • Suppress conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node; therefore, topical beta blockers are contraindicated in patients with bradycardia or advanced AV block. • Do not use in patients with compromised ventricular dysfunction, cardiogenic shock, or with systolic congestive HF • D/c at first sign of cardiac failure • Contraindicated with hypotension • Use with caution: poorly controlled DM and hyperthyroidism • Surgical patients should be monitored closely for cardiac failure o Withdraw before surgery 2 days prior • Contraindicated with Raynaud’s disease or PVD, CVD • Preg cat C: fetal anomalies and fetotoxicity in animal studies Prophylaxis for opthalmia neonatorum • Common patient group: infants younger than 1 month who presents with conjunctivitis should have Gram's stain, antigen detection tests, and cultures of the eye discharge to rule out gonococcal, chlamydial, or HSV origin. • Chlamydia is the most common cause of neonatal conjunctivitis • Gonococcal conjunctivitis is the most serious cause of ophthalmia neonatorum owing to concerns about the bacteria causing blindness • Prophylaxis: Administration of antibiotic eye medication within 1 hour of delivery • Erythromycin ointment 0.5% (0.25 to 0.5-inch ribbon in each eye) • Chlamydial conjunctivitis is not prevented by prophylactic use of erythromycin at birth therefore any mucopurulent eye discharge in the first few weeks of life should be evaluated for chlamydia. Glaucoma: Treatment, dosing, and patient education: • IOP damages the optic nerve • Leading cause of blindness worldwide • 6-8 times more likely in African Americans than Caucations • Antiglaucoma medications are prescribed by ophthalmologists. Dosage is determined by the clinical condition of the patient. Treatment and dosing • Current medical therapies are aimed at o decreasing the production of aqueous humor at the ciliary body and o Increasing the outflow of this fluid from the angle structures • Requires evaluation and treatment by an ophthalmologist o FNPs need to be aware of the medications prescribed, drug interactions, and ADRs • Antiglaucoma agents are prescribed by ophthalmologists and dosage is determined by the clinical condition of the patient • Four categories: Beta Blockers, adrenergic agonists, miotics, and carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitors o Beta Blockers: Betaxolol, carteolol, metipranolol, levobunolol, timolol o Adrenergic Agonists Apraclonidine, brimonidine o Miotics Carbachol, pilocarpine, echothiophate o Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Acetazoleamide, brinzolamide, dorzolamide, methazolamide Patient education • The patient should be instructed to administer the medication exactly as the ophthalmologist has prescribed • Abruptly stopping the medication can increase adverse effects. • The patient should have been instructed by the ophthalmologist regarding the adverse effects of the medication. o Reinforcement may be necessary. If the patient is experiencing adverse effects from the medication, the primary care provider can facilitate a referral back to the ophthalmologist. Allergic or Vernal conjunctivitis: Treatment, dosing, and patient education • Occurs in response to a variety of allergens • Vernal conjunctivitis refers to conjunctivitis that occurs primarily in the spring, usually because of an allergen. • The mast cell stabilizers (lodoxamide, cromolyn sodium) may be used to treat vernal conjunctivitis and may be used safely for up to 3 months. Treatment and Dosing • Ketotifen (H1 blocker) for allergic conjunctivitis and ocular pruritus. o The dose used in adults and children over age 3 is 1 drop in the affected eye every 8 to 12 hours • Levocabastine (H1 blocker): allergic conjunctivitis and ocular pruritis o 1 drop in the affected eye 4 times a day. • Mast Cell Stabilizers: o Cromolyn sodium (1-2 gtt, 4-6 times/day) [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 23, 2020
Number of pages
20
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 23, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
175