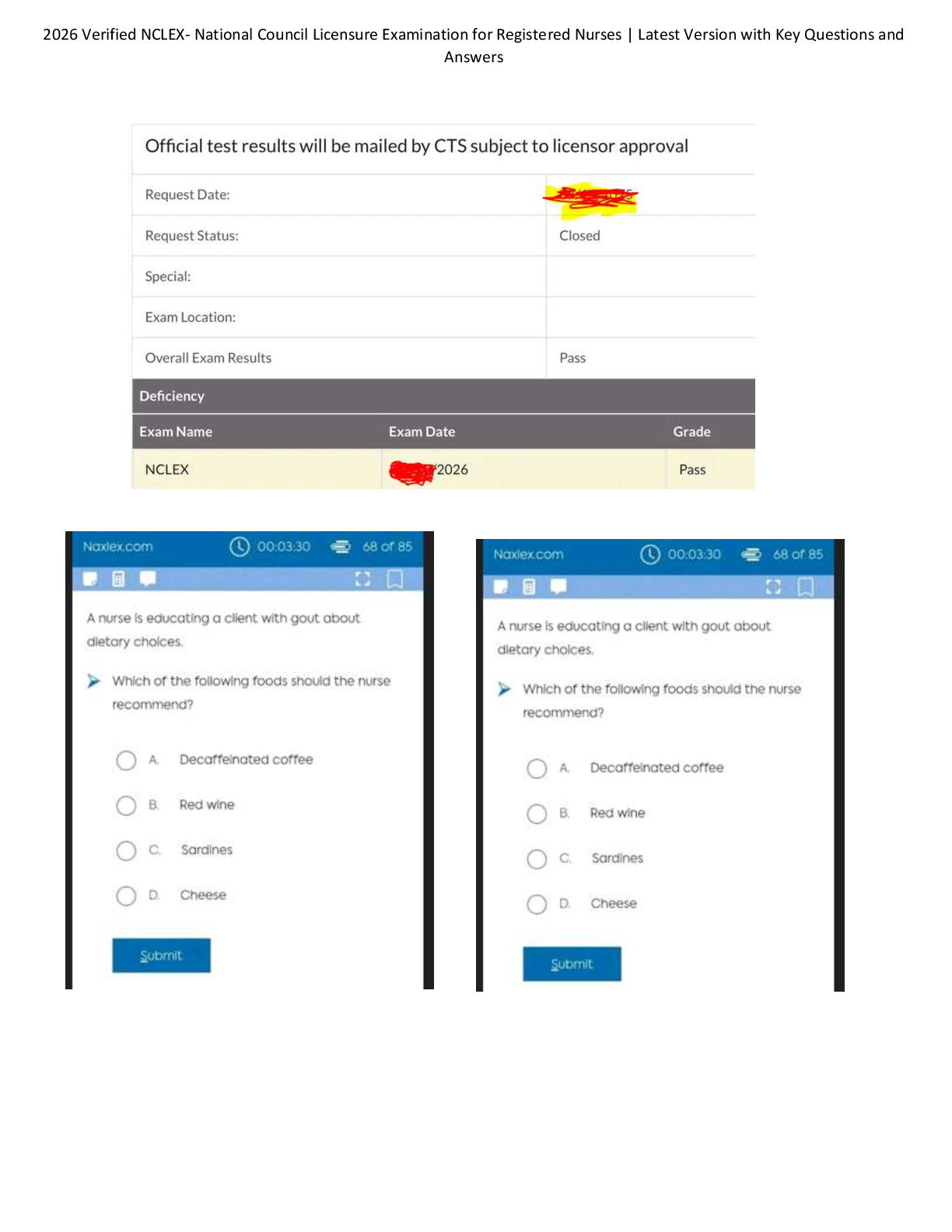
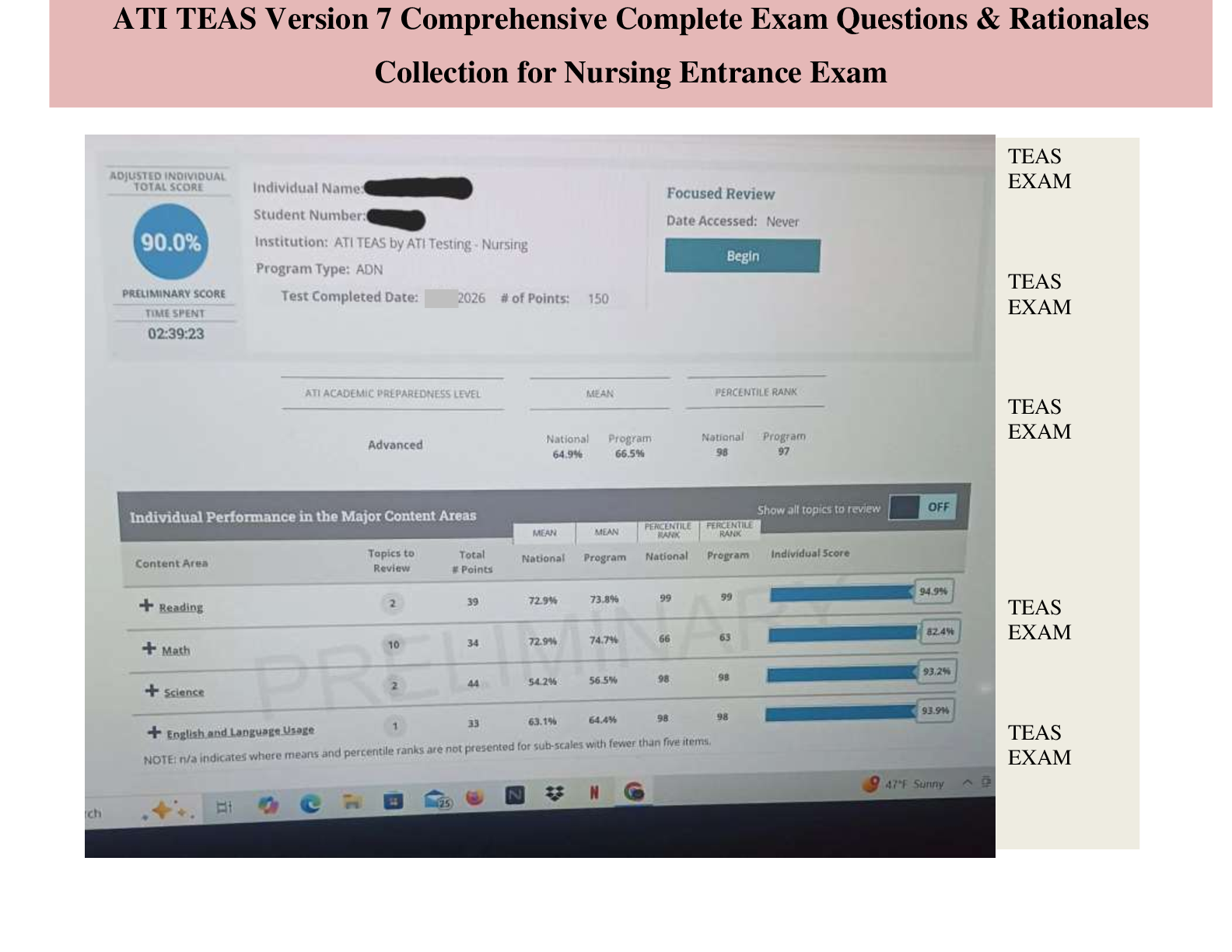
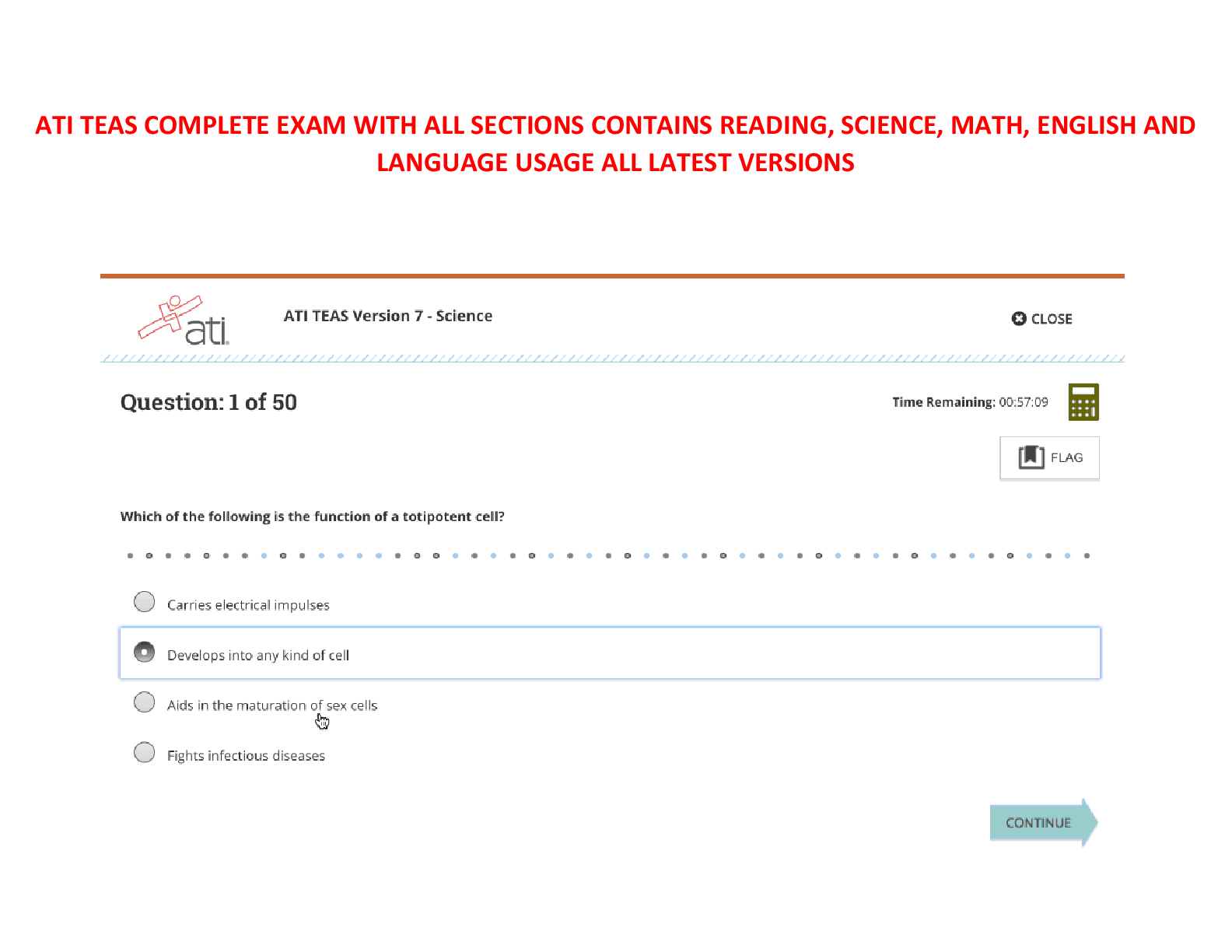
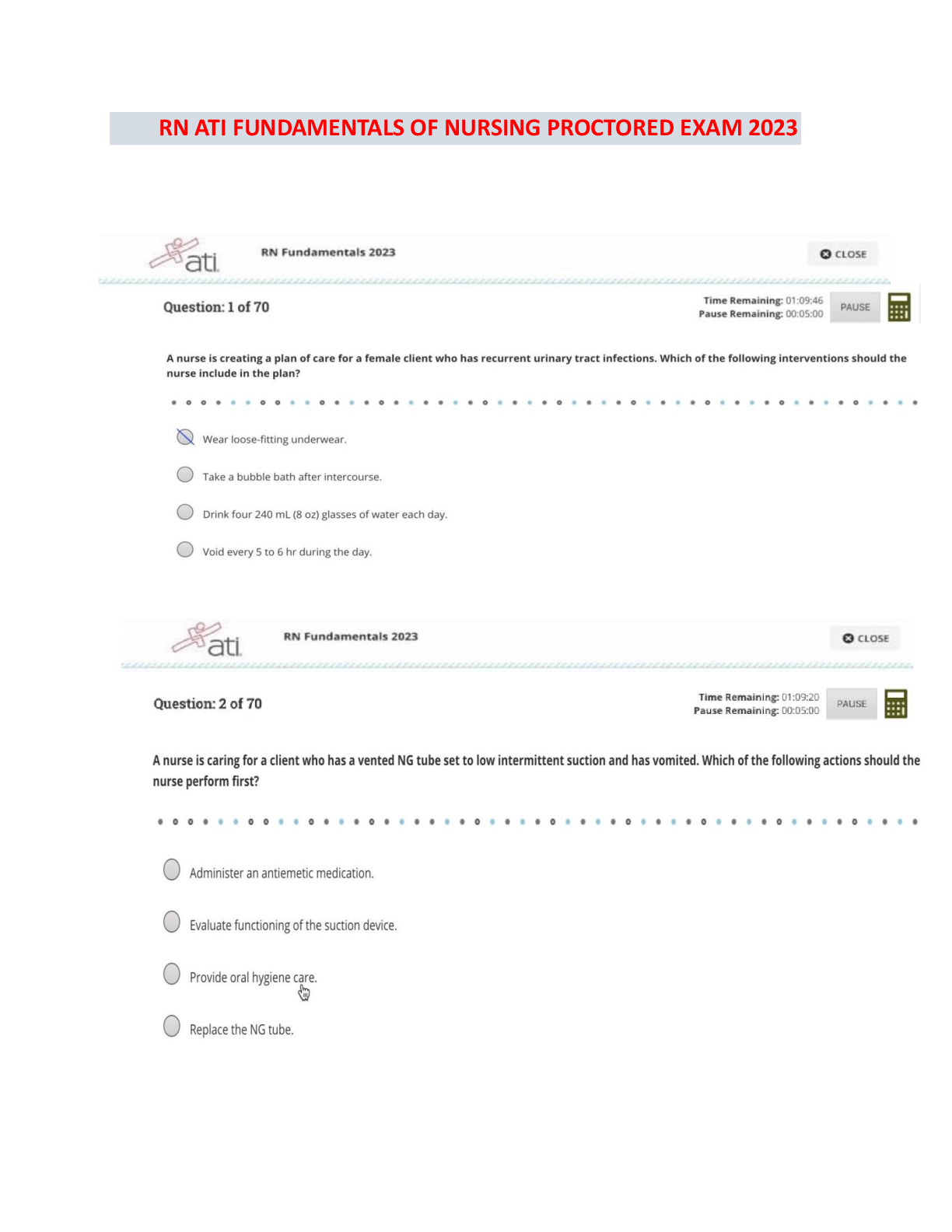
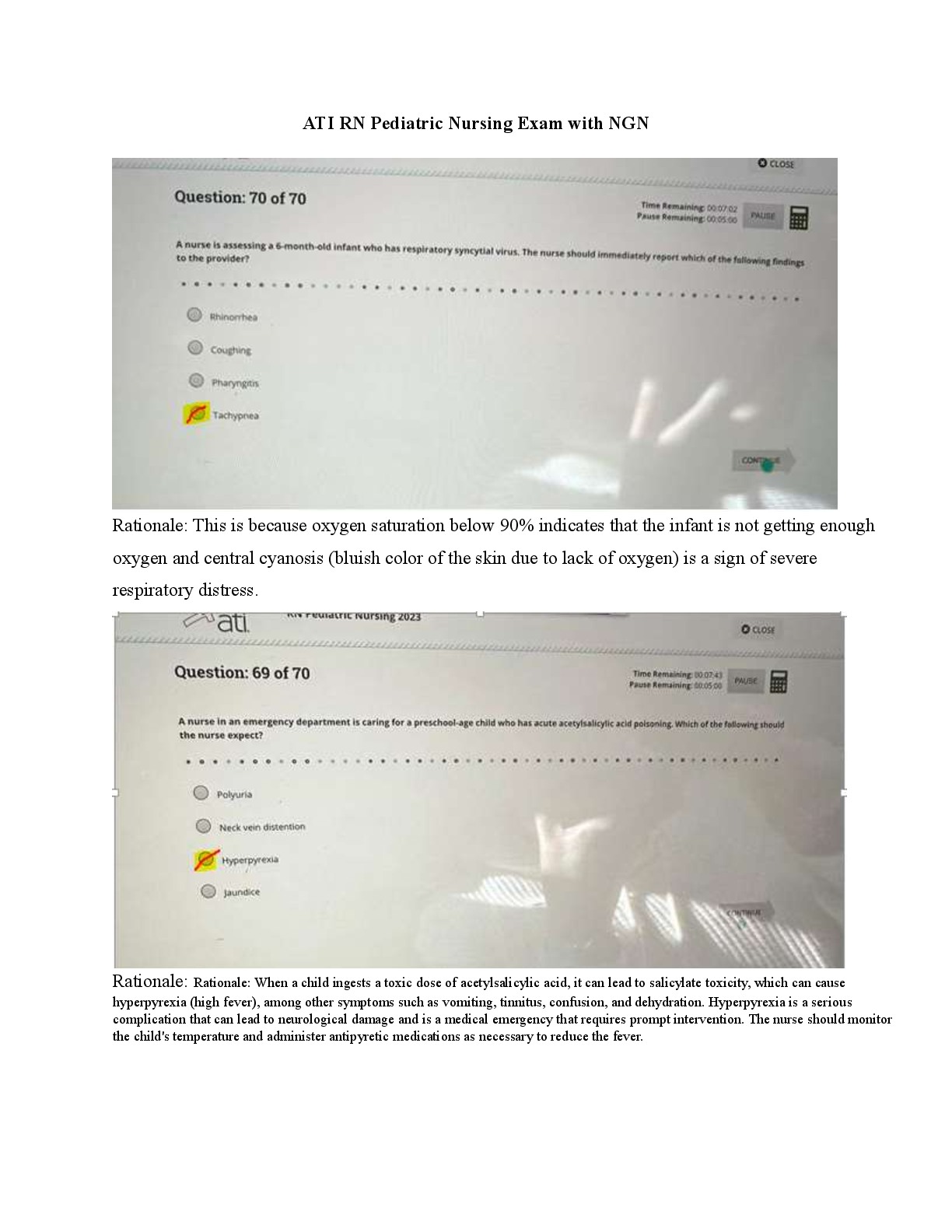
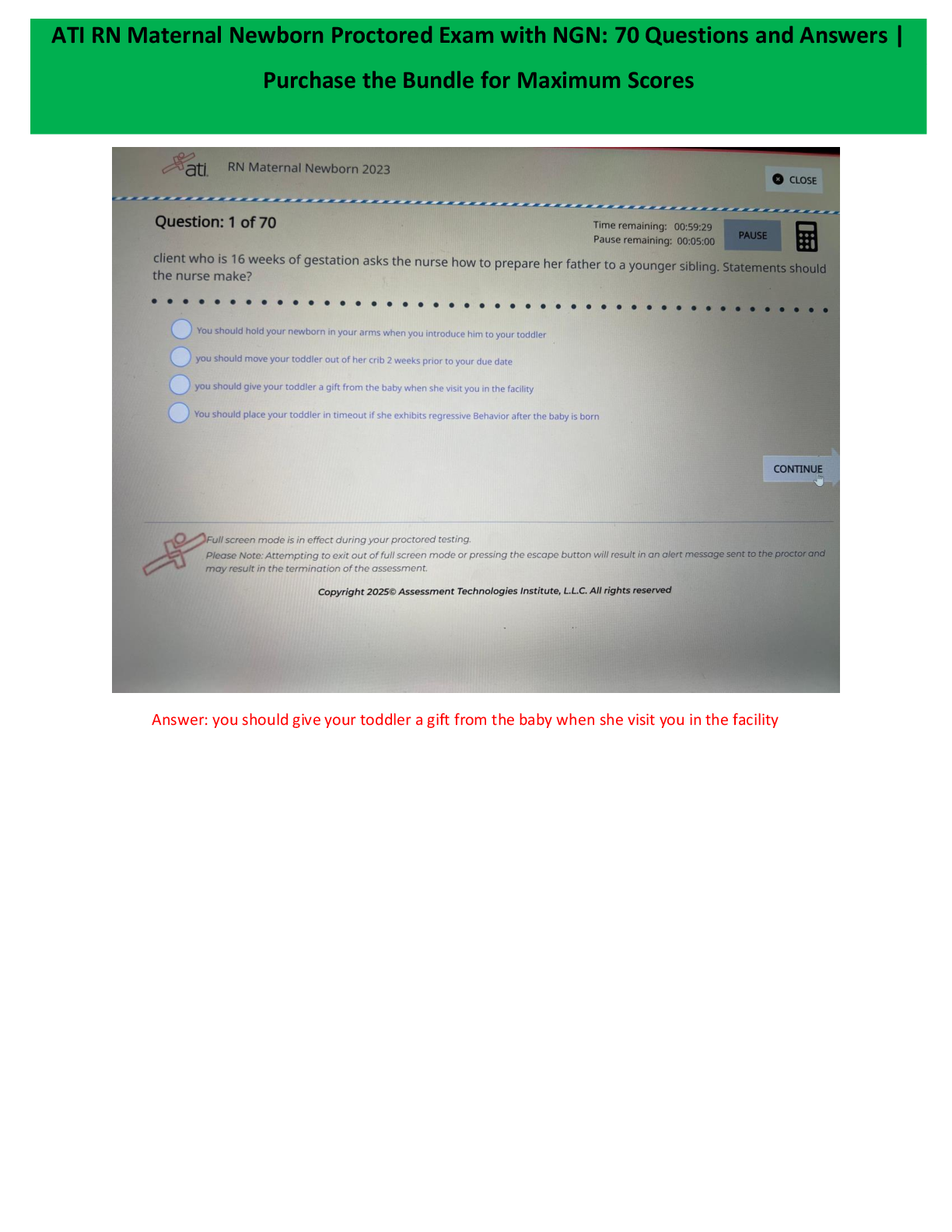
Questions and Answers > GIZMOS: CHEM 8689. Student Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular Forces. Pass rate 96%.
$ 8

Test Bank For Society The Basics 15th Edition (Global Edition) By John Macionis
$ 20

CRM IBHRE|QUESTION AND ANSWERS| GUARANTEED TO PASS CONCEPTS
$ 3

COS4861 104/0/2020 Natural Language Processing Year module
$ 5

WESTCHESTER COMMUNITY COLLEGE>HISTORY>Primary Professional Military Education (Enlisted) Block 1 to 7 / PPME Block 1-7 (test-bank) updated
$ 16.5

FF2 Final Exam Study Guide IFSTA Questions And Answers( Complete top Solution Rated A
$ 10.5
.png)
BioChem C785 - WGU - Module 2 - all questions graded A
$ 9

Test Bank - Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing
$ 65

C724 (Information Systems Management) - WGU Complete Solution Guide.
$ 19

eBook Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 4th Edition By Berk, DeMarz, Harford
$ 25

Specimen mark scheme 2 set 2 Bio.pdf
$ 9.5

Understanding Research Findings Test Bank Q&A Graded A+
$ 12

NR 509 Week 6 Retired Test Quiz
$ 10

NR599: Mid Term Study Set_2020, NR599: Final Exam Study Set_June 2020
$ 12

ACT/SAT Prep Final Exam Review
$ 10.5

ATI PN COMPREHENSIVE 2020 PROCTORED
$ 10
.png)
AQA A-level HISTORY 7042/2S Component 2S The Making of Modern Britain, 1951-2007 Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 10

WGU c170 PROJECT WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 8

RVE 5306 Questions and Answers Graded A
$ 8

EDCO 735 / EDCO735 QUIZ 2
$ 10

Yanique- 4.4 Practise Questions S SCIENCE 2022 ( 100% VERIFIED CORRECT ANSWERS)
$ 5

AQA A-level CHEMISTRY Paper 1 Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Ms 2021
$ 9.5

SBB 5261 Exam 3 Questions and Answers Rated A+
$ 8

IELTS MOST UP TO DATE EXAMS 2023