HR Chapter 4 Diversity in the workforce LATEST 2022/2023.
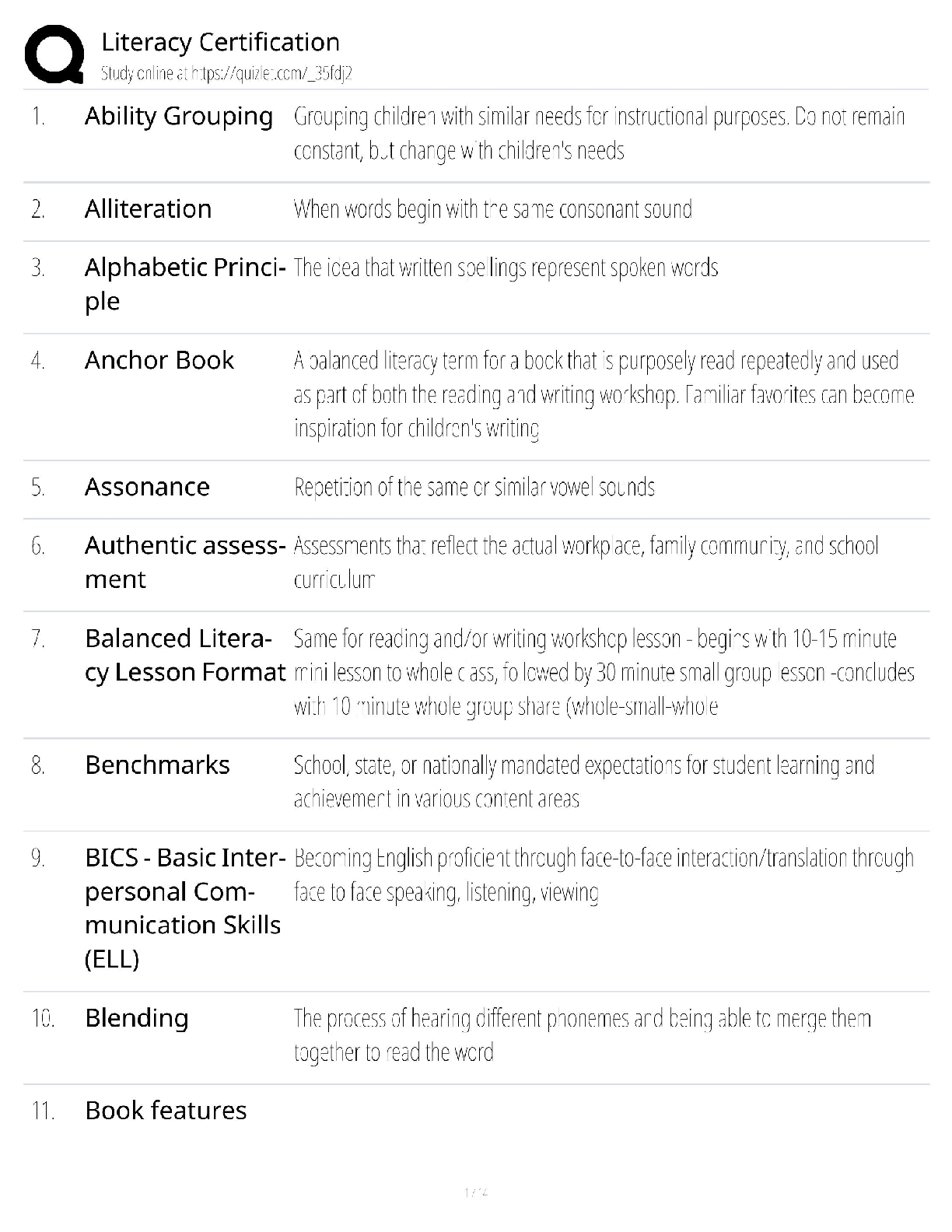
Document Content and Description Below
9 categories protected under federal law - ☑☑age
disability
genetic information
national origin
pregnancy
race and color
religion and sex
Employment discrimination laws and regulations are
...
enforced by - ☑☑The Equal Employment
Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) - ☑☑An agency established by the Civil Rights Act
of 1964 (Title VII)
The agency's mission is to stop and remedy unlawful employment discrimination.
Specifically, the EEOC is charged with "enforcing protections against employment discrimination on the
bases of race, color, national origin, religion, and sex."
Congress has expanded the agency's jurisdiction over the years and the EEOC is now responsible for
enforcing the
- _____________________
-______________________
-______________________
-______________________-______________________ - ☑☑- Equal Pay Act of 1963 (APA)
- The Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (ADEA)
- Section 501 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973
- Titles I and V of the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA)
- Title II of the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008 (GINA)
In 1972, Congress expanded Title VII protections to include federal government employees and granted
the EEOC authority to - ☑☑Pursue independent litigation against private employers under Title VI
(Note that state and local laws may provide broader discrimination protections. If in doubt, contact your
state department of labor for clarification)
You are preparing a briefing on discrimination law for new managers and supervisors. You want to start
with a big picture view. Which of the following would best serve that purpose? - ☑☑Discrimination
protections legislation is applicable to all employment decisions
Civil Rights Act of 1964 - ☑☑Ended segregation in public places and banned employment discrimination
on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin
- One of the crowning legislative achievements of the civil rights movement
Title VII makes it unlawful... - ☑☑To discriminate against any employee or applicant for employment
because of race or color in regard to hiring, termination, promotion, compensation, job training, or any
other term, condition, or privilege of employment.
Title VII is applicable to..... - ☑☑Private sector employers with fifteen or more employees, federal
government employers, employment agencies, and labor organizations.An employer is permitted to take employment actions that would otherwise be held as discriminatory if
the decision is based on a _____________________ - ☑☑bona fide occupational qualification (BFOQ)
Civil Rights Act of 1991 - ☑☑Amended the original civil rights act, making it easier to bring
discrimination lawsuits while also limiting punitive damages that can be awarded in those lawsuits
- Re-established an employers burden of proof and the disparate impact theory of discrimination
The Act also extended employment discrimination protection to employees of Congress and Title VII and
ADA coverage to include American and American-controlled employers operating abroad
You are preparing a briefing on discrimination law for new managers and supervisors. Your specific focus
is Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Which of the following is best summarizes the protections in
the original Act? - ☑☑Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits discrimination based on race,
color, religion, sex, and national origin
Which of the following best summarizes the protections provided in the 1991 version of the Civil Rights
Act? - ☑☑The Civil Rights Act of 1991 established the ability to file suit and receive compensatory and
punitive damage awards in intentional discrimination cases
The Equal Pay Act (APA) of 1963 makes it illegal to - ☑☑Pay different wages to men and women if they
perform equal work in the same workplace
*The law also makes it illegal to retaliate against a person because the person complained about
discrimination, filed a charge of discrimination, or participated in an employment discrimination
investigation or lawsuit.*
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) of 1976 - ☑☑Protects applicants and employees 40
years or older from discrimination because of age and for retaliation for a discrimination complaint or
related action- It is generally unlawful to to state an age-related preference in job advertisements except when age is
demonstrated to be a BFOQ
Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 - ☑☑The Act makes it illegal to discriminate against a woman
because of pregnancy, childbirth, or a medical condition related to pregnancy or childbirth
Treats discrimination based on pregnancy-related conditions as illegal sex discrimination
- The law also makes it illegal to retaliate against a person because the person complained about
discrimination, filed a charge of discrimination, or participated in an employment discrimination
investigation or lawsuit.
Title I of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 - ☑☑Title I makes it illegal to discriminate
against a qualified person with a disability in the private sector and in state and local governments.
The law also makes it illegal to retaliate against a person because the person complained about
discrimination, filed a charge of discrimination, or participated in an employment discrimination
investigation or lawsuit.
The Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) of 2008 - ☑☑GINA makes it illegal to
discriminate against employees or applicants because of genetic information.
Genetic information includes information about an individual's genetic tests and the genetic tests of an
individual's family members, as well as information about any disease, disorder or condition of an
individual's family members (i.e. an individual's family medical history).
Executive orders generally extend discrimination protections to - ☑☑federal workers, including those
working under federal contracts
Executive Order (E.O.) 11246 - ☑☑Issued by President Lyndon B. Johnson,
prohibits federal contractors from discriminating "against any employee or applicant for employment
because of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin."Amended by President Obama (E.O. 13672)[8] to extend protection to include sexual orientation or
gender identity.
E.O. 11478 - ☑☑Issued by President Nixon
Bars discrimination against federal employees on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin,
disability, and age.
Amended by President Clinton (E.O 13087) to include sexual orientation as a protected category.
Amended by President Obama (E.O. 13672) to extend protection to include gender identity as a
protected category.
You are discussing an incident of alleged age discrimination with a manager. The manager states that his
employment action can't be considered age discrimination since the affected employee is only 40. How
should you respond? - ☑☑It can be considered age discrimination, since the protected age is 40 or older
Phillips v. Marin Marietta Corp. (1971) - ☑☑The Supreme Court holds that Title VII's prohibition against
sex discrimination means that employers cannot discriminate on the basis of sex plus other factors such
as having school age children.
In practical terms, EEOC's policy forbids employers from using one hiring policy for women with small
children and a different policy for males with children of a similar age
Griggs v. Duke Power Co. (1971) - ☑☑The Supreme Court decides that where an employer uses a
neutral policy or rule, or utilizes a neutral test, and this policy or test disproportionately affects
minorities or women in an adverse manner, then the employer must justify the neutral rule or test by
proving it is justified by business necessity.
The Court reasons that Congress directed the thrust of Title VII to the consequences of employment
practices, not simply the motivation. This decision paves the way for EEOC and charging parties tochallenge employment practices that shut out groups if the employer cannot show the policy is justified
by business necessity.
Espinoza v. Farah Manufacturing Co. (1973) - ☑☑The Supreme Court holds that non-citizens are entitled
to Title VII protection and states that a citizenship requirement may violate Title VII if it has the purpose
or effect of discriminating on the basis of national origin.
Alexander v. Gardener-Denver Co. (1974) - ☑☑The Supreme Court rules that an employee who submits
a discrimination claim to arbitration under a collective bargaining agreement is not precluded from suing
his or her employer under Title VII.
The court reasons that the right to be free of unlawful employment discrimination is a statutory right
and cannot be bargained away by the union and employer.
UAW v. Johnson Controls (1991) - ☑☑The Supreme Court addresses the issue of fetal hazards. In this
case, the employer barred women of childbearing age from certain jobs due to potential harm that
could occur to a fetus. The Court rules that the employer's restriction against fertile women performing
"dangerous jobs" constitutes sex discrimination under Title VII.
The Court further rules that the employer's fetal protection policy could be justified only if being able to
bear children was a bona fide occupational qualification (BFOQ) for the job. T
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages