Bio 171 Exam 1
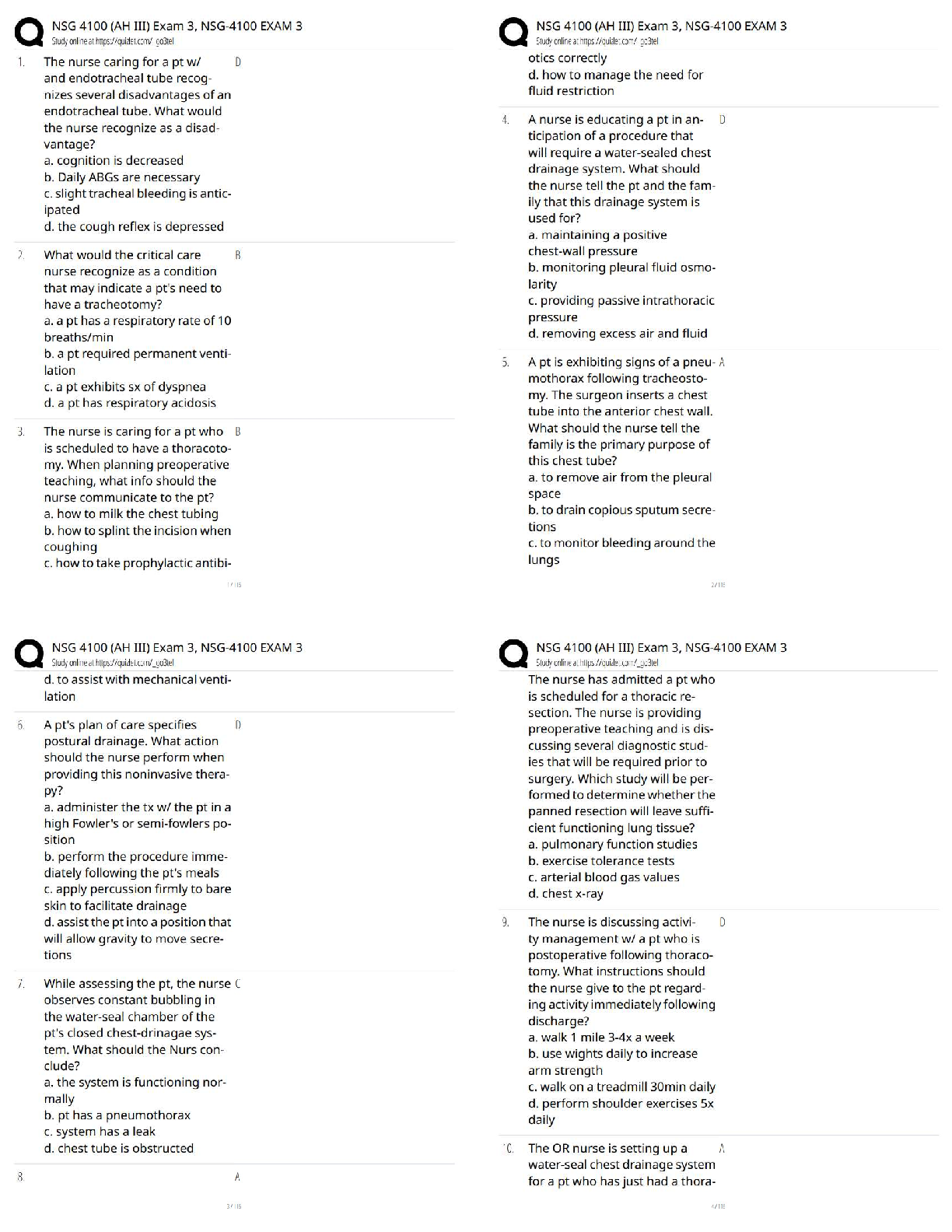
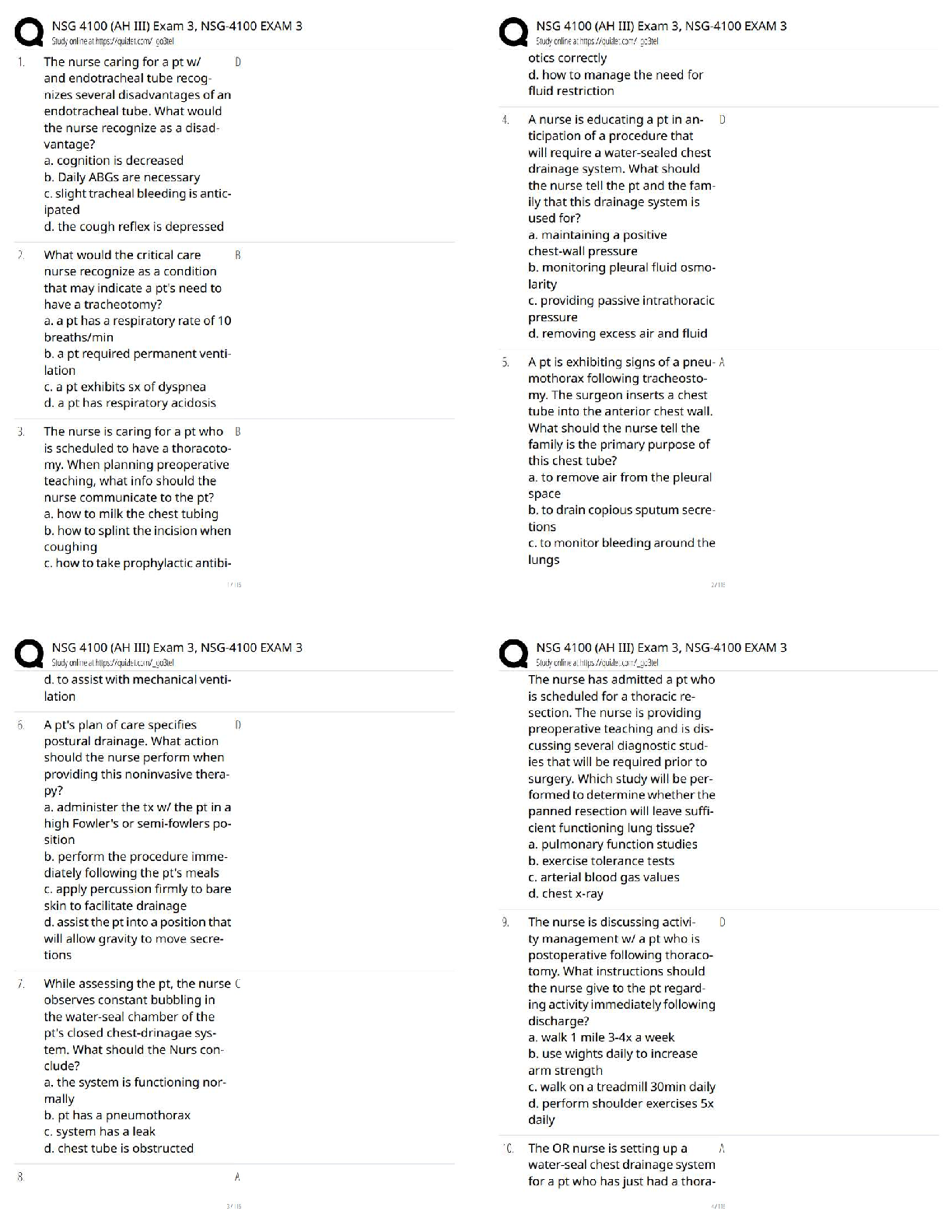
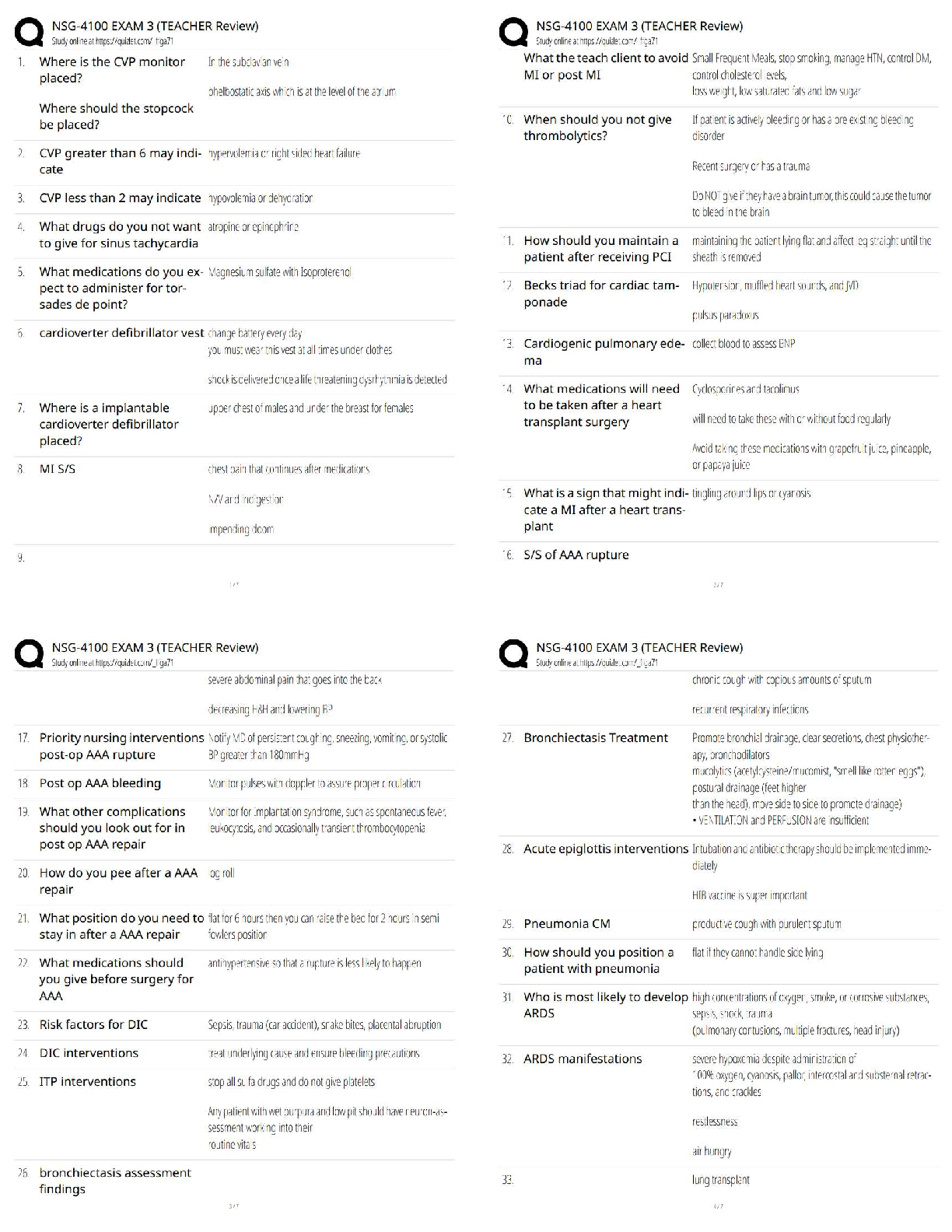
archaea Answer- like bacteria. Are able to live in extreme environment
bacteria Answer- microorganisms that are the basis of fermentation & infectious diseases. Typically one-celled, have no chlo
...
Bio 171 Exam 1
archaea Answer- like bacteria. Are able to live in extreme environment
bacteria Answer- microorganisms that are the basis of fermentation & infectious diseases. Typically one-celled, have no chlorophyll, multiply by simple division, & can be seen only with a microscope. They occur in 3 main forms: spherical, rod-shaped, & spiral
eukaryote Answer- an organism that uses aerobic cellular respiration to break down compounds including oxygen into cellular energy. A human or animal cell
most recent common ancestor Answer- of any set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all organisms in a group are directly descended.
prokaryote Answer- an organism lacking a true nucleus: in some systems of biological classification, any of a superkingdom of organisms, including the viruses & monerans
phylogenetic tree Answer- a graph illustrating evolutionary relationships among various entities that are known to share a common ancestor
nucleic acid Answer- any group of complex compounds found in all living cells & viruses, composed of purines, pyrimidines, carbohydrates, & phosphoric acid. Nucleic acids in the form of DNA & RNA control cellular function & heredity
DNA Answer- a nucleic acid that contains the genetic code
RNA Answer- a long, single-stranded chain of cells that processes protein
transcription Answer- the synthesis of messenger RNA from a DNA template through the formation of base pairs, resulting in a transfer of genetic information that codes for amino acid sequences composing proteins
translation Answer- the process by which messenger RNA directs the amino acid sequence of the growing polypeptide during protein synthesis
tRNA Answer- transfer RNA
mRNA Answer- messenger RNA
rRNA Answer- ribosomal RNA
gene Answer- the definition of a gene is a unit on a chromosome that determines a specific trait in an organism
amino acid Answer- any of a large group of organic acids containing a carboxyl group, COOH, & an amino acid group, NH
protein Answer- the definition of a protein is a substance that has amino acids, compounds & carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, & sometimes sulfur is found in many foods
cell membrane Answer- a layer of tissue that surrounds a cell
ribosome Answer- a tiny particle made up a nucleic acids & proteins that exist in large numbers in the gel-like substance in between every cell in the body
genetic code Answer- the set of DNA & RNA sequences used in the synthesis of an organism's proteins. It is the biochemical basis of heredity & nearly universal in all organisms
phospholipid Answer- a group of lipids that contain a phosphate ester as part of the structure & yield on hydrolysis phosphoric acid, an alcohol, fatty acid & a nitrogenous base: found in all living cells
carbohydrate Answer- the definition of a carbohydrate is an organic compound that occurs in living tissues or food & that can be broken down into energy by people or animals
characteristics of living organisms Answer- -complexity, with precise spatial organization on several scales
-the ability to change in response to the environment
-the ability to reproduce
-the capacity to evolve
1st law of thermodynamics Answer- energy can not be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics Answer- states that the degree of disorder in the universe tends to increase
entropy Answer- amount of disorder in a system
variable Answer- is changed by the experimenter from one treatment to the next
cell Answer- the simplest entity
central dogma Answer- the pathway from DNA to RNA (specifically to form an RNA called messenger RNA to protein)
natural selection Answer- calls on complex mathematical formulations, but at heart its main principles are simple, indeed unavoidable
environmental varition Answer- variation among individuals due to differences in the environment
genetic variation Answer- differences in the genes that are transmitted from parents to their offspring
artificial selection Answer- selection over many centuries has resulted in remarkable variations among dogs. Charles Darwin called this "selection under domestication" & noted that it resembles selection that occurs in nature
double helix Answer- structure composed of 2 strands coiled around each other to form a sort of spiral structure
experimentation Answer- a disciplined & controlled way of asking & answering questions about the world in an unbiased manner
null hypothesis Answer- predicts no effect
negative control Answer- the variable is not changed & no effect is expected
positive control Answer- a variable is introduced that has a known effect to be sure that the experiment is working properly
independent variable Answer- the manipulation performed on the test group by the researchers
dependent variable Answer- the effect that is being measured
standard errors Answer- the "average" of a study, may not be an accurate representative of the "average" of the actual population
cell division Answer- the process by which cells make more cells
asexual reproduction Answer- parent cell divides & forms 2 daughter cells. Identical copies of the genetic material. Because DNA replication is not completely error free, the daughter cells may carry small genetic differences or mutations compared to the parent cell
sexual reproduction Answer- results in offspring that receive genetic material is supplied by the female parent & is present in the egg; the other half is contributed by the male sperm
gametes Answer- eggs & sperms are specialized cells known as gametes. Merge together during fertilization to form a
[Show More]








.png)








.png)