*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > CEN TOX CEN 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (All)
CEN TOX CEN 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Document Content and Description Below
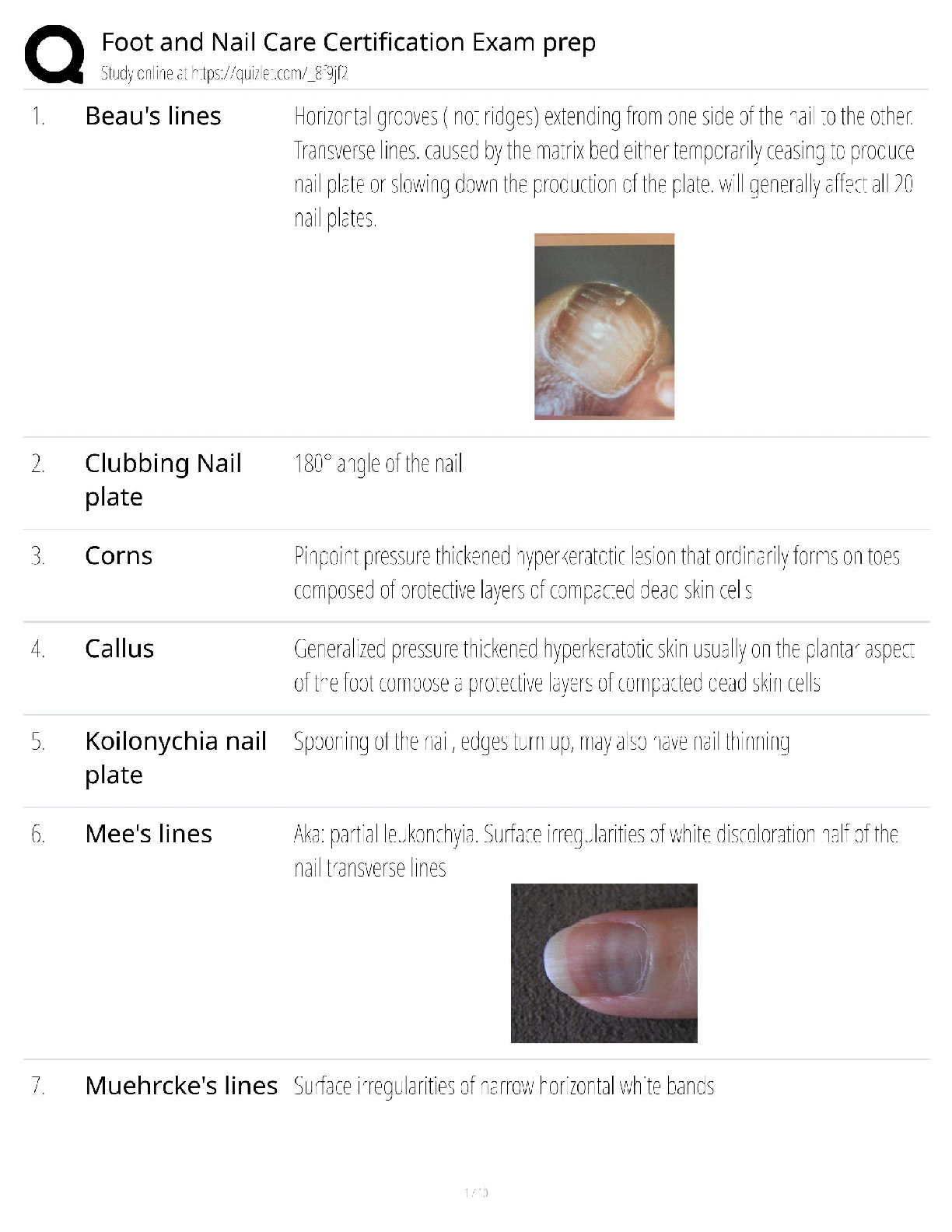
CEN TOX CEN 2 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS For a patient with beta-blocker toxicity, you should prepare for which intervention? Correct answer- Transcutaneous pacer insertion Patients with beta-bl ... ocker toxicity may require transcutaneous pacing to treat bradycardia caused by the toxicity. Hemodialysis has limited usefulness in patients with beta-blocker toxicity. In addition to calcium gluconate, which drugs may be administered to treat calcium channel blocker toxicity? A.Sodium bicarbonate and amiodarone (Cordarone) B. Flumazenil (Romazicon) and naloxone (Narcan) C. N-acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) and Atropine D. Insulin (Humalog) and glucagon (GlucaGen) Correct answer- Several antidotes may be used to treat calcium channel blocker toxicity, including calcium gluconate or chloride, insulin (Humalog), and glucagon (GlucaGen). Rhinorrhea, tearing, yawning, dilated pupils, and abdominal pain are the signs and symptoms of withdrawal from which drug? Correct answer- Heroin Rhinorrhea, tearing, yawning, dilated pupils, and abdominal pain are the signs and symptoms of withdrawal from heroin, an illicit opiate that is a central nervous system depressant. For a patient with benzodiazepine toxicity, which intervention is appropriate for enhancing drug elimination? A. Gastric lavage B. Activated charcoal administration C. Hemodialysis D. Charcoal hemoperfusion Correct answer- Administer activated charcoal promptly and safely to enhance benzodiazepine elimination. When a blood sample is drawn at the appropriate time, the serum level of which drug reflects the degree of acute toxicity? A. Ibuprofen (Motrin) B. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) C. Morphine (MS Contin) D. Phencyclidine hydrochloride (PCP) Correct answer- When the initial blood sample is drawn at least 4 hours after acute acetaminophen (Tylenol) ingestion, the serum level can be plotted on the Rumack-Matthew nomogram to assess the peak acetaminophen level and determine the risk of hepatoxicity. Quantitative drug levels of ibuprofen (Motrin), morphine (MS Contin), and phencyclidine hydrochloride (PCP) are not usually available or helpful except for documenting ingestion. With an overdose, which category of drugs produces coronary artery spasms? Correct answer- Central nervous system stimulants One of the cardiac effects of central nervous system stimulant toxicity is coronary artery spasms. Which antidysrhythmic is most appropriate for treating ventricular dysrhythmias caused by tricyclic antidepressant toxicity? A. Amiodarone (Cordarone) B. Procainamide (Pronestyl) C. Quinidine (Quinidex) D. Digoxin (Lanoxin) Correct answer- Amiodarone (Cordarone) is the most appropriate antidysrhythmic for treating ventricular dysrhythmias caused by tricyclic antidepressant toxicity. Procainamide (Pronestyl) and quinidine (Quinidex) are contraindicated in tricyclic antidepressant toxicity because of the potential for QRS widening. Digoxin (Lanoxin) is not an antidysrhythmic. It controls the heart rate by blocking the sodium-potassium pump. A patient is admitted after taking an overdose of alprazolam (Xanax). Which antidote should you expect to administer to this patient? A. Flumazenil (Romazicon) B. Naloxone (Narcan) C. Calcium gluconate D. Cyproheptadine (Periactin) Correct answer- Alprazolam (Xanax) is a benzodiazepine, and flumazenil (Romazicon) is the antidote for a benzodiazepine overdose. Naloxone (Narcan) is the antidote for opiate toxicity. Calcium gluconate is one of several antidotes for calcium channel blocker toxicity. Cyproheptadine (Periactin), a serotonin antagonist, is used to block serotonin syndrome in toxicity due to an overdose of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) toxicity may occur with lower acetaminophen doses in patients with which disorder? A. Cardiomyopathy B. Asthma C. Alcohol abuse D. Disseminated intravascular coagulation Correct answer- Acetaminophen toxicity may occur with lower acetaminophen doses in patients with alcohol abuse, malnutrition, or preexisting hepatic dysfunction and in those who take isoniazid (INH), anticonvulsant medications (such as phenytoin [Dilantin] or carbamazepine [Tegretol]), or other cytochrome P450 oxidizers. Cardiomyopathy, asthma, and disseminated intravascular coagulation do not affect acetaminophen levels. Family members bring a geriatric patient with confusion and delirium to the emergency department. They report that her symptoms have progressed over the past few days since she started using BENGAY for her arthritis. Which medication is a likely cause of these symptoms? A. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) B. Salicylate C. Iron D. Digoxin (Lanoxin) Correct answer- BENGAY contains salicylate, and chronic salicylate poisoning can cause confusion and delirium in geriatric patients. Other possible causes include sepsis, pneumonia, and anticholinergic ingestion. Acetaminophen (Tylenol), iron, and digoxin (Lanoxin) toxicity are not likely to cause confusion and delirium. An overdose of which nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug can cause seizures? A. Ketorolac (Toradol) B. Celecoxib (Celebrex) C. Indomethacin (Indocin) D. Piroxicam (Feldene) Correct answer- An overdose of piroxicam (Feldene) or mefenamic acid (Ponstel) or the ingestion of a large amount of naproxen (Aleve) or ketoprofen (Orudis) can cause seizures. Ketorolac (Toradol) can cause renal failure. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 31 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 30, 2022
Number of pages
31
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 30, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
97