Health Care > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > FISDAP Trauma. Contains 120 Questions with Answer Key (All)
FISDAP Trauma. Contains 120 Questions with Answer Key
Document Content and Description Below
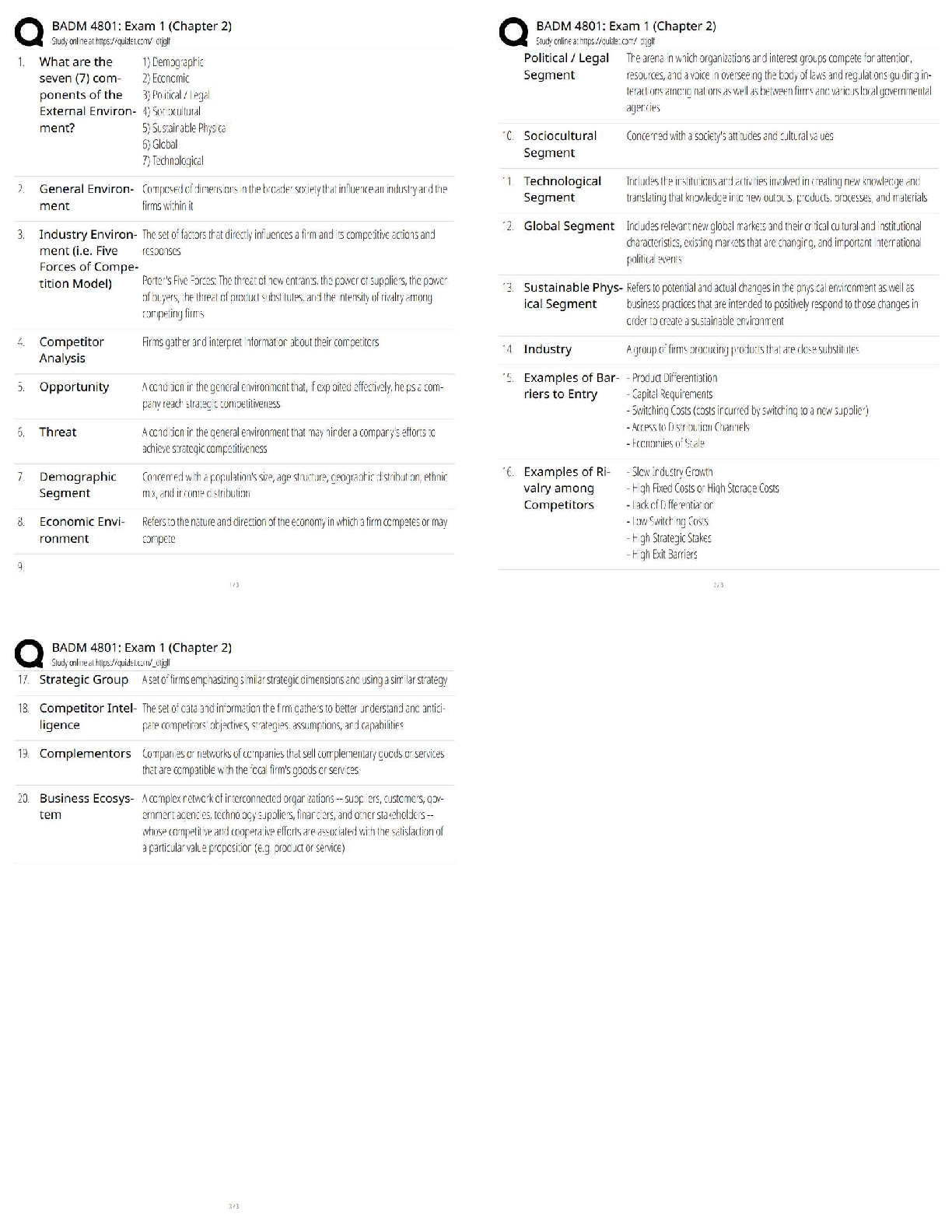
FISDAP Trauma Questions with Answers 1. An alert 18 year old female is found trapped in her car after a single motor vehicle crash. The air bag deployed and she denies any head or neck pain, but sh ... e complains of hip and left leg pain. When she is finally extricated from the car, her vital signs begin to collapse. What shock is she transitioning from? A. neurogenic shock to hypovolemic shock. B. decompensated shock to compensated shock. C. compensated shock to decompensated shock. D. decompensated shock to hypovolemic shock. 2. Which of the following mechanism of injuries would NOT be significant for an adult? A. Death in the same passenger compartment. B. Fall from more than ten feet. C. Ejection from vehicle. D. Altered mental status. 3. A 20 year old female has burns on her chest, abdomen, and on the anterior side of her right arm. What percentage of body is burned? A. 22.5% B. 27% C. 40.5% D. 18% 4. Before placing an unconscious 6 year old on a long backboard, what should you do? A. Place padding directly underneath the head. B. Place padding underneath the shoulders. C. Contact the parents for consent. D. Asses vital signs. 5. What best defines shock? A. Lack of adequate perfusion to the tissues. B. Hemorrhage exceeding 50% of total blood volume. C. Deficiency of vascular tone due to hemorrhage. D. Inadequate cerebral blood flow. 6. Your patient's vehicle was struck by another motorist from behind. What should you do? A. Perform a head-to-toe examination. B. Stabilize the cervical spine. C. Administer high-flow oxygen. D. Apply a half-spine immobilization device. 7. An 18 year old female was hit and has 4 teeth pushed into the upper gums of her jaw. She complains of severe pain and discomfort. Bleeding is minimal and vital signs are BP 120/90, R 16, P 88, SpO2 96%. What should you do? A. Administer aspirin for pain. B. Insert an oropharyngeal airway to maintain patency. C. Apply oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 15 lpm. D. Monitor her bleeding and ensure a patent airway. 8. An injury produced by wounding forces of compression and change of speed, both of which can disrupt tissue is defined as. A. Third degree Trauma. B. Penetrating trauma. C. Blunt trauma. D. Cavitation. 9. A 34 year old female has been bleeding vaginally for two hours. She is anxious, alert, and oriented. Her skin is cool, pale, and diaphoretic. Vital signs are BP 116/70, P 118, R 20. What should you suspect? A. Hypotensive shock B. Hypertensive shock C. Decompensated shock D. Compensated shock 10. What is a contraindication of a traction splint? A. Signs of hypoperfusion B. Swelling or deformity to the thigh C. Pelvic fracture D. Potential spinal injury 11. A 56 year old male involved in a car accident complains of chest and abdominal pain. Pulses differ by 10 mmHg systolic bilaterally and lung sounds are muffled. To which artery should you suspect a rupture? A. Subclavian artery B. Carotid artery C. Iliac artery D. Radial artery Scenario: 12. A 32 year old female attempted to commit suicide by taking sleeping pills and cutting her wrists. She has dark red blood oozing from the wrist lacerations. Vital signs are BP 90/52, P 130 and weak, R 18. What type of bleeding and shock is she experiencing? A. Venous bleeding with hypovolemic shock. B. Capillary bleeding with cardiogenic shock. C. Arterial bleeding with hypovolemic shock. D. Venous bleeding with neurogenic shock. 13. Unequal pupils are a result of pressure on which structure? A. Occulomotor nerve B. Central medulla C. Trochlear membrane D. Vagus nerve 14. A 41 year old male has been injured in an explosion at a chemical laboratory. He has a ruptured tympanic membranes and sinus injuries. At what phase of the blast did the patient sustain the sinus injuries? A. Primary B. Ultimate C. Tertiary D. Secondary 15. When protecting the cervical spine of a suspected trauma patient, what should you do? A. Place gentile traction to straighten the cervical spine. B. Hold the cervical spine in the position found. C. Place a rigid collar on the neck prior to continuing with the rest of the assessment. D. Hold the neck in a neutral, in-line position. 16. What is a mechanism of obstructive shock? A. Myocardial infarction B. Spinal cord injury C. Acute fluid loss D. Tension pneumothorax 17. Which of the following is the first sign of shock that usually appears in patients? A. Changes in vital signs B. Pale, cool, and clammy skin C. Altered mental status D. Nausea and vomiting 18. Which of the following describes bruising or discoloration behind the ears as a result of a fractured skull? A. Babinski's B. Silver fork C. Cushing's D. Battle's 19. What is the correct technique when splinting a suspected finger fracture? A. Apply a straight, flat, and rigid splint to the finger. B. Place an arm board under the wrist and wrap with curlex. C. Tape the fractured finger to a neighboring finger only. D. Immobilize the hand and finger in a pillow and apply ice. 20. After initial treatments of an arterial bleed in the left forearm are unsuccessful. What should you do? A. Apply a tourniquet. B. Lower the extremity. C. Apply pressure to the radial artery. D. Apply pressure to the subclavian artery. 21. A 12 year old male has suffered a blast injury. What phase would projectiles have caused injury to the patient? A. Secondary B. Primary C. Tertiary D. Quaternary 22. When the vascular container enlarges without proportional increase in the fluid volume, what type of shock should you suspect? A. Decompensated B. Hypovolemic C. Cardiogenic D. Distributive 23. A 26 year old female complains of chest pain after a motor vehicle accident. Auscultation of lung sounds reveals distant heart tones. Vital signs are BP 160/70, P 56, R 22 and she has distended neck veins. What should you suspect? A. Hemothorax B. Abdominal aortic aneurysm C. Congestive heart failure D. Pericardial tamponade 24. A 34 year old male involved in a motorcycle crash presents with tachycardia, hypotension and muffled heart tones. What should you suspect? A. Pericardial tamponade B. Hemopneumothorax C. Traumatic asphyxia D. Tension pneumothorax 25. What organ is located in the upper right quadrant? A. Spleen B. Liver C. Kidney D. Pancreas 26. An alert, ambulatory, 26 year old female admits to laying her motorcycle down at 25 mph to avoid a crash. She has extreme pain to her left side where you note severe abrasions. She denies any neck or back pain. What should you do? A. C-collar and immobilize her fully in the standing position. B. Oxygen and transport in a semi-sitting position of comfort. C. C-collar and transport her on his left side. D. Sterile dressings and treat her pain with ice. 27. A 20 year old female was involved in a car crash. She complains of midline neck pain and is unable to move her extremities. What secondary injury should you suspect? A. Difficulty breathing B. Ruptured vertebrae C. Vertebral swelling D. Subluxation 28. A unrestrained 24 year old female driver hit an electrical pole and struck the steering wheel. She appears pale and complains of nausea and abdominal pain. What organ is LEAST likely to suffer an injury as a result of this impact? A. Liver B. Stomach C. Spleen D. Diagphram 29. A 28 year old female has full thickness burns to her hands and arms after being shocked by an electrical outlet. Vital signs are BP 150/90, R 20, P 84. What should you do? A. Cover her wounds with moist sterile dressings. B. Irrigate her burns with normal saline. C. Apply dry sterile dressings to her wounds. D. Administer ice to her burns. Scenario: 30. A 38 year old male has been struck with a brick. His words are incomprehensible, and he has no eye opening or motor response. He has unequal pupils and has blood draining from his left ear. Vital signs are BP 178/110, P 58, R 8. What should you suspect? A. A narcotic overdose B. A basal skull fracture C. Hypovolemic shock D. Subdural hematoma 31. What is an injury to ligaments around a joint called? A. Fracture B. Strain C. Sprain D. Dislocation 32. A 16 year old male has a broken nose. He is bleeding heavily from both nostrils. What should you do? A. Pinch his nose and lean him forward. B. Pinch his nose and lean him back. C. Gently pack both nostrils with sterile gauze. D. Apply direct pressure to his nostrils. 33. A 18 year old male has hypotension, bradycardia, and warm dry skin following a hard hit during a football game. What should you suspect? A. Septic shock B. Neurogenic shock C. Hypovolemic shock D. Cardiogenic shock Scenario: 34. An 80 year old male complains of leg pain. His left foot is pulseless, discolored, and cool to the touch. He had surgery two days prior with no complications. What should you suspect? A. Diabetes B. Normal post surgery occurrence. C. Medication overdose D. A blood clot 35. A 29 year old female fell from an 18 foot roof. During your rapid trauma assessment, where are you most likely to find life-threatening injuries? A. Abdomen, pelvis, arms B. Head, chest, abdomen C. Head, neck, extremities D. Chest, pelvis, extremities 36. How quickly should you expect a clot to form from a venous laceration? A. 11-14 minutes B. 7-10 minutes C. 4-6 minutes D. 1 minute 37. A 60 year old male fell onto a coffee table yesterday and he woke up this morning complaining of diffuse, dull abdominal pain. You note periumbilical bruising. What is this known as? A. Grey-Turner's sign B. Kehr's sign C. Crohn's sign D. Cullen's sign 38. A 56 year old female has an arm injury with arterial bleeding. The dressing becomes soaked with blood. What should you do? A. Apply additional dressing material with direct pressure. B. Remove and replace the dressing with a thicker dressing. C. Wrap an elastic bandage around the blood soaked dressing. D. Cover the existing dressing with an occlusive dressing. 39. A 19 year old female has a pencil impaled in her left eye. Vital signs are BP 130/90, R 18, P 84.  What should you do? A. Assess her ability to track movement with her right eye. B. Apply oxygen by non-rebreather mask at 15 lpm. C. Stabilize the pencil and cover her other eye in a dressing. D. Stabilize the pencil with a plastic cup. Scenario: 40. A 20 year old male struck his head while jumping into a swimming pool. He is unconscious and apneic. Vital signs are BP 88/70, P 80. There is a large amount of swelling and deformity in the cervical spine area. What should you do? A. Apply and inflate MAST B. Use the head tilt/chin lift to open his airway C. Secure him to a long spineboard D. Administer oxygen via non-rebreather mask Scenario: 41. A 45 year old male has fallen down a flight of stairs. He is unresponsive and has diminished breath sounds bilaterally with subcutaneous emphysema around the base of his neck. What should you suspect? A. Hemothorax B. Fractured treachea C. Flail chest D. Pneumothorax 42. A 52 year old female was the passenger in a car crash in which the airbag deployed. She complains of violent pain in her left shoulder. What is this known as? A. Kehr's sign B. Cullen's sign C. Grey-Turner's sign D. Shoulder dystocia 43. A 10 year old boy fell off his bicycle and is now experiencing slow, even bleeding from his left elbow. Which of the following would be the most likely complication resulting from the injury? A. Contamination and infection. B. Air embolism interfering with heart rhythm. C. Locating the child's legal guardian. D. Major blood loss. 44. An intoxicated 45 year old homeless man was hit in the chest. He complains of pain with inspiration. Bilateral lung sounds are clear. Vital signs are BP 130/80, P 76, R 12, SpO2 94%. What should you suspect? A. Head injury B. Pericardial tamponade C. Tension Pneumothorax D. Rib fractures 45. A 56 year old male tripped and fell into a manhole in the sidewalk. He complains of chest pain and tenderness when he takes a deep breath. Lung sounds are clear but diminished bilaterally. Vital signs are BP 140/90, P 90, R12. What is the most likely cause of his symptoms? A. Tension pneumothorax B. Rib fractures C. Flail chest D. Left sided hemothorax 46. Your patient has a small, sucking puncture wound on the right side of his chest. How should you dress the wound? A. Roller gauze. B. Moist gauze. C. Butterfly bandages. D. An occlusive dressing. 47. A 31 year old female has gun shot wound to the right lateral chest. She is awake and alert with obvious difficulty breathing. Where should she be transported? A. Respiratory center B. Local hospital C. Emergency department D. Trauma center 48. You are at an amusement park when you witness a 19 year male being stabbed in the arm. After assuring the scene is safe, you approach and see that he is experiencing slow, steady bleeding. You have disposible gloves in your pocket, but no bandages. You should A. Send a bystander to locate a tourniquet. B. Apply direct pressure to the wound using your gloved hand. C. Locate a first aid kit and control the bleeding with bandages. D. Elevate the arm and use a pressure point to control bleeding. 49. An unrestrained 47 year old female is in cardiac arrest after car crash on the freeway. She has been pulseless for 20 minutes and CPR was withheld. What should you do? A. Start CPR and contact medical control to terminate efforts. B. Provide chest compressions for 2 minutes then apply the AED. C. Apply the AED and start CPR simultaneously. D. Look for signs of occult bleeding. 50. A 25 year old pregnant patient was ejected from a motor vehicle. She is apneic and pulseless. What should you do? A. Prepare for delivery. B. Provide CPR and transport. C. Transport in the left lateral recumbent position. D. Avoid contaminating the scene. 51. A 25 year old female has a distended abdomen and muffled lung sounds after a car accident. BP 130/80, P 96, R 24. What should you suspect? A. Abdominal evisceration B. Pericardial tamponade C. Ruptured bowel D. Tension pneumothorax 52. What are the general principles for the management of a dislocation? A. Traction and realignment. B. Splinting in a position of comfort. C. Pain management and realignment. D. Splinting in the position found. 53. An alert and oriented 35 year old female is sitting on the ground after a car accident. Vital signs are BP 90/62, P 96, R 24 and shallow. She denies any numbness or tingling in her extremities. What should you do? A. Reassess her vitals B. Apply oxygen by nasal cannula C. Perform full spinal immobilization D. Transport immediately 54. What findings would indicate a serious mechanism of injury during a motor vehicle crash? A. The front end of the car has crumpled without intrusion into the passenger compartment. B. The patient has a 1" laceration to his face and his left shoulder is bruised. C. The windshield is badly cracked on the passenger's side. D. The steering wheel is deformed, and the steering column is damaged. 55. What patient would NOT be triaged as a red? A. A patient with an obstructed airway. B. A patient with a sucking chest wound. C. A patient in decompensated shock. D. A patient with a 4 inch thigh laceration. 56. What is the initial treatment of an abdominal evisceration? A. Apply a moist sterile dressing. B. Apply cold pack to the injury. C. Apply a dry sterile dressing. D. Carefully reinsert of the organs. 57. If transport is delayed or prolonged, and if circulation is impaired, an attempt should be made to reposition a grossly deformed fracture or dislocated joint (if allowed by medical control or protocol). The exception is an injury to the _____ A. Knee B. Elbow C. Ankle D. Hip 58. A 22 year old male complains of shortness of breath with diminished lung sounds on the right side. Vital signs are BP 130/90, P 86, R 24. What should you suspect? A. Pneumothorax B. Tension pneumothorax C. Exacerbation of COPD D. Asthma attack 59. A 23 year old motorcyclist was struck by an automobile. He complains of hip and leg pain. Your exam reveals a tender pelvis, deformed left upper leg, and a compound fracture to the left lower leg. What should you use? A. Hare traction splint B. Long backboard C. Bilateral SAM splints D. Anti-shock trousers 60. A 27 year old female was involved in an assault. She has a 10 cm long cut across her lower abdomen and you see her lower intestine push out each time she breathes out. What should you do? A. Apply a gloved hand and gently push downwards. B. Wrap her lower abdomen in dry sterile dressings. C. Irrigate her wound with 500 mL normal saline. D. Apply a moist dressing then an occlusive dressing. 61. A factory worker has a 3/4 inch laceration on his forehead that bleeds through the dressings despite direct pressure. What should you do? A. Apply unilateral carotid pressure. B. Remove the dressing and apply direct digital pressure. C. Continue direct pressure and apply additional dressings. D. Apply pressure to the facial artery. 62. A 24 year old male was stabbed in the thigh. Bright red blood spurts from the wound. What should you suspect that the patient severed? A. Vein B. Artery C. Tendon D. Ligament 63. A 60 year old male with a head injury is moaning and making incomprehensible sounds. He withdrew when you started his IV but is otherwise not moving. His eyes are wide open. What is his Glascow Coma Score? A. 13 B. 6 C. 3 D. 10 64. What type of impact to an unrestrained occupant commonly results in a multiple system injury? A. Rotational B. Lateral C. Broadside D. Frontal 65. A 45 year old male has a small puncture wound to his hand after cleaning his pressure washer. You notice swelling in his palm and fingers. What should you do? A. Wrap the hand in curlex B. Irrigate the wound with saline C. Apply ice and splint the hand D. Elevate and splint the hand 66. A 72 year old female was in a motor vehicle collision. She has a right ulnar fracture with no distal circulation. What should you do? A. Attempt to realign the fracture B. Splint the fracture in position found C. Apply a traction splint D. Transport immediately 67. What the minimum systolic blood pressure that will perfuse all vital organs? A. 90 mmHg B. 70 mmHg C. 80 mmHg D. 60 mmHg 68. An 18 year old female is found conscious and alert, but trapped in her car. She denies any head or neck pain, but she complains of hip and left leg pain. When she is finally extricated from the car, her vital signs begin to collapse. What should you suspect? A. Neurogenic shock B. Air embolism C. Internal injuries D. Crush syndrome 69. What is NOT included in the management of a minor venous laceration? A. Pressure point B. Elevation C. Direct pressure D. Tourniquet 70. Which of the following mechanisms of injury would likely result in coupcontrecoup trauma? A. A front-impact motor vehicle collision. B. Diving into shallow water. C. A fall from over 20 feet. D. A low-energy projectile. 71. Hollow Organs ________ while solid organs Bleed ____________? A. Profusely bleed, very slowly B. Rupture, Rupture C. Ooze Blood, Profusely D. Rupture, Profusely 72. A patient has excessive bleeding from the neck. What should you apply? A. A tourniquet B. A band-aid C. An occlusive dressing D. A pressure dressing 73. Contents of the Chest are protected by ____________ A. Mediastinum B. False Ribs C. Sternum D. Ribs 74. A 22 year old male was hit several times in the face at the bar. Vital signs are BP 130/82, P 110, R 24. He is hostile and cannot remember his name or address. He refuses any emergency care. What should you do? A. Explain the consequences of not allowing you to treat him and then have him sign a refusal form. B. Call for the police to obtain a transport hold on him. C. Have him sign a refusal form and leave the scene. D. Have his friends drive him to the hospital as you follow behind in your ambulance. 75. You are dispatched to a residence where a 10-year-old girl fell onto a jagged piece of metal. She has a gaping laceration to the right upper arm that is spurting bright red blood. The mother tried to control bleeding with a towel, but it kept soaking through. How would you manage this patient? A. Place direct pressure on wound, elevate pt’s arm, place tourniquet Proximal to the injury B. Immediately place PASG C. Place direct pressure on wound, elevate pt’s arm, place tourniquet Distal to the injury D. Call for Immediate ALS intercept, they need to place a Tourniquet on pt’s arm and start a small bore IV. 76. A 21 year old female involved in a car crash has a bruise to the right side of her chest with paradoxical motion. What should you suspect? A. Flail chest segment B. Cardiac tamponade C. Tension pneumothorax D. Traumatic asphyxia 77. A 22 year old female involved in a car accident has a 10 cm laceration across her abdomen. You see her large intestine protruding. What should you do? A. Irrigate the wound with normal saline. B. Put gentle pressure on the large intestine. C. Cover the injury with a dry sterile dressing. D. Apply a moist and occlusive dressing. 78. List all regions of human vertebral column. A. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal. B. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, coccygeal, coccyx. C. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal, coccyx. D. Intervertebral, coccyx, lumbar, thoracic. 79. Which of the following patients should be transported to a trauma center? A. A 60 year old with rib pain after a motor vehicle collision. B. A 45 year old female stabbed in the flank. C. A 22 year old male with a closed ulnar fracture. D. A 25 year old male who fell ten feet. 80. A 16 year old female fell while rollerskating and is now confused and agitated. What should you suspect? A. Head and chest injuries. B. Head and spinal injuries. C. Abdominal and extremity injuries. D. Abdominal and spinal injuries. 81. In which of the following situations would you remove an impaled object? A. knife in the lung B. piece of metal in the abdomen C. wire in the right cheek D. steel rod through the leg 82. The posterior chest region contains the_____________? A. Posterior Vena Cava B. Spinal Column C. Sternum D. Jugular veins 83. A 13 year old has fallen 15 feet. He has a deformed right thigh and is lethargic to respond. What should you do? A. Apply a traction splint. B. Obtain a sample history. C. Immediately attempt to contact his parents. D. Manually stabilize the c-spine. 84. A 34 year old male was involved in a car accident. He has significant facial trauma and is bleeding profusely from his mouth and nose. When performing your assessment, what findings are most indicative of neurological disorders? A. Changes in level of consciousness B. Narrowing pulse pressure C. Tachycardia and hypotension D. Head trauma 85. A 24 year old female responds to a sternal rub by opening her eyes and moaning incomprehensibly. She tries to push your hands away from her sternum. What is her Glasgow Coma Scale score? A. 6 B. 3 C. 12 D. 9 86. A 26 year old female has difficulty breathing after a motor vehicle accident. Lung sounds are distant on her left side and she has paroxysmal chest rise. What should you do? A. Insert an oral airway. B. Wrap her chest in bandages. C. Apply a nonrebreather mask at 15 lpm. D. Ventilate her with a BVM. 87. A 22 year female has lower leg deformity, moderate bleeding from the forehead, and signs and symptoms of shock following a motor vehicle collision. What should you do? A. Open the airway and monitor the vital signs every 15 minutes. B. Complete a detailed trauma assessment and patient history. C. Perform primary assessment, stabilize, and transport. D. Splint and bandage the patient's injuries before transporting. 88. An 18 year old male was struck in the head by a large rock. When caring for this patient, what should you continually reassess? A. Locomotor function. B. Level of consciousness. C. Quality and degree of pain. D. Pulse motor sensory. 89. What will initial compensatory mechanisms do during hemorrhaging? A. Increase stroke volume and increase cardiac output. B. Increase cardiac output and reduce mean arterial pressure. C. Decrease respiratory rate and increase heart rate. D. Decrease peripheral vascular resistance and increase respiratory rate. 90. In the field, you splinted a patient with a deformed humerus. Enroute to the hospital, you cannot feel a pulse in the limb. What should you do? A. Loosen the splint and reassess the pulse. B. Remove the splint and apply manual stabilization. C. Make a note in your report and call medical control. D. Reposition the extremity at a level below the heart. 91. A 19 year old female with head trauma has hypertension, bradycardia, Cheynes-Stokes respirations and withdraws from pain. Which area of the brain is likely affected? A. Medulla B. Temporal lobe C. Cerebellum D. Hypothalamus 92. What bone should you use a traction splint on? A. Radius B. Femur C. Tibia D. Humerus 93. A 19 year old male struck his head against the platform while doing a reverse flip. Vital signs are BP 88/70, P 96, R 8 What type of shock is he in? A. Hemorrhagic B. Distributive C. Hypovolemic D. Cardiogenic 94. A 45 year old male was bitten by a dog and has wounds to his left arm and leg. What should you do? A. Allow the injuries to continue bleeding to clean the wounds. B. Irrigate the wounds with saline and wrap with dry curlex. C. Cover with moist and occlusive dressings. D. Establish two large bore IVs and administer an analgesic. 95. A 17 year old male has a knife impaled in his left chest. Vital signs are BP 170/90, R 10, P 97. What should you do? A. Perform positive pressure ventilations. B. Attempt to remove the knife. C. Stabilize the knife with dressings. D. Auscultate lung sounds. 96. How does the body try to compensate during uncontrolled bleeding? A. Increasing the heart rate B. Increasing blood clotting mechanisms C. Decreasing the respiratory rate D. Decreasing blood pH 97. <img src="http://www.fisdap.net/~lbriguglio/testing_images/MH2009/aeh82892_3709_edt .jpg"><br> What does this picture show? A. An open femur fracture. B. A closed femur fracture. C. An open tibia fracture. D. A closed tibia fracture. 98. A 40 year old male is unresponsive and pale, and you notice a deformity above his right wrist and bruising around his navel. His wife tells you that her husband was out drinking the previous evening and he stumbled while walking up the front steps. What should you suspect? A. An extremity fracture B. Alcohol poisoning C. Hypoglycemia D. Internal bleeding 99. Open wounds that sometimes cause significant blood loss are called A. Abrasions. B. Punctures. C. Lacerations. D. Contusions. 100. A 39 year old male has an angulated deformity to the humerus. You cannot feel a distal pulse and the limb is blue. What should you do? A. Contact medical control for pain medication orders. B. Attempt to pull gentle traction and realign the bones. C. Transport emergently to the closest hospital. D. Splint with a sling and swathe, apply ice, and transport. Scenario: 101. A 37 year old male has been pulled from the water after diving into a shallow lake. He is unconscious, flaccid, and has diaphragmatic breathing. Vital signs are BP 100/70, P 68, R 20. What should you do? A. Manually stabilize the cervical spine. B. Insert a blind airway device. C. Apply high-flow oxygen. D. Activate air-medical transport. 102. A gunshot wound is an example of a A. Laceration. B. Deformity. C. Contusion. D. Penetration. 103. Which of the following is used in the management of a pelvic fracture with hypotension? A. Pneumatic Anti-Shock Garment. B. Buddy splinting the legs to each other. C. Securing the patient to a backboard. D. Unilateral traction device with two ankle straps. 104. How should you treat an impaled object in the abdomen? A. Manual secure the object and inflate the pneumatic anti-shock garment to stabilize the object. B. Remove the object, and apply a porous dressing moistened with sterile saline to the wound. C. Remove the object, apply an occlusive dressing to the wound. D. Secure the object, control bleeding, and use bulky dressings to stabilize the object. 105. While on scene of a two car T-Bone Type accident, a bystander comes up to you and states, I think my husband just died! Upon arrival to patient you find him to be unresponsive although his is breathing. Pt is noted to have a large hematoma to the frontal region of his head. Patients family states that patient has a long medical history including COPD, CAD, and Diabetes. Upon assessment you find his vitals to be BP 130/60, Pulse 80, Respirations 18. Your next step should be? A. Obtain a BGL, and request ALS assistance. B. Place patient on a LSB and rapidly transport to the nearest Urgent Care. C. Give Oral Glucose, because you are sure that his blood sugar is low. D. Place patient on High Flow O2, transport patient to the nearest burn center. 106. A 32 year old male has an open wound on his arm after an unknown chemical powder was spilled on it. What should you do? A. Wrap the wound in sterile gauze B. Irrigate the wound with water C. Identify the chemical and obtain a set of vitals D. Brush the powder off the wound 107. An 8 year old complains of severe lower leg pain. He was released from a local emergency room 8 hours ago following treatment for a closed tibia fracture. The whole lower leg is swollen, pale and has decreased sensation. What should you suspect? A. Compartment syndrome B. An acute arterial occlusion C. An associated calf muscle strain D. Ineffective immobilization 108. A 16 year old male was freed from entanglement in a motor vehicle crash. His right arm is amputated below the elbow. What should you do with the amputation? A. Wrap it in moistened gauze, place it in a bag, and keep it cool. B. Place it in a bag packed with ice and transport with patient. C. Wrap it in a dry gauze and keep it warm during transport. D. Place it into its anatomical position and wrap it with dry gauze. 109. How much blood can a patient lose in the abdomen if left untreated? A. 1000 L B. 10 L C. 1500 L D. 15 L 110. A 20 year old male struck his head on a diving board and is unconscious and apneic. Vital signs are BP 88/70, P 80. He has a large amount of swelling and deformity in the cervical spine area. What should you suspect? A. Cerebral contusion B. Increased intracranial pressure C. Cervical spine injury D. Hypovolemic shock 111. What is the primary concern in a patient suffering from a severe facial injury due to blunt trauma? A. Bleeding control B. Transport facility C. Adequate Breathing D. Airway control 112. A 52 year old male was the unrestrained driver in a frontal impact car crash. Which of the following injuries would lead you to believe the patient traveled "up and over" the dashboard instead of "down and under"? A. Ruptured diaphragm B. Cervical spine fracture C. Patellar dislocation D. Flail chest 113. An 18 year old female with a suspected cervical spine injury has a significant amount of blood in her mouth. What should you do? A. Assess the her respiratory rate for no longer than 30 seconds. B. Stabilize her head and suction her airway. C. Perform a jaw-thrust maneuver and attempt to ventilate her. D. Perform a jaw-thrust and finger sweep in order to remove blood from her mouth. 114. A 57 year old female was the unrestrained driver in a frontal impact collision. Which of the following injuries would lead you to believe she traveled "up and over" the dashboard, instead of "down and under"? A. A flail chest B. A patellar dislocation C. A cervical spine fracture D. A ruptured diaphragm 115. A 29 year old male crashed his motorcycle. He is unconscious and the lower portion of jaw is torn from his face. He has gurgling respirations with bleeding into throat. What should you do? A. Insert an oropharyngeal airway. B. Apply a c-collar and administer blow-by oxygen. C. Perform a head chin tilt and apply a non-rebreather mask. D. Apply a nasal cannula and suction as needed. 116. What is the most serious complication of vaginal bleeding? A. Pelvic inflammatory disease B. Yeast infection C. Pregnancy D. Hypovolemic shock 117. A 20 year old male has a 4 cm long by 3 mm wide cut along his right forearm. How should you classify this wound? A. Abrasion B. Avulsion C. Contusion D. Laceration 118. An 8 year old male has a 22 caliber gunshot wound to the lower left abdomen. The wound has been dressed but continues to bleed. Vitals are BP 118/68, P 92, SpO2 96%. What should you do? A. Apply direct pressure to the wound. B. Remove the soaked dressing and apply a new one. C. Administer oxygen. D. Auscultate lung sounds. 119. In a compound extremity fracture involving the loss of distal pulses, what your first priority in providing care? A. Pulling traction B. Bleeding control C. Splinting D. Rapid Transport [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

THIS BUNDLE CONTAINS ALL Field Internship Student Data Acquisition Project (FISDAP), Practice tests, Exams, Study Guides Plus Questions and Answers.
FISDAP Trauma. Contains 120 Questions with Answer Key FISDAP Cardiology Exam 41 Practice Questions & Answer Key FISDAP Airway. 70 Questions & Answer key FISDAP Cardiology. 75 Questions and An...
By QuizMaster 3 years ago
$45
13
Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 31, 2022
Number of pages
26
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 31, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
101