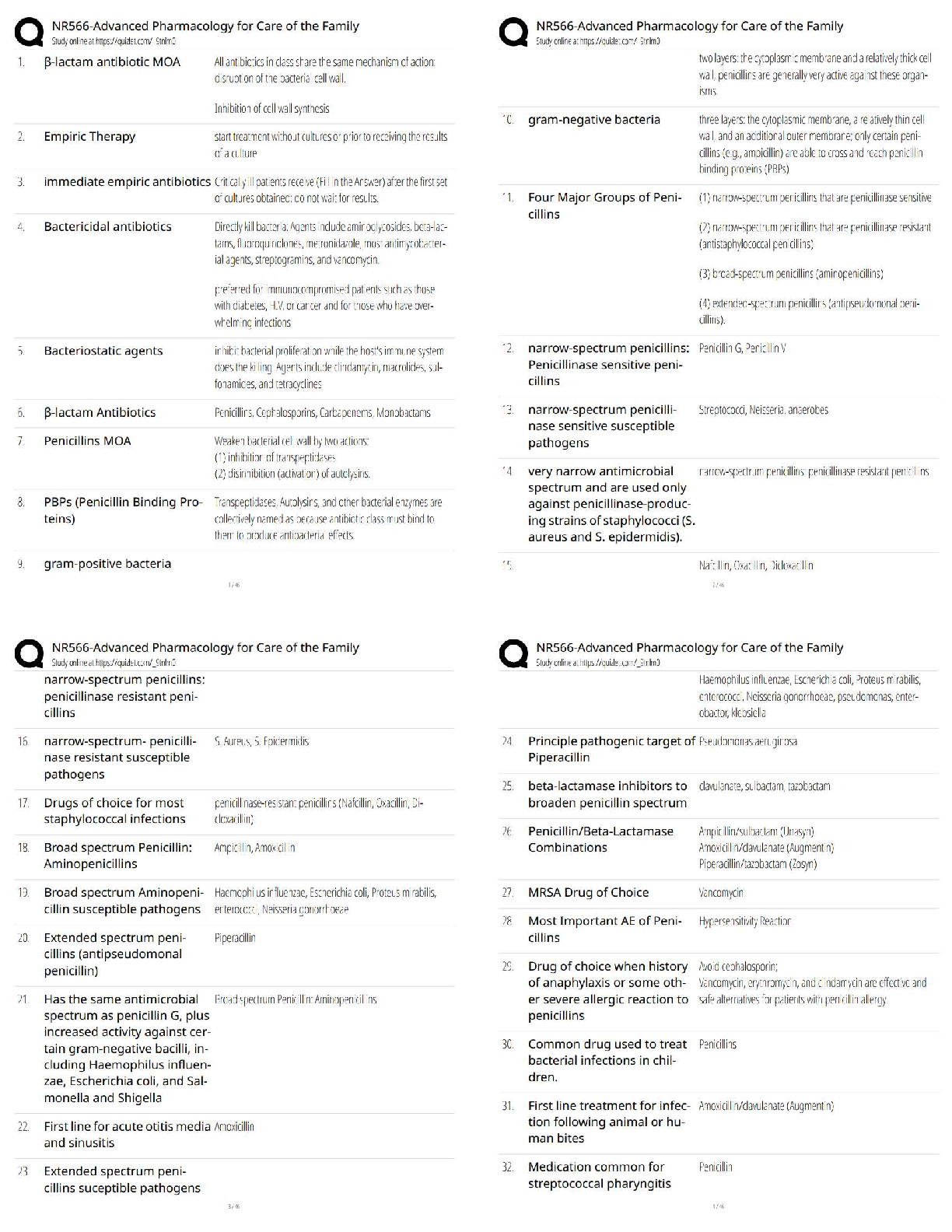
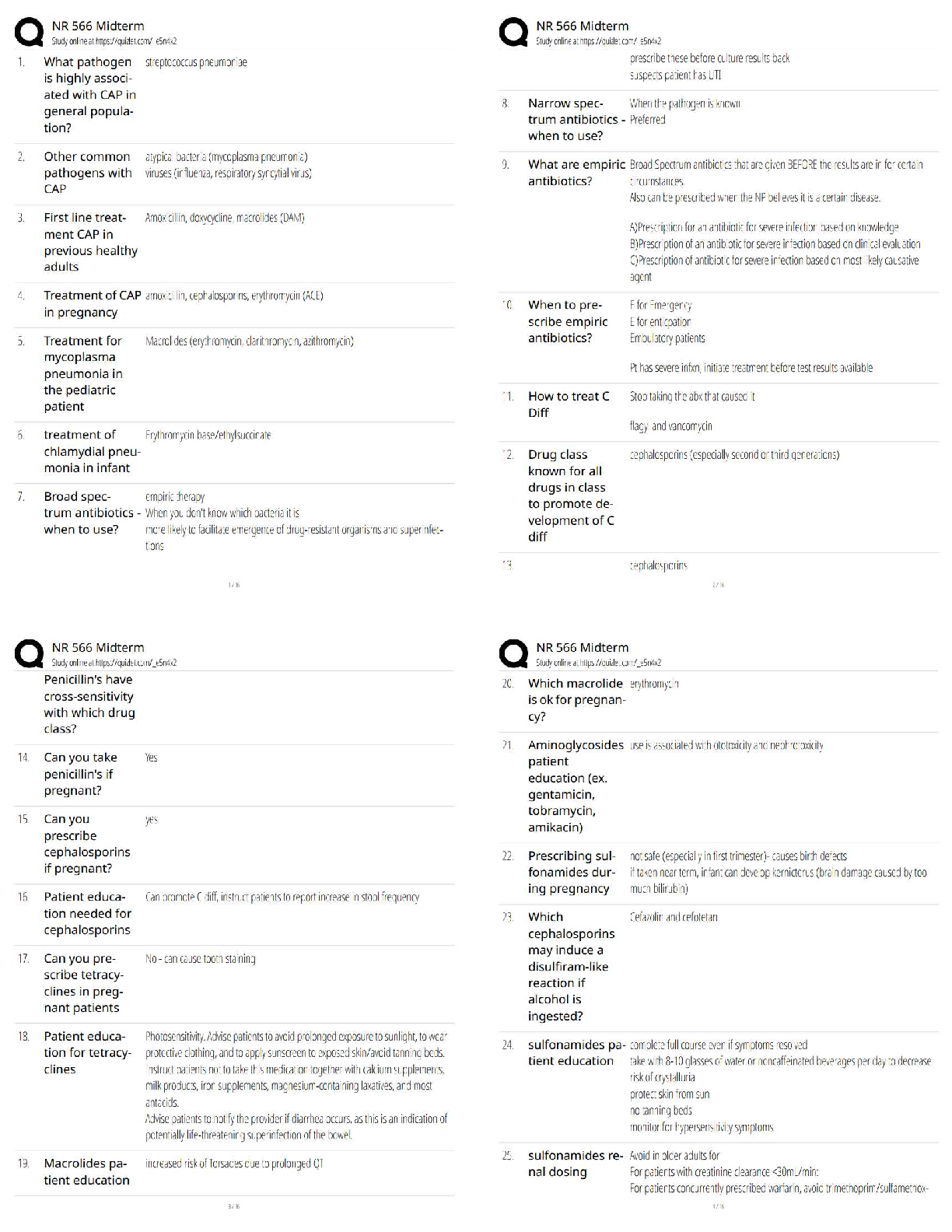
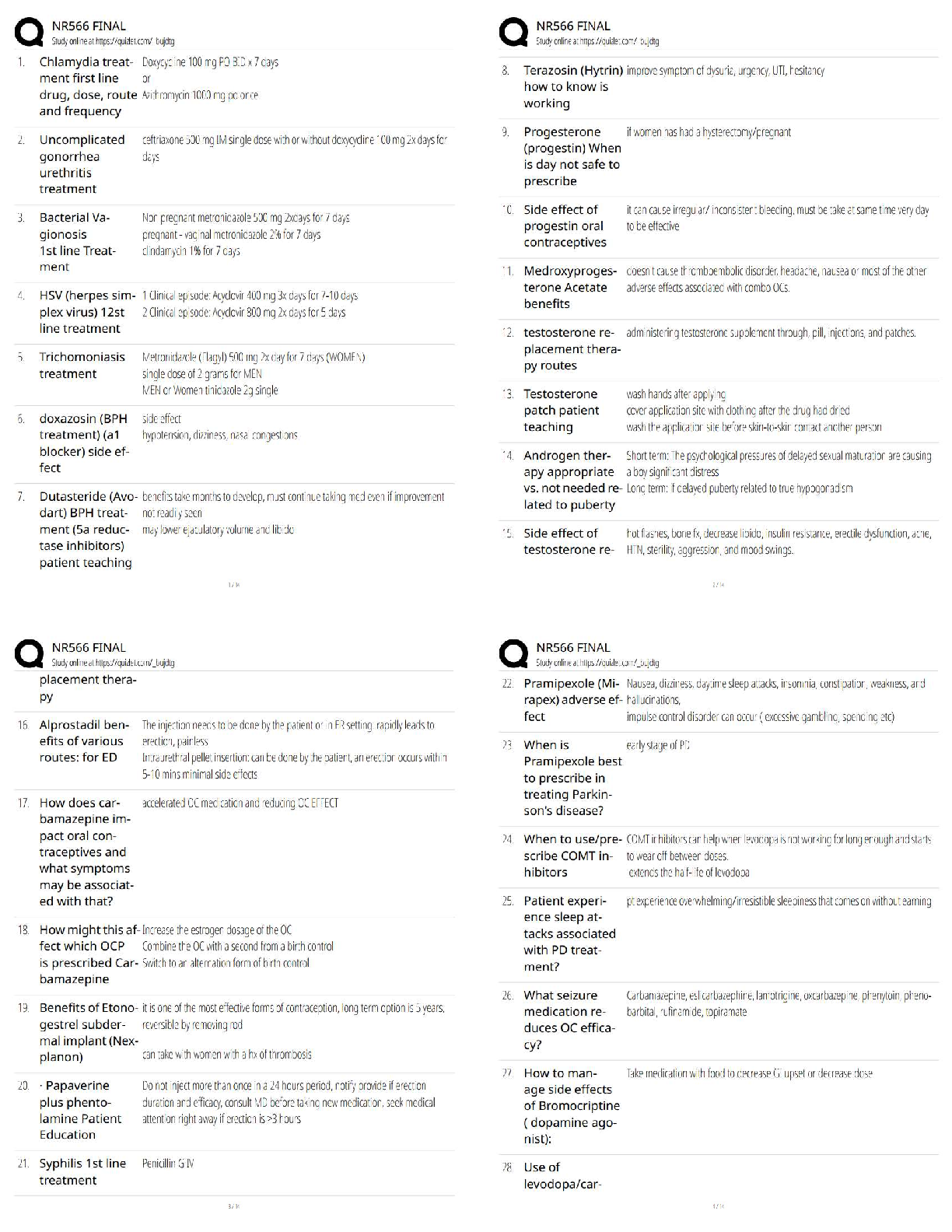
NR503-Population Health Epidemiology and Statistical Principles Midterm (Chamberlain.edu)
Document Content and Description Below
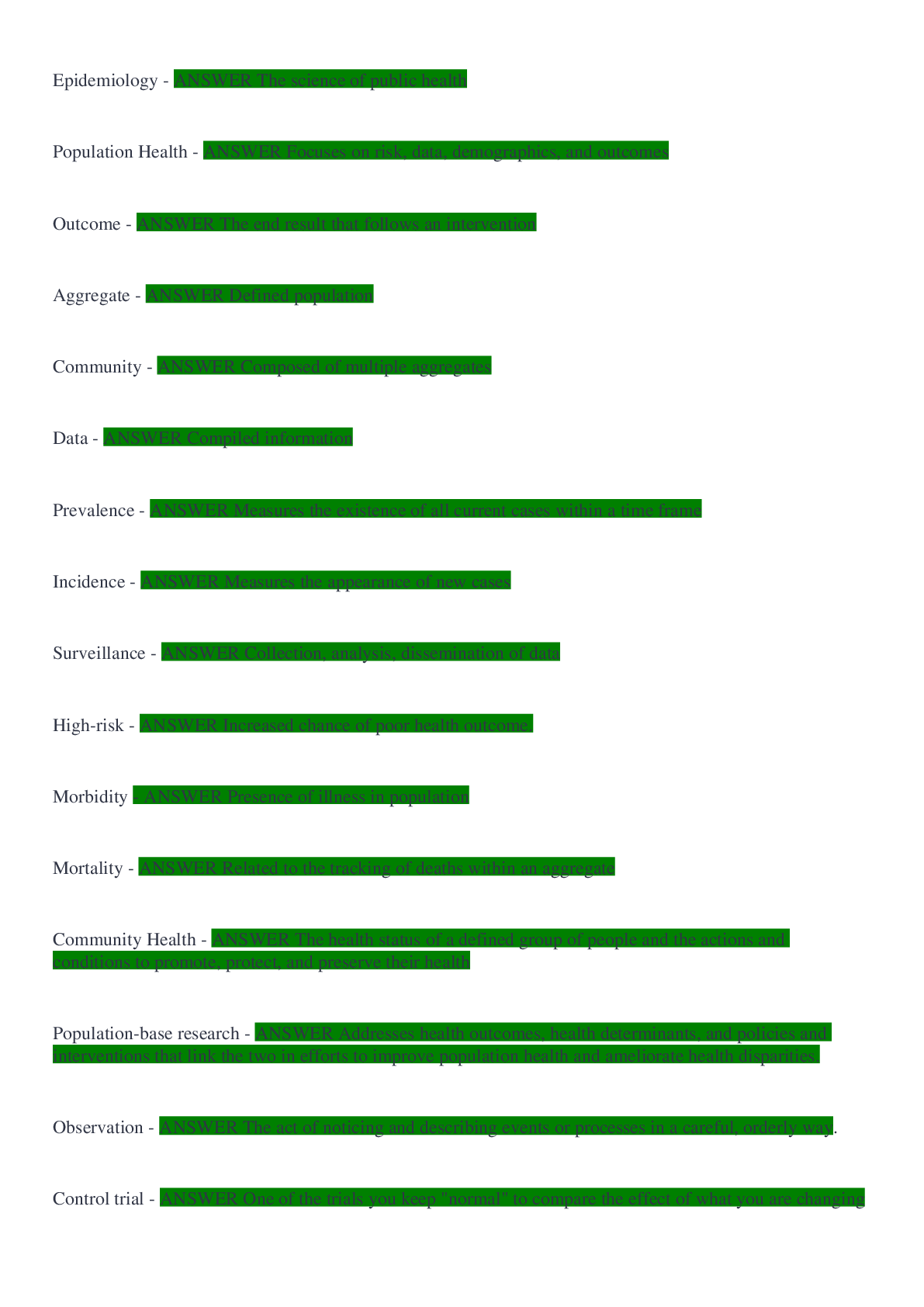
Epidemiology - ANSWER The science of public health
Population Health - ANSWER Focuses on risk, data, demographics, and outcomes
Outcome - ANSWER The end result that follows an intervention
Ag
...
gregate - ANSWER Defined population
Community - ANSWER Composed of multiple aggregates
Data - ANSWER Compiled information
Prevalence - ANSWER Measures the existence of all current cases within a time frame
Incidence - ANSWER Measures the appearance of new cases
Surveillance - ANSWER Collection, analysis, dissemination of data
High-risk - ANSWER Increased chance of poor health outcome.
Morbidity - ANSWER Presence of illness in population
Mortality - ANSWER Related to the tracking of deaths within an aggregate
Community Health - ANSWER The health status of a defined group of people and the actions and conditions to promote, protect, and preserve their health
Population-base research - ANSWER Addresses health outcomes, health determinants, and policies and interventions that link the two in efforts to improve population health and ameliorate health disparities.
Observation - ANSWER The act of noticing and describing events or processes in a careful, orderly way.
Control trial - ANSWER One of the trials you keep "normal" to compare the effect of what you are changing
Infectious disease - ANSWER A disease that is caused by a pathogen and that can be spread from one individual to another.
Chronic disease - ANSWER a disease that develops gradually and continues over a long period of time
Environmental exposures - ANSWER Being in the presence of some substance in an environment. Typically, that substance is pollution or a hazardous waste.
Reproductive Health - ANSWER Sexual health, autonomy, reproductive freedom/decision-making
Genetics - ANSWER The scientific study of heredity
Data Critique - ANSWER Checking sources for validity, reliability, and credibility
Primary prevention - ANSWER Prevents the onset of disease; reduce the incidence of disease.
Secondary prevention - ANSWER Detect disease early and preventing it from getting worse
Tertiary prevention - ANSWER Reducing the symptoms of a disease and improve quality of life.
Social Justice - ANSWER Justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society.
Campaign for Action - ANSWER Seven major, interrelated issues that together contribute to a healthier America through nursing
Vital Statistics - ANSWER Births, deaths, marriages, divorces, fetal deaths, and induced termination of pregnancies.
Inter-professional collaboration - ANSWER Multiple health workers from different professional backgrounds working together with patients, families, carers (caregivers), and communities to deliver the highest quality of care
HP2020 - ANSWER The federal government's prevention agenda for building a healthier nation
Determinants of health - ANSWER A range of factors that influence the health status of individuals or populations
Risk analysis - ANSWER The process of identifying and analyzing potential issues that could negatively impact key business initiatives or critical projects in order to help organizations avoid or mitigate those risks
Validity (of screening test) - ANSWER The ability of a test to distinguish correctly who has a disease.
Sensitivity (of tests) - ANSWER The ability of a test to correctly identify those who have a disease. The number of true positives (true positive rate)
Specificity (of tests) - ANSWER The ability of a test to correctly identify those who do not have the disease (true negative rate).
Positive Predictive Value (PPV) - ANSWER The proportion of patients/clients with a positive test result who have the condition of interest
Negative Predictive Value (NPV) - ANSWER The proportion of patients/clients with a negative test result who do not have the condition of interest.
Descriptive epidemiology - ANSWER The aspect of epidemiology concerned with organizing and summarizing health-related data according to time, place, and person
Risk factor - ANSWER A condition that may adversely affect an individual's health.
Absolute risk - ANSWER The incidence of disease in a population. ✔ The probability or chance of an event. It is usually used for the number of events (such as a disease) that occurred in a group, divided by the number of people in that group
Relative risk - ANSWER The ratio of the risk of disease in exposed individuals to the risk of disease in non-exposed individuals
Odds ratio - ANSWER The ratio of the odds of development of disease in a non-exposed person ✔
Attributable risk - ANSWER How much of the risk (incidence) of the disease we hope to prevent if able to eliminate exposure to the agent in question. ✔
Incidence rate - ANSWER The number of new cases of a disease that occurs during a specified period of time in a population at risk for developing the disease
Prevalence rate - ANSWER The number of affected persons present in the population at a specific time divided by the number of persons in the population at that same time
Epidemiological triangle - ANSWER A model for explaining the organism causing the disease and the conditions that allow it to reproduce and spread. (Host, Agent, Environment).
Confounding Variables (CV) - ANSWER An "extra" variable that you didn't account for. They can ruin an experiment and give you useless results
Levels of Evidence - ANSWER A rating system for judging the strength of a study's design. Based on the methodological quality of their design, validity, and applicability to patient care
Rapid cycle improvement model - ANSWER A "quality improvement method that identifies, implements and measures changes made to improve a process or a
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages





.png)

.png)


.png)