Economics > EXAM > Questions and Answers > University of California, Los Angeles ECON 103 Decision Tree Exam (All)
Questions and Answers > University of California, Los Angeles ECON 103 Decision Tree Exam
Document Content and Description Below
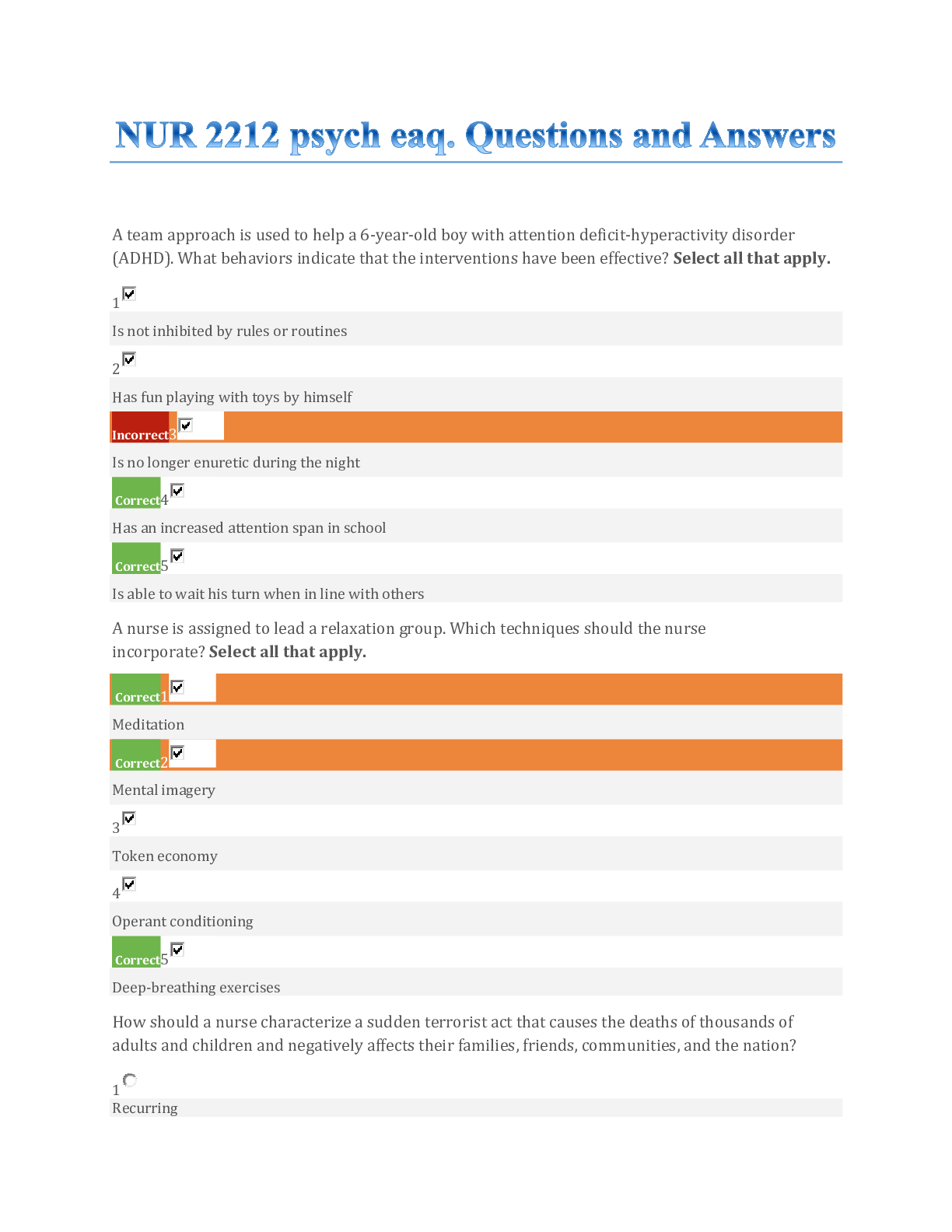
University of California, Los Angeles ECON 103 Decision Tree Exam Question 1 Correct The difference between game trees and decision trees is: Select one: A. that game trees are not useful in st... rategic situations B. that decision trees describe actions that depend on the behavior of rivals C. that game trees have interactive payoffs D. that decision trees are a function of many individuals and the state of nature E. none of the above Feedback Question 2 Correct If a firm has a dominant strategy: Select one: A. its optimal strategy depends on the play of rivals B. its optimal strategy is always the same, even if payoffs change C. it is determined by the behavior of only one key rival D. its optimal strategy is independent of the play of rivals Feedback Question 3 Correct A Nash equilibrium occurs when: Select one: A. each player has a dominant strategy B. each player receives the same final payoff C. each player believes it is doing the best it can given the behavior of rivals D. there is no dominant strategy for any player E. payoffs are independent of the actions taken by rivals Feedback Question 4 Correct If player 1 has a dominant strategy, then player 2: Select one: A. must also have a dominant strategy B. may or may not have a dominant strategy, but will always lead to a Nash equilibrium C. may or may not have a dominant strategy D. will not be able to reach an optimal solution to the game E. will block this dominant strategy and force player 1 to another strategy Feedback Question 5 Correct Getting to a Nash equilibrium requires: Select one: A. each knowing the opponent's payoffs and cooperation B. Neither cooperation nor knowing the opponent's payoffs C. cooperation but not knowing the opponent's payoffs D. either cooperation or knowing the opponent's payoffs, depending on the game Feedback The correct answer is: Neither cooperation nor knowing the opponent's payoffs Question 6 correct Given the following payoff matrix, who has a dominant strategy? Select one: A. it depends on what the other player does B. both players C. neither player D. A does; B doesn't E. B does; A doesn't Feedback Question 7 correct Given the following payoff matrix, what will A's profits be? Select one: A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. unknown until B's action is observed Feedback Question 8 Correct Which pair of strategies would cooperative cartel members A and B choose given this payoff matrix? Select one: A. W, Y B. W, Z C. X, Y D. X, Z E. either X, Y or W, Z Feedback Question 9 correct Which pair of strategies would competing firms A and B choose given this payoff matrix? Select one: A. W, Y B. W, Z C. X, Y D. X, Z E. Either X, Y or W, Z Feedback Question 10 Correct Strategic foresight is the ability to make decisions today that are rational based on: Select one: A. complete uncertainty about the future B. our best information about what will happen in the future C. what we know only about behavior in the past D. information that we have only about our own behavior in the past E. incorrect information about the past Question 11 Correct A subjective definition of probability is: Select one: A. a weighted average of different peoples' degrees of certainty of an event's occurring B. a theoretical probability distribution C. a person's degree of certainty of an event's occurring D. an expected value of a particular outcome E. the number of occurrences of an event in a large number of repetitions of an experiment Feedback Question 12 correct You pay $3.75 to roll a normal die 1 time. You get $1 for each dot that turns up. Your expected profit from this venture is: Select one: A. -$0.75 B. -$0.25 C. $0.25 D. $3.00 E. $3.50 Feedback Question 13 correct Billy Joe Bob thinks he will win $3 with probability P, otherwise he will win $11. His expected payoff is: Select one: A. $3 + $8P B. $11 - $8P C. $7 D. $3 + $11P E. $11 - $3P Feedback Question 14 correct Betty Gamble is willing to pay exactly, but not more than, $20 to get a deal where she has a 1/3 chance of winning $30 and a 1/6 chance of winning $6 and will win $20 otherwise. Betty is: Select one: A. risk-averse and profit maximizing B. risk-averse, not profit maximizing C. risk loving and profit maximizing D. risk loving, not profit maximizing E. risk-neutral Feedback question 15 correct A company chooses one of four options; then nature decides whether the choice works. If it does not work, the company has two updating options, each with three possible payoffs. How many decision forks are on the tree depicting this? Select one: A. 5 B. 12 C. 17 D. 28 E. 36 Feedback [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 06, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
94

















.png)



