*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 14: Impulsivity, Compulsivity, and Addiction. Questions with 100% accurate answers. (All)
Chapter 14: Impulsivity, Compulsivity, and Addiction. Questions with 100% accurate answers.
Document Content and Description Below
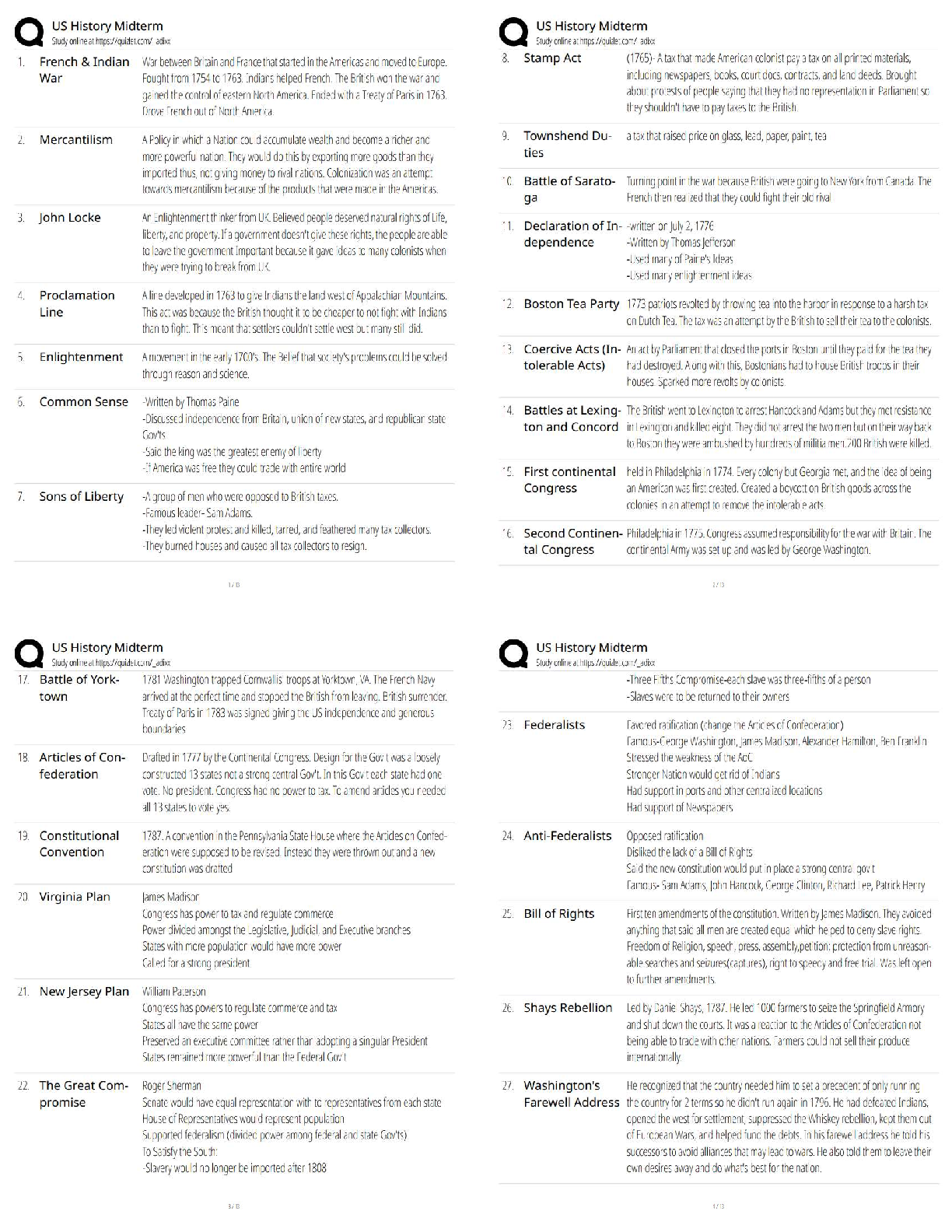
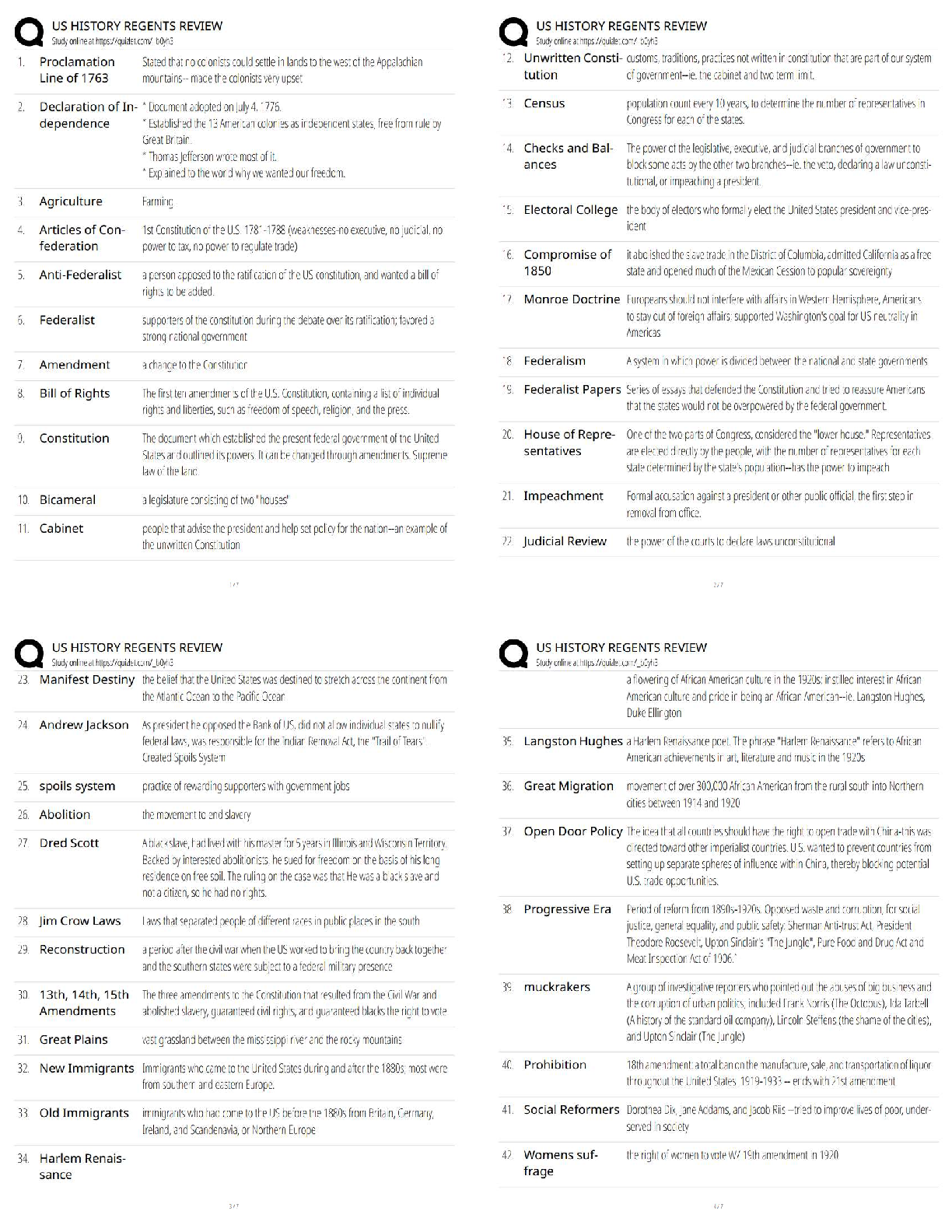
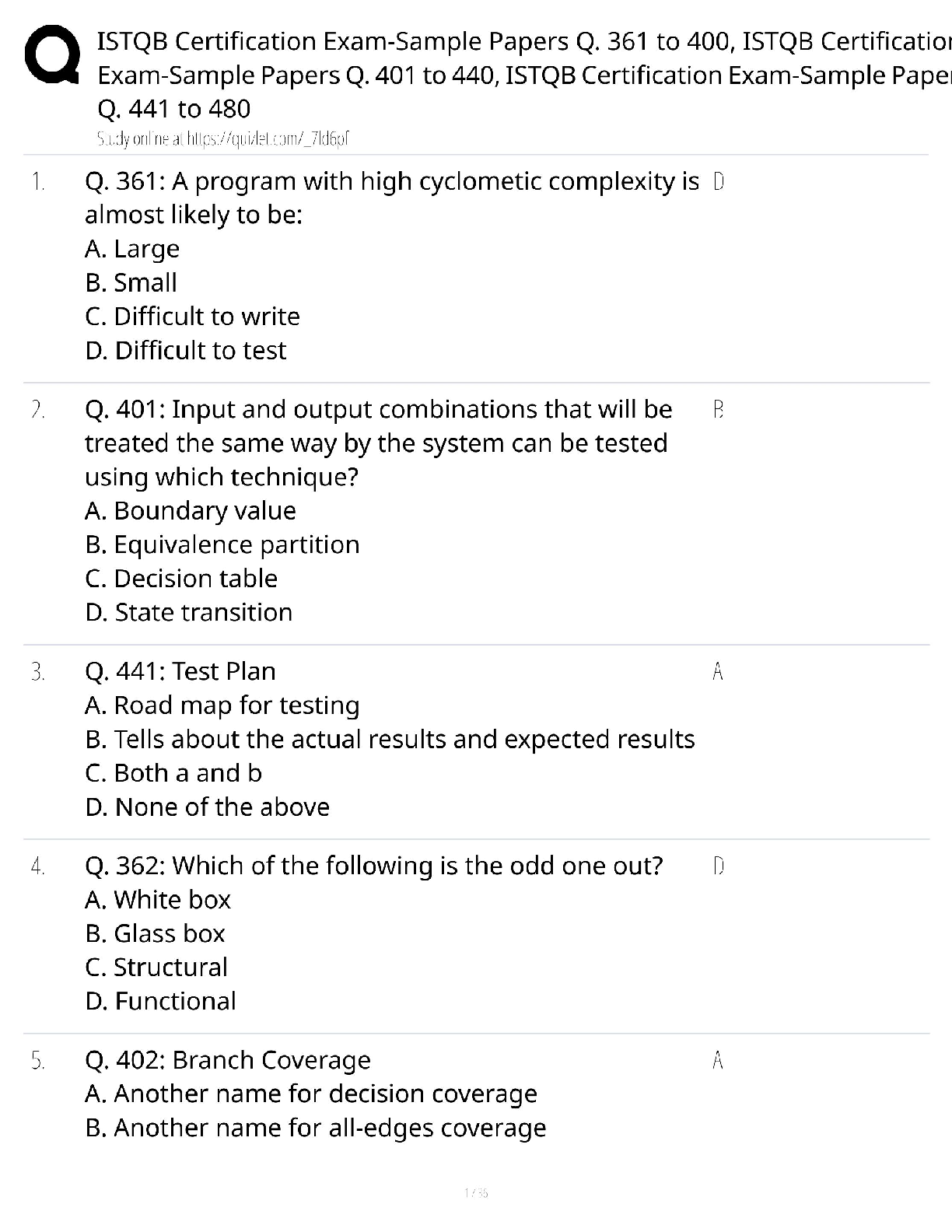
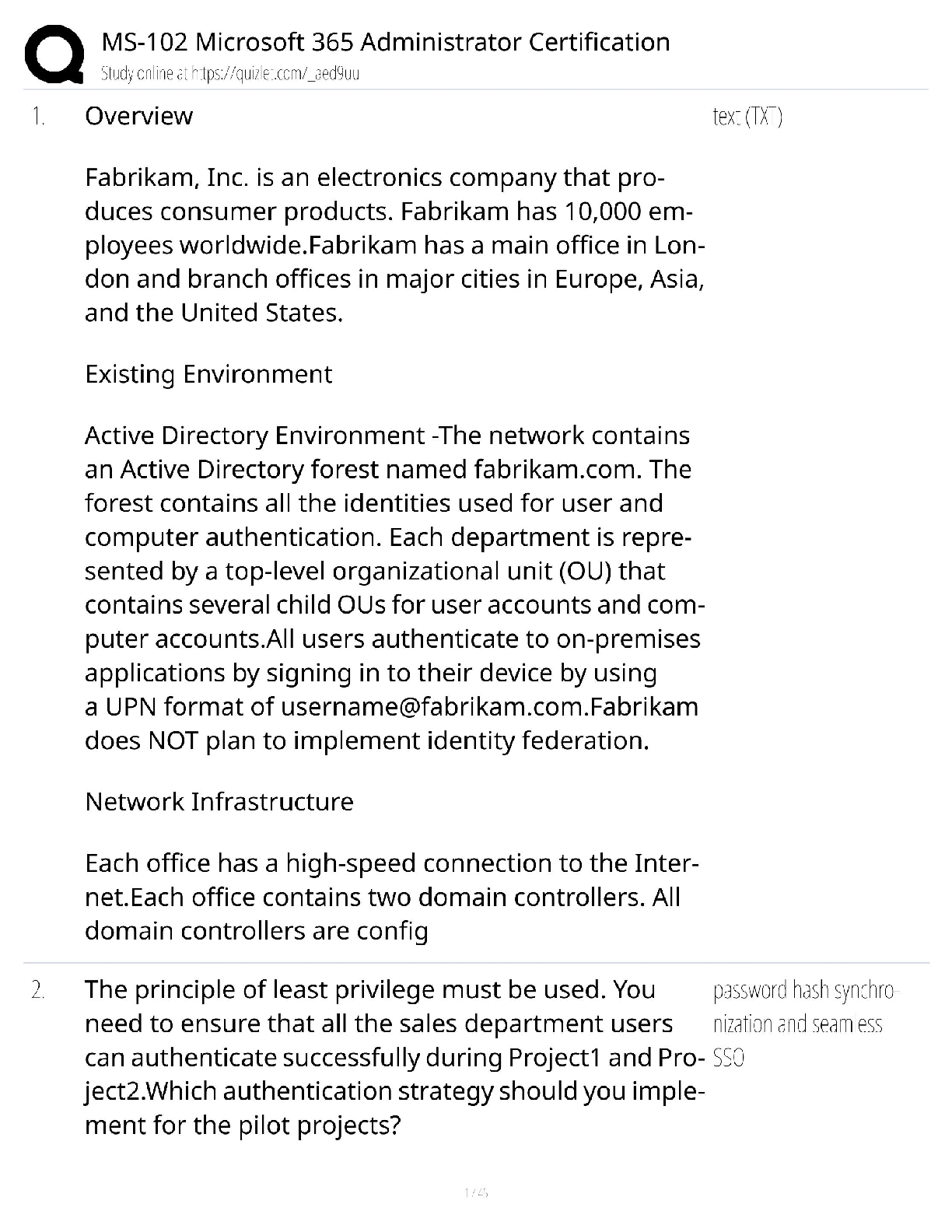
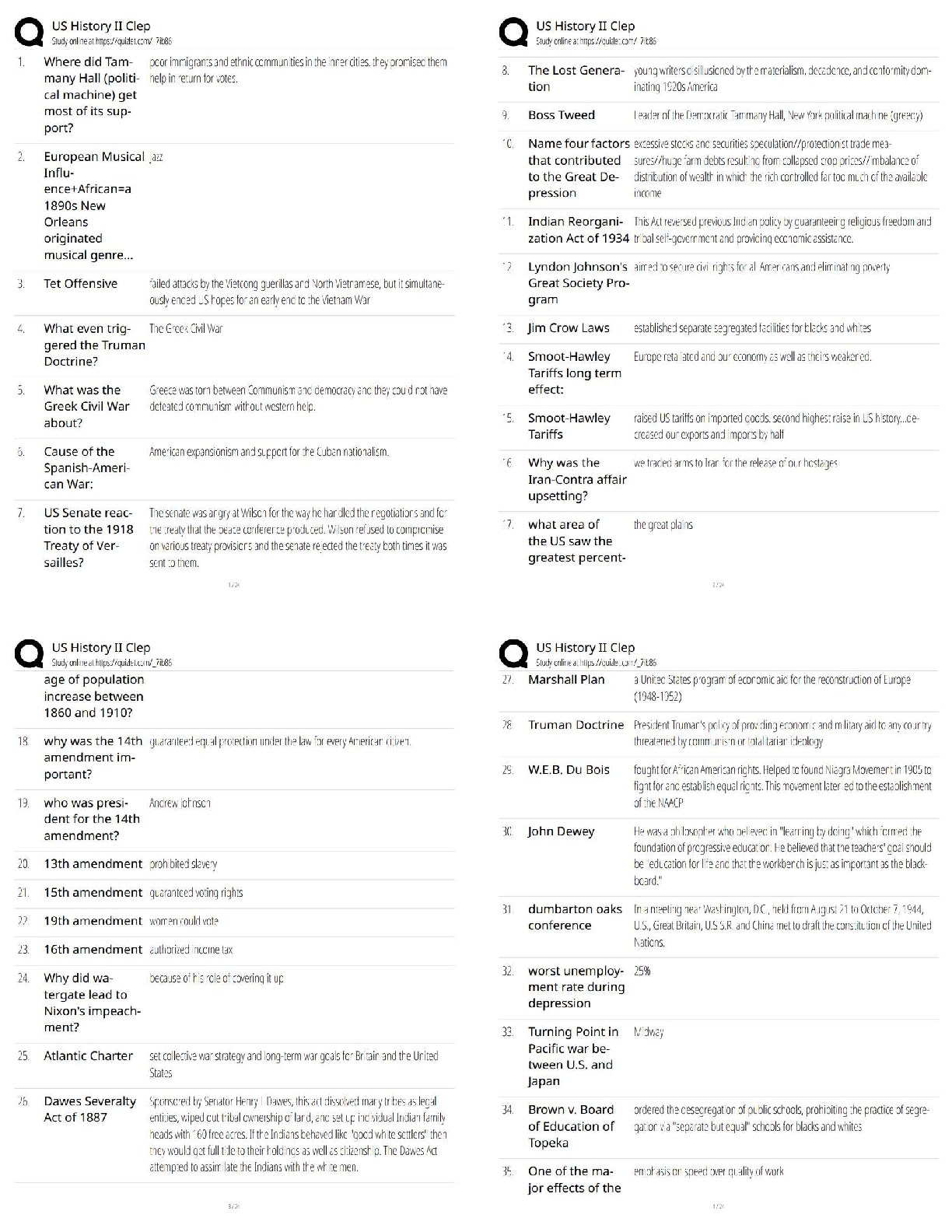
what is an endophenotype? - ✔✔-sxs linked to specific brain circuits that are present trans-diagnostically as a dimension of psychopathology that cuts across many psych disorders. cause of impu ... lsive-compulsive disorders? What disorders fall in this category? - ✔✔-Impulsive: pyromania, kleptomania, intermittent explosive, mania, ADHD, impulsive violence, BPD, antisocial behavior - MOA: inability to stop the initiation of actions. defined as acting without forethought; the lack of reflection on consequences; inability to postpone reward with preference for immediate reward over greater but delayed reward; failure of motor inhibition often choosing risk behavior (lacking willpower). Involves a circuit centered from the ventral striatum > thalamus > VMPFC > ventral striatum. Compulsive: ASD, Tourette's, body dysmorphic, sin picking, trichotillomania, OCD, somatization, hypochondriasis, compulsive shopping, compulsive internet use, paraphilas, hypersexuality - MOA: inability to terminate ongoing actions. Defined as inappropriate actions to a situation which persist and often result in undesirable consequences. Compulsions are characterized by inability to adapt behavior after negative feedback. Habits form that are responses to your environment even though consequences aren't desirable to you. These are conditioned responses to a conditioned stimulus that has been reinforced in the past. This differs from goal directed behavior because this is mediated by your knowledge and desire for the consequences. Compulsions have been stamped into your brain previously as soon as you get the stimuli your brain automatically gets the compulsion. Goal directed behavior requires cognitive resources whereas compulsions have be done with minimal cognitive effort which can be beneficial, but in these disorders it is maladaptive. Involves circuit that starts with the dorsal striatum > thalamus > OFC > dorsal striatum. both: drug addiction, gambling, obesity/BED - MOA: impulsive acts like drug use, gamgling and obesity eventually become compulsive due to neuroplastic changes that use the dorsal habit system and cause impulses in the ventral loop to the dorsal loop. Note: both impulsivity and compulsivity are forms of cognitive inflexibility OCD related spectrum disorders - ✔✔-OCD Hair pulling (trichotillomania) Skin picking Body dysmorphic disorder Hoarding Tourette's/tic disorder ASD Hypochondriasis Somatization Substance/behavioral addictions - ✔✔-Drug Gambling Internet Food Shopping Disruptive/impulse control disorders - ✔✔-Pyromania Kleptomania Intermittent explosive Impulsive violence BPD Self harm/parasuicidal behavior Antisocial behavior CD ODD Mania ADHD Sexual disorders - ✔✔-Hypersexual Paraphilias why can't impulsive-compulsive disorders be stopped? - ✔✔-The problem is in the cortical circuits that normally suppress these behaviors. Impulsivity starts in the ventral striatum, compulsivity starts in the dorsal striatum. Usually the PFC suppresses these drives (willpower). So both could be a result of relaxation of this control by the PFC. Or they could be a result of too much pressure (stimuli) from the bottom up (ventral striatum or dorsal striatum). anatomically: impulsivity is an action outcome that's a ventrally dependent learning system. Compulsivity is a habit system that is a dorsally dependent learning system. Many behaviors start as impulses in the ventral loop of reward and motivation and then over time migrate dorsally due to neuroadaptions and neuroplasticity that form a habit which becomes compulsive. Going from 1 loop to another involves regulatory input from the hippocampus and amygdala (possibly why those with PTSD have higher addiction rates). - if you look at drug addiction it starts ventral and goes dorsal. The initial use is voluntary which is linked to impulsive personality traits but as they abuse the drug they lose control over drug seeking and taking behavior which becomes compulsive. The impulsive to take a drug initially gives a high but if this doesn't happen frequent enough there is a lack of triggering neuroplastic cascades from ventral to dorsal and this will remain under your control (you are occasionally bad). But if the impulsive drug use is repeated too often then it becomes a compulsion to reduce the sxs of withdrawal. The pleasure that using initially causes reduces over time requiring increased doses or more frequency. High impulsivity predisposes someone to develop compulsions quicker (switching over to habit learning loop quicker, if they have accelerated habit formation they may be at risk for addiction). Once you have a compulsion you are like Pavlov's dogs with an involuntary conditioned compulsion with willpower inadequate to interrupt destructive perseverations of the behavior (a compulsion). what is rebound? - ✔✔-the exaggerated expression of the original condition that some pts experience right after cessation of an effective tx. Explain the mesolimbic DA circuit as pathway of reward - ✔✔-Drugs that cause addition increase DA in the ventral striatum (NA). The mesolimbic DA pathway is overly active in addiction causing too much DA (interestingly this is also the case in schizophrenia and may be the reason for high comorbid SUD in schizophrenia). When you get natural highs (from accomplishments or sex) your body releases endorphins, anandamide (brains own marijuana), ACH (brains own nicotine), and DA (brains own cocaine and amphetamine). Drugs of abuse use the mesolimbic pathway to release DA to amounts not possible naturally. Impulsive-compulsive acts can also cause this release of DA causing addiction to these obsessions/compulsions. Over time with drugs of abuse though you start a cascade of neuroadaption in [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 07, 2022
Number of pages
14
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
179