1.Q :
The AGACNP is reviewing a chart of a head-injured patient. Which of the following would alert the
AGACNP for the possibility that the patient is over hydrated, thereby increasing the risk forincreased
intracrani
...
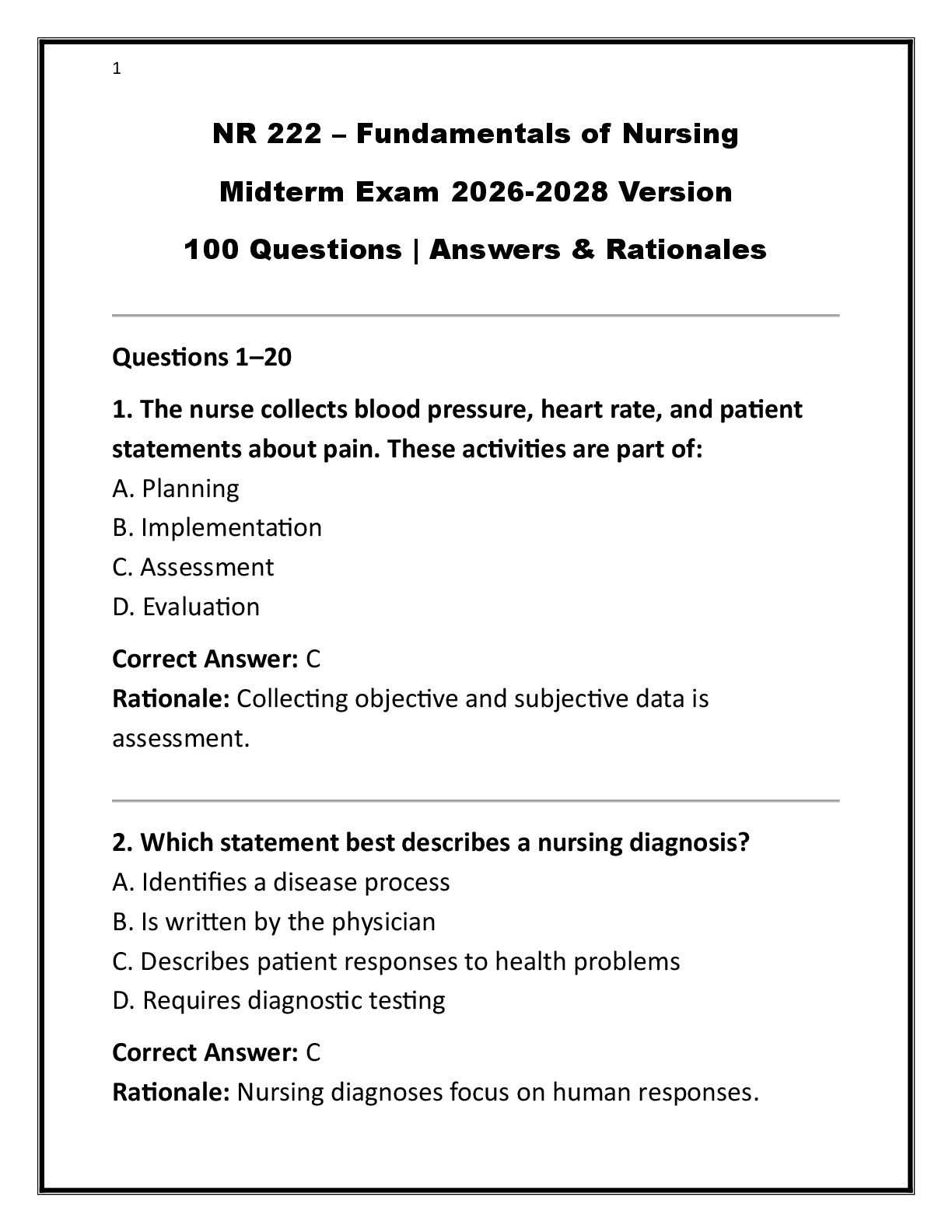
1.Q :
The AGACNP is reviewing a chart of a head-injured patient. Which of the following would alert the
AGACNP for the possibility that the patient is over hydrated, thereby increasing the risk forincreased
intracranial pressure?
A. BUN = 10
B. Shift output = 800 ml, shift input
=825 ml Unchanged weight
C. Serum osmolality = 260
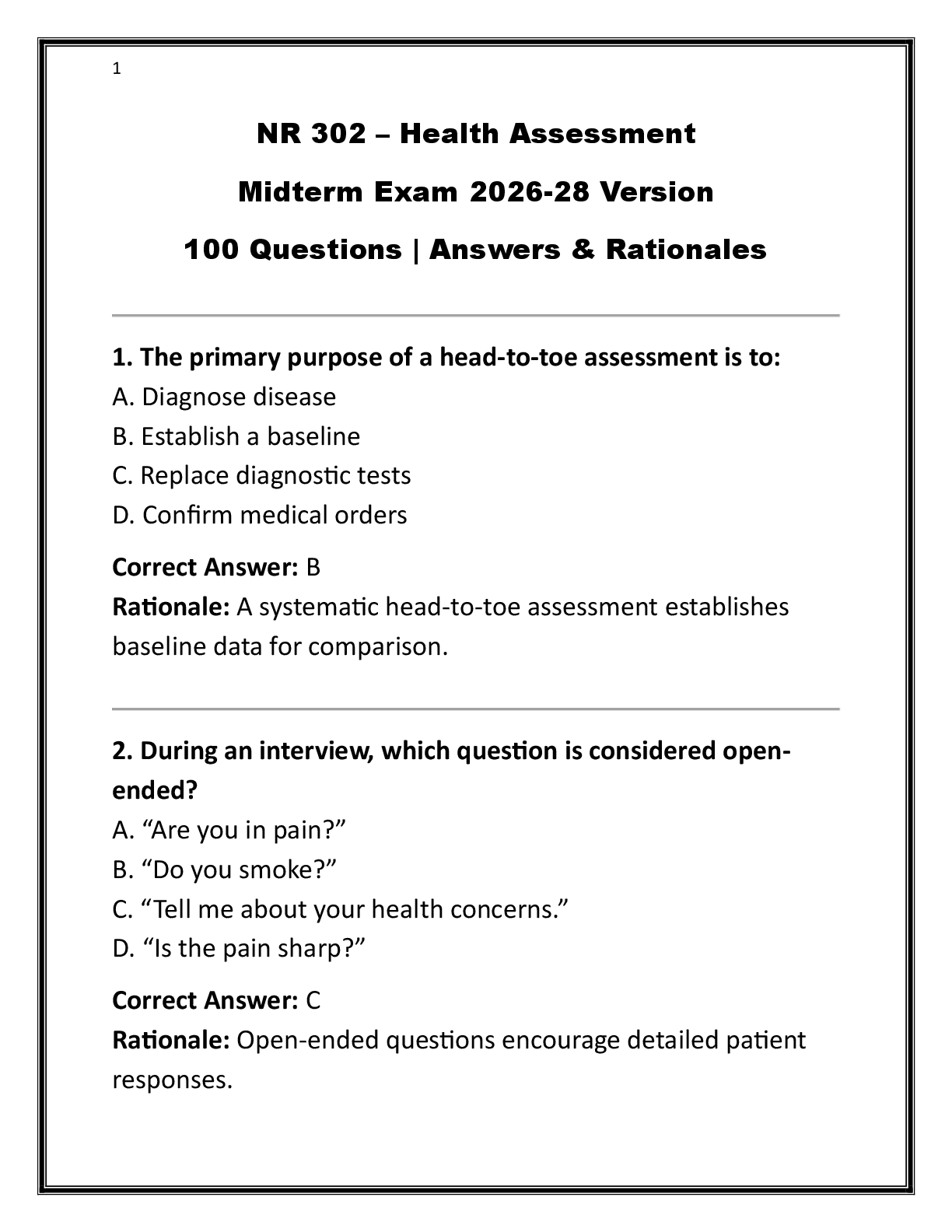
2. Q :
A patient who has been in the intensive care unit for 17 days develops hyponatremic hyperosmolality.
The patient weighs 132 lb (59.9 kg), is intubated, and is receiving mechanicalventilation. The serum
osmolality is 320 mOsm/L kg H2O. Clinical signs include tachycardia andhypotension. The adultgerontology acute care nurse practitioner's initial treatment is to:
A. reduce serum osmolality by infusing a 5% dextrose in
0.2%sodium chloride solution
B. reduce serum sodium concentration by infusing a 0.45%
sodiumchloride solution
C. replenish volume by infusing a 0.9% sodium chloride solution
D. replenish volume by infusing a 5% dextrose in water solution.
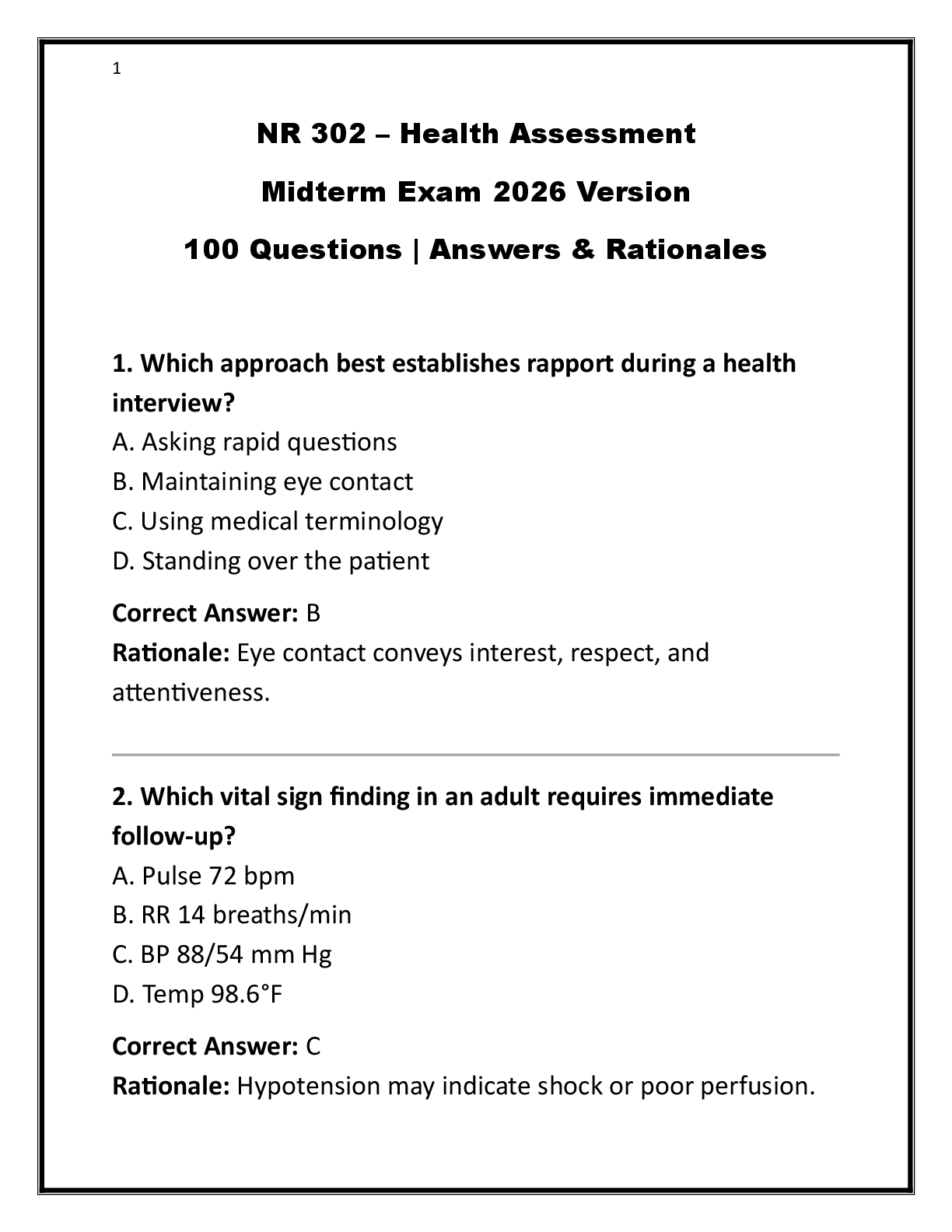
3. Q :
A 16-year-old male presents with fever and right lower quadrant discomfort. He complains of
nausea and has had one episode of vomiting, but he denies any diarrhea. His vital signs are
asfollows: temperature 101.9°F, pulse 100 bpm, respirations 16 breaths per minute, and blood
pressure 110/70 mm Hg. A complete blood count reveals a WBC count of 19,100 cells/µL. The
AGACNP expects that physical examination will reveal:
A. + Murphy’s sign
B. + Chvostek’s sign
C. + McBurney’s sign
D. + Kernig’s sign
4. Q :
Myasthenia gravis is best described as:
A. An imbalance of dopamine and acetylcholine in the
basal ganglia Demyelination of peripheral ascending
nerves
B. Demyelination in the central nervous system
C. An autoimmu
[Show More]
.png)