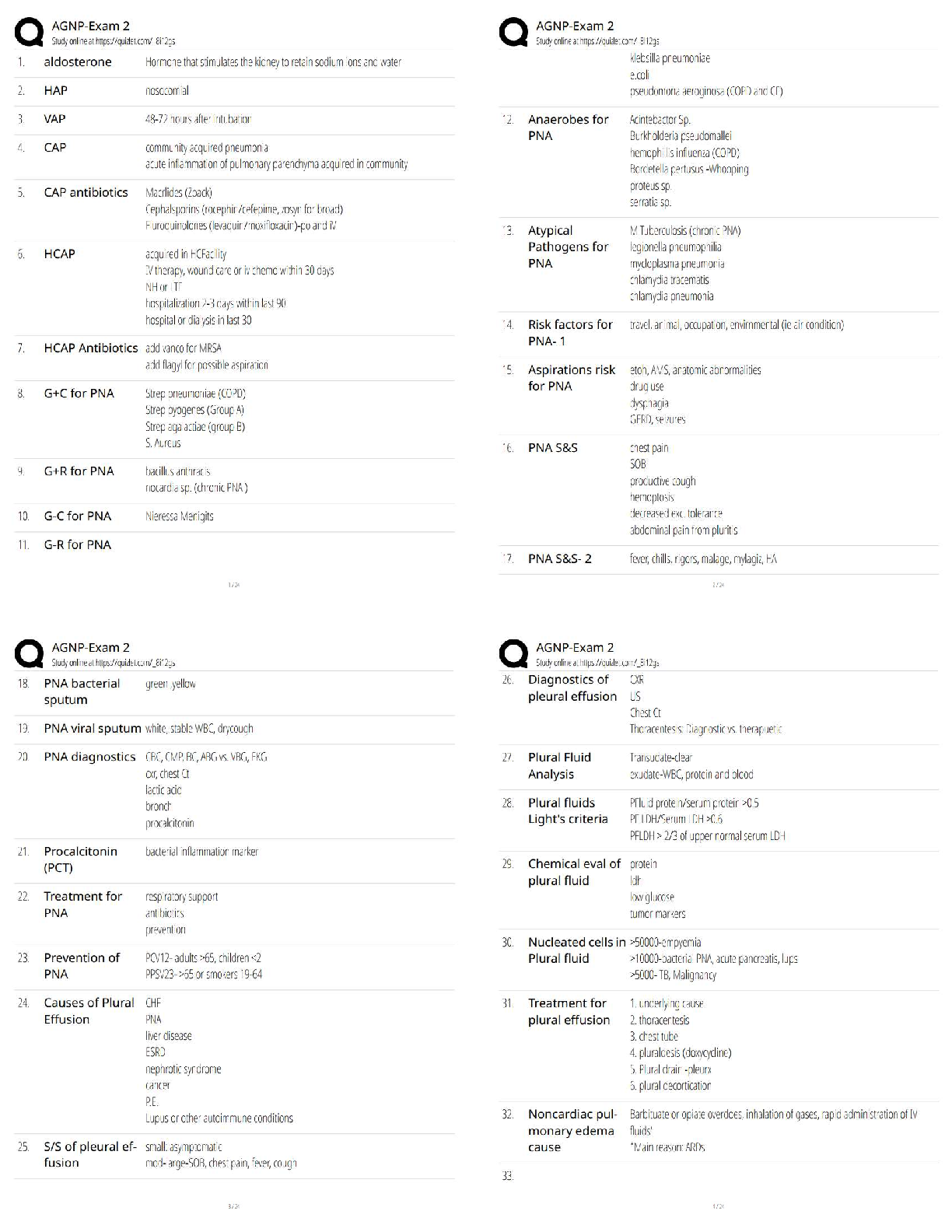
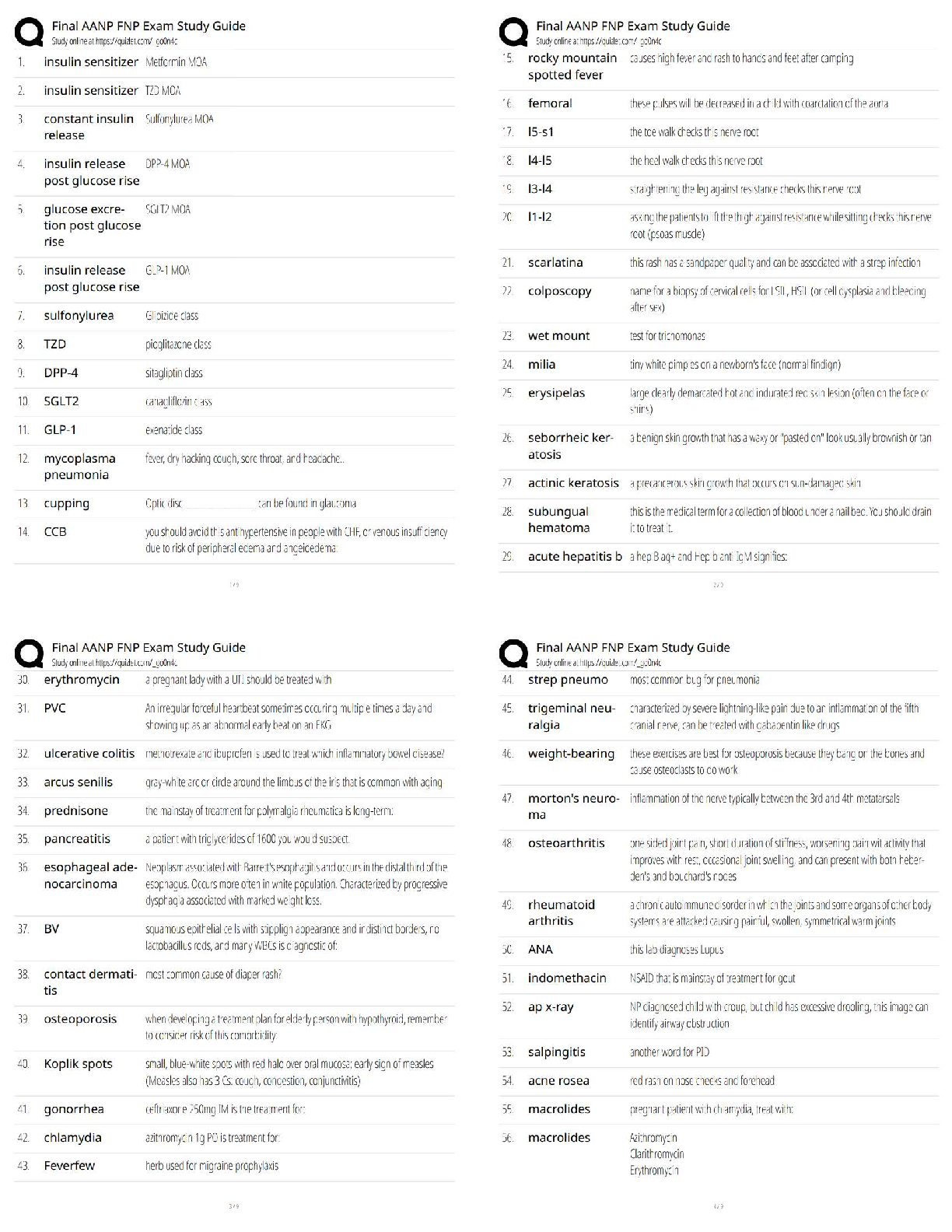
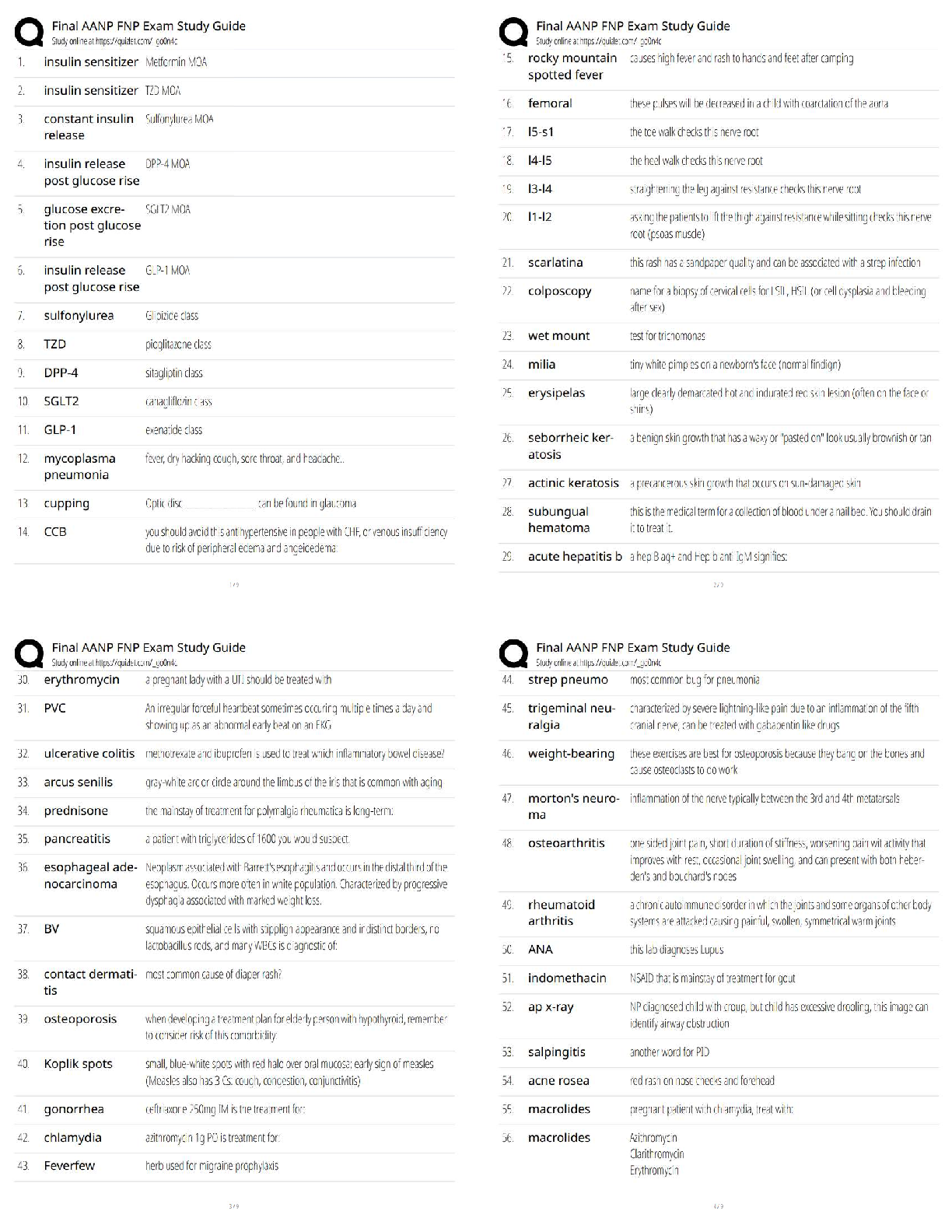
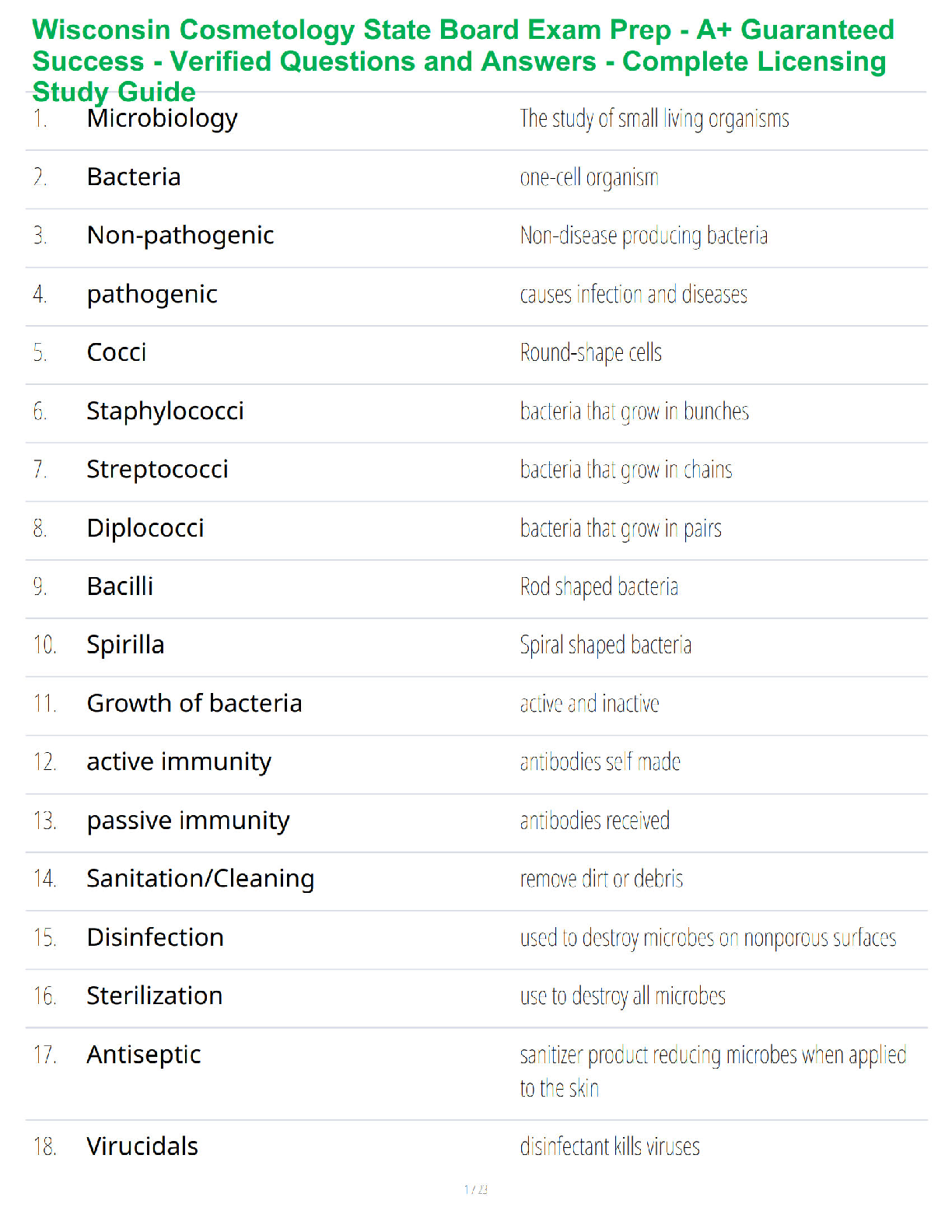
Name: ______RENSTREL LAXAMANA_______________ Date: ____OCT 16, 2020_________
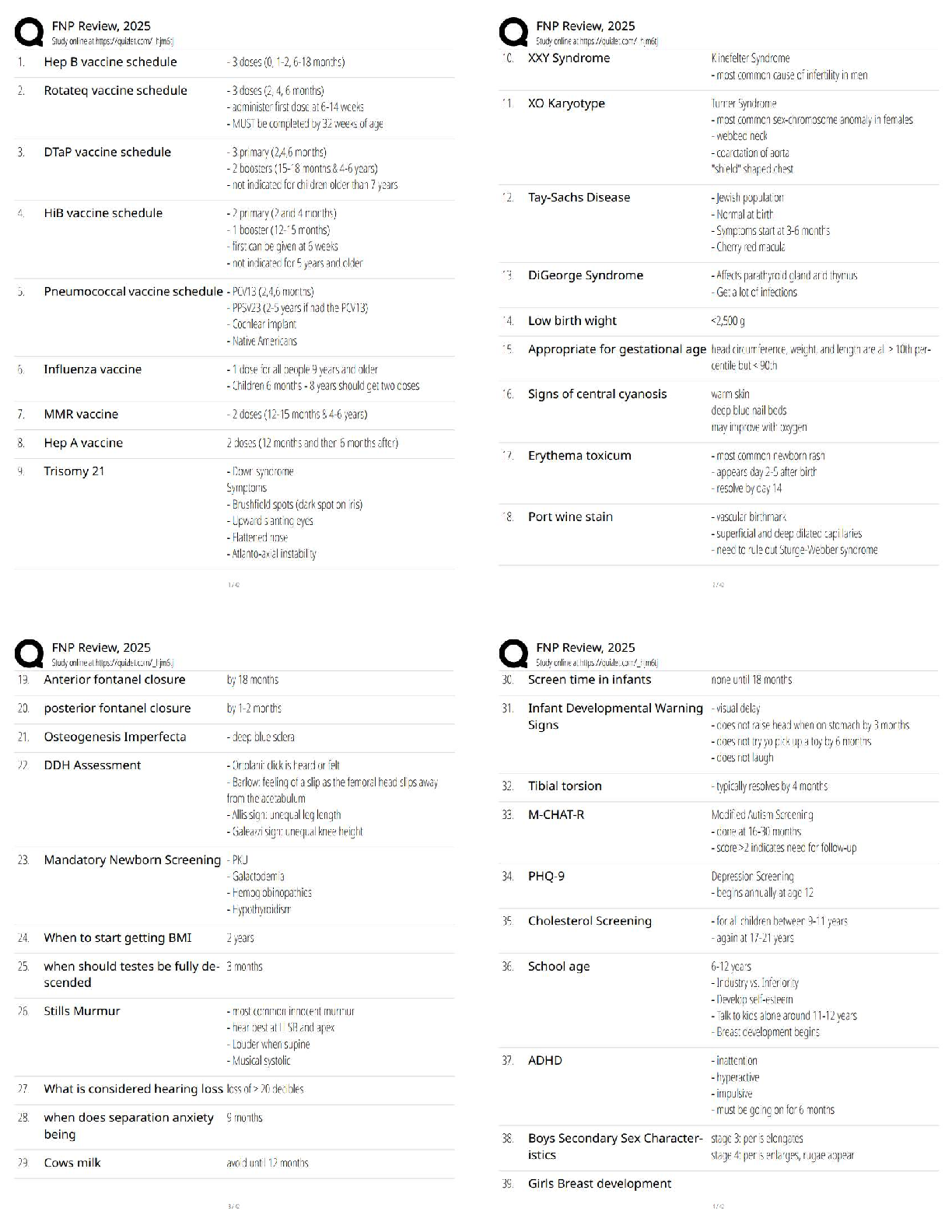
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
Vocabulary:atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule,
...
Name: ______RENSTREL LAXAMANA_______________ Date: ____OCT 16, 2020_________
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
Vocabulary:atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule,
electron configuration, Hund’s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion principle, period, shell, spin,subshell
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
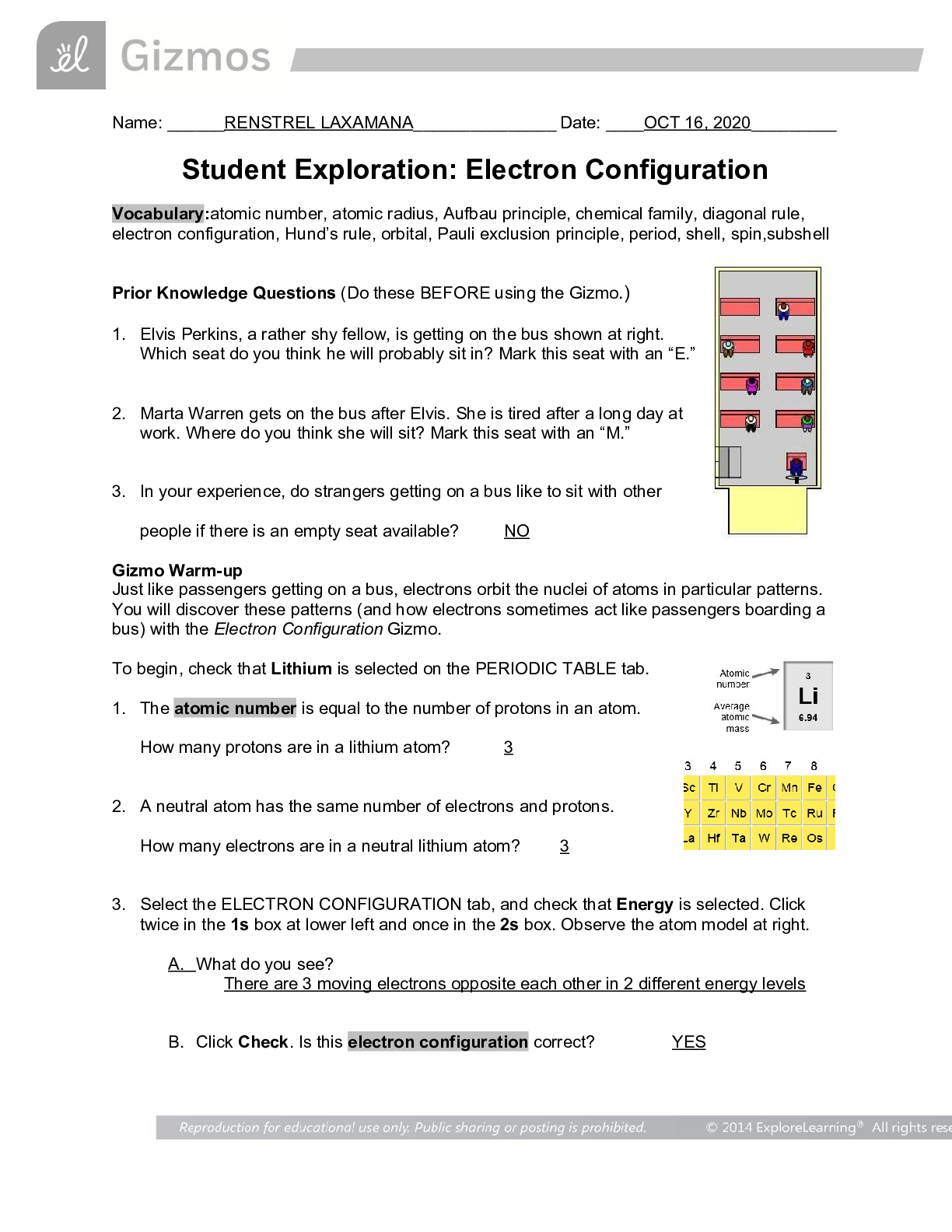
1. Elvis Perkins, a rather shy fellow, is getting on the bus shown at right.
Which seat do you think he will probably sit in? Mark this seat with an “E.”
2. Marta Warren gets on the bus after Elvis. She is tired after a long day at
work. Where do you think she will sit? Mark this seat with an “M.”
3. In your experience, do strangers getting on a bus like to sit with other
people if there is an empty seat available? NO
Gizmo Warm-up
Just like passengers getting on a bus, electrons orbit the nuclei of atoms in particular patterns.
You will discover these patterns (and how electrons sometimes act like passengers boarding a
bus) with the Electron Configuration Gizmo.
To begin, check that Lithium is selected on the PERIODIC TABLE tab.
1. The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an atom.
How many protons are in a lithium atom?
2. A neutral atom has the same number of electrons and protons.
How many electrons are in a neutral lithium atom?
3. Select the ELECTRON CONFIGURATION tab, and check that Energy is selected. Click
twice in the 1s box at lower left and once in the 2s box. Observe the atom model at right.
A. What do you see?
B. Click Check. Is this electron configuration correct?
Introduction: Electrons are arranged in orbitals, subshells, and shells. These levels of
organization are shown by the boxes of the Gizmo. Each box represents an orbital.
.
Question: How are electrons arranged in elements with atomic numbers 1 through 10?
Click Check. What is the electron configuration of hydrogen? 1s1
Lithium: Beryllium: Boron1
5. Arrange: Click Next element to select carbon. Add a second electron to the first 2porbital.
Click Check.What feedback is given? Electrons are not properly arranged in energy levels
6. Rearrange:Hund’s rule states that electrons will occupy an empty orbital when it is available
Activity A (continued from previous page)
7. Compare: How are the electrons in the 2p subshell similar to passengers getting on a bus?
8. Practice: In the spaces below, write and illustrate electron configurations for the next four
9. Apply: Atoms are most stable when their outermost shell is full. If their outermost shell is not
full, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until the shell fills up. While doing this,
10. Think and discuss: Select the PERIODIC TABLE tab, and look at the second row, or period,
of the table. How does this row reflect the subshells of the second shell?
The second row of the table indicates that the electrons are filled in the second energy
level of the atom and thus the atom may consists of up to two blocks of orbitals, the s and
the porbitals.
Question: How do the radii of atoms change across a period of the periodic table?
2. Arrange: Create a proper electron configuration for sodium. After clicking Check, note the
Electron configuration and the Atomic radius now listed at right.
check, and record the electron configuration and atomic radius below.
Magnesium electron configuration: _1s22s22p63s2__ Atomic radius: __145 picometers___
4. Gather data: Create electron configurations for the next six elements. Record the electron
configuration and atomic radius of each. (Note: The symbol for picometer is pm .)
5. Analyze: How does the atomic radius change across a period of the periodic table?
The atomic radius of an atom decreases across a period of the periodic table.
(Activity B continued on next page)
Activity B (continued from previous page)
6. Interpret: Select the ATOMIC RADIUS tab. What do you notice? There is a decreasing
pattern of the atomic radius of the graph as the atomic number increases.
7. Predict: On the ATOMIC RADIUS tab click Clear. Select the PERIODIC TABLE tab.
Elements in the same column of the periodic table are called chemical families, or groups.
How do you think the size of atoms will change from top to bottom within a chemical family?
8. Test: Hydrogen, lithium, and sodium are all in the same chemical family. Use the Gizmo to
find the atomic radius of each, and list them below.
9. Analyze: How does the atomic radius change as you go from the top to the bottom of a
chemical family? The atomic radius increases
10. Challenge: Think about the factors that control atomic radius and the patterns you’ve seen.
A. Why does the atomic radius decrease as electrons are added to a shell?
B. Why does the atomic radius increase as you go from the top to the bottom of a
chemical family?
11. Think and discuss: Compare the electron configurations of hydrogen, lithium, and sodium.
Why do you think these elements are grouped in the same family?
Question: How are the electron configurations of elements beyond argon determined?
1 .
What feedback is given? Electrons not placed in the correct energy levels
Is this configuration correct? YES What is the configuration? 1s22s22p63s23p64s1
3. Arrange: Click Next element and add an electron for calcium. Click Check.
What is the electron configuration for calcium? 1s22s22p63s23p64s2
4. Arrange:Click Next element and add an electron for scandium. Try different orbitals until
you find the right one. What is the configuration for scandium? 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1
5. Observe: Scandium is the first element to contain electrons in the dsubshell. How many
orbitals does the dsubshell have, and how many electrons can fit in the d subshell?
The d subshell have 5 orbitals and can fit 10 electrons.
6. Infer: Select the PERIODIC TABLE tab. The middle section of the table contains ten groups
that make up the transition metals. Why do you think this section is ten columns wide?
Because this section makes up the dblock which holds a maximum of 10 electrons.
Subshells are filled based on the energy level
(Activity C continued on next page)
Activity C (continued from previous page)
8. Make a rule: Next to Subshells ordered by, select
Number. The diagonal rule at right shows which subshell
will be filled next. To follow the rule, move down along an
arrow until you reach the end of the arrow. Then move to
the start of the next arrow to the right.
A. Which subshell is filled after
B. Which subshell is filled after
C. Which subshell is filled after
9. Practice: Determine the electron configurations of the following elements. Use the Gizmo to
check your work. (Note: In some cases, the diagonal rule doesn’t work perfectly. If you
submit a theoretically correct configuration, the Gizmo will give you the actual configuration.)
10. Infer: Select the PERIODIC TABLE tab. Earlier you saw that the transition metals represent
the filling of the d subshells. Now locate the purple lanthanides and actinides on the bottom
rows of the periodic table.
A. How many elements are in the lanthanides series? 14
B. Which subshell is represented by the lanthanides series? f
C. Which subshell is represented by the actinides series? f
D. In general, how does the shape of the periodic table relate to electron configuration?
The shape of the periodic table correlates on the how the electrons of an atom
are arranged.
[Show Less]
[Show More]