NG tube nursing considerations and interventions
- Assess for N/V increased abdominal distention, placement of tube.
at least every four hours, check NG tube for proper placement and tube patency and
output
monitor n
...
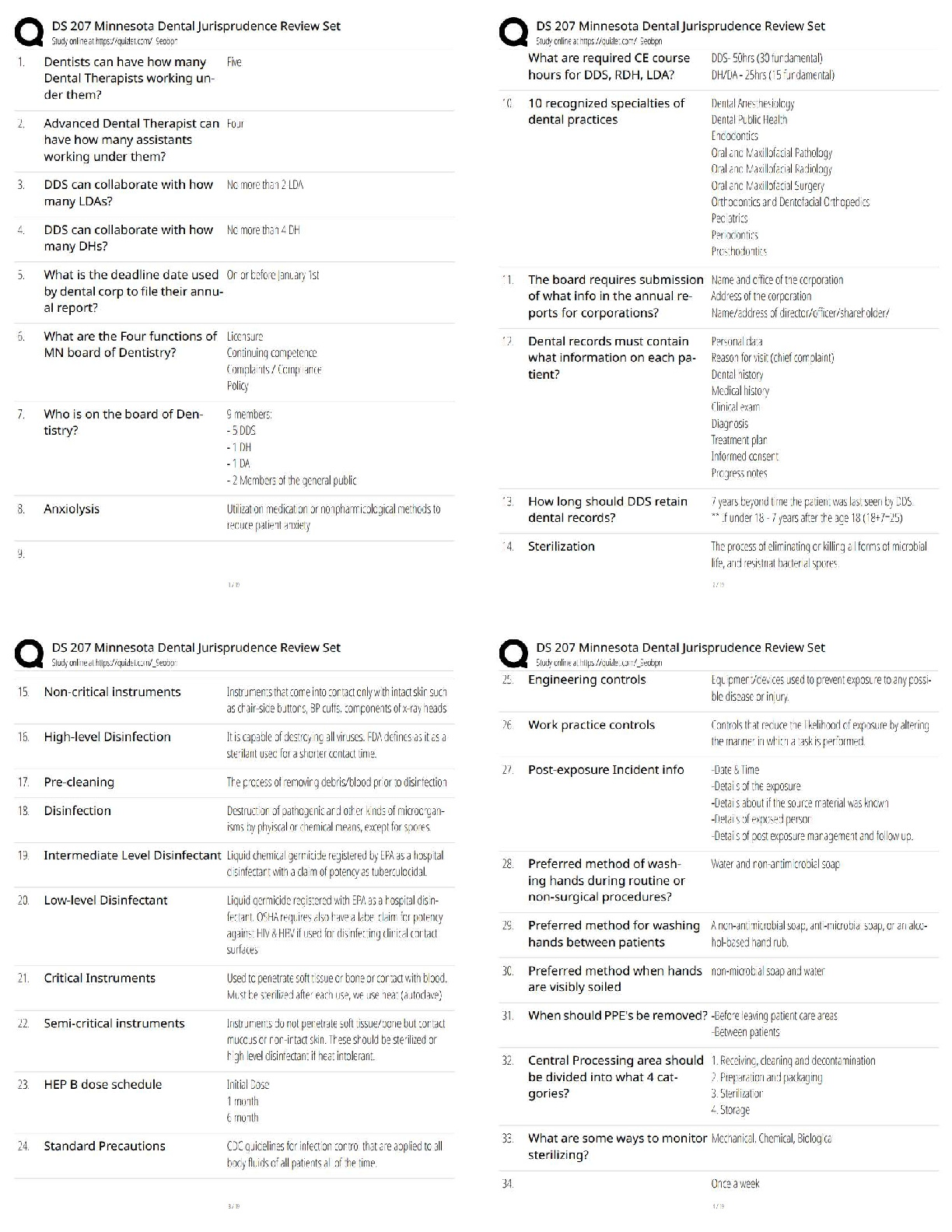
NG tube nursing considerations and interventions
- Assess for N/V increased abdominal distention, placement of tube.
at least every four hours, check NG tube for proper placement and tube patency and
output
monitor nasal skin for irritation
use a device that secures the tube to the nose to prevent accidental removal
assess for peristalsis by auscultating bowel sounds with the suction disconnected
(suction makes peristalsis sounds)
After placement: aspirate contents and irrigate the tube every 4 hours with 30mL of
saline, new bag every 24 hours
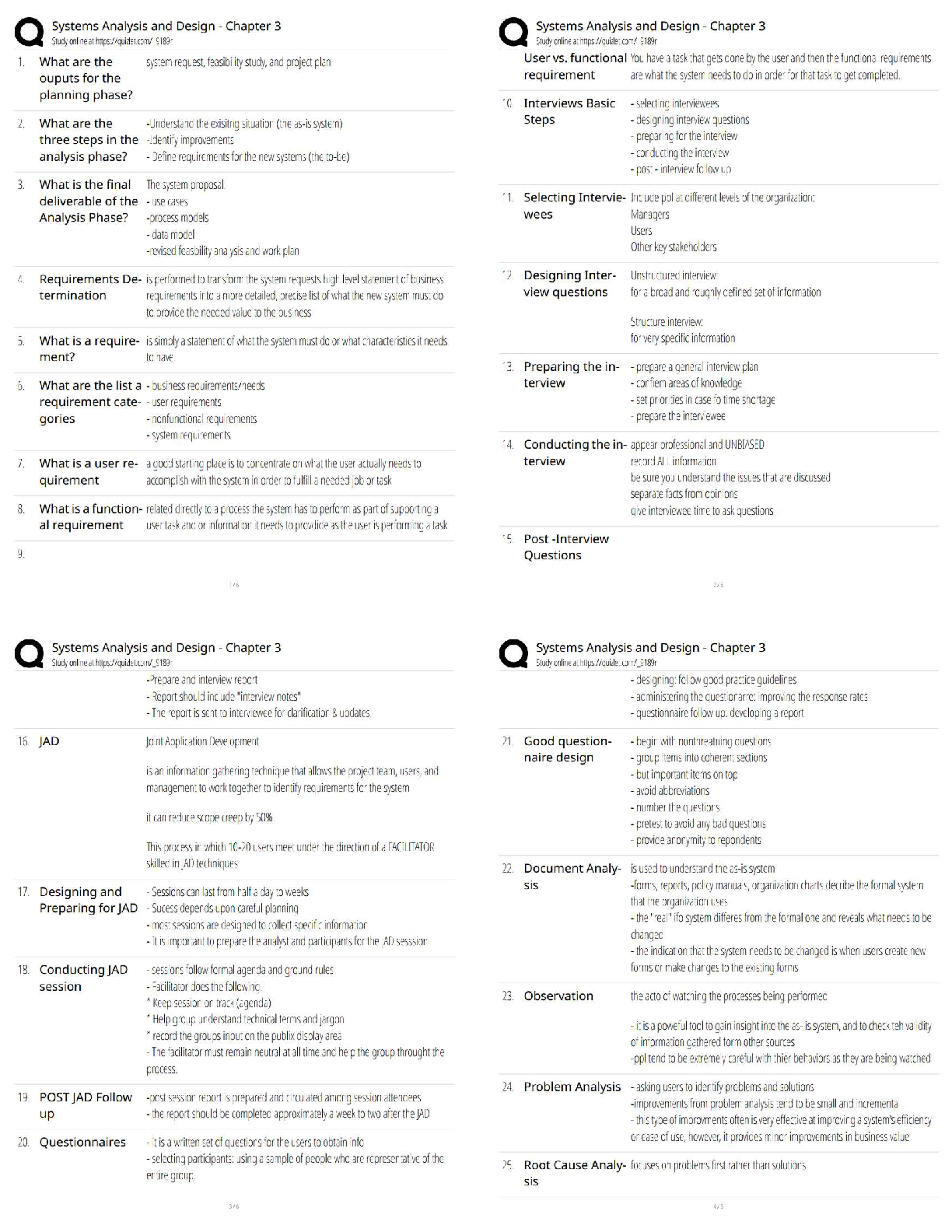
2. Ostomy nursing considerations/ education
- Measurement of stoma- measure every week
Cut hair around stoma
Appearance of normal stoma
Signs and symptoms of complication
Measurement of stoma
Nutrition: veggies cause gas
Protecting the stoma
Use mild soap to clean around stoma
3. Mechanical bowel obstruction
- caused from tumors, hernias, adhesions, vascular disorders, and fecal impaction
4. Non-mechanical bowel obstruction
- caused from neurogenic, physiologic, or chemical imbalances as a result of an MI,
shock, peritonitis, or hypokalemia
5. IBS s/sx and cause
- Chronic or recurrent diarrhea
Constipation
Abdominal pain
Bloating
Causes: The exact cause is unknown.
6. IBS assessment findings
- Ask patients about hx of weight change
Fatigue
Malaise
Abdominal pain or changes in bowel pattern
Ask if the patient has had or has any GI infections.
Ask about nutrition hx use of caffeine, beverages sweetened with sorbitol or fructose
can cause bloating or diarrhea.
Assess abdomen location, intensity, and quality of pain. The LLQ is usually where they
feel pain.
7. IBS tx
- Diet modification (Low residue-low fiber, high protein, high calorie)
Stress reduction
Medications such as bulk forming laxatives, antidiarrheal agents
8. GI bleed s/sx
- sharp, sudden, persistent, and severe epigastric or abdominal pain, bloody or black
stools, bloody vomit or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
9. GI bleed causes
- Alcohol or tobacco use
Increased stress
Dietary habits
History of H. Pylori, GI surgery
Prescription or OTC drugs
10. GI bleed assessment
- epigastric tenderness, dyspepsia (indigestion), rigid board like abdomen with rebound
tenderness and pain, assess for fluid volume deficit
11. GI bleed tx
- Drug therapy
Nutrition therapy
Complementary therapy
Nonsurgical-Monitor patient carefully & immediately report changes to HCP, monitor
hematocrit, hemoglobin, lavage? PPIs, histamine antagonists, antacids
Surgical-NG tube, endoscopic therapy (clot to stop bleeding)
12. Anal rectal abscess
- Develops from collection of pus in rectal
[Show More]






 Exit Exam Brand New Questions and Answers Guaranteed Pass With A+ Score.png)
 exit exam – Brand New Q As! Guaranteed Pass w-A+ Actual Screenshots w-Questions & Answers Included!!! Test Taken 4-11-2022 (I scored 1162!!!).png)


.png)


.png)
.png)