uworld NCLEX Questions AND ANSWERS
2. Increasing temperature, decreasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing blood pressure
A change in vital signs may be a late sign of increased intracranial pressure. Tren
...
uworld NCLEX Questions AND ANSWERS
2. Increasing temperature, decreasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing blood pressure
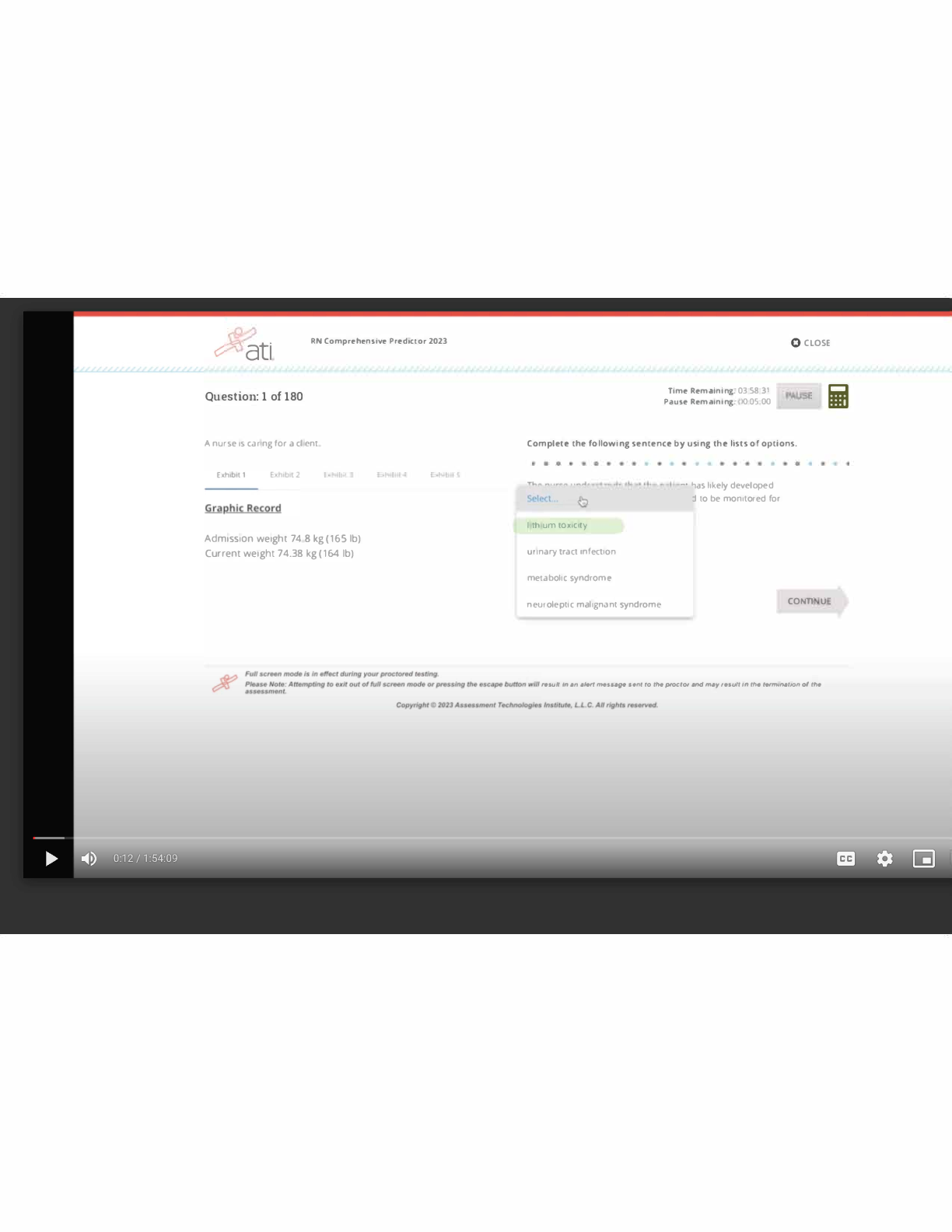
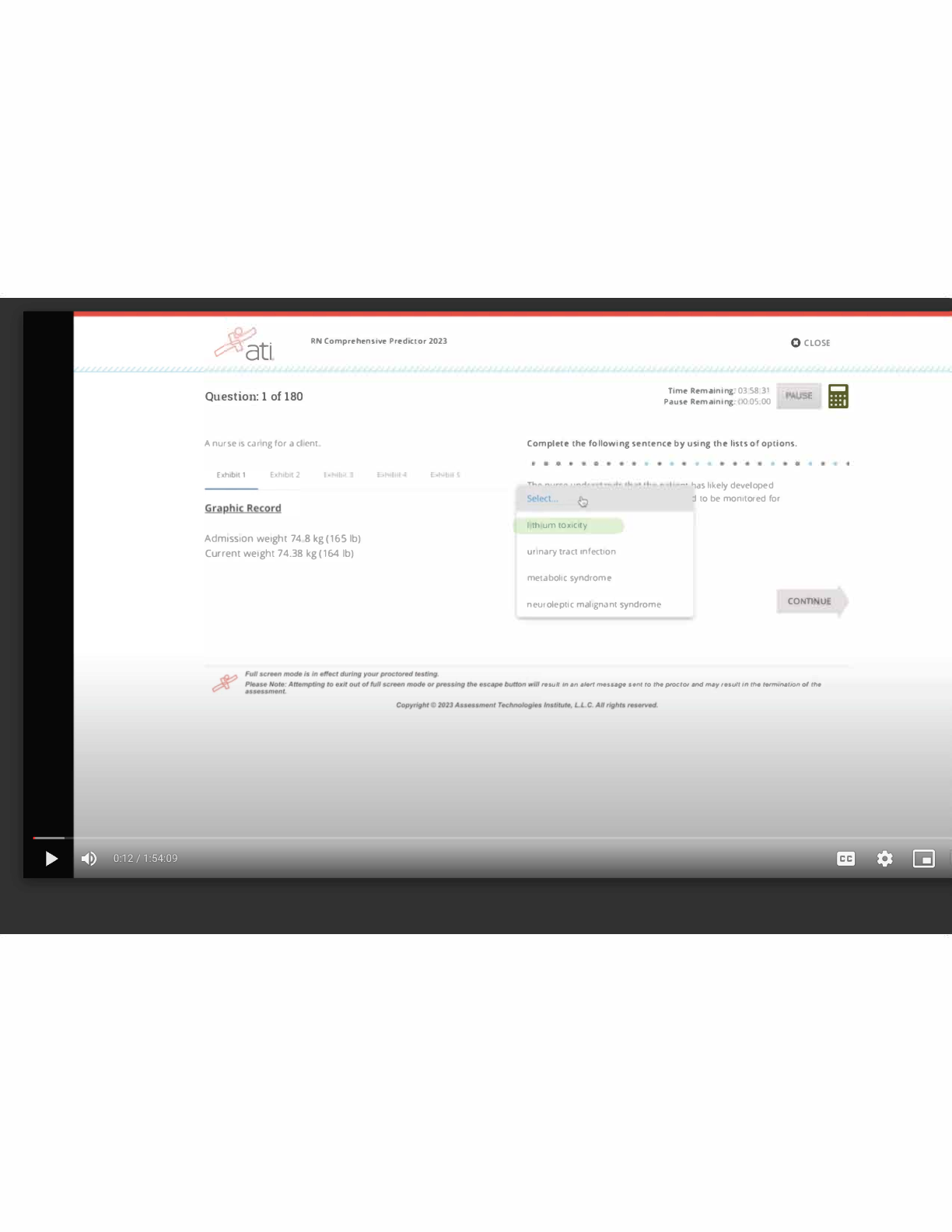
A change in vital signs may be a late sign of increased intracranial pressure. Trends include increasing temperature and blood pressure and decreasing pulse and respirations. Respiratory irregularities also may occur. Correct Answer: The nurse is caring for the client with increased intracranial pressure. The nurse would note which trend in vital signs if the intracranial pressure is rising?
1. Increasing temperature, increasing pulse, increasing respirations, decreasing blood pressure
2. Increasing temperature, decreasing pulse, decreasing respirations, decreasing blood pressure
3. Decreasing temperature, decreasing pulse, increasing respirations, decreasing blood pressure
4. Decreasing temperature, increasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing blood pressure
2, 3, 4
The nurse should maintain ICP by elevating the head of the bed 15 - 20 degrees and monitoring neurologic status. An ICP >15 mmHg with 20 to 25 mmHg as upper limits of normal indicates increased ICP, and the nurse should notify the HCP. Coughing and range of motion exercises will increase ICP and should be avoided in the early postoperative stage. Correct Answer: The nurse has established a goal to maintain intracranial pressure (ICP) within the normal range for a client who had a craniotomy 12 hours ago. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
1. Encourage the client to cough to expectorate secretions.
2. Elevate the head of the bed 15 - 20 degrees.
3. Contact the HCP if ICP is >15 mmHg.
4. Monitor neurologic status using the Glasgow Coma Scale.
5. Stimulate the client with active range-of-motion exercises.
3
The clear drainage must be analyzed to determine whether it is nasal drainage or CSF. The nurse should not give the client tissues because it is important to know how much leakage of CSF is occurring. Compressing the nares will obstruct the drainage flow. It is inappropriate to tilt the head back, which would allow the fluid to drain down the throat and not be collected for a sample. It is inappropriate to administer an antihistamine because the drainage may not be from postnasal drip. Correct Answer: What should the nurse do first when a client with a head injury begins to have clear drainage from the nose?
1. Compress the nares
2. Tilt the head back
3. Collect the drainage
4. Administer an antihistamine for postnasal drip
4
Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the ears or nose may accompany basilar skull fractures. CSF can be distinguished from other body fluids because the drainage will separate into bloody and yellow concentric rings on dressing material, called a halo sign. The fluid also tests positive for glucose. Correct Answer: A client has clear fluid leaking from the nose following a basilar skull fracture. Which finding would alert the nurse that cerebrospinal fluid is present?
1. Fluid is clear and tests negative for glucose.
2. Fluid is grossly blood in appearance and has a pH of 6
3. Fluid clumps together on the dressing and had a pH of 7
Fluid separates into concentric rings and tests positive for glucose.
1, 2, 4
Hemiparesis is a weakness of one side of the body that may occur after a stroke. It involves weakness of the face and tongue, arm, and leg on one side. These clients are also aphasic: unable to discriminate words and letters. They are generally very cautions and get anxious when attempting a new task. Complete bilateral paralysis does not occur in hemiparesis. The client with right-sided hemiparesis has weakness of the right arm and leg and needs assistance with feeding, bathing, and ambulating. Correct Answer: The nurse is assigned to care for a client with complete right-sided hemiparesis from a stroke. Which characteristics are associated with this condition? Select all that apply.
1. The client is aphasic.
2. The client has weakness on the right side of the body.
3. The client has complete bilateral paralysis of the arms and legs.
4. The client has weakness on the right side of the face and tongue.
5. The client has lost the ability to move the right arm but is able to walk independently
6. The client has lost the ability to ambulate independently, but is able to feed and bathe himself or herself without assistance.
4
Homonymous hemianopsia is loss of half of the visual field. The client with homonymous hemianopsia should have objects placed in the intact field of vision, and the nurse also should approach the client from the intact side. The nurse instructs the client to scan the environment to overcome the visual deficit and does client teaching from within the intact field of vision. The nurse encourages the use of personal eyeglasses, if they are available. Correct Answer: The nurse has instructed the family of a client with stroke who has homonymous hemianopsia about measures to help the client overcome the deficit. Which statement suggests that the family understand the measures to use when caring for the client?
1. We need to discourage him from wearing eyeglasses.
2. We need to place objects in his impaired field of vision.
3. We need to approach him from the impaired field of vision.
4. We need to remind him to turn his head to scan the lost visual field.
3
Thrombolytic enzyme agents are used for clients with a thrombotic stroke to dissolve emboli, this reastablishing cerebral perfusion. They do not increase vascular permeability, cause vasoconstriction, or prevent further hemorrhage. Correct Answer: What is the expected outcome of thrombolytic drug therapy for stroke?
1. Increased vascular permeability
2. Vasoconstriction
3. Dissolved emboli
4. Prevention of hemorrhage
3, 1, 4, 2
To protect the client from falling, the nurse first should ease the client to the floor. It is important to protect the head and maintain a patent airway since altered breathing and excessive salivation can occur. The assessment of the postictal period should include level of consciousness and vital signs. The nurse should record details of the seizure once the client is stable. The events preceding the seizure, timing with descriptions of each phase, body parts affected and sequence of involvement, and autonomic signs should be recorded. Correct Answer: The nurse sees a client walking in the hallway who begins to have a seizure. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
1. Maintain a patent airway.
2. Record the seizure activity observed.
3. Ease the client to the floor.
4. Obtain vital signs.
1, 2, 5, 6
Seizure precautions may vary from agency to agency, but they generally have some common features. Usually, an airway, oxygen, and suctioning equipment are kept available at the bedside. The side rails of the bed are padded, and the bed is kept in the lowest position. The client has an intravenous access in place to have a readily accessible route if antiseizure medications must be administered, and as part of the routine assessment the nurse should be checking the patency of the catheter. The use of padded tongue blades is highly controversial, and they should not be kept at the bedside. Forcing a tongue blade into the mouth during a seizure more likely will harm the client who bites down during seizure activity. Risks include blocking the airway from improper placement,
[Show More]