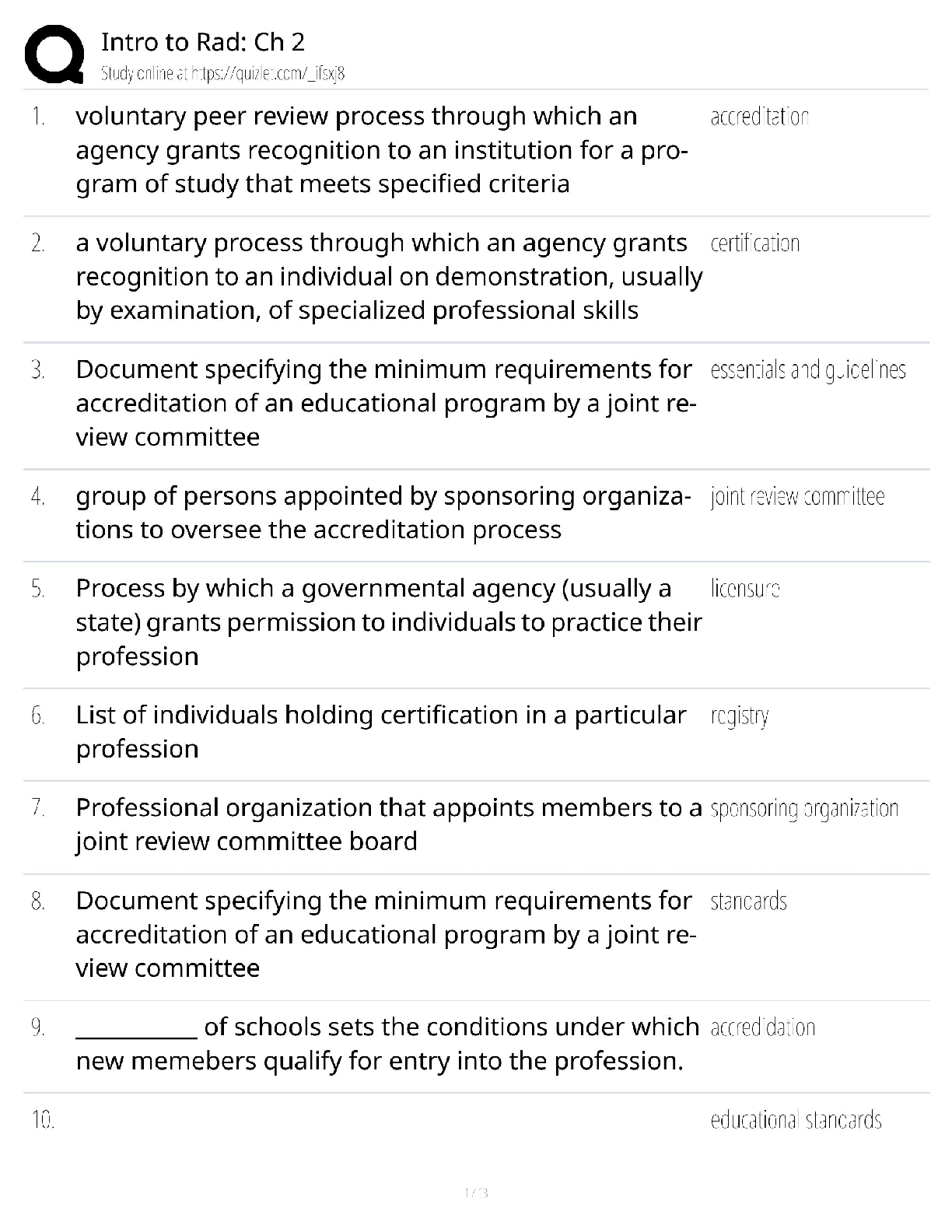
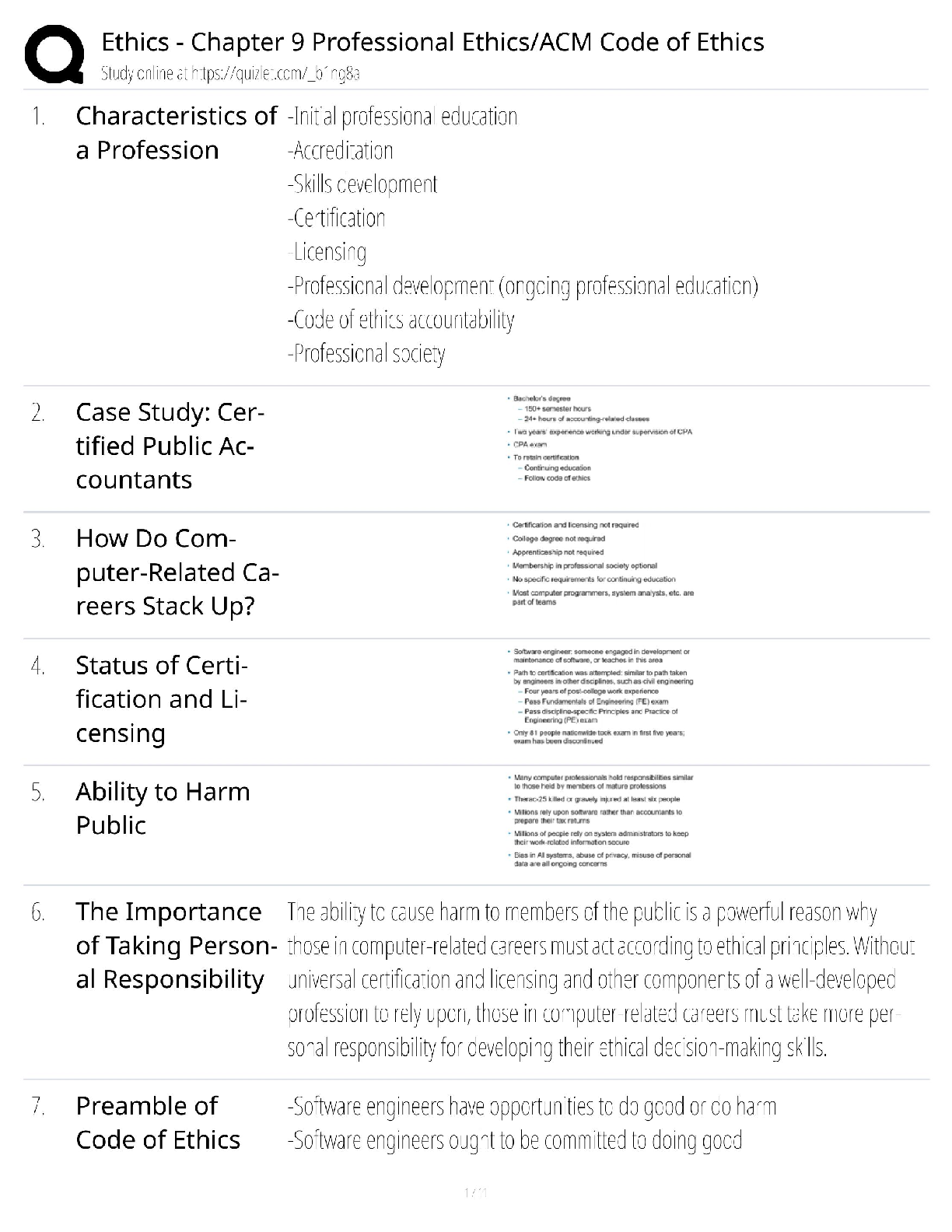
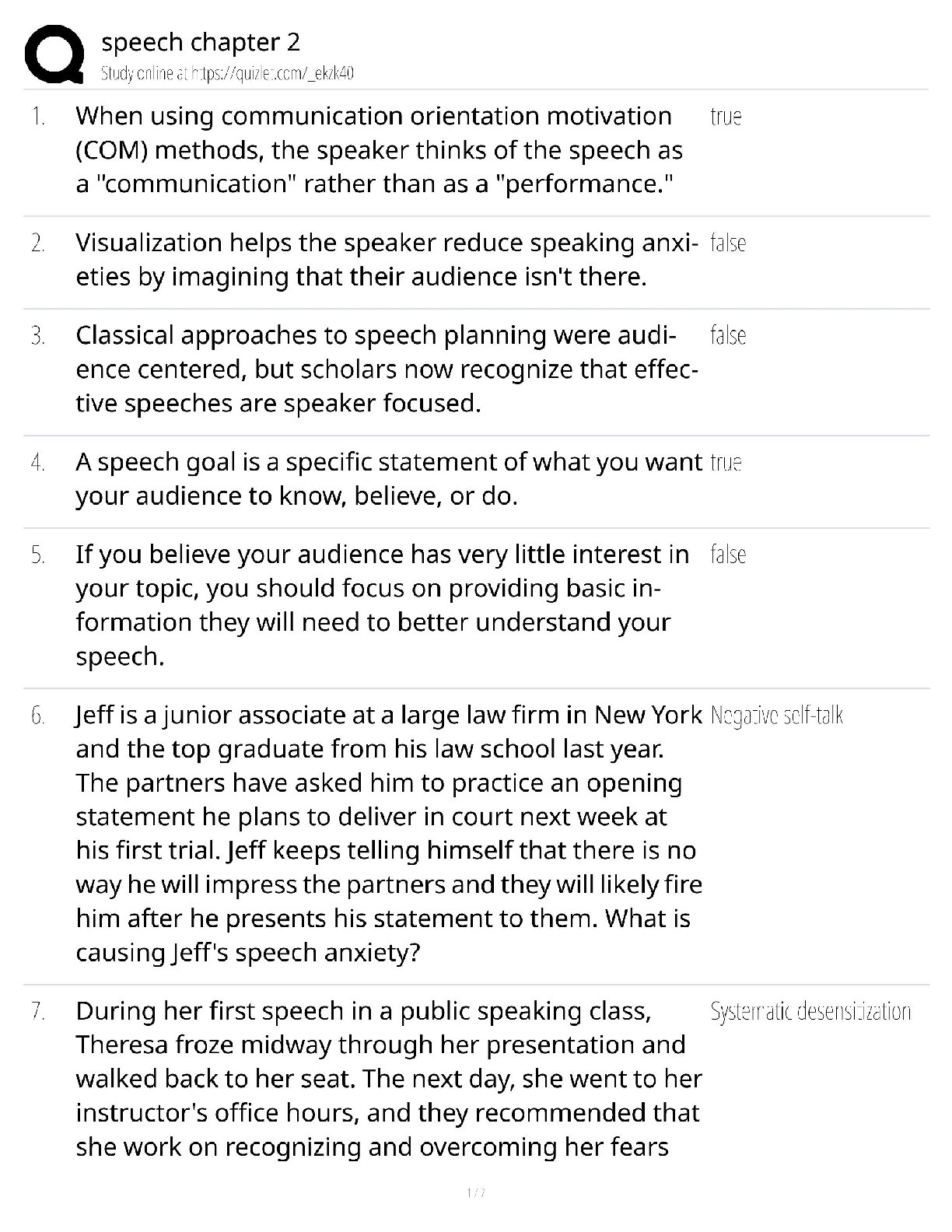
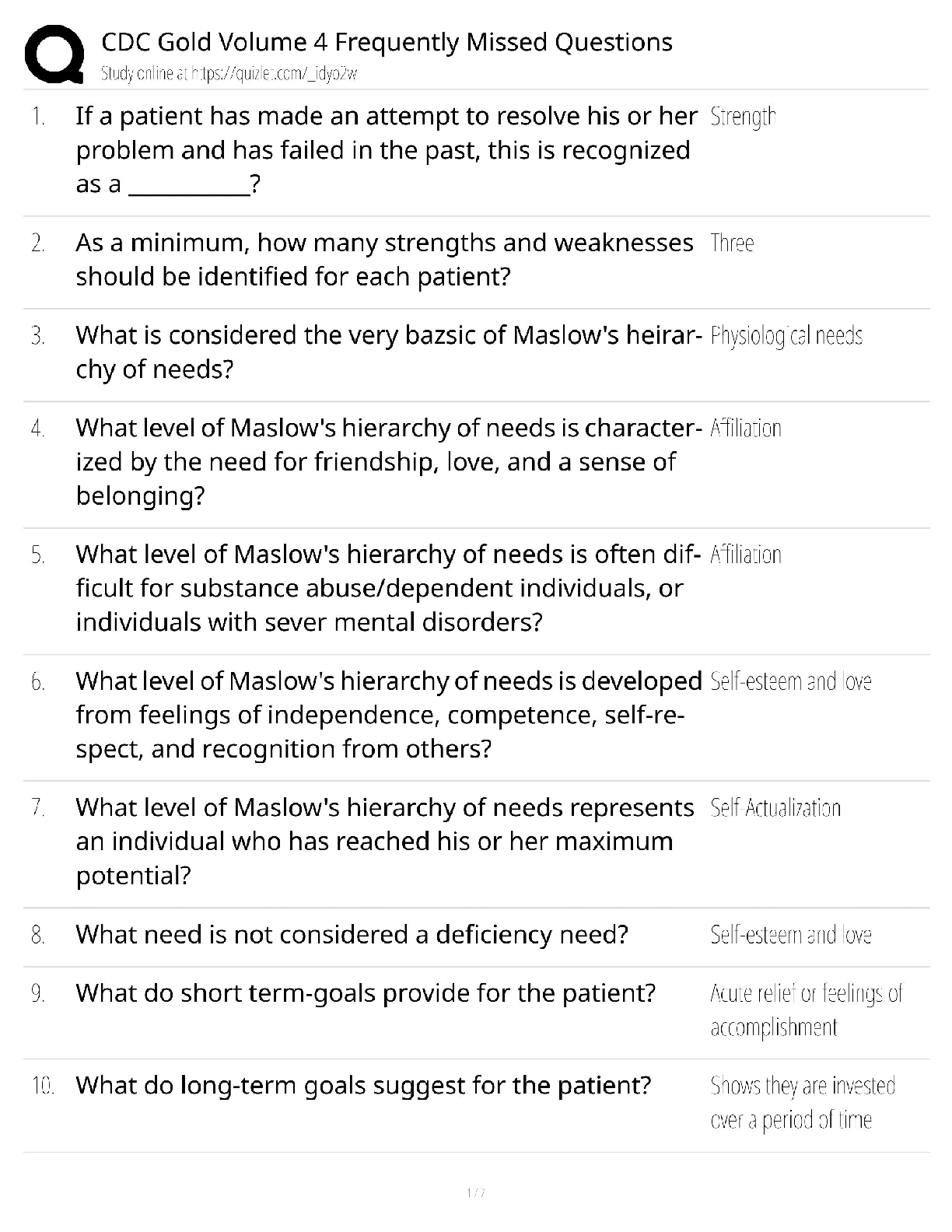
*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > TMC Practice Exam Questions and answers, Latest Update, 100% pass rate. (All)
TMC Practice Exam Questions and answers, Latest Update, 100% pass rate.
Document Content and Description Below
TMC Practice Exam Questions and answers, Latest Update, 100% pass rate. A 48 year-old female is admitted to the ED with diaphoresis, jugular venous distension, and 3+ pitting edema in the ankles. ... These findings are consistent with A. liver failure. B. pulmonary embolism. C. heart failure. D. electrolyte imbalances - ✔✔Heart failure A patient is admitted to the ED following a motor vehicle accident. On physical exam, the respiratory therapist discovers that breath sounds are absent in the left chest with a hyperresonant percussion note. The trachea is shifted to the right. The patient's heart rate is 45/min, respiratory rate is 30/min, and blood pressure is 60/40 mm Hg. What action should the therapist recommend first? A. Call for a STAT chest x-ray. B. Insert a chest tube into the left chest. C. Needle aspirate the 2nd left intercostal space. D. Activate the medical emergency team to intubate the patient. - ✔✔Needle aspirate the 2nd left intercostal space. All of the following strategies are likely to decrease the likelihood of damage to the tracheal mucosa EXCEPT A. maintaining cuff pressures between 20 and 25 mm Hg. B. using the minimal leak technique for inflation. C. using a low-residual-volume, low-compliance cuff. D. monitoring intracuff pressures. - ✔✔monitoring intracuff pressures. A 52 year-old post-operative cholecystectomy patient's breath sounds become more coarse upon completion of postural drainage with percussion. The respiratory therapist should recommend A. continuing the therapy until breath sounds improve. B. administering dornase alpha. C. administering albuterol therapy. D. deep breathing and coughing to clear secretions. - ✔✔deep breathing and coughing to clear secretions. A 65 kg spinal cord injured patient has developed atelectasis. His inspiratory capacity is 30% of his predicted value. What bronchial hygiene therapy would be most appropriate initially? A. IS / SMI B. IPPB with normal saline C. postural drainage and percussion D. PEP therapy - ✔✔IPPB with normal saline A patient on VC ventilation has demonstrated auto-PEEP on ventilator graphics. Which of the following controls, when adjusted independently, would increase expiratory time? 1. Tidal volume 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Inspiratory flow 4. Sensitivity - ✔✔1, 2, and 3 only Which of the following would be the most appropriate therapy for a dyspneic patient who has crepitus with tracheal deviation to the left and absent breath sounds on the right? A. Perform chest physiotherapy B. Administer an IPPB treatment C. Insert an endotracheal tube D. Insert a chest tube - ✔✔Insert a chest tube A 55 year-old post cardiac surgery patient has the following ABG results: pH 7.50, PaCO2 30 torr, PaO2 62 torr, HCO3 25 mEq/L, SaO2 92%, HB 14 g/dL, BE +2. Venous blood gas results are pH 7.39, PvCO2 43 torr, PvO2 37 torr, and SvO2 66%. Calculate the patient's C(a-v)O2. A. 2.5 vol% B. 4.0 vol% C. 5.0 vol% D. 5.5 vol% - ✔✔5.0 vol% A patient on VC, SIMV with a VT of 500 mL has a PIP of 25 cm H2O, Pplat of 15 cm H2O and PEEP of 5 cm H2O. What is the patient's static lung compliance A. 25 mL/cm H2O B. 35 mL/cm H2O C. 45 mL/cm H2O D. 50 mL/cm H2O - ✔✔50 mL/cm H2O Immediately after extubation of a patient in the ICU, the respiratory therapist observes increasing respiratory distress with intercostal retractions and marked stridor. The SpO2 on 40% oxygen is noted to be 86%. Which of the following would be most appropriate at this time? A. cool mist aerosol treatment B. aerosolized racemic epinephrine C. manual ventilation with resuscitation bag and mask D. reintubation - ✔✔reintubation Which of the following patients would most likely benefit from pressure support ventilation? A. An intubated patient with an absent respiratory drive. B. A patient on SIMV with a set rate of 12/min and total rate of 24/min. C. A patient with acute lung injury. D. A patient who requires short-term post-operative ventilatory support. - ✔✔A patient on SIMV with a set rate of 12/min and total rate of 24/min. A patient receiving mechanical ventilation has developed a temperature of 99.9° F with purulent secretions over the last 12 hours. The respiratory therapist has also noted a steady increase in peak inspiratory pressure. What initial recommendation should be made to address these changes? A. Initiate bronchial hygiene therapy. B. Obtain a sputum gram stain. C. Administer IPV. D. Insert a CASS tube. - ✔✔Obtain a sputum gram stain. Which of the following information may be obtained from a FVC maneuver during bedside pulmonary function testing? 1. FEV1 2. PEFR 3. FRC 4. RV - ✔✔1 and 2 only The respiratory therapist is providing patient education for a patient who is being discharged home on aerosol therapy. The most important reason for the patient to follow the recommended cleaning procedures using a vinegar/water solution is that this solution will A. sterilize the equipment. B. retard bacterial growth. C. kill all micro-organisms and spores. D. extend the equipment life. - ✔✔Retard bacterial growth A patient who complains of dyspnea is noted to have a dry, non-productive cough. On physical examination, breath sounds are diminished on the right, tactile fremitus is decreased and there is dullness to percussion over the right lower lobe. The respiratory therapist should suspect that the patient is suffering from A. pneumonia. B. pulmonary embolism. C. pleural effusion. D. bronchiolitis. - ✔✔pleural effusion Which of the following suction catheters would be appropriate to use for a patient with a size 8.0 mm ID endotracheal tube? A. 8 Fr B. 10 Fr C. 12 Fr D. 14 Fr - ✔✔12 Fr A patient who is receiving continuous mechanical ventilation is fighting the ventilator. His breath sounds are markedly diminished on the left, there is dullness to percussion on the left, and the trachea is shifted to the left. The most likely explanation for the problem is that A. the patient is disconnected from the ventilator. B. the patient is experiencing diffuse bronchospasm. C. the endotracheal tube has slipped into the right main stem bronchus. D. the patient has developed a left tension pneumothorax. - ✔✔the endotracheal tube has slipped into the right main stem bronchus The respiratory therapist notes a developing hematoma after an arterial blood gas was drawn from the right radial artery. The immediate response is to A. notify the charge nurse. B. apply a pressure dressing. C. apply pressure to the site. D. perform a modified Allen's test. - ✔✔apply pressure to the site. A patient's breathing pattern irregularly increases and decreases and is interspersed with periods of apnea up to 1 minute. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of this problem? A. Diabetes insipidus B. Renal failure C. Metabolic acidosis D. Elevated intracranial pressure - ✔✔Elevated intracranial pressure What value for the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) is consistent with mild obstructive sleep apnea? A. Less than 5 B. 5 to 15 C. 16 to 30 D. Greater than 30 - ✔✔5 to 15 While monitoring a newborn utilizing a transcutaneous monitor, you notice a change in PtcO2 from 60 to 142 torr and simultaneously the (PtcCO2) changes from 37 to 2 torr. What is the most likely explanation for these changes? A. Upper airway obstruction B. Poor peripheral perfusion C. Air leak around the sensor D. Device is out of range - ✔✔Air leak around the sensor A patient on the general medical ward is on a 28% air entrainment mask with the flowmeter set at 5 L/min. What is the total flow delivered to the patient? A. 5 L/min B. 55 L/min C. 88 L/min D. 140 L/min - ✔✔55/Lmin Which of the following measurements is most indicative of pulmonary edema? A. Heart rate of 120/min B. Blood pressure of 92/72 mm Hg C. Pulmonary artery pressure of 25/10 mm Hg D. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure of 30 mm Hg - ✔✔Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure of 30 mm Hg Sleep apnea can be defined as repeated episodes of complete cessation of airflow for A. 5 seconds or longer. B. 10 seconds or longer. C. 15 seconds or longer. D. 20 seconds or longer. - ✔✔10 seconds or longer A patient in the ICU receiving mechanical ventilation has just undergone a fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedure in which a tissue biopsy was collected. Immediately following the procedure, the respiratory therapist notes that the peak inspiratory pressure on the ventilator has increased. Potential causes for this include all of the following EXCEPT A. hypoxemia. B. pneumothorax. C. pulmonary hemorrhage. D. bronchospasm/laryngospasm. - ✔✔hypoxemia What size endotracheal tube would be appropriate for an adult female patient? A. 6.0 to 6.5 mm B. 6.5 to 7.0 mm C. 7.0 to 7.5 mm D. 7.5 to 8.0 mm - ✔✔7.0 to 7.5 mm The respiratory therapist has been asked to measure Auto-PEEP on a patient receiving mechanical ventilation. In order to do this, the therapist should A. initiate an inspiratory hold just after the next ventilator-delivered breath. B. initiate an expiratory hold just prior to the next ventilator-delivered breath. C. subtract Pplat from Pdyn. D. subtract set PEEP from the measured Pplat. - ✔✔initiate an expiratory hold just prior to the next ventilator-delivered breath. A patient who suffered trauma in an ATV accident is being monitored in the ICU. A pulmonary artery catheter has been placed and the following data is available: PvO2 46 torr PCWP 19 mm Hg PAP (mean) 10 mm Hg CVP 12 cm H2O Cardiac Output 3L/min The respiratory therapist should recommend 1. IV fluid challenge 2. positive inotropic agent 3. inhaled nitric oxide 4. diuretic therapy - ✔✔2 and 4 What is the primary advantage of volume-controlled ventilation as compared to pressure-controlled ventilation? A. VC limits and controls PIP. B. VC provides a constant minute ventilation. C. VC ensures better patient-ventilator synchrony. D. VC delivers a decelerating flow pattern. - ✔✔VC provides a constant minute ventilation. Bronchial breath sounds heard over the lung periphery indicate A. narrowed airways. B. obstructed bronchi. C. lung consolidation. D. pulmonary edema. - ✔✔lung consolidation. During a pre-operative evaluation, bedside spirometry results are as follows: FVC 88% of predicted, FEV1 85% of predicted, FEV1/FVC 82% of predicted and FEF25-75 81% of predicted. How should the respiratory therapist interpret these results? A. a mild restrictive disorder B. a mild obstructive disorder C. normal lung function D. mixed obstructive/restrictive disorder - ✔✔normal lung function A 55 year-old male patient is being evaluated for pulmonary rehabilitation. During a cycle ergometer cardiopulmonary stress procedure, the patient has a heart rate of 100/min and a respiratory rate of 20/min. He suddenly begins to complain of chest pain and severe shortness of breath. The respiratory therapist should A. reduce the speed of the bike. B. administer supplemental oxygen. C. gradually reduce the workload and monitor closely. D. terminate the procedure immediately. - ✔✔terminate the procedure immediately. At 1 minute post-delivery, a newborn has blue extremities with a pink body, heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 20/min with a weak cry, cough reflex is present, and there is some flexion of the extremities. At 5 minutes post-delivery, the infant is completely pink, heart rate is 140/min, respiratory rate is 40/min, cough reflex is present, and the baby is active with a strong cry. What APGAR scores should be assigned? A. 4 & 8 B. 5 & 9 C. 5 & 10 D. 6 & 10 - ✔✔6 & 10 The respiratory therapist is asked to administer 2.5 mg of albuterol to a patient via small volume nebulizer. The medication is available in a 0.5% solution. What volume of albuterol should be administered? A. 0.25 mL B. 0.50 mL C. 1.25 mL D. 2.5 mL - ✔✔0.50 mL After consulting on management of a patient with pneumonia and atelectasis, the pulmonologist has documented in the Progress Notes a need to change the patient's treatment regimen. The respiratory therapist should A. continue the current treatment plan. B. report the change in treatment plan to the next shift. C. check the electronic medical record for new physician orders. D. disregard the information until notified by the shift supervisor. - ✔✔check the electronic medical record for new physician orders. A 60 kg (132 lb) patient is being mechanically ventilated with the following settings: VC, A/C; VT 500 mL, respiratory rate 12/min, FIO2 1.00 and 10 cm H2O PEEP. The patient's peak airway pressure is 60 cm H2O and his SpO2 is 85%. A current chest x-ray shows diffuse bilateral infiltrates. Which of the following is the most appropriate action in order to reduce peak airway pressure? A. Increase the frequency. B. Change to airway pressure release ventilation. C. Decrease the inspiratory time. D. Increase PEEP to 15 cm H2O. - ✔✔Change to airway pressure release ventilation. In order to verify the accuracy of a lab-based spirometer device, the respiratory therapist should utilize a A. rotameter. B. 3.0 L syringe. C. Wright respirometer. D. pneumotachometer. - ✔✔3.0 L syringe. While performing diagnostic chest percussion, the respiratory therapist notes decreased resonance to percussion. Which of the following are potential causes of this finding? 1. pneumothorax 2. pleural effusion [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 44 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

TMC EXAM BUNDLE, QUESTIONS WITH ACCURATE ANSWERS
ALL VERSIONS OF TMC EXAM PAPERS, BUNDLED QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS, LATEST UPDATES
By bundleHub Solution guider 3 years ago
$38
16
Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 25, 2022
Number of pages
44
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 25, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
101