Financial Accounting > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MANAGEMENT 301 Supply Chain Management (SCM) midterm Exam Questions and Answers. 100% Correct. (All)
MANAGEMENT 301 Supply Chain Management (SCM) midterm Exam Questions and Answers. 100% Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
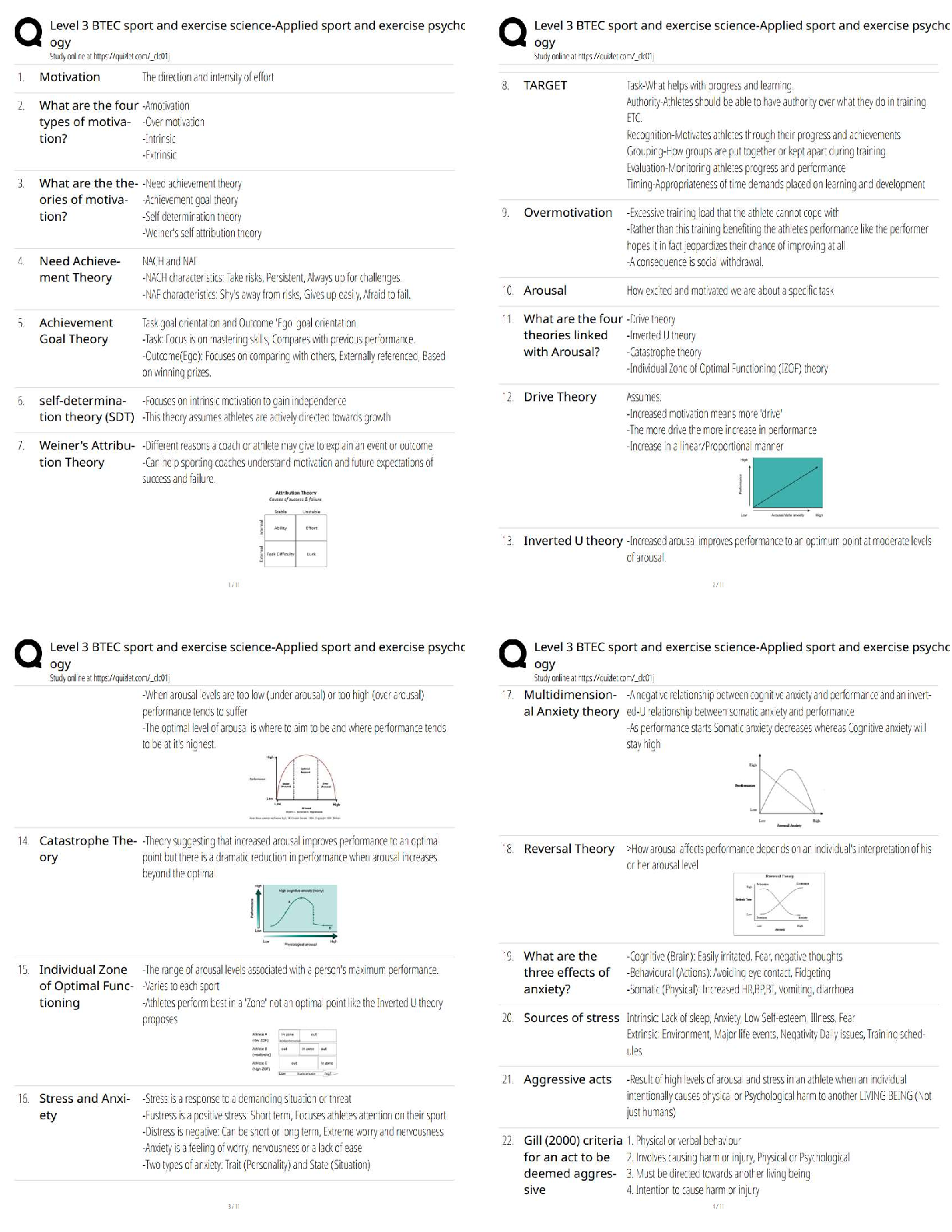
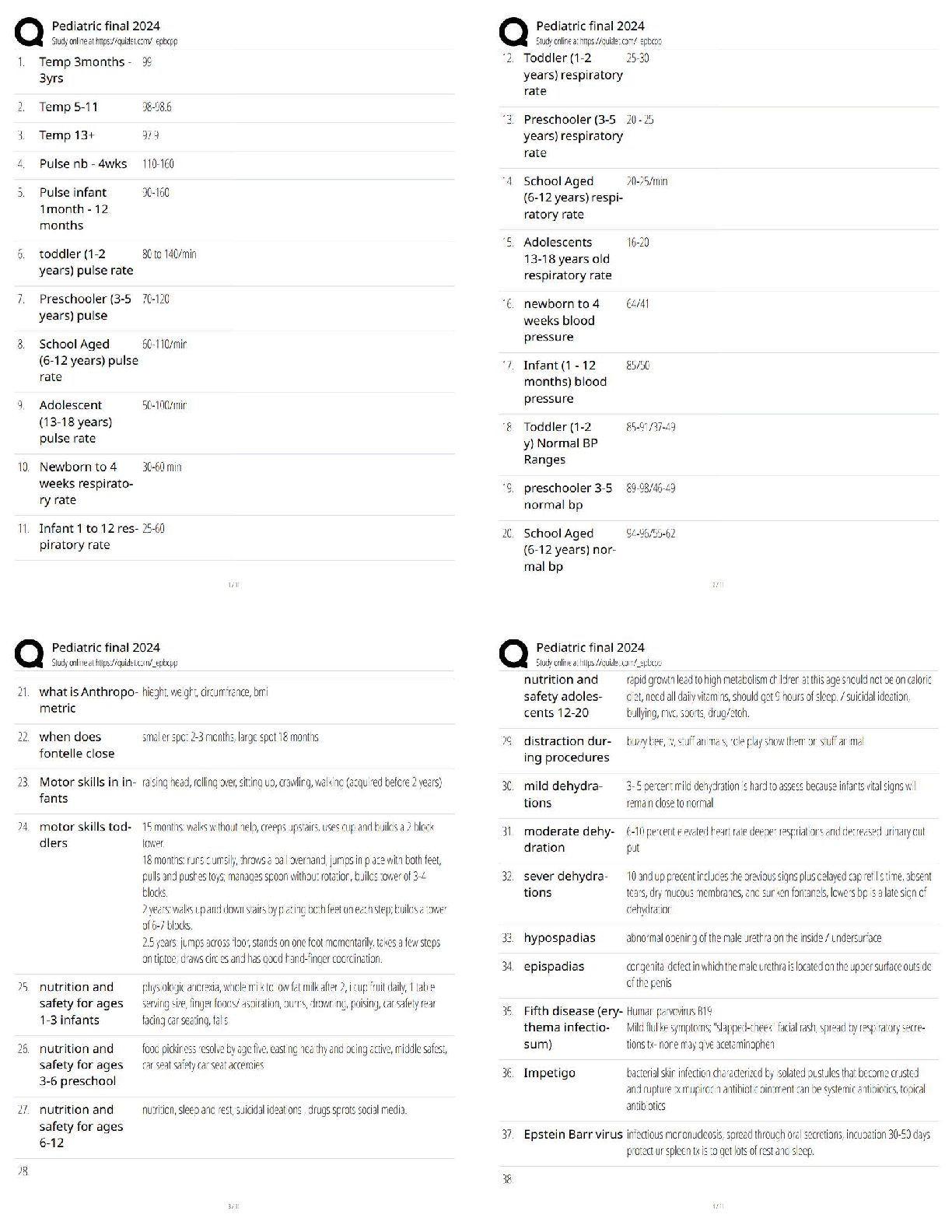
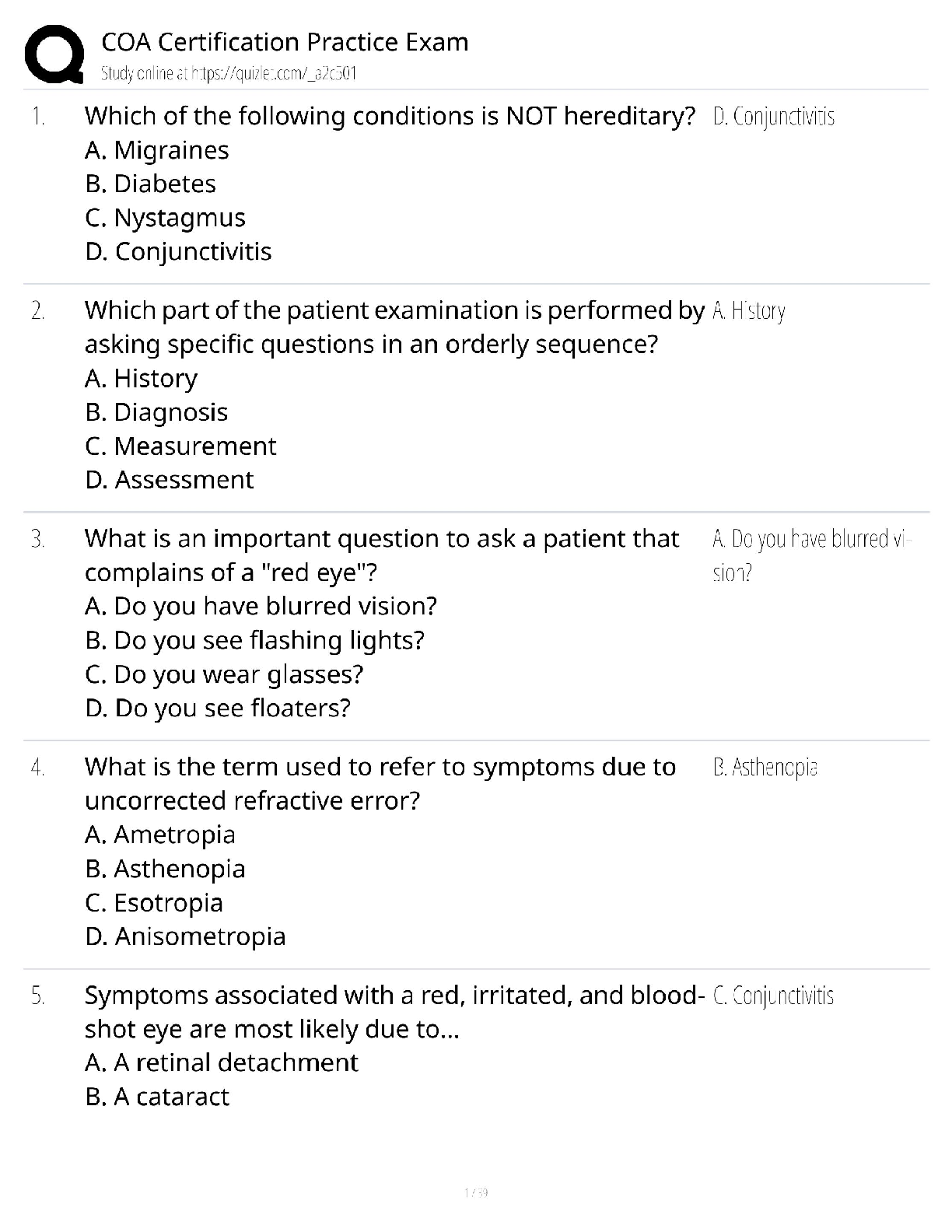
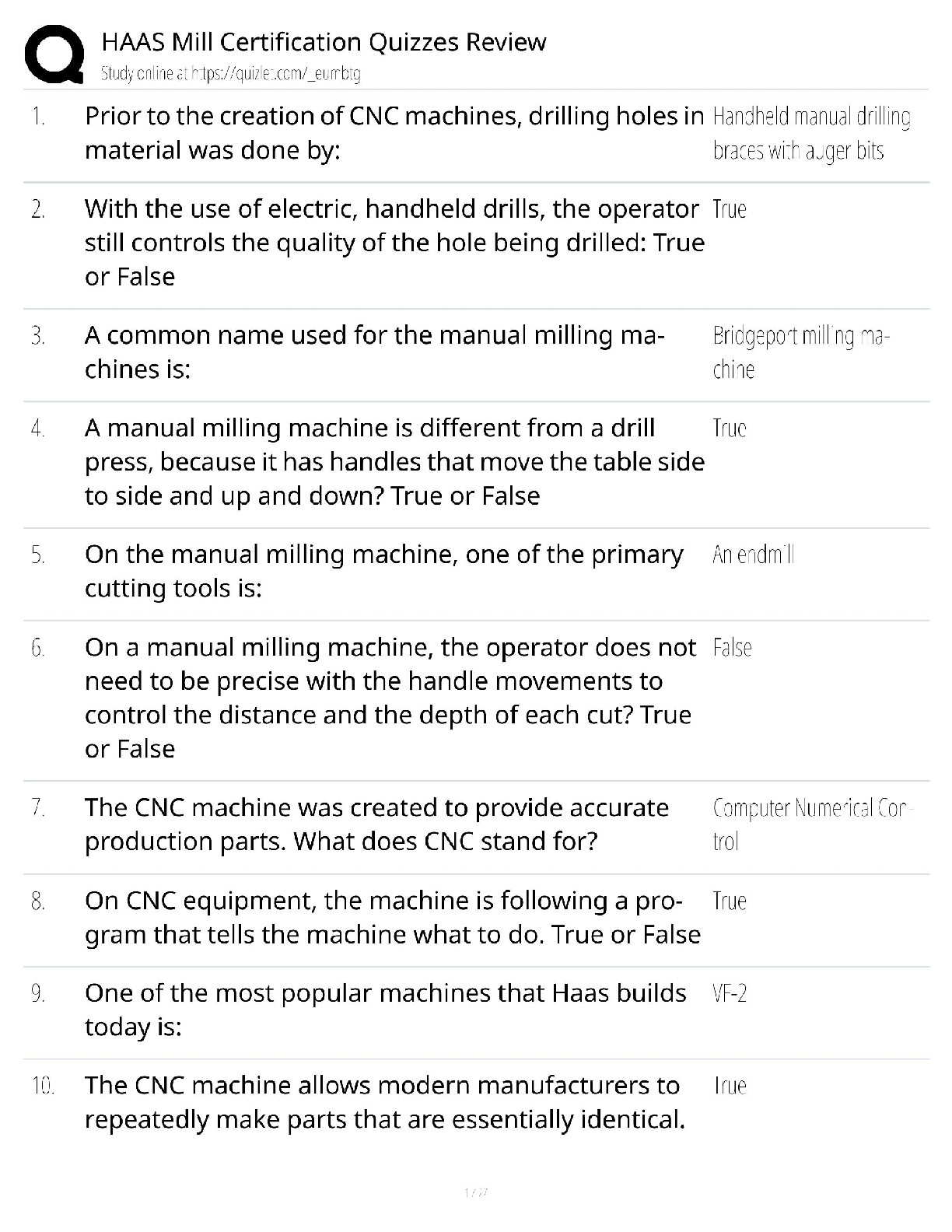
MANAGEMENT 301 Supply Chain Management (SCM) midterm Exam Questions and Answers 1. Which of the following is an illustration of a company that has vertically integrated? a. A computer manufacturer ... that acquires its computer components supplier b. A computer manufacturer that acquires warehouses to aid in its product distribution c. A computer components supplier that begins to assemble computers for sale to consumers d. All of these D 1 p. 5 2. Successful modern supply chain management typically includes the practice of: a. Keeping high inventories throughout the supply chain b. Always purchasing materials with the lowest per unit cost c. The sharing of information between supply chain partners d. Leadership through the practice of issuing ultimatums to your supply chain partners C 1 p. 5 3. According to the textbook, which of the following statements is TRUE? Consumers buy products based on a combination of: a. Cost, quality, manufacturer, and simplicity of use b. Cost, quality, availability, and brand c. Cost, quality, advertising, store preference, and appearance d. Cost, quality, availability, maintainability, and reputation D 1 p. 6 4. Which of the following is a reverse logistics activity: a. Recycling products and components b. Delivering finished goods to your customer c. Developing a collaborative relationship with your supplier d. Managing the quality of products A 1 p. 6 5. According to the textbook, conditions which must be present for successful supply chain management include: a. Vertical Integration b. Corporate contracts regarding performance expectations c. Short-term company focused performance d. Cooperation among firms D 1 p. 8 6. A certain supply chain is made up of: 1. Raw Materials Supplier 2. Components Manufacturer 3. A firm that manufacturers Sub-assemblies 4. End Item Manufacturer 5. Wholesale Distributor 6. Local Retail Chain Warehouse Who is considered the second tier supplier of the firm that manufacturers Sub-assemblies? a. Raw Materials Supplier b. Wholesale Distributor c. The final end item consumer d. Components Manufacturer e. Local Retail Chain Warehouse A 1 p. 9 7. A certain supply chain is made up of: 1. Raw Materials Supplier 2. Components Manufacturer 3. A firm that manufacturers Sub-assemblies 4. End Item Manufacturer 5. Wholesale Distributor 6. Local Retail Chain Warehouse Who is considered the End Item Manufacturer's second tier supplier? a. Raw Materials Supplier b. Wholesale Distributor c. The final end item consumer d. Components Manufacturer e. Local Retail Chain Warehouse D 1 p. 9 8. The following is an example of the bullwhip effect: a. Barkley's produces a defective product and thus realizes an excessive increase in consumer returns b. Barkley's products are so successful that it adds a new retailer for distribution c. Barkley's incorrectly anticipates consumer demand resulting in stockouts at several popular retailers d. Barkley's is unhappy with the performance of a distributor which causes a chain-reaction of replacements to companies involved in its supply chain C 1 p. 11 9. The term Supply Chain Management and the field of study it represents today seems to have emerged in the: a. 1980's b. 1970's c. 1960's d. 1990's A 1 p. 12-13 10. Which of the following would be considered a third party provider? a. A Raw materials supplier b. An intermediate component manufacturer c. A firm that leases storage warehousing d. An end product manufacturer C 1 p. 14 11. Which of the following was a popular way in the 1990's of developing radically new business processes in an effort to reduce waste and increase performance? a. Business process reengineering b. Benchmarking c. Process integration d. Vertical integration A 1 p. 14 12. Which of the following can be classified as a 3PL? a. A company that offers warehousing services b. A company that offers transportation services c. A company that offers customs clearing services d. All of these D 1 p. 14 13. The following supply chain concept was introduced in the 1990's in an attempt to reduce waste and increase performance: a. Business Process Reengineering b. Offshoring c. Vertical Integration d. Material Requirement Planning A 1 p. 14 14. According to the text, the FOUR important elements of the supply chain are: a. Purchasing, manufacturing, transportation, retail stores b. Purchasing, operations, logistics, integration c. Purchasing, manufacturing, logistics, transportation d. Purchasing, operations, manufacturing, distribution B 1 p. 15 15. Encouraging or helping a firm's suppliers to perform in a desired fashion can be referred to as: a. Progressive procurement b. Supplier management c. Right-shoring d. Supply chain performance management B 1 p. 16 16. One operational method for controlling and managing inventory is the implementation of a software system which can be referred to as: a. Material requirements planning (MRP) b. Demand capacity tracking (DCT) c. Inventory sourcing (IS) d. Demand process reengineering (DPR) A 1 p. 17 17. Which of the following acronyms is NOT paired with its correct "translation?" a. TQM Total Quality Management b. JIT Just-in-Time c. MRP Materials Requirements Planning d. ERP Estimated Response Parameters D 1 p. 17 18. Which of the following statements is TRUE? a. Supply chain management was invented by the auto manufacturing industry b. Strategic partnerships are seen as one of the foundations of supply chain management c. Purchasing is seen as the final and most difficult step in the supply chain d. Service response logistics is the digital distribution of services B 1 p. 17 19. Which of the following acronyms is NOT paired with its correct "translation?" a. TQM Total Quality Management b. JIT Just-in-Time c. MRP Manufacturing Responsiveness and Planning d. ERP Enterprise Resource Planning C 1 p. 17 20. Lean production is typically associated with which of the following company's production systems? a. Proctor and Gamble b. Toyota c. Boeing d. Intel B 1 p. 19 21. Transportation management, customer relationship management, network design, and service response logistics are all important issues that are most closely related to: a. Purchasing b. Manufacturing c. Integration d. Logistics D 1 p. 19-20 22. Which of the following is strategy usually employed by lean organizations in an effort to ensure continued quality compliance among suppliers and with internal production facilities? a. MRP II b. Six Sigma c. 3PL d. CAPS B 1 p. 19 23. Assembly or production of finished products, producing the right amount of product, and ensuring that finished products meet specific quality, cost, and customer service requirements are all important issues that are most closely related to: a. Purchasing b. Operations c. Integration d. Distribution B 1 p. 19 24. Right-shoring refers to: a. An expansion of the supply chain b. Contraction activities within the supply chain c. An increase in the responsiveness of the supply chain d. A decrease in the responsiveness of the supply chain B 1 p. 23 25. Which of the following is a system that aids in controlling inventory? a. MRP b. ERP c. AARP d. Both MRP and ERP D 1 p. 23 CHAPTER2 1. The hybrid purchasing system, such as the one utilized by Harrah's, includes many benefits. In such a system the regional office preserves four fundamental purchasing rights. Which of the following is NOT one of those rights? a. Allow suppliers to bid for each purchase b. Select the supplier c. Use whichever pricing method is appropriate d. Monitor contacts with potential suppliers A 1 p. 38 2. According to the textbook, the Las Vegas division of Harrah's Entertainment utilizes which of the following purchasing structures? a. Autocratic b. Decentralized c. Centralized d. Hybrid (centralized-decentralized) D 1 p. 38 3. The primary goals of purchasing include all EXCEPT: a. Secure materials at the lowest cost b. Ensure the highest quality raw materials are purchased c. Improve the quality of finished goods produced d. Maximize customer satisfaction B 1 p. 40 4. The measurement of the impact of change in purchase spend on a firm profit before taxes, assuming gross sales and other expenses remain unchanged, is referred to as: a. Break-Even Analysis b. Direct Offset c. Profit-Leverage Effect d. Leveraging Purchase Volume C 1 p. 42 5. When calculating Return on Investment, current assets include: a. Cash, Accounts Receivable, and Inventory b. Cash, Accounts Receivable, and Equipment c. Accounts Receivable, Equipment, and Real Estate d. Equipment, Buildings, and Real Estate A 1 p. 42 6. Which type of requisition is used for materials and standard parts that are requested on a recurring basis? a. Open requisition b. Blanket requisition c. Traveling requisition d. Recyclable requisition (Cyc-Rec) C 1 p. 43 7. Inventory Turnover can be calculated by: a. Ratio of average inventory cost over cost of goods sold b. Ratio of cost of goods sold over average inventory cost c. Ratio of inventory days in stock over average inventory cost d. Ratio of average inventory cost over inventory days in stock B 1 p. 43 8. A pre-printed order form for purchasing materials and standard parts that are requested on a recurring basis is referred to as: a. Material Requisition b. Purchase Requisition c. Planned Order Release d. Traveling Requisition D 1 p. 44 9. A form of purchasing that is placed directly to the supplier and suitable when firms use the same components to make standard goods over a relatively long period of time is referred to as: a. Material Requisition b. Purchase Requisition c. Planned Order Release d. Traveling Requisition C 1 p. 44 10. When a material is not available in the warehouse and there is no current supplier for the item, the buyer must identify a pool of suppliers and issue a: a. Request for Quotation b. Purchase Order c. Contract for Sale d. Sales Order A 1 p. 45 11. On occasion, firms assist suppliers, new or old, to improve their processing capabilities, product or service quality, delivery effectiveness, and cost performance by providing the required technical and financial assistance. This is referred to as: a. Supplier development b. Outsourcing c. Centralized purchasing d. Supplier hybridization A 1 p. 45 12. The Uniform Commercial Code governs the purchase and sale of goods in the US except in the state of: a. Hawaii b. Louisiana c. Mississippi d. South Dakota B 1 p. 46 13. Which of the following documents is considered the buyer's offer to purchase products or services from a supplier, is legally binding once the supplier accepts it, and usually has the terms and conditions of purchase preprinted on the back of the document? a. Purchase requisition b. Planned order release c. Material requisition d. Purchase order D 1 p. 46 14. Benefits derived from implementing e-procurement systems include all of the following EXCEPT: a. Allows buyers to submit bids and suppliers to respond to those bids in real time b. Increases the accuracy in communication between buyers and suppliers c. Creates numerous additional job opportunities in the purchasing department d. Tracking bids and transactions is easier and faster C 1 p. 48-49 15. Benefits derived from implementing an e-procurement system include all EXCEPT: a. Time Savings b. Real Time Access c. Trackability d. Decentralized Purchasing D 1 p. 49 16. Which of the following illustrates Forward Vertical Integration? a. Microsoft starting a new division that designs and manufactures clothing b. Ford automotive buying additional machines for production c. Subway sandwich company buying a bakery to make the bread for their sandwiches. d. Sony buying trucks to deliver their finished goods inventories to their customers' warehouses D 1 p. 53 17. If a distribution company that focused on warehousing and distribution of grocery items decided to purchase a chain of grocery stores, the distribution company would be exemplifying: a. Backward vertical integration b. Forward vertical integration c. Backward horizontal integration d. Forward horizontal integration B 1 p. 53 18. Which of the following would be a good reason to outsource (buy) versus making? a. A firm lacks the technology or expertise to produce an item b. To utilize existing capacity within a company's own firm c. To have more direct control over the design and production of an end item d. No competent supplier presently produces the needed item A 1 p. 53-55 19. Given the following make-buy information, what would be the break-even point? Make Option Buy Option Fixed Costs $7500 $1500 Variable Costs $ 4 $ 9 a. 1200 units b. 1708 units c. 690 units d. 460 units A 1 p. 55-56 20. Given the following make-buy information, what would be the break-even point? Make Option Buy Option Fixed Costs $15000 $1250 Variable Costs $ 5 $ 10 a. 917 units b. 2875 units c. 1083 units d. 2750 units D 1 p. 55-56 21. As firms seek to improve the products they offer to the market, companies are seeking help from their suppliers in new product design and development through: a. Supplier certification programs b. Manufacturer certification programs c. Early supplier involvement d. Total Cost of Ownership initiatives C 1 p. 58 22. Which of the following is a reason that single sourcing is considered risky/bad? a. The buyer's required ordering quantities are very low b. Larger orders make quantity discounts more likely c. The limited (finite) capacity of one supplier d. Decreases the item to item quality variability of items purchased C 1 p. 60-61 23. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. More than 50% of each sales dollar typically goes towards covering supply chain costs b. Decentralized purchasing means not having any purchasing departments and allowing all employees to act as purchasing agents c. Electronic procurement systems can aid a company in saving both time and money d. If a firm lacks the technology to make a required component they will need to consider buying/outsourcing. B 1 p. 62-63 24. Which of the following is NOT a form of countertrade? a. Barter b. Offset c. Incoterming d. Counterpurchase C 1 p. 64-65 25. While most public procurement is focused on goals similar to those of purchasing departments in the private sector, U.S. federal government purchases must comply with the: a. Federal Acquisition Regulation b. Fair Standards and Equitable Purchases Act c. Federal Code of Conduct for Procurement d. Services and Materials Acquisition Act A 1 p. 66 CHAPTER3 1. According to the text, key ingredients for developing successful supply partnerships include all of the following EXCEPT: a. Personal relationships b. Individualized objectives c. Mutual benefits and needs d. Performance metrics B 1 p. 75-76 2. Which of the following is important in developing successful relationships in a partnership? a. Commitment by top management b. Interpersonal relationships between employees of the companies c. Mutual/compatible needs that result in a win-win situation for the partners d. All of these D 1 p. 76-77 3. Which of the following is NOT important in developing a successful strategic alliance? a. Developing performance metrics b. Developing efficient processes that will remain unchanged for the duration of the partnership c. Investigating the capabilities and core competencies of the supplier d. Open lines of communication that both promote sharing and secure confidentiality B 1 p. 77-78 4. According to the text, one of the most basic and successful approaches to protecting trade secrets is: a. Threat of litigation b. Working with law makers to increase fines and sentences for those that steal trade secrets c. Requiring employees and vendors to sign non-disclosure agreements d. Requiring employees and partners to get ISO 9000 certified C 1 p. 78 5. According to the text, the goal of a good performance evaluation system is to provide metrics that are: a. Understandable, easy to measure, focused on value-added results b. Understandable, quantitative, focused of cost-related results c. Understandable, qualitative, focused on performance-related results d. Understandable, quantitative, focused on quality-related results A 1 p. 78 6. The combination of the purchase price of a good and additional costs incurred before or after product delivery can be referred to as: a. Total cost of acquisition b. Total cost of ownership c. Purchase requisition cost d. Total procurement cost B 1 p. 79 7. Costs associated with investigating alternative suppliers and investigating alternative delivery options can be classified as: a. Pre-transaction costs b. Post-transaction costs c. Transaction costs d. All of these A 1 p. 80 8. The process of certifying a new supplier is considered what type of major cost category? a. Pretransaction Cost b. Supplier-Development Cost c. Transaction Cost d. Turnover Cost A 1 p. 80 9. Field failures, loss of goodwill, a decreased reputation, and warranty costs can all be classified as: a. Pre-transaction costs b. Post-transaction costs c. Transaction costs d. All of these B 1 p. 81 10. Which of the following is TRUE? a. SRM software modules are very affordable (less than $50,000) and can be implemented with a week. b. ISO 75000 is the supplier award given to the highest rated supplier in Japan. c. The key to successful partnerships is developing performance measures with weights greater than 3.50. d. Continuous improvement and change management are both keys to building successful partnerships. D 1 p. 81 11. An organization's process for evaluating the quality systems of key suppliers in an effort to eliminate incoming inspections can be referred to as: a. Quality Systems Certification b. Supply Management c. Supplier Inspection d. Supplier Certification D 1 p. 84 12. Benefits of implementing an effective supplier certification program include all or the following EXCEPT: a. Building long-term relationships b. Reducing time spent on incoming inspections c. Increasing supplier base d. Recognizing excellence C 1 p. 84 13. When using a Weighted Criteria Evaluation System to evaluate suppliers, all of the following are true EXCEPT: a. Select the key dimensions of performance based on what is important to the consumer b. The weights for all dimensions must sum to 1 c. Evaluate each of the performance measures on a rating between zero and one-hundred d. Multiply the dimension ratings by their respective important weights and then sum to get an overall weighted score A 1 p. 84 14. A company using a weighted-criteria evaluation system has established these 5 categories and the appropriate weight in parentheses: Quality (0.30) Responsiveness (0.20) Delivery (0.20) Cost (0.20) Technology (0.10) Company X received the following ratings in each of the five categories: Quality(90), Responsiveness(80), Delivery(80), Cost(90), Technology(90). What is their total score? a. 87.0 b. 85.5 c. 86.0 d. 84.0 C 1 p. 85 15. A company using a weighted-criteria evaluation system has established these 3 categories and the appropriate weight in parentheses: Quality(0.30), Delivery(0.20), Cost(0.50). The scores for each category are shown below. Which of the following companies has the highest total score? a. Company A: Quality(90), Delivery(80), Cost(60) b. Company C: Quality(70), Delivery(80), Cost(80) c. Company B: Quality(70), Delivery(90), Cost(80) d. All companies scored the same. C 1 p. 85 16. A company using a weighted-criteria evaluation system has established these 3 categories and the appropriate weight in parentheses: Quality(0.30), Delivery(0.40), Cost(0.30). The scores for each category are shown below. Which of the following companies has the highest total score? a. Company A: Quality(90), Delivery(80), Cost(60) b. Company C: Quality(70), Delivery(95), Cost(60) c. Company B: Quality(70), Delivery(80), Cost(80) d. All companies scored the same. D 1 p. 85 17. A company using a weighted-criteria evaluation system has established these 5 categories and the appropriate weight in parentheses: Quality (0.25) Responsiveness (0.10) Delivery (0.20) Cost (0.25) Technology (0.20) Company X received the following ratings in each of the five categories: Quality(90), Responsiveness(90), Delivery(80), Cost(80), Technology(90). What is their total score? a. 87.0 b. 85.5 c. 86.0 d. 86.5 B 1 p. 85 18. Which third party certification was adopted by the European Union in 1992 that caused US suppliers wanting to stay competitive in European Union countries to get certified? a. ISO 14000 b. ISO 9000 c. European Supplier Certification Initiative (ESCI '92) d. EU Third Party Initiative B 1 p. 87 19. Direct benefits of ISO 14000 include: a. Reduced defect rates b. Improved on-time delivery rates c. Reduction of pollution emission d. All of these C 1 p. 89 20. According to the textbook, which of the following companies utilizes a supplier development program called Supplier Continuous Quality Improvement (SQDI) focused on improving the quality of the goods and services purchased and minimize the time needed to inspect incoming products? a. Target b. Boeing c. Intel d. General Motors C 1 p. 90 21. The Hormel company awards their Hormel Food Corporation's No. 1 Award to their top supplier. How often to the give this award? a. Every year b. Every 6 months c. Every 5 years d. Every 10 years C 1 p. 91 22. The acronym SRM refers to: a. Supplier Requisition Monitoring b. Supplier Relationship Management c. Shipment Response Monitoring d. Supply chain Relationship Management B 1 p. 92 23. Streamlining the processes and communications between the buyer and supplier using software applications that enable these processes to be managed more efficiently and effectively can be referred to as: a. CRM b. SRM c. ISO 9000 d. SCSS B 1 p. 92 24. Summers, Inc. needs to generate a list of good/services purchased per supplier. Which type software program can the manager consult to obtain the information? a. ISO 9000 b. ISO 14000 c. SRM d. SCSS C 1 p. 93 25. SRM software should be capable of: a. Automating transactional processes b. Making information flow between partners more visible c. Integration of the supply chain making it possible to monitor multiple departments and processes both internally and externally d. All of these D 1 p. 94 CHAPTER4 1. All of the following are reasons for the increasing use of ethical and sustainable sourcing practices EXCEPT: a. Global population growth b. Increasing environmental awareness c. Legislation requiring corporate ethical and sustainable sourcing d. Declining worldwide levels of natural resources C 1 p. 101 2. Managing a firm's external resources in ways that support the long-term goals of the firm can be referred to as: a. Ethical souring b. Functional sourcing c. Strategic sourcing d. Hybrid Sourcing C 1 p. 101 3. The management of the firm's external resources through identification and selection of suppliers, management of supplier relationships, and monitoring and rewarding supplier performance in an effort to support the long-term goals of the organization is called: a. Buyer-supplier integration b. Acceptance sampling c. Procurement rationalization d. Strategic sourcing D 1 p. 101 4. Which of the following is NOT a step suggested in the Supply Chain Sourcing Strategy Framework? a. Classify supplier items as either innovative or functional b. Define the goals of the supply chain and check for consistency with products and firm strategy c. Distribute free samples of all purchased products to the end-user for detailed evaluation and feedback on supply chain development d. Identify and evaluate the capabilities of suppliers and then identify areas which could be improved C 1 p. 101-102 5. Which of the following are considered outcomes of implementing a supplier evaluation and selection criteria? a. Allows firm to screen out poor performing suppliers in its present supplier base. b. Allows firm to screen out undesirable suppliers that they may be considering for future purchases. c. Allows firm and its suppliers to develop a better corporate relationship d. All of these D 1 p. 101-102 6. The application of ethical principles to business situations can be referred to as: a. Business ethics b. Social responsibility c. Ethical Sourcing d. Strategic Sourcing A 1 p. 102 7. The following term refers to an act that creates the greatest good for the greatest number of people: a. Rights and duties b. Corporate responsibility c. Utilitarianism d. Social sustainability C 1 p. 102 8. The purchasing managers at Sunnydale Corporation decide to intentionally increase purchases from small, women-owned suppliers. This decision can be considered: a. Illegal b. Unethical c. Ethical Sourcing d. Utilitarianism C 1 p. 103 9. The Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI) does NOT include which of the following: a. Children under 13 shall not be employed b. Working hours are not excessive c. Regular employment is provided d. Freedom of association and the right to collective bargaining are respected A 1 p. 104 10. Wal-mart is the driving force behind a system of measurement intended to influence how products are made and purchased in the future. This system of measurement is the: a. Greenstream b. ISO 17000 c. Retail carbon footprint d. Global sustainability index D 1 p. 106-107 11. According to the EcoMarkets survey, which surveys over 6000 private and public buyers, the most popular aspect of green sourcing is: a. Recycling b. Material reuse c. Energy conservation d. Packaging reuse C 1 p. 108 12. Which of the following would most likely be considered a functional product? a. PDA Personal Digital Assistant b. HDTV High Definition Televisions c. DVD recorders d. Disposable Camera D 1 p. 109 13. The textbook outlined a Supply Chain Ethical and Sustainability Sourcing Strategy Framework. How many steps are in this framework? a. 3 b. 5 c. 6 d. 10 C 1 p. 109-111 14. Harold's Fish Shop decides to reduce its purchases from poorly performing fish suppliers and focus future orders with suppliers that have been top-performing in the past. This is an example of: a. Supply base rationalization b. Supplier development c. Top-tier supplier selection d. Selective sourcing B 1 p. 112 15. Hard-bargaining sourcing departments focused on decreasing purchasing spend may experience which of the following from their suppliers? a. Lower levels of quality from their suppliers b. Lower levels of service from their suppliers c. Deteriorating buyer-supplier relationships d. All of these D 1 p. 112-113 16. An outsourcing program can result in all of the following positive outcomes, except: a. Reducing staffing levels b. Decreased need for supplier management c. Cost reduction d. Gains in manufacturing flexibility B 1 p. 113-114 17. Variations of outsourcing include all of the following EXCEPT: (C; 114) a. Co-sourcing b. Selective sourcing c. Front sourcing d. Insourcing C 1 p. 114 18. One of the most value enhancing activities performed by a supplier, for a key customer, which minimizes carrying costs and can avoid stockouts: a. Early supplier involvement scheduling b. Vendor managed inventory c. Strategic inventory planning d. Purchase spend reduction forecasting B 1 p. 116 19. Which of the following is FALSE? a. The use of 3PL's has been increasing as companies seek more effective supply chain strategies. b. VMI provides retail facilities the opportunity to communicate to manufacturers that the customers are requesting customized items c. The use of 3PL providers allows companies to gain competitive advantages without having to gain the required knowledge through firsthand experience. d. VMI allows suppliers to manage their customers' inventory provided they have the capability to see inventory levels in real time B 1 p. 116 20. Which of the following is TRUE? a. VMI stands for Vertically Managed Inventory b. 3PL stands for Third Party Leverage c. VMI stands for Vendor-Managed Inventory d. 3PL stands for Three Point Logistics C 1 p. 116 21. The inventory level where suppliers replenish their customer's inventory with a predetermined order quantity is called the: a. Channel Equity Level b. Reorder point c. Bill Back d. MRO point B 1 p. 116-117 22. According to the textbook, collaborative relationships place a relatively lower importance rating on which of the following competitive priorities: a. Speed of Delivery b. Cost c. Product Quality d. Frequency of deliveries B 1 p. 120-121 23. The primary benefits of ____ include costs savings and freeing up time for purchasing staff to concentrate on the firm's core activities. a. eProcurement b. Insourcing c. The Ethical Trade initiative d. Six Sigma B 1 p. 121 24. Which of the following can be used as a punishment for suppliers that perform poorly? a. Elimination of future business with the focal firm b. Downgrade the supplier's status c. Billback penalty d. All of these D 1 p. 123 25. Benchmarking is: a. A system of performance metrics that seeks to motivate suppliers to perform better. b. A practice where companies attempt to learn and apply the best practices of other companies. c. A system of marking defective inbound inventory so it can quickly be identified for return to the supplier. d. A program where suppliers compete for contracts, but those companies who are outbid are provided advice for winning future contracts CHAPTER5 1. Which of the following indices provided by the Institute for Supply Management (ISM) is considered the most important by economists because it is a composite of five weighted, seasonally adjusted indices? a. Purchasing Managers Index b. Export Orders Index c. Production and Inventory Index d. New Orders Index A 1 p. 134 2. According to the textbook, which of the following is NOT a way to closely match supply and demand? a. Holding high amounts of inventory b. Maintaining a rigid pricing system c. Utilizing overtime d. Hiring temporary workers B 1 p. 135 3. The impact of poor communication and inaccurate forecasts resonates along the supply chain and results in the: a. Bullwhip effect b. Delphi method c. CPFR effect d. Mean deviation A 1 p. 136 4. Inaccurate forecasts can result in negative outcomes like: a. Stockouts and poor responsiveness to market dynamics b. High inventory costs of inventory and increased profits c. Material shortages and decreased costs of obsolescence d. Low inventory costs of inventory and stockouts A 1 p. 136 5. Which one of the following is not a type of qualitative forecasting? a. Sales force composite b. Consumer survey c. Jury of executive opinion d. Naïve method D 1 p. 138 6. The following are all common qualitative forecasting models EXCEPT: a. Jury of Executive Opinion b. Trend Variation c. Delphi Method d. Sales Force Composite B 1 p. 138 7. Which of the following statements is FALSE: a. Time Series forecasting is based on the assumption that the future is an extension of the past b. Cause-and-Effect forecasting assumes that one or more factors are related to demand and, therefore, can be used to predict future demand c. All quantitative methods become less accurate as the forecast's time horizon increases d. It is generally not recommended to use a combination of both quantitative and qualitative methods D 1 p. 139 8. Your company is conducting forecasting that revolves around the current recession and expansion of the U.S. economy. This type of forecasting can be referred to as what component of a time series? a. Trend Variations b. Cyclical Variations c. Seasonal Variations d. Random Variations B 1 p. 139 9. The following time-series approach to forecasting uses historical data to generate a forecast and works well when demand is fairly stable over time: a. Naïve Forecast b. Weighted Moving Average c. Simple Moving Average d. Exponential Smoothing C 1 p. 140 Data Set E1 Period Sales Volume 1 10000 2 12400 3 14250 4 15750 5 20500 6 18500 7 15750 8 20500 9 21500 10 22550 10. Using Data Set E1, what would be the forecast for period 7 using a four period moving average: (Choose the closest answer.) a. 17625 b. 15225 c. 15300 d. 17250 D 1 p. 140 11. Using Data Set E1, what would be the forecast for period 6 using a five period weighted moving average? The weights for each period are 0.05, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, and 0.35 from the oldest period to the most recent period, respectively. (Choose the closest answer.) a. 16500 b. 17825 c. 14575 d. 16275 A 1 p. 140 12. Using Data Set E1, what would be the forecast for period 6 using the exponential smoothing method? Assume the forecast for period 5 is 14000. Use a smoothing constant of = 0.4 (Choose the closest answer.) a. 14575 b. 26100 c. 16600 d. 19700 C 1 p. 143 13. Using the actual demand shown in the table below, what is the forecast for May (accurate to 1 decimal) using a 4-month weighted moving average and the weights 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 (with the heaviest weight applied to the most recent period)? Nov. Dec. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. 39 36 40 38 48 46 a. 44.4 b. 43.0 c. 42.5 d. 41.6 A 1 p. 140 14. Given the following information, calculate the forecast (accurate to 2 decimals) for period three using exponential smoothing and = 0.3. Period Demand Forecast 1 64 59 2 70 a. 36.90 b. 57.50 c. 61.50 d. 63.35 D 1 p. 143 15. The exponential smoothing forecast has the same value as the naïve forecast when in the exponential smoothing model is equal to: a. 0 b. 0.5 c. 1 d. Insufficient information provided to determine answer C 1 p. 143 16. The equation for a simple linear regression that saw sales averaging $225,000 over the last ten periods, and advertising budgets averaging $3,000 over the last 10 periods is: Y = 3250 + 120x This indicates that a $1 increase in advertising will increase sales by: a. $3370 b. $250 c. $120 d. $1875 C 1 p. 144 17. One common Cause-and-Effect Model used is: a. Regression analysis b. Linear Trend Forecast c. Moving Average Forecast d. Mean Absolute Deviation A 1 p. 145 18. Some measures of forecasting accuracy include mean absolute deviation, mean absolute percentage error, and mean squared error. The formula for each is dependent on the forecast error, which is calculated by using the equation: a. Actual demand for period t divided by the forecasted demand for period t b. Actual demand for period t plus the forecasted demand for period t c. Actual demand for period t minus the forecasted demand for period t d. The average of Actual demand for period t and forecasted demand for period t C 1 p. 148 19. If a tracking signal is positive, which one of the following is true? a. Actual value is higher than forecast b. Actual value is less than forecast c. Actual value is equal to forecast d. Unable to draw any conclusion A 1 p. 148 Data Set E2 Month Actual Forecast 1 10 11 2 8 10 3 9 8 4 6 6 5 7 8 20. A forecasting method has produced the following data over the past 5 months shown in Data Set E2. What is the mean absolute deviation (accurate to 2 decimals)? a. 0.60 b. 1.20 c. 1.00 d. 1.25 C 1 p. 148 21. Based on the information in Data Set E2, what is the mean squared error (accurate to 2 decimals)? a. 7.00 b. 1.40 c. 1.00 d. 0.80 B 1 p. 148 22. What does the acronym CPFR represent? a. Coordinated planning and forecasting relationships b. Collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment c. Centralized purchasing and forecasting relationships d. Collaborative purchasing, forecasting, and receivables B 1 p. 151 23. According to textbook, the top three challenges for CPFR implementation include all of the following except: a. Making organizational and procedural changes b. Trust between supply chain partners c. Cost d. Supplier lead times D 1 p. 156 24. According to textbook, which of the following companies is a leading forecasting software provider? a. Just Enough b. SAS c. Business Forecast Systems, Inc. d. All of these D 1 p. 156-159 25. According to textbook, which of the following companies is recognized as a leader in CPFR software solutions? a. Autonomy b. Cloud software c. JDA software d. Transperion D 1 p. 161 CHAPTER6 1. Which of the following is an engineering document that shows an inclusive listing of all the component parts and assemblies making up the final product? a. Master Production Schedule b. Bill of Materials c. Distribution Requirement Plan d. Resource Requirement Plan B 1 p. 167 2. The goal of resource planning is to minimize the discrepancy between capacity and: a. Resources b. Demand c. Workload d. Supply B 1 p. 168 3. Which of the following consists of different products that share similar characteristics, components or manufacturing processes? a. Resource tree b. Product family c. Dependant allocation d. Implosion factor B 1 p. 168 4. Which of the following seeks to develop short range plans seeking to effectively and efficiently manage components and/or subassemblies over time period of few days to a few weeks? a. RRP b. MPS c. RCCP d. MRP D 1 p. 169 5. To check the feasibility of the Master Production Schedule, one would look to: a. Rough-Cut Capacity Plan b. Material Requirement Plan c. Capacity Requirement Plan d. Distribution Requirement Plan A 1 p. 170 | p. 188 6. Which of the following is a Long Range Materials Plan: a. Aggregate Production Plan b. Master Capacity Plan c. Materials Requirements Plan d. Capacity Requirements Plan A 1 p. 170 7. In a bill of materials, items at which level are independent demand items? a. Level 0 b. Level 1 c. Level 2 d. Level 3 A 1 p. 170 8. Which of the following basic production strategies used for addressing the aggregate planning problem would work best with make-to-order manufacturing firms? a. Capacity Production Strategy b. Chase Production Strategy c. Level Production Strategy d. Backlog Production Strategy B 1 p. 171 9. Which of the following could be considered a master production schedule for a service firm? a. The reservation book utilized by a restaurant b. The employee shift schedule utilized by an auto shop c. A hospital patient's personal information fill d. The recipe book utilized by a chef at a restaurant A 1 p. 175 10. Which of the following is NOT one of the three basic methods used to calculate the available-to-promise quantities? a. Discrete available-to-promise b. Cumulative available-to-promise without looking ahead c. Indiscrete available-to-promise d. Cumulative available-to-promise with looking ahead C 1 p. 177 11. Which of the following MRP terms represents a committed order awaiting delivery for a specific period? a. Projected on-hand inventory b. Time bucket c. Net requirement d. Scheduled receipt D 1 p. 184 12. Which of the following MRP terms represents the parts demanded by a parent? a. Gross requirement b. Component c. Net requirement d. Scheduled receipt B 1 p. 184 13. Which number should be placed in the spot presently filled with the X? Item ABC-Level 1 1 2 3 4 Gross Requirements 20 20 50 30 Schedule Receipts 25 Projected on Hand Inventory 30 10 15 40 10 Net Requirements Planned Order Releases X Q = 25; LT = 2; SS = 10 a. 50 b. 75 c. 10 d. 20 B 1 p. 186 14. Which number should be placed in the spot presently filled with the X? Item ABC-Level 1 2 3 4 Gross Requirements 40 65 35 10 Schedule Receipts 60 Projected on Hand Inventory 70 30 25 20 10 Net Requirements Planned Order Releases X Q = 30; LT = 2; SS = 10 a. 10 b. 15 c. 30 d. 60 C 1 p. 186 15. Which number should be placed in the spot presently filled with the X? Item ABC-Level 1 2 3 4 Gross Requirements 20 10 40 X Schedule Receipts 25 Projected on Hand Inventory 25 30 20 30 25 Net Requirements Planned Order Releases 50 Q = 25; LT = 2; SS = 20 a. 20 b. 5 c. 10 d. 15 B 1 p. 186 16. Which number should be placed in the spot presently filled with the X? Item ABC-Level 1 2 3 4 Gross Requirements 20 20 10 15 Schedule Receipts 20 Projected on Hand Inventory 50 30 30 20 X Net Requirements Planned Order Releases 40 Q = 20; LT = 3; SS = 20 a. 20 b. 5 c. 45 d. 35 C 1 p. 186 17. The acronym ERP is short for: a. Enterprise Resource Planning b. Electronic Resource Provider c. Executive Resource Plan d. Electronic Requirements Provider A 1 p. 191 18. Which of the following is considered an advantage/benefit of utilizing in ERP system? a. Utilizes multiple databases in order to provide up-to-date information b. Increases the privacy level within an organization, thus functional departments can more easily protect their data from supporting or dependent functional departments c. Allows organizations to more easily communicate information about operational changes to supply chain members d. Increases the bullwhip effect C 1 p. 191-193 19. Which of the following is considered an advantage/benefit of utilizing an ERP system? a. Fairly inexpensive to purchase and implement b. Enables the company to utilize a single centralized database system, thus eliminating duplicate data entry. c. Flexible enough that it allows different companies with different business models to mold the new ERP system to fit the company's business model d. All of these B 1 p. 193 20. While ERP is a relatively new technology, it has grown rapidly since the early 1990s. Which of the following is the reason that has contributed to its rapid growth? a. The year 2000 millennium bug b. The trend for companies to eliminate their supply chain partners c. The increased use of email during the 1990's d. All of these A 1 p. 194-195 21. Organizations that choose to implement one single system with all of the desired applications from a single vendor versus choosing to implement the best applications or modules for each of the different functional departments associated with the supply chain is said to have chosen a(n): a. Best-of-breed solution b. Elite integrator solution c. Single integrator solution d. Premier application solution C 1 p. 195-196 22. Organizations that choose to implement the best applications or modules for each of the different functional departments associated with the supply chain versus choosing to implement one single system with all of the desired applications from a single vendor is said to have chosen a(n): a. Best-of-breed solution b. Elite integrator solution c. Multi-modular solution d. Premier application solution A 1 p. 196 23. According to the textbook, which of the following is considered a reason that ERP implementations fail? a. The organization may lack the necessary workforce and expertise to properly implement the system b. Top management becomes overcommitted to the point where they constantly encourage the employees during implementation c. Organizations tend to spend too much time and money training their employees on the new system d. All of these A 1 p. 196-197 24. Not all ERP software is designed to provide the exact same tools, nonetheless, some of the common modules usually included in ERP software packages include: a. Customer Relationship Management and human resource management b. Human resource management and accounting and finance c. Supplier relationship management and customer relationship management d. All of these D 1 p. 200-201 25. Which of the following is NOT a common module of ERP systems? a. Human Resources Management b. Customer Relationship Management c. Marketing Resources Management d. Supply Chain Management C 1 p. 200-201 CHAPTER7 Dependent demand and independent demand items differ in that I. for any product, all components are dependent-demand items II. the need for independent-demand items is forecast III. the need for dependent-demand items is calculated a. I only b. I & II only c. I & III only d. II & III only e. I, II & III E 1 p. 212 2. Which of the following would most likely be considered a dependent demand item? a. Bicycle tires used to assemble a bicycle b. Television (TV) c. Couch d. Lawn Mower A 1 p. 212 3. Which of the following cannot be considered as independent demand items? a. wholesale and retail merchandise items b. maintenance, repair, and operating supplies at a manufacturing company c. maintenance, repair, and operating supplies at a service firm d. raw material items that become part of the final product at a manufacturing firm e. service industry items such as hospital supplies or office supplies for law firms D 1 p. 212 4. ____, such as lubricants for machines, are used in the production process, but do not become parts of the final products. a. Raw materials b. Work-in-process c. Maintenance, repair and operating supplies d. Finished goods e. Cycle stock C 1 p. 213 5. Companies hold a supply of inventory for all of the following reasons EXCEPT: a. meet variation in product demand b. increase production change/setup costs c. allow production scheduling flexibility d. purchase in bulk to take advantage of quantity discounts e. maintain independence of operations (Decoupling) B 1 p. 212-213 6. Which of the following is a disadvantage of excessive inventory? a. It hides production and other problems. b. It leads to higher inventory ordering cost. c. It leads to lower average inventory. d. It eliminates cycle stock. e. It reduces the need to conduct cycle count. A 1 p. 212-214 7. Which of the following is not an example of an ordering cost for products purchased from a supplier? a. the cost of transmitting the order b. the cost of receiving the product c. the cost associated with processing the invoice d. the opportunity cost of not ordering from a least cost supplier e. the cost of handling the product D 1 p. 214 ABC Inventory Matrix Use the graph below to answer the question(s). 8. In the ABC Inventory Matrix, inventory in area Y suggests a. under-stocked A and B items. b. under-stocked B and C items. c. overstocked A and B items. d. over-stocked B and C items. e. inventory matches sales. E 1 p. 217-218 9. In the ABC Inventory Matrix, inventory in area Z suggests a. under-stocked A and B items. b. under-stocked B and C items. c. overstocked A and B items. d. over-stocked B and C items. e. inventory matches sales. D 1 p. 217-218 10. Which of the following is NOT an assumption of the classic Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)? a. Lead time is known and constant. b. Demand is known and constant. c. Instantaneous replenishment. d. There is no quantity discount. e. The production rate must be greater than the consumption rate. E 1 p. 225-226 11. The primary purpose of the basic economic order quantity model is a. to calculate the reorder point, so that replenishments take place at the proper time b. to minimize the sum of carrying cost and holding cost c. to maximize the customer service level d. to minimize the sum of setup cost and holding cost e. to calculate the optimum safety stock D 1 p. 225-226 12. If an item is ordered at its economic order quantity, the annual carrying cost should be: a. slightly less than the annual ordering cost. b. equal to the annual ordering cost. c. twice the annual purchase price. d. the square root of the annual ordering cost. e. cannot be determined because there is insufficient information provided. B 1 p. 225-229 13. What inventory factor may be omitted from the basic EOQ derivation because it is a constant? a. Annual order-processing cost b. Annual purchase cost of goods c. Annual capital cost d. Annual setup costs e. all of these B 1 p. 226 14. Which of the following is not an assumption of the economic order quantity model? a. Demand is known, constant, and independent. b. Lead time is known and constant. c. Quantity discounts are not possible. d. Production and use can occur simultaneously. e. The only variable costs are setup cost and holding (or carrying) cost. D 1 p. 226 15. The cost of a widget is $5, and the carrying rate is 40%; cost of processing an order is $25, annual demand is for 400 widgets, and supply and usage patterns are stable. What is the economic order quantity (EOQ)? a. 5 b. 20 c. 25 d. 100 e. 200 D 1 p. 228 16. If usage is constant, as order size increases, annual order costs ____ but annual carrying costs ____. a. increase ..... increase b. decrease ..... decrease c. increase ..... decrease d. decrease ..... increase e. remain the same ..... increase D 1 p. 229 17. Which one of the following statements regarding the economic order quantity is true? a. The EOQ model combines several different item orders to the same supplier. b. If an order quantity is larger than the EOQ, the annual holding cost exceeds the annual ordering cost. c. The EOQ model assumes a variable demand pattern. d. When the interest rate drops, both the holding cost and the EOQ decreases. e. EOQ is used to determine the optimum shipping quantity. B 1 p. 225-229 18. Use this information below to calculate the optimal order quantity: Annual demand for backpacks is 43,000 units The cost to place an order is $220 The per unit cost of the item is $60.00 The annual holding rate is 37.5% Choose the closest answer. a. 920 units b. 250 units c. 710 units d. 830 units A 1 p. 226-229 19. If your company had an annual purchase cost of items equal to $2,000,000, an annual holding cost of $150,000 and an annual ordering cost of $750,000 this scenario would reveal that: a. Your fixed lot size was lower than the EOQ b. Your fixed lot size was equal to the EOQ c. Your fixed lot size was higher than the EOQ d. Nothing because there is insufficient information to discern where the EOQ would be. A 1 p. 226-229 20. The EOQ model with quantity discounts attempts to determine a. what is the lowest purchasing price. b. whether to use fixed-quantity or fixed period order policy. c. how many units should be ordered. d. what is the shortest lead time. e. what is the lowest amount of inventory necessary to satisfy a certain service level. C 1 p. 227-231 Figure 7-1 Use the graph below to answer the question(s). 21. Which of the following is TRUE in relation to Figure 7-1? a. Curve J represents the annual ordering cost, and curve K represents the annual holding cost. b. A lot size of G has an annual total cost of about C. c. At lot size H both holding costs and ordering costs exceed the annual total cost. d. The EOQ is most likely lot size G, and curve L is the annual ordering cost curve. D 1 p. 226-229 22. If the actual order quantity is the economic order quantity in a problem that meets the assumptions of the model, the average amount of inventory on hand a. is zero b. is affected by the amount of product cost c. is one-half of the economic order quantity d. is smaller than the holding cost per unit e. cannot be determined from the given information C 1 p. 228-230 23. In the absence of demand and delivery lead time variation, if demand is eight per day and purchase lead time is four days, the reorder point is: a. 3. b. 8. c. 32. d. 35. e. 56. C 1 p. 236-238 24. In the absence of demand and delivery lead time uncertainty, reorder point is the ____. a. demand during lead time b. safety stock c. sum of demand during lead time and safety stock d. economic order quantity e. average inventory A 1 p. 236-238 25. The UNLV Bookstore sells a unique calculator to college students. The demand for this calculator has a normal distribution with an average daily demand of 20 units and a standard deviation of 4 units per day. The lead time for this calculator is very stable at 9 days. Compute the statistical reorder point that results in a 95 percent in-stock probability (Z = 1.65). a. 19.8 units b. 80 units c. 180 units d. 199.8 units e. 720 units D 1 p. 236-241 CHAPTER8 1. While the philosophy of Six Sigma means different things to different people and is practiced differently in different companies, according to the textbook, two of the more important and agreed-upon elements of Six Sigma are: a. Minimizing inventories and increasing material flow b. Focusing on the customer and workforce involvement c. Rewarding employees and keeping defect rates below 2% d. Minimizing inventories and keeping defect rates below 1% B 1 p. 251 2. The Quick Response program, developed in the 1980's, was an offshoot of the following supply chain concept: a. Efficient Consumer Response b. Six Sigma c. Just-in-Time d. Cross Docking C 1 p. 253 3. Efficient Consumer Response was initially developed in the 1990's for the following industry: a. Fashion b. Grocery c. Small Electronics d. Automobile B 1 p. 253 4. Lean thinking is a philosophy incorporating tools which seek to optimize: a. Human Resources b. Assets c. Productivity d. All of these D 1 p. 253 5. Modern supply chains simultaneously pursue the goals of high-quality, fast response, and low cost because customers nowadays want both high levels of quality and responsiveness. A key manufacturing philosophy that emphasizes waste elimination and minimizing inventories to expose problems is: a. Just-in-time b. Quick Response c. Efficient Consumer Response d. Total Quality Management A 1 p. 253 6. Japanese manufacturing firms sometimes create cooperative coalitions with their suppliers in order to provide the suppliers with a certain degree of financial support. What are these cooperative coalitions called? a. Jidoka Networks b. Keiretsu Networks c. Kanban Networks d. Kaizen Networks B 1 p. 253 7. The following is a term that refers to error- or mistake proofing: a. Kaizen b. Muda c. Lean layouts d. Poka-yoke D 1 p. 254 8. Which company probably played the largest role in the development of the Toyota Production System? a. General Motors b. Ford c. Chrysler d. Boeing B 1 p. 253-257 9. Which of the following are among the most important elements of the lean production philosophy? a. Quality inspections and a standardized product line b. Fully automated assembly lines and a large supplier base c. Large inventories and quality inspections d. Waste reduction and continuous improvement D 1 p. 257 10. Lean production emphasizes all of the following EXCEPT: a. Continuous improvement b. Reduction of waste c. Synchronization of material flows d. Large batch sizes D 1 p. 257 11. Successful supply chains evolve through stages; the internally focused stage is characterized by all of the following EXCEPT: a. Functional silos b. Top-down management c. Long-term planning d. Internal measures used to monitor performance C 1 p. 259 12. Successful supply chains evolve through stages; the following stage is characterized by an emphasis on cost reduction: a. Internally Focused b. Functional Integration c. Internal Integration d. External Integration B 1 p. 259 13. Which of the following best describes the five S's? a. These were originally Japanese words relating to industrial housekeeping b. Five ways to reduce inventories on the shop floor c. These are five different kinds of manufacturing layouts d. Refer to methods for reducing setup times A 1 p. 259 14. The element of lean involving firms working with buyers and customers with the mutual goal of eliminating waste, improving speed, and improving quality is referred to as: a. Waste reduction b. Lean supply chain relationships c. Lean layouts d. Continuous improvement B 1 p. 260 15. Which of the following is NOT one of the Seven Wastes? a. Excess inventories b. Environmental waste c. Waiting time d. Scrap and rework B 1 p. 260-261 16. All of the following are included in the seven wastes EXCEPT: a. Overproducing b. Overprocessing c. Overspending d. Waiting C 1 p. 261 17. Which of the following layouts is primarily designed to process parts, components, or jobs requiring the same or similar processing steps, saving duplication of equipment and labor: a. Work centers b. Production kanban c. Work-in-process d. Manufacturing Cells D 1 p. 264 18. Which of the following is NOT consistent with the lean philosophy? a. Cross-training employees to increase processing flexibility b. Developing a culture of continuous improvement within the organization c. Increasing batch size to take advantage of economies of scale d. Positioning WIP inventories near each processing center C 1 p. 265 19. Calculate the inventory container size required given the following: Demand rate = 10 parts per hour, Safety stock required = 15% Number of containers = 14, Time to cycle through entire system = 6 hours a. 2 parts b. 3 parts c. 4 parts d. 5 parts D 1 p. 265 20. Lean production systems are sometimes referred to as pull systems because demand from customers activates the production actions of the manufacturing facilities. In order for this demand to be communicated to everyone in the supply chain/manufacturing facility a signal must be passed from downstream processing centers to the upstream processing centers. This system of relaying signals is referred to as a: a. Kanban System b. Semaphore System c. Keiretsu Network d. TQM Network A 1 p. 265-267 21. Calculate the defects per million opportunities (DPMO) given the following: Blake, owner of Blakester's T-shirt Shoppe, keeps track of customer complaints. For each T-shirt sold, there are four possible complaints: T-shirt shrinks, poor quality, design wears off, and doesn't fit right. Each week, Blake calculates the rate of T-shirt "defects" per total T-shirts sold, and then uses this information to determine his company's DPMO. During the past week, his company sold 1200 T-shirts. His company received 22 customer shrinkage complaints, 16 poor quality complaints, 12 design wears off complaints, 8 doesn't fit right complaints. Calculate his firm's DPMO. a. 69,600 b. 0.193 c. 5.8 x 106 d. 12,083 D 1 p. 268 22. Which of the following quality gurus believed that companies should strive for zero defects and that quality was, in a sense, free since quality improvement programs invariably paid for themselves? a. Juran b. Deming c. Baldrige d. Crosby D 1 p. 274 23. According to the text, the ability to satisfy customer expectations can be referred to simply as: a. Reliability b. Lean Six Sigma c. Quality d. Durability C 1 p. 275 24. A company that produces 8 pound bags of rice gathered 5 samples of 6 bags each. The weights of each bags' contents are listed below. Bag Number Sample 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 7.98 8.34 8.02 7.94 8.44 7.68 2 8.33 8.22 8.08 8.51 8.41 8.28 3 7.89 7.77 7.91 8.04 8 7.89 4 8.24 8.18 7.83 8.05 7.9 8.16 5 7.87 8.13 7.92 7.99 8.1 7.81 What would you plot on the x-bar chart for sample 2? a. All of the following numbers: 8.33, 8.22, 8.08, 8.51, 8.41, 8.28 b. All of the following numbers: 8.34, 8.22, 7.77, 8.18, 8.13 c. Only 8.130 d. Only 8.305 D 1 p. 286-288 25. A company sells eggs in boxes with 12 cartons and 12 eggs in each carton, thus there are 144 eggs in each box. The organization wants to construct a P-chart to track the proportion of broken eggs in each sample. If the company used one box of eggs in each sample in the dataset, what would be the centerline, upper control limit(UCL), and lower control limit(LCL) for the appropriate P-chart? (Use z = 3.) Choose the closest answer. Sample Eggs Sample Eggs Sample Eggs 1 3 8 6 15 5 2 5 9 4 16 0 3 3 10 9 17 2 4 4 11 2 18 6 5 2 12 6 19 2 6 4 13 5 20 1 7 2 14 1 TOTAL 72 a. Centerline = 0.50, UCL = 0.625, LCL = 0.375 b. Centerline = 0.025, UCL = 0.64, LCL = 0 c. Centerline = 0.30, UCL = 0.70, LCL = 0 d. Centerline = 0.083, UCL = 0.152, LCL = 0.014 B 1 p. 289-290 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 40 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 20, 2020
Number of pages
40
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 20, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
212