*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR449 Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing – pn Comprehensive Exam Practice MCQ's thoroughly revised (All)
NR449 Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing – pn Comprehensive Exam Practice MCQ's thoroughly revised with 100% correct answers
Document Content and Description Below
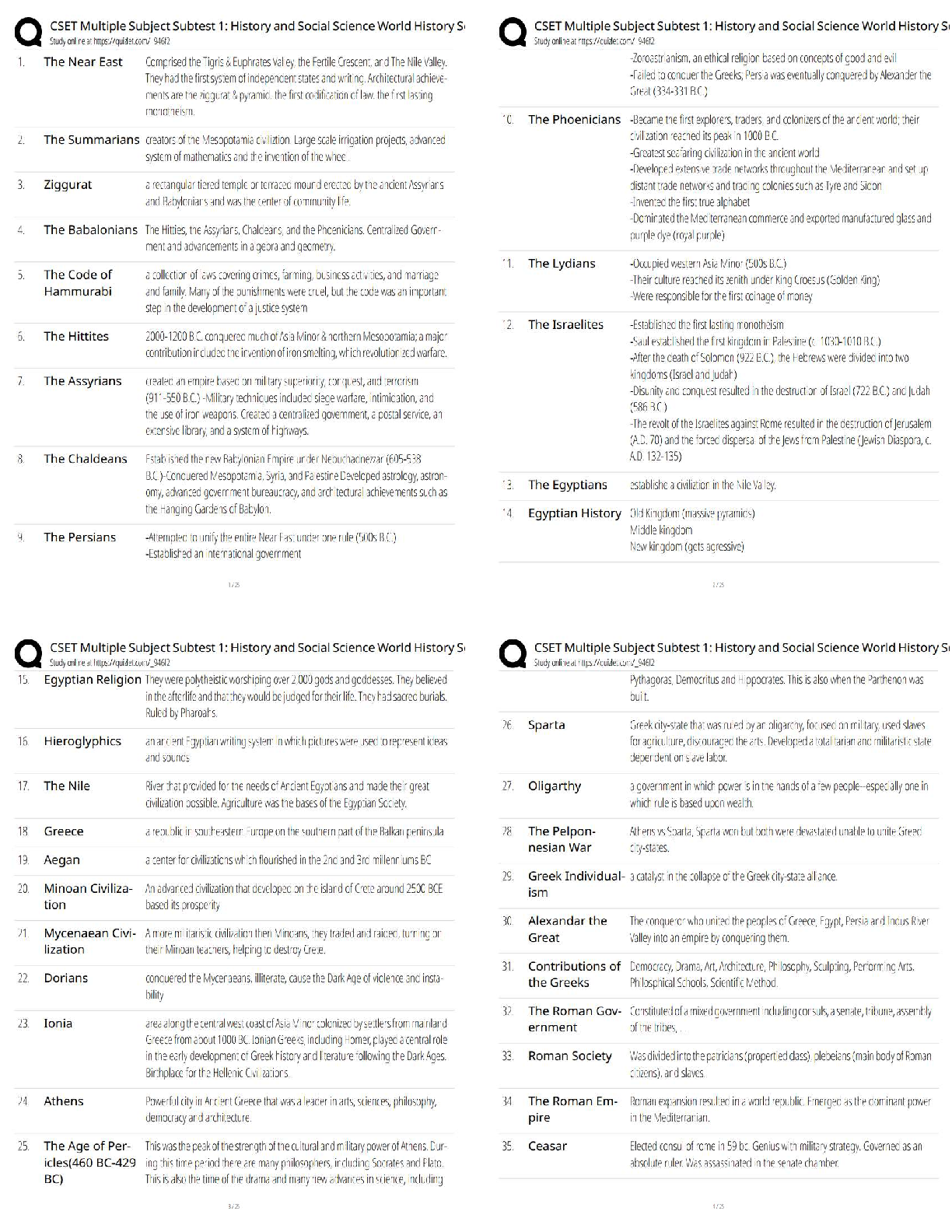
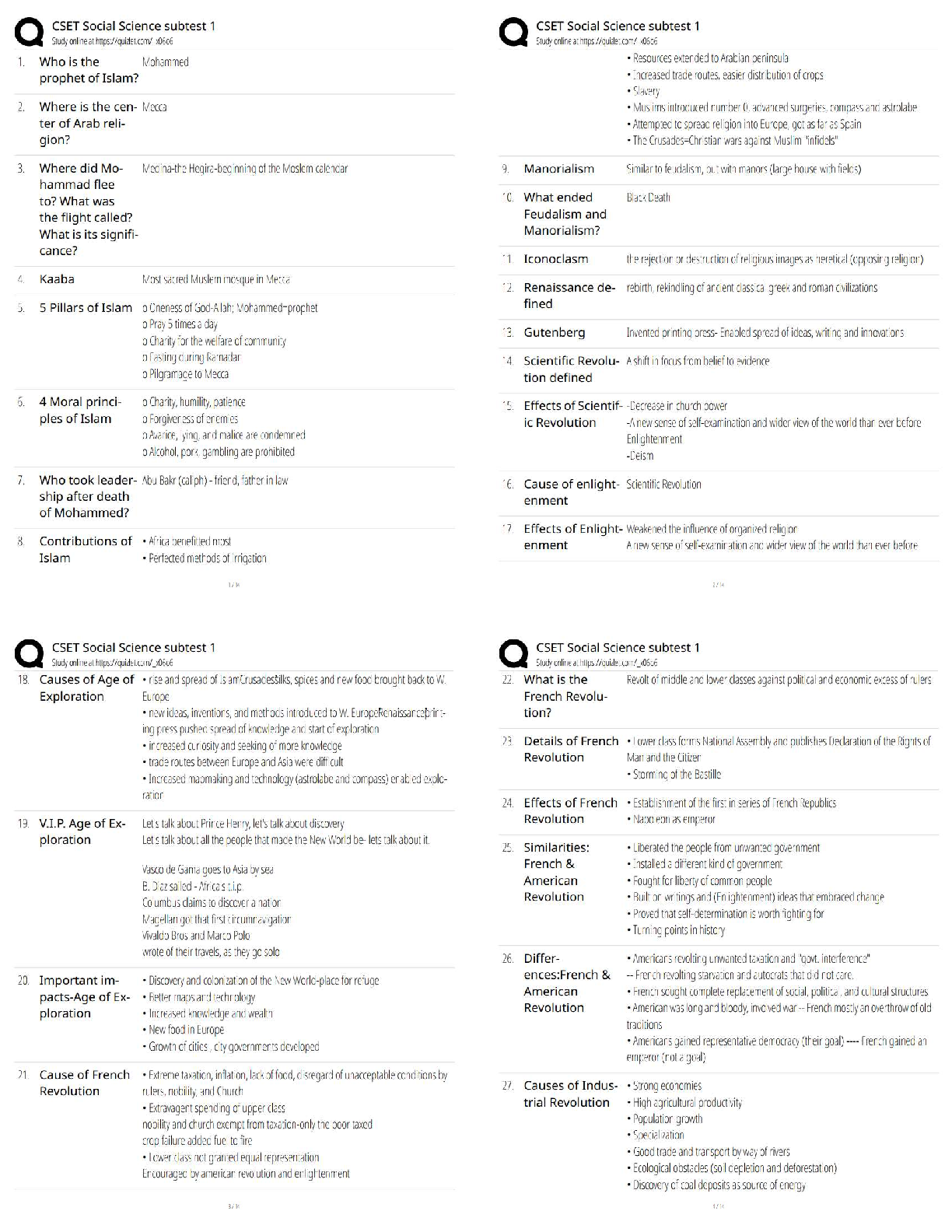
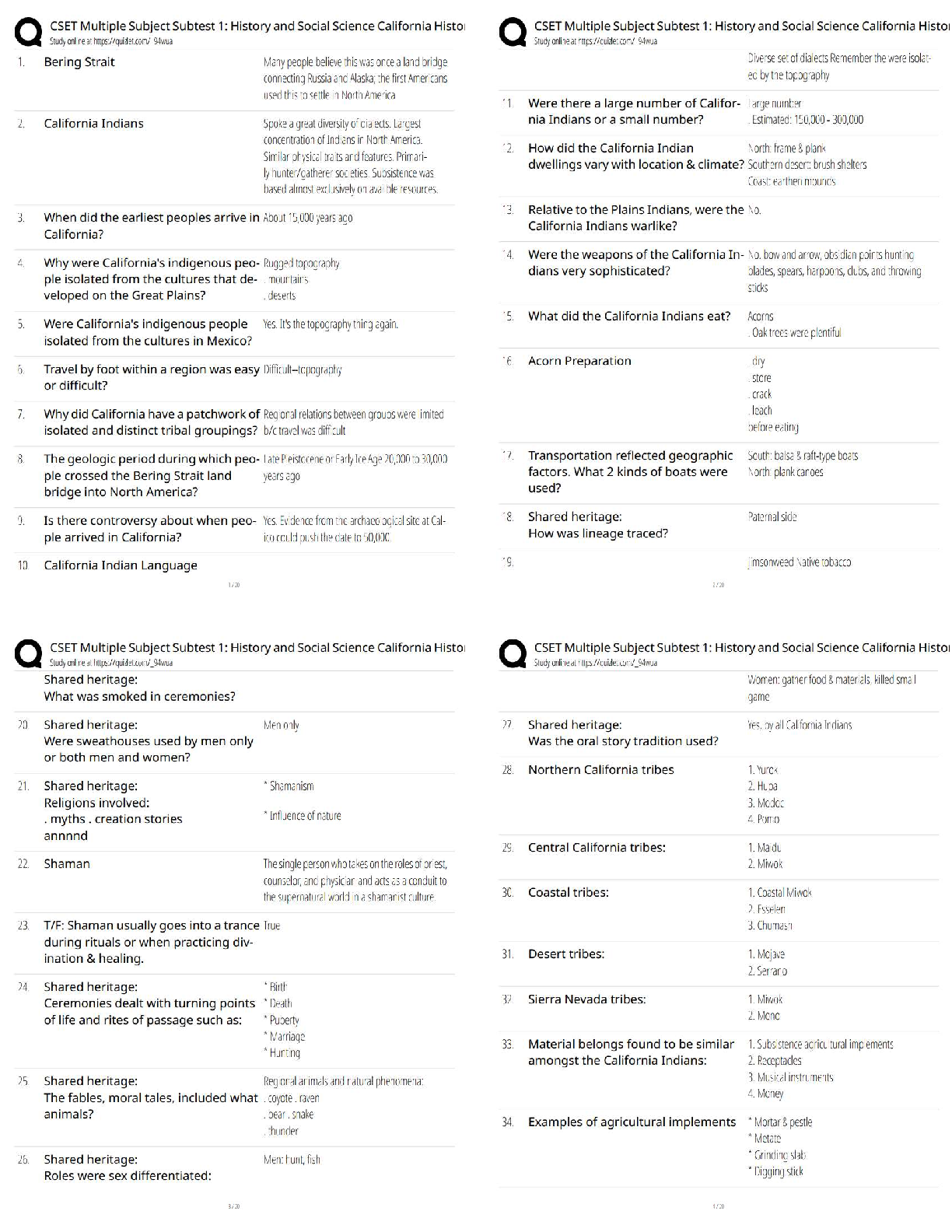
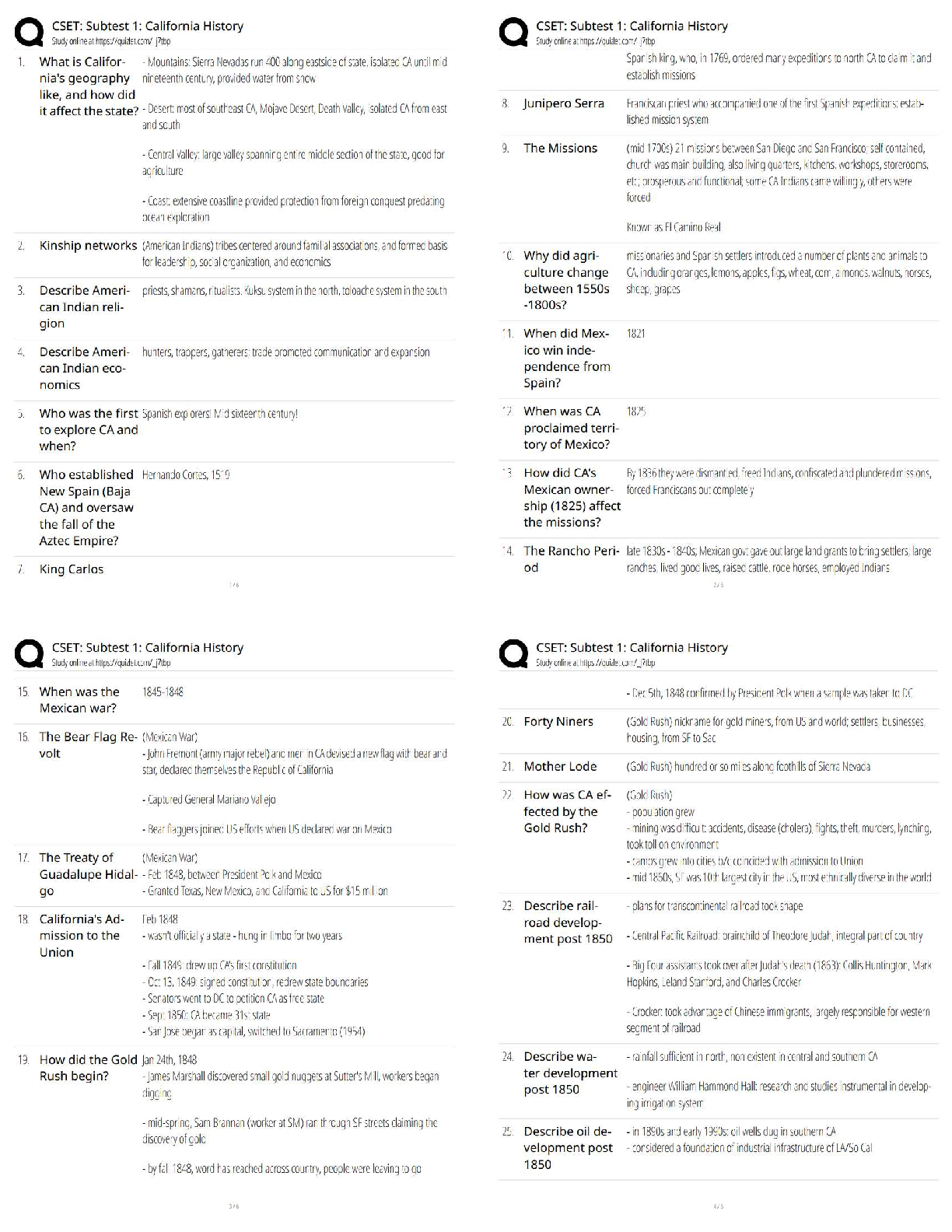
NR449 Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing – pn Comprehensive Exam Practice MCQ's NR449 Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing – pn Comprehensive Exam Practice MCQ's thoroughly revised with 100% correct ... answersNursing research is significant to the profession of nursing because it promotes what?NR449 Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing – pn Comprehensive Exam Practice MCQ's 1. Nursing research is significant to the profession of nursing because it promotes what? 2. Which aspect of the scientific investigation of nursing practice is also a fundamental concept of American Nurses Association (ANA)'s Code for Nurses? 3. Nurses who do not conduct research need to understand the nursing research process for which of these reasons? 4. Which of these actions demonstrates the role of a knowledgeable consumer of nursing research? 5. Members of the nursing staff are to participate in a unit-based clinical research study. Which research-related actions would be expected of a nurse with a baccalaureate nursing degree? 6. Which statement describes the role of the nurse in research? 7. What is the primary value of evidence-based nursing practice? a. Implementing the most cost-effective nursing practices when providing patient care b. Incorporating research findings with clinical expertise when individualizing patient care 8. A novice nurse researcher is comparing the processes used in nursing research and evidence-based practice. What differences, if any, exist between the two processes? d. In evidence-based practice, qualitative studies are critically appraised to answer a clinical question, whereas in nursing research, quantitative studies are reviewed to provide a foundation for the study. 9. A nurse is analyzing a research article. Where in the article is the nurse likely to find the research question and study purpose? 10. The nurse researcher is conducting a research study using subjects who will be interviewed regarding their experience with postpartum depression. For which of these reasons would the researcher selects a qualitative, rather than quantitative, research design? a. Quantitative research is usually conducted in natural settings using data that are words rather than numbers. 11. The nurse is analyzing a research article. To determine if an integrative review was performed as part of the study, the nurse must understand that this type of review is what? a. A summary of research studies on a focused topic that used a specific statistical methodology b. A synthesis of the research and theoretical literature on a specific area without a statistical analysis c. A synthesis of qualitative articles on a focused topic using a specific qualitative 12. When assessing the strength of a body of evidence used in a research study for consistency, the nurse should determine what? a. Extent to which the study's design, implementation, and analysis minimize bias b. Number of studies that have evaluated the research question, including overall 13. The nurse is analyzing a qualitative research article. In which section of the article is the nurse likely to find a summary of legal-ethical issues considered in the study? 14. The nurse is analyzing a qualitative research article. In which section of the article should the nurse expect to find a discussion of the research findings? 15. The nurse is using the critical reading process to analyze a research article. The nurse identifies the main theme of the article and states it in two sentences, using the nurse's own words. The nurse is using a strategy to promote which type of understanding? Rationale: The correct answer is B. Strategies for comprehensive understanding include restating the main idea or theme of the article in one's own words. 16. The nurse is using the critical reading process to analyze a research article. The nurse is using a list of criteria to determine how well the researcher performed each step of the research process. The nurse is using a strategy to promote which type of understanding? 17. Which of the following is a critical step for the quality improvement process in health care settings? a. Outlining general long-range goals b. Identifying current successful practices 1. Which statement(s) describe the actions of the baccalaureate nurse graduate as a participant in the nursing research process? (Select all that apply.) a. Administering care at the bedside according to a research protocol Which aspects of the nursing research process are common to nurses at all educational levels? (Select all that apply.) a. Disseminating research findings in research reports b. Maintaining the protection of patients who are subjects in a study All nurses should be aware that research is related to practice. All nurses can be a part of a clinical team that applies research to practice. For the baccalaureate nursing student, education in nursing research has which outcomes? (Select all that apply.) The student should learn how research is related to clinical nursing practice. The student should learn skills in the critical analysis of research to assist in decisions about applying research findings in nursing practice. Developing nurse researchers at a younger age is a priority for the future in the nursing profession for which reasons? (Select all that apply.) a. Enhancing the discipline's scientific development . 1. What difference, if any, exists between a research question and a hypothesis? a. A research question is practice based, and a hypothesis is theory based. b. A hypothesis attempts to answer the question posed by the research problem. 2. How is a hypothesis related to a theory? a. Hypotheses can be developed in the absence of a theoretical framework. 3. A nurse makes these statements. Which one has the greatest potential as an area of nursing research? a. "Most of our hospital's admissions come in at night." b. "It is difficult to find personnel willing to work the night shift." 4. The nurse has identified a clinical problem as a potential research question. Which of these steps should the nurse take next? 5. In a research study, what are the properties of interest that differ in value? 6. A nurse researcher proposes a study of teenage mothers and their experience with postpartum depression. Which of these considerations would affect the feasibility of the study? a. Availability of participants 7. What is the key difference between independent and dependent variables? a. The dependent variable should change in response to manipulation by the independent variable. b. The independent variable should change in response to manipulation by the dependent variable. c. Although both the dependent and independent variables are manipulated, only the dependent 8. When designing a research study, the nurse should have which of these understandings about independent and dependent variables? a. All research problem statements should contain a dependent and an independent variable. 9. A nurse's research question is, "How does maternal employment among health care professionals affect infant health during the first 6 months of life?" In this question, what is the dependent variable? a. Infant health b. Maternal employment 10. A nurse has defined the research question as, "How does oral nutritional supplementation during dialysis treatments affect the serum albumin levels of adult patients who have chronic kidney disease Stage 5?" In this question, what is the independent variable? a. Adult patients with chronic kidney disease Stage 5 11. A nurse has defined the research question as, "Is there a relationship between self-esteem and body weight among postmenopausal women?" What type of research-question format (or research design) is implied by this question? a. Correlational nonexperimental 12. A nurse has defined the research question as, "What is the lived experience of late-stage pregnancy loss among women older than 35 years?" What type of research-question format (or research design) is implied by this question? 13. Which research question is testable as currently written? a. Should parents addicted to crack cocaine be permitted to raise their children? b. Is the classroom an appropriate place to teach sex education to 10-year-old children? 14. What is the purpose of a hypothesis for any study? a. To identify the dependent and independent variables b. To provide direction for the study by indicating the expected outcomes c. To define the appropriate measures needed to test the research problem d. To provide a means of determining the feasibility of the proposed study 15. Which hypothesis fails to meet the criteria of testability? d. Postoperative patients who receive around-the-clock scheduled analgesics will have lower levels of pain compared with postoperative patients who receive analgesics on an as-needed (PRN) schedule. 16. Which hypothesis is nondirectional? a. Hospitals with an infection-control nurse will have fewer instances of sepsis among inpatients than hospitals without an infection-control nurse. b. There will be a greater weight loss among dieting patients who receive a weekly supportive 17. The nurse has defined the hypothesis as, "There will be no difference in the number of adverse events among patients discharged two days after an abdominal hysterectomy compared with patients discharged 4 days after an abdominal hysterectomy." This statement is an example of what? no relationship between the independent (postoperative days) and dependent (adverse events) variables. If in the statistical analysis a significant relationship is found, the null hypothesis would be rejected. 18. The nurse notes these statements in a research article: This study explores changes in coping and emotion that occur between the preoperative and the postoperative period. Further, the relationships between coping and emotion preoperatively and postoperatively are evaluated. Finally, the influence of preoperative coping and emotion on postoperative emotion is documented. The statements describe the aims or goals that the investigator hoped to achieve with the research and thus reflect the purpose of the study. 19. A nurse states the purpose of a research study as, "This study will compare the effect of warm and cold applications on the resolution of intravenous (IV) infiltrations in hospitalized older-adult patients in the early postoperative period." In this statement, what constitutes the independent variable(s)? variables, which will be manipulated and influence the dependent (outcome) variable resolution of IV infiltrations. 20. A nurse describes the hypothesis of a research study as, "There is a positive relationship between nurses' attitudes toward AIDS patients and the number of AIDS patients they have cared for in practice." This statement is an example of what? 21. The nurse has identified a patient situation that may be an area for study. The initial review of the literature helps the investigator to identify what? a. The number of subjects required for the studyof prior research, or the need to extend the knowledge base in a particular research area. It also identifies variables essential to consider in refining the research question. 22. Which hypothesis would be classified as a statistical hypothesis? a. Oxygen inhalation at 2 L/min by nasal catheter will decrease oral temperature measured with an electronic thermometer. b. Oxygen inhalation at 2 L/min by nasal catheter will not affect oral temperature measured with an electronic thermometer. 23. Which of these statements is correctly phrased as a clinical question for evidence-based practice? a. What is the best method to insert an enteral feeding tube in an adult patient? b. Are there differences in the characteristics of various brands of enteral feeding tubes? c. In addition to aspiration, what are the most problematic complications of enteral tube feedings? population (adult patients), intervention (methods of determining stomach placement), comparison (among methods), and outcome (prevent aspiration). 1. The review of literature is important to the research process for which of these reasons? a. It guides all steps of the research process. b. It provides a vehicle to disseminate the findings of the study. 2. The "6S" pyramid hierarchy of preappraised evidence developed by DiCenso, Bayley, & Haynes (2009) provides a means to help nurse consumers of research find pre appraised evidence for clinical questions. Using this model, which level of evidence would be highest? a. Summaries such as clinical practice guidelines An even higher level of the 6S pyramid is Computerized Decision Support Systems (CDSS), which integrate evidence-based clinical information into an electronic medical record. At present, these systems are not a reality in most institutions and, therefore, they were not included as an option in this question. 3. For which of these reasons would a nurse researcher include refereed journals in the literature review? 4. A research article has undergone a blind review for a peer-reviewed journal. The nurse reading the research article should understand which of the following about this review process? a. The reviewers of the article did not know the identity of the other reviewers. b. The reviewers of the article did not know the identity of the author. c. The criteria used to review the article were not known to the author. d. The criteria used to review the article were determined by the reviewers. 5. For which of these reasons would a nurse researcher decided to use secondary sources in a review of the literature? a. They provide material written by the person who conducted the study. 6. Which is an example of a primary source in a literature review? 7. Which is an example of a secondary source in a literature review? a. An oral history of a nurse researcher b. An investigator's report of a research study c. A summary and critique of another's scholarly work d. An autobiography of a developer of a nursing theory 8. Which of these electronic databases is the most relevant and frequently used source for nursing literature? 9. When comparing MEDLINE & CINAHL databases, which difference will the nurse find? a. Coverage of MEDLINE dates back to 1975, whereas coverage of CINAHL to 1980. b. MEDLINE's journal coverage includes more than 10,000 biomedical journals, whereas CINAHL's coverage includes more than 5000 journals. c. MEDLINE's database size is more than 21 million records, whereas CINAHL's database size is more than 3.2 million records. d. MEDLINE has more than 500 Evidence-Based Care Sheets, whereas CINAHL has more than 50 Evidence-Based Care Sheets. 10. A general timeline for a literature search for an academic paper or project is to go back how far in the literature? a. At least the last 6 months to 2 years 11. A nurse is encouraged to use a Boolean operator to more efficiently perform an electronic search of the literature. The nurse should understand that a Boolean operator is what? a. A specialized reference librarian who can assist in searches of electronic medical and nursing databases b. A software program that enables combinations of permissions and restrictions for a database words or groups of words in the literature search. These include the words, "and," "or," and "not." 12. Which command is an example of a Boolean connection used when ordering an electronic literature search? 13. Which website is an important source for clinical evidence but limited as a provider of primary documents for literature reviews? 14. What is considered to be essential to a thorough and relevant review of the literature? a. Use of both published and unpublished sources b. Critical evaluation of mainly primary sources 15. Which objective of a review of the literature is unique to a review for research purposes, rather than a review for evidence-based practice? a. Discover conceptual frameworks used to examine problems b. Generate useful research questions and hypotheses 16. Which of these factors limits the usefulness of the World Wide Web as a source of information for research consumers? a. Downloading from the Web can be a slow process. Many sources are not data based and primary sources. It is not always evident which sources are data based and which are not. 17. When the nurse researcher conducts an electronic literature search, the search yields more than 7000 citations for the topic. The researcher should make which of these interpretations of the findings? a. The search was comprehensive. 18. Why would a nurse researcher choose to use multiple online fee-based databases such as CINAHL and MEDLINE? a. The charges for these services are minimal. 19. A study published in a nursing research journal is titled, "Effects of nocturnal hemodialysis on physiological and psychological parameters of patients with end-stage kidney disease." The nurse should recognize that this study belongs to which of these types of reference? 20. Literature reviews are usually organized according to what? a. The order in which materials are retrieved 1. Which phrase correctly defines a theory? a. The operational definition of the study's conceptual framework b. The assumptions and beliefs of the worldview of the researcher 2. In which way are theory and practice interrelated for the hospital-based nurse researcher? a. Practice is the operational definition of theory. b. Practice provides the opportunity to test theory. 3. Which nursing theory is classified as a Grand Nursing Theory? a. Polk's Theory of Resilience b. Mishel's Uncertainty in Illness Theory Rationale: The correct answer is C. Orem's theory is a Grand Nursing Theory since it is an all-inclusive conceptual structure that includes views on person, health, and environment. 4. Situation-specific nursing theories are becoming more popular in nursing research for which of these reasons? a. Increased emphasis on evidence-based practice 5. A graphic or symbolic representation of a phenomenon not directly observable, which allows the reader to visualize key constructs and their interrelationships, is called what? a. A concept 6. How is a model related to a concept or concepts? a. A model tests conceptual theories. b. A concept defines the purpose of a model. c. Relationships between or among concepts are demonstrated in a model. d. Concepts generate the theoretical basis for knowledge depicted in a model. 7. Pender's health promotion model is an example of what type of theory? a. Grand nursing theory b. Middle-range nursing theory 8. Which statement is an operational definition of a concept? a. Death anxiety is an uncomfortable feeling on contemplation of one's own death, measured by Templar's Death Anxiety Scale (Templar, 1986). b. Pain is a pattern of responses to protect the organism from harm (Sternbach, 1979). 9. When reading a report of the results of a nursing research study, the nurse notices that the theoretical framework is drawn from a discipline other than nursing. When critiquing the theoretical framework, the nurse should determine the answer to which of these questions? a. Does the research have implications across disciplines? b. Is the researcher a recognized leader in the discipline of nursing? c. Does the author have special expertise or education in the discipline from which the theoretical framework is derived? 10. Which research report title suggests that theory was generated as the outcome of the study, rather than being used as the framework for the study? a. Women's experiences of undergoing CABG surgery (Banner, D., et al., 2011) b. Couple functioning and post-traumatic stress symptoms in U.S. army couples: The role of resilience (Melvin, K.C., et al., 2011) c. A randomized, clinical trial of education or motivational-interviewing-based coaching of women's experiences of a specific cardiac surgical procedure suggests a qualitative research study and the generation of a situation-specific theory or model. 11. Which research report title suggests that theory was used as the framework for the study, rather than being generated as the outcome of the study? a. The experiences of nurse practitioners providing health care to the homeless (Seilor, A.J. & Moss, V.A., 2012) b. A transformative decision-making process for mammography screening among rural, low-income women (Purtzer, M.S., 2012) 1. When critiquing a research study's theoretical framework, the nurse should keep in mind which information? (Select all that apply.) a. Theoretical frameworks guide hypothesis formulation in qualitative and quantitative research studies. c. A theoretical framework of a nursing research study must be based on nursing theories or models. d. A theoretical framework may not be identified in all types of nursing research. Not all research studies have a stated theoretical framework. In fact, qualitative research reports rarely cite theoretical frameworks. 1. The measures used by a nurse researcher to maintain uniformity of conditions in a quantitative research study refer to which aspect of the study? 2. What is the overall purpose of the research design in a quantitative research study? a. To determine sample size b. To identify the problem statement 3. In which of these ways does the nurse researcher's literature review help select the appropriate study design? a. By enlarging the scope of the study's hypotheses b. By objectively assessing available knowledge of the area 4. When reviewing a research report, the nurse determines that all aspects of a study systematically and logically follow from the research problem. Which condition has been met? 5. Which factor is most likely to be a mediating variable in a study to determine if high doses of vitamin C help reduce the subjects' susceptibility to influenza? a. The subjects' use of influenza vaccine b. The subject' knowledge of vitamin C's functions 6. A nurse researcher is designing a quantitative research study involving a specific group of patients admitted to local hospitals. Which factor would negatively affect the feasibility of this study? a. The local region has a high percentage of families that could participate in the study. b. Potential study subjects represented less than 1% of hospital admissions during the year previous to the study. 7. A nurse is designing a study to determine whether a videotape or a written pamphlet is more effective in teaching young women how to perform a breast self-examination (BSE). Which of these actions would provide the best control for a mediating variable? a. Include identical content in both BSE teaching methods b. Exclude subjects who already perform BSE on a regular basis 8. How would a nurse researcher ensure that the sample used in a quantitative study is homogeneous? a. Use eligibility criteria to limit extraneous variables relevant to the study. b. Randomly assign subjects to either the experimental or the control group. 9. How could a nurse researcher's use of a homogeneous sample weaken a research study? a. By decreasing the reliability of the findings b. By decreasing the generalizability of the findings c. By increasing the number of subjects needed to reach statistical significance d. By increasing the risk that the findings were the result of chance alone 10. Why should a nurse researcher want to limit or eliminate extraneous variables in a study? a. More research questions would be required to account for extraneous variables. b. Extensive statistical analysis would be required to justify the presence of extraneous variables. 11. When should a nurse researcher include an extraneous variable as part of a study's design? a. When excluding the variable would limit the study's generalizability b. When the variable is an important consideration for the study's outcome 12. A study is examining the effect of a new antilipemic drug, compared with placebo, on lipoprotein levels in postmenopausal women. Which of these actions represents the researcher's attempt at consistency in data collection to control extraneous variables? a. Drawing the serum lipoprotein levels of all subjects at the same time of day c. Using the same room for drawing blood for lipoprotein levels of all subjects d. Ensuring that all subjects are postmenopausal women taking lipid-lowering medication 13. A nurse researcher assigns half a study sample to an experimental group and the other half to a control group. What does this action represent? a. Instrumentation of the independent variable variable. 14. For which of these reasons would a nurse researcher choose to assign subjects randomly to groups in a study? a. To help ensure that all groups within a study are representative of the larger population b. To increase the chance that the study groups will be different from each other with regard to 15. A nurse researcher assigns subjects to experimental and control groups in such a manner that each subject in a population has an equal chance of being selected. What is the researcher using? Randomization is the process of obtaining subjects so that each has an equal chance of being selected for experimental or control groups. 16. The issue of control would be less important in a quantitative study with which type of research design? Control is less important in exploratory studies because the researcher is investigating an area in which little literature exists. 17. Which situation represents a threat to internal validity in an experimental study measuring the effect of a videotape of discharge instructions for patients who underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery? d. Data collection for the videotape and control groups took 1 year. of the true effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable(s). 18. The nurse researcher designed a study examining anxiety among elementary school children. If a widely publicized murder of a child occurred in the city during the time frame of the study, what type of threat to internal validity would the murder represent? The murder would represent a historical event threatening internal validity. 19. A nurse researcher should consider mortality a threat to the study's internal validity for which of these reasons? a. There is concern that the intervention may have harmful effects on subjects. b. Those who dropped out of the study may be different than those who remained in the study. who drop out or who are otherwise lost from a study may differ in some important way from remaining subjects and therefore threaten internal validity. 20. A nurse researcher can control for selection bias in a study by taking which of these actions? consistently applied help obtain a representative sample and decrease the risk of selection bias. 21. External validity refers to which of these issues? a. The relationship existing between the independent variable and the study outcomes b. The influence of a specific event on the independent variable 22. Which of these situations describes a reactive (Hawthorne) effect? a. Control subjects in an intervention study to reduce anxiety also experience a reduction in anxiety. b. The subjects in an intervention support group continue the support group after the study has ended. c. Subjects become concerned after learning that they received a placebo, not the treatment, during the study. 23. A nurse researcher is investigating the effect of type of operating room mattress and surgical position on tissue interface pressures in healthy young adults. Which component of research is most affected by the choice of subjects? selection affects external validity (generalizability), especially because most surgical patients are not healthy young adults. 24. What action by a nurse researcher will help eliminate bias on the dependent variable? a. Establishing strict eligibility criteria for the study participants b. Ensuring that all data are collected by a single researcher for impact on the dependent variable. 1. A nurse researcher is planning to write a proposal for a research study using a quantitative design. To maintain control in the study, the nurse should include which elements? (Select all that apply.) 2. A nursing student is reviewing a research study in which researchers used a pretest/posttest design to examine the effect of an AIDS education intervention on teenagers' knowledge about the condition over a school year. What threats to internal validity could be present? (Select all that apply.) Testing is a threat to internal validity because use of a pretest may affect subjects' subsequent responses to a posttest. 3. What should the nurse researcher consider when determining the feasibility of a research question? (Select all that apply.) The researcher must determine whether a sufficient number of eligible subjects will be available and willing to participate in the study. Before embarking on a study, the researcher should itemize the expenses and project the total cost of the project. 4. Which factors would be considered threats to internal validity? (Select all that apply.) because the effect of taking a pretest may affect the subjects' posttest performance (the dependent variable). Selection bias occurs if precautions are not taken to obtain a representative sample. Randomly assigning subjects to groups helps to minimize selection bias. 1. The nurse is critiquing a research study that used an experimental design. How can the nurse determine if the study's results are able to infer causality? a. The relationship between independent and dependent variables must be reciprocal. b. The relationship between independent and dependent variables must not be explainable by 2. The nurse is critiquing a research study that involves subjects undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer. Which finding would meet a criterion for inferring causality between performance of exercise and adaptive behavior of the subjects receiving chemotherapy? a. Adaptive behavior began before the exercise program was initiated. b. Adaptive behavior occurred in the control group over time. c. The level of adaptive behavior increased in direct proportion to an increase in the intensity of the exercise. 3. The experimental treatment initiated by the researcher can be described as what kind of variable? 4. Which of these criteria is most important when evaluating the results of an experimental research study? a. The size of the experimental group compared with the size of the control group. b. The validity that the experimental treatment caused the desired effect on the outcome. c. The congruence of research questions to the purpose and hypotheses. The validity of experimental study results depends on how well the researcher has controlled alternative explanatory variables. 5. Compared with a quasi-experimental design, which of these characteristics should a nurse expect to see only in a true experimental design? Random assignment to groups is not present in a quasi-experimental study. 6. Which factor should be the primary consideration when determining the validity of experimental study findings? c. The credentials and previous experience of the researcher 7. In which way is the independent variable handled differently in a study with a true experimental design compared with a study with a quasi-experimental design? a. An experimental design requires an independent variable, whereas a quasi-experimental design neither identifies nor requires an independent variable. b. Although both designs identify an independent variable, the nature of the groups (randomized versus nonrandomized) means that manipulation may result in different results. c. Experimental designs demonstrate that the independent variable is related to the outcome, and quasi-experimental studies allow for independent variables that stand alone. d. Although both designs identify an independent variable, experimental designs identify it experimental designs is the randomization of groups. Independent variables are manipulated in both designs. 8. Random assignment of subjects to experimental and control groups has which of these effects? are equally distributed within groups, thus reducing systematic bias. 9. Randomization strengthens an experimental study in which of these ways? a. It reduces the risk that a subject will be harmed by participation in the study. b. It ensures that the experimental group and the control group have the same number of participants. c. It allows the study to proceed without the researchers knowing which group is the that emerge in a study are related to the treatment condition and not to chance alone. 10. Control is important in an experimental research study for which of these reasons? a. It ensures maintenance of participant confidentiality. b. It introduces one or more constants into the experimental situation. c. It prevents data collection from extending beyond the original time specified for the study. variables on the interaction of the identified independent and dependent variables. Control of variables makes it possible to explain a study's findings with accuracy. 11. In a true experimental study, the control group is the group that does what? a. Receives the experimental treatment b. Receives the placebo treatment 12. Which action would increase the control of an experimental study? a. Establishing strict criteria for subject selection b. Allowing participants to decide whether or not to be in the experimental group 13. A study of a program to help people quit cigarette smoking had three groups of subjects. The first group received one supportive phone call 10 days after attending a program on strategies to resist smoking. A second group received a supportive phone call every week for 6 c. Manipulation of the treatment dose d. Control of extraneous variables 14. A study of a program to help people quit cigarette smoking had three groups of subjects. The first group received one supportive phone call 10 days after attending a program on strategies to resist smoking. A second group received a supportive phone call every week for 6 a. Program on strategies to resist smoking b. Elimination of cigarette smoking c. Weekly supportive phone call 15. What type of threat to validity is minimized by the use of a Solomon four-group design? 16. An after-only nonequivalent control group design would be appropriate to study which of these research questions? a. What is the effect of the cause of spousal death on widows' self-esteem? b. What is the effect of preoperative teaching on vascular complications after orthopedic surgery? preoperative teaching) and randomization is not used to assign subjects to groups. It makes the assumption that the two groups are equivalent and comparable before the introduction of the intervention. 17. A quasi-experimental study design would be a better choice for a research study than an experimental study design in which of these situations? a. The study is to be conducted in a laboratory setting. 18. The nurse researcher is planning a study in which subjects will not be randomly assigned to groups. Which type of design would be appropriate for this study? a. Nonequivalent control group design b. Posttest only control group design experimental design in which subjects are not randomly assigned to groups. 19. A planned quasi-experimental study using a nonequivalent control group design has several extraneous variables that threaten its internal validity. The nurse researcher's actions should be based on which understanding? a. The results of the study will not be statistically significant. b. The random assignment of subjects to groups will nullify the intervening variables. 20. A quasi-experimental research design would be preferable to an experimental design in which of these situations? a. A smaller sample size is sufficient to obtain significant results. b. Demonstration of a cause-and-effect relationship is the desired outcome. 21. A study was conducted to determine if videotaped instruction was more effective than written instructions (a pamphlet) to teach menopausal women the benefits of regular mammograms. Which condition would be considered an antecedent variable? a. There were 38 subjects in the pamphlet group and 34 subjects in the videotape group. b. During the study, 50% of the videotape group received flu shots, whereas 25% of those in the pamphlet group received flu shots. c. Four members of the pamphlet group had mothers who had been diagnosed with breast cancer, but no members of the videotape group had mothers who had been diagnosed with breast cancer. d. While participating in the study, five members of the videotape group began performing 22. In a study using a true experimental design, which of these methods would control for antecedent variables? a. Manipulation of the independent variable to groups helps ensure that antecedent (preexisting) variables will be similarly distributed between groups. 23. How are threats to validity affected when studies are conducted in real-world settings? a. Threats to both internal and external validity are increased. b. Threats to both internal and external validity are decreased. 24. How are threats to validity affected when studies are conducted in laboratory settings? a. Threats to both internal and external validity are increased. b. Threats to both internal and external validity are decreased. c. Threats to internal validity are decreased, whereas threats to external validity are increased. populations). 1. Which are characteristics of quasi-experimental research designs that are considered weaknesses, compared with experimental designs? (Select all that apply.) a. Cost of implementation b. Confidence in making causal assertions c. Subject to contamination of internal validity Quasi-experimental designs are particularly subject to contamination of internal validity by extraneous variables. Findings of quasi-experimental studies may be due to the influence of extraneous variables, rather than the experimental treatment (independent variable). 2. A research study in a laboratory setting incorporates 4 groups (2 control and 2 experimental) in which only 1 experimental group and 1 control group are pretested, while all 4 groups are post tested. Which descriptions of the design are accurate? (Select all that apply.) a. Experimental design b. After-only experimental design Solomon four-group design. The example describes a Solomon four-group design. 3. A nurse researcher is planning a quantitative (experimental) research study to test the effect of a new wound product on wound healing. Which of these factors is necessary to implement an experimental pretest-posttest design? (Select all that apply.) a. Inclusion of a second control group c. Use of two posttreatment data collection times possible to collect pretest data. Random assignment must be possible for both treatment and 4. A research study is planned to determine the effect of nutritional supplementation and type of support surface on the rate of wound healing in sacral myocutaneous flap failures. Which is an independent variable in this study? (Select all that apply.) a. Rate of wound healing b. Sacral myocutaneous flap interventions or treatments (independent variables). Nutritional supplementation is one of the specified interventions or treatments (independent variables). 5. Which research designs could be classified as experimental? (Select all that apply.) d. After-only nonequivalent control group design e. One-group pretest-posttest design design. The after-only design is an experimental design. A true experimental pretest-posttest control group design is an experimental design. 6. Which research designs could be classified as quasi-experimental? (Select all that apply.) e. One-group pretest-posttest design design. A one-group pretest-posttest design is a quasi-experimental design. A time-series design is a quasi-experimental design. 1. What is the first question that should be asked in determining whether a cross-sectional design or a longitudinal design should be used in a quantitative study? a. Is there an independent variable? b. What is the nature of the problem being studied? 2. Which data collection method is most appropriate for an RN researcher to use in a survey study? c. Unstructured interview d. Questionnaires 3. Why would a nurse researcher choose to use research studies that examine the associations or relationships between variables? a. A causal relationship can be determined between the variables. b. Greater manipulation of the variables is possible in this type of study. 4. Why would a nurse researcher choose not to use a survey study design? a. Data analysis is limited with a survey design. b. Information collected is relatively superficial. c. Results are never applicable beyond the study population. 5. A nurse researcher would choose to use a correlational study of multiple variables for which purpose? a. To identify the independent variable b. To test whether one variable causes another variable 6. Why would a nurse researcher choose to use a correlational design for a nonexperimental study? a. It represents an efficient and effective method of collecting a large amount of data about a problem. b. Many questionnaires and instruments are already developed and have been determined to be valid and reliable. 7. A nurse researcher will choose to use a developmental study design to do what? a. Allow comparison of the results of qualitative studies of a phenomenon to the results of quantitative studies of the same phenomenon b. Allow reanalysis of existing data for a secondary purpose not stated in the original research design permits exploration of the changing nature of relationships of variables over time. 8. Which statement about cross-sectional studies is most accurate? a. More than one group can be compared. b. Only descriptive data can be measured. 9. A nurse researcher would decide to use a longitudinal or prospective design for which reason? a. It is associated with data that are focused and deep. b. It allows the overall study to be more manageable for the researcher. c. It allows the issue of maturation to be avoided as a threat to internal validity. d. It allows the nurse researcher to avoid the use of tools or instrumentation. 10. A nurse researcher would decide to use a retrospective or ex post facto study for which reason? a. Obtaining informed consent is not an important issue. b. There is maximal opportunity to manipulate the independent variable. 11. A nurse researcher will choose an ex post facto design over more a correlational design for which reason? a. It is easier to implement. b. The independent variable can be manipulated. 12. Which type of study should be used when data are collected at only one point in time? Cross-sectional design is associated with data collection at one point in time. 13. Data collection instruments were sent to the same sample of women at six different times during the first year of living with breast cancer. What type of study design does this exemplify? 14. What threat to internal validity is most closely associated with a longitudinal design? A major disadvantage of longitudinal design is loss of research subjects. 15. What study design allows study participants to serve as their own controls, allowing early trends in the data to emerge? as their own controls, and trends in the data can emerge. 16. The longitudinal study and the prospective study are similar for which reason? a. Each moves forward in time. Longitudinal and prospective designs both move forward in time for data collection. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$14.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 16, 2020
Number of pages
10
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 16, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
224







.png)


.png)