Building Information System
13.1 How Does Building New Systems Produce Organizational Change?
Systems Development and Organizational Change
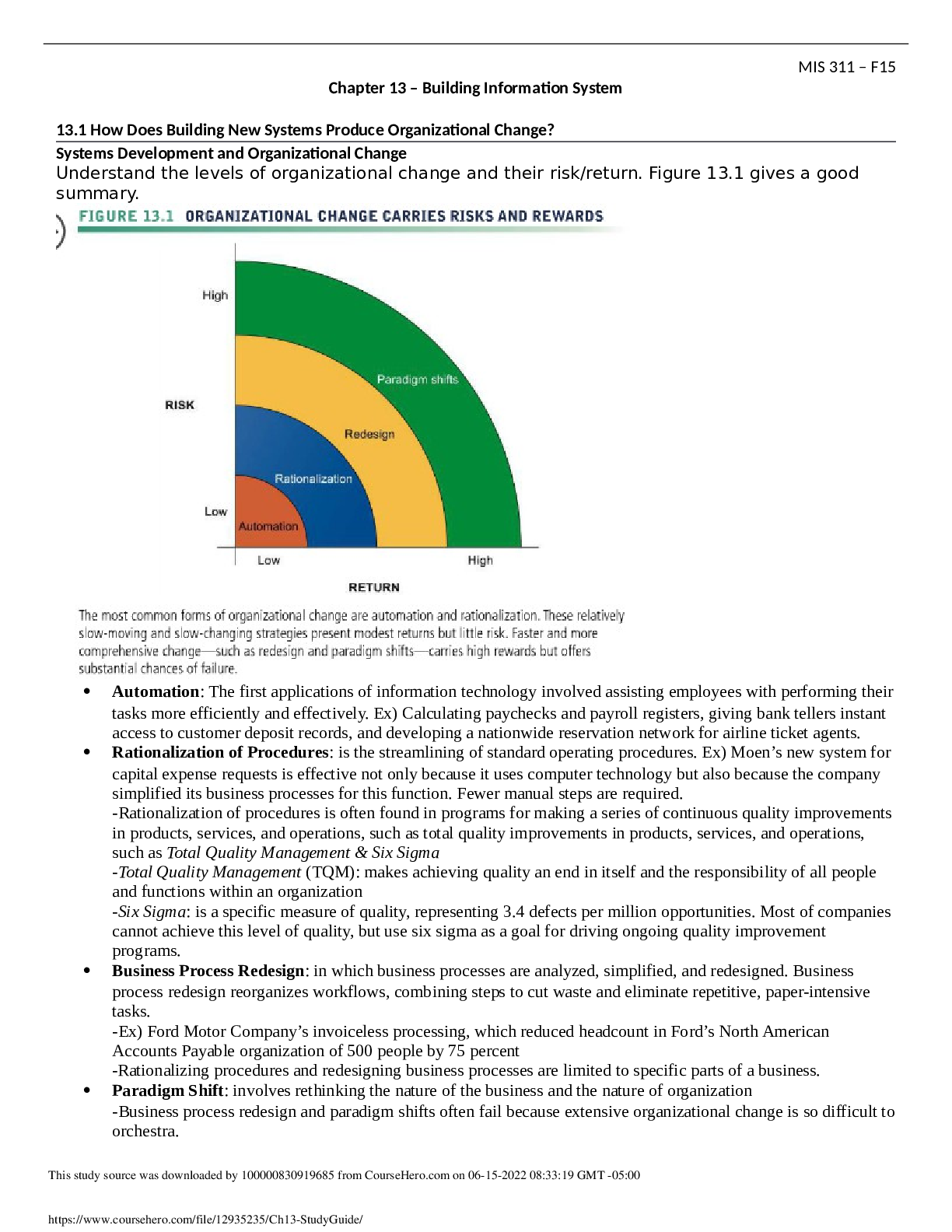
Understand the levels of organizational change and their risk/return. Figure
...
Building Information System
13.1 How Does Building New Systems Produce Organizational Change?
Systems Development and Organizational Change
Understand the levels of organizational change and their risk/return. Figure 13.1 gives a good
summary.
Automation: The first applications of information technology involved assisting employees with performing their
tasks more efficiently and effectively. Ex) Calculating paychecks and payroll registers, giving bank tellers instant
access to customer deposit records, and developing a nationwide reservation network for airline ticket agents.
Rationalization of Procedures: this is the streamlining of standard operating procedures. Ex) Moen’s new system for
capital expense requests is effective not only because it uses computer technology but also because the company
simplified its business processes for this function. Fewer manual steps are required.
-Rationalization of procedures is often found in programs for making a series of continuous quality improvements
in products, services, and operations, such as total quality improvements in products, services, and operations,
such as Total Quality Management & Six Sigma
-Total Quality Management (TQM): makes achieving quality an end in itself and the responsibility of all people
and functions within an organization
-Six Sigma: is a specific measure of quality, representing 3.4 defects per million opportunities. Most of the companies
cannot achieve this level of quality, but use six sigma as a goal for driving ongoing quality improvement
programs.
Business Process Redesign: in which business processes are analyzed, simplified, and redesigned. Business
process redesign reorganizes workflows, combining steps to cut waste and eliminate repetitive, paper-intensive
tasks.
-Ex) Ford Motor Company’s invoice less processing, which reduced headcount in Ford’s North American
Accounts Payable organization of 500 people by 75 percent
-Rationalizing procedures and redesigning business processes are limited to specific parts of a business.
Paradigm Shift: involves rethinking the nature of the business and the nature of the organization
-Business process redesign and paradigm shifts often fail because extensive organizational change is so difficult to
orchestra.
This study source was downloaded by 100000830919685 from CourseHero.com on 06-15-2022 08:33:19 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/12935235/Ch13-StudyGuide/MIS 311 – F15
Business Process Redesign
Business process redesign vs. business process management
-Many businesses today are trying to use IT to improve their business processes. Some of these systems entail incremental
process change, but others require more far-reaching redesign of business processes. To deal with these changes,
organizations are turning to Business Process Management.
-BPM provides a variety of tools and methodologies to analyze existing processes, design new processes, and optimize
those processes.
Read the 5 steps and know their order. Skip the rest including the Tools for BPM.
1. Identify processes for change: understanding what business processes need improvement
2. Analyze existing processes: Existing business processes should be modeled and documented. The process design
team identifies redundant steps, paper-intensive tasks, bottlenecks, and other inefficiencies
3. Design the new process: Once the existing process is mapped and measured in terms of time and cost, the process
design team will try to improve the process by designing a new one
4. Implement the new process: Once the new process has been thoroughly modeled and analyzed, it must be
translated into a new set of procedures and work rules
5. Continuous measurement: Once a process has been implemented and optimized, it needs to be continually
measured.
13.2 What Are the Core Activities In the Systems Development Process?
-The activities that go into producing an information system solution to an organizational problem or opportunity are
called Systems Development
-System development is a structured kind of problem solved with distinct activities. These activities consist of systems
analysis - systems design – programming – testing - conversion - production and maintenance
Systems Analysis
Know the 6 steps, their definitions, and order
Class discussions on the steps
1. Systems analysis -> types of feasibility studies (class discussions)
-System analysis is the analysis of a problem that a firm tries to solve with an information system. It consists of defining
the problem, identifying its causes, specifying the solution, and identifying the information requirements that must be met
by a system solution
-Feasibility study to determine whether that solution is feasible, or achievable, from a financial, technical and
organizational standpoint.
-The feasibility study determines whether the proposed system is expected to be a good investment, and whether the
technology needed for the system is available and can be handled by the firm’s information systems specialists, an
whether the organization can be handle the changes introduced by the system.
-Information requirements of a new system involve identifying who needs what information, where, when, and how.
-Requirements analysis carefully defines the objectives of the new or modified system and develops a detailed description
of the functions that the new system must perform.
2. System design -> activities in this stage (class discussions)
-System analyses describes what a system should do to meet information requirements, and systems design shows how the
the system will fulfill this objective
-System designer details the system specifications that will deliver the functions identified during systems analysis.
-The role of End Users: Users must have sufficient control over the design process to ensure that the system reflects their
business priorities and information needs, not the biases of technical staff.
[Show More]