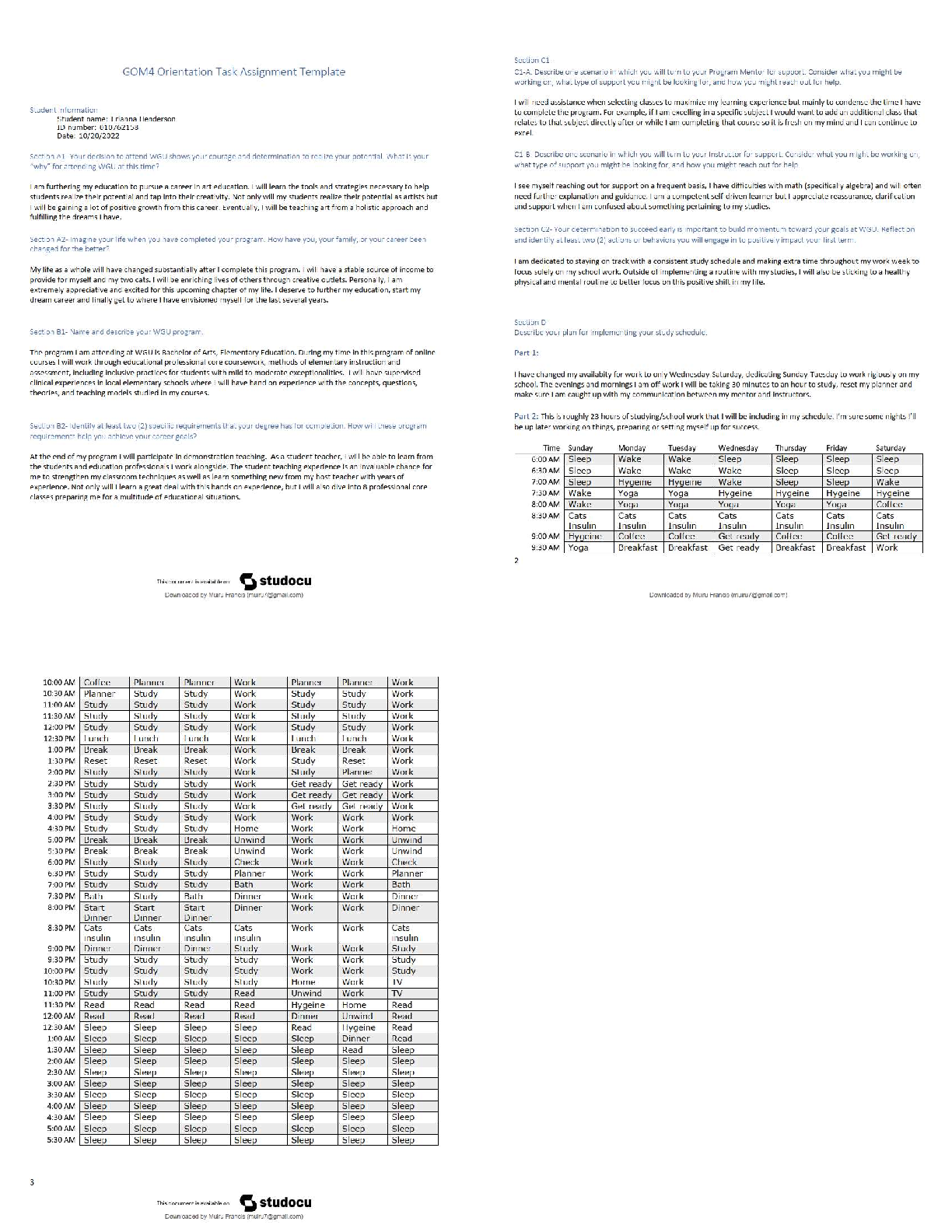
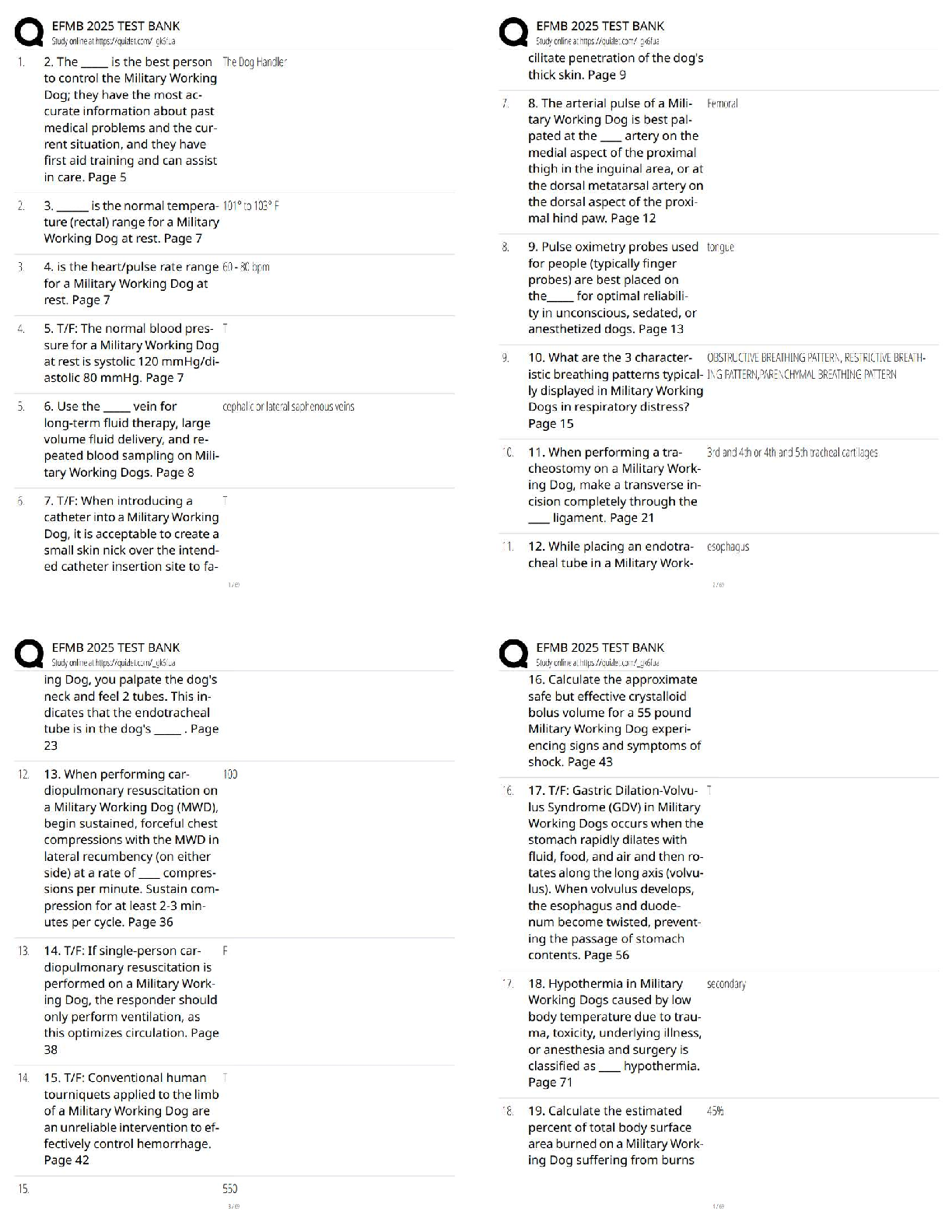
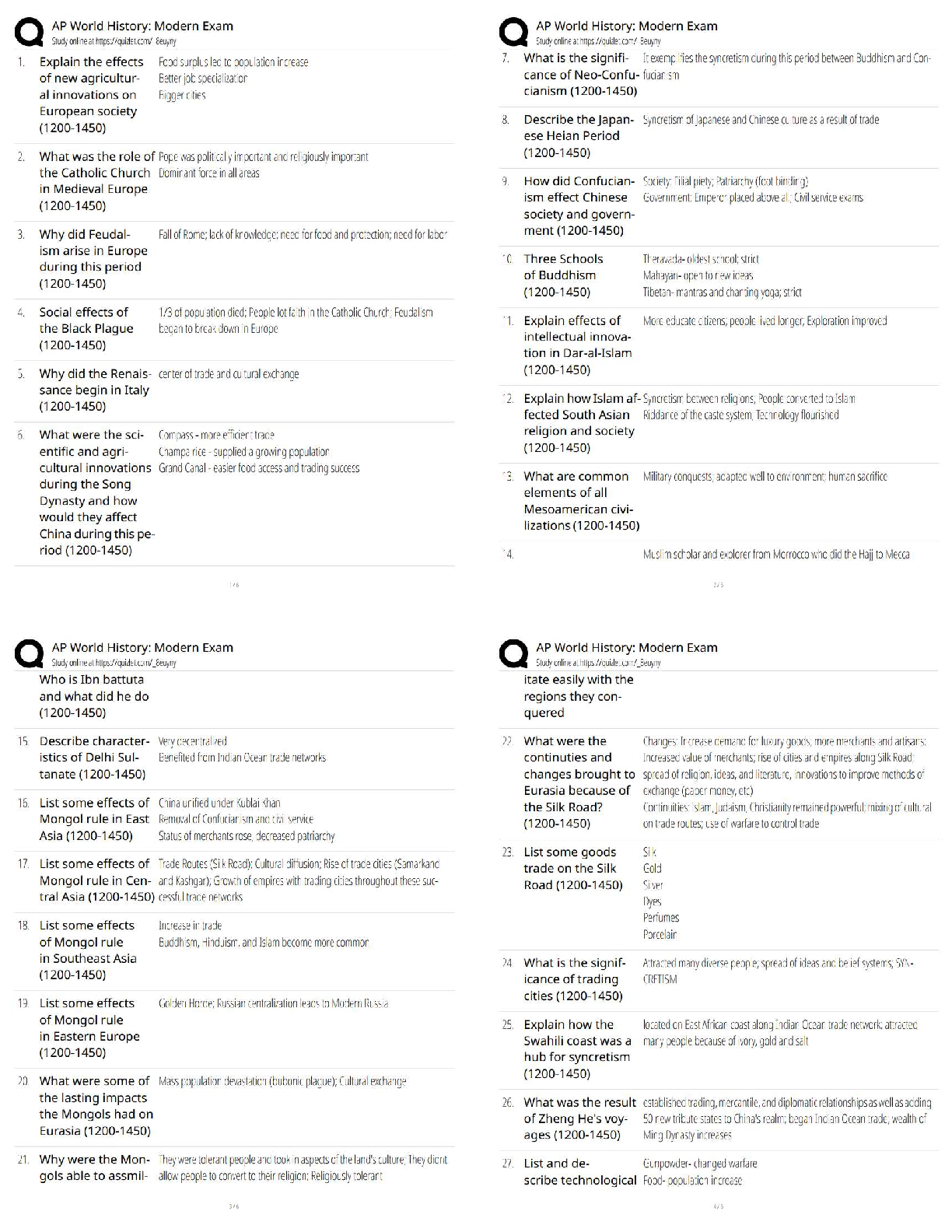
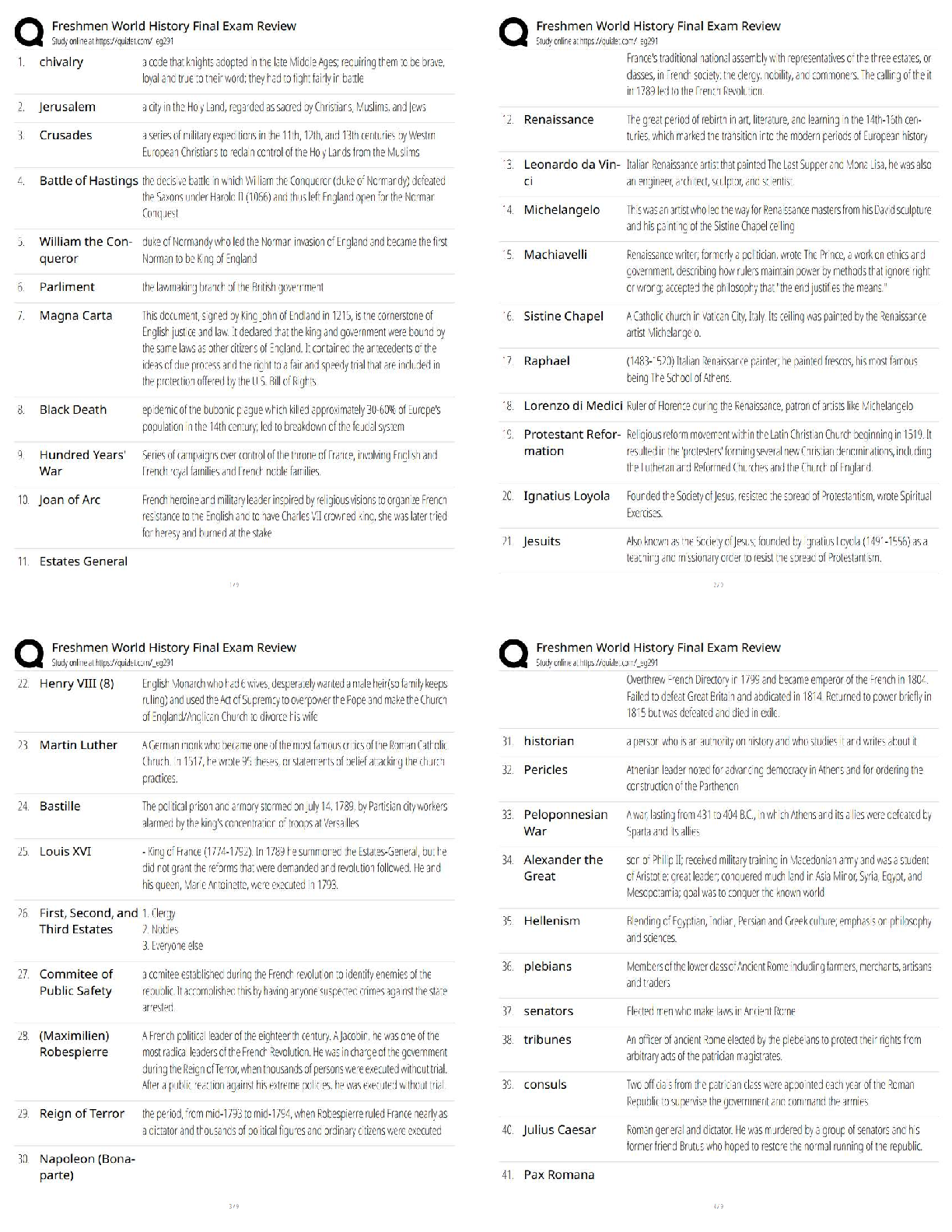
Deposition of dielectric thin films RF Magnetron Sputtering MM 731: Experiments in advanced materials processing (Lab.)
$ 10

ATI RN EXIT EXAM FORM A
$ 23

PSY 550 Week 3 Assignment, Informed Consent and Debriefing