Health Care > EXAM > PHI 103 Week 2 Quiz QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALL CORRECT (All)
PHI 103 Week 2 Quiz QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALL CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
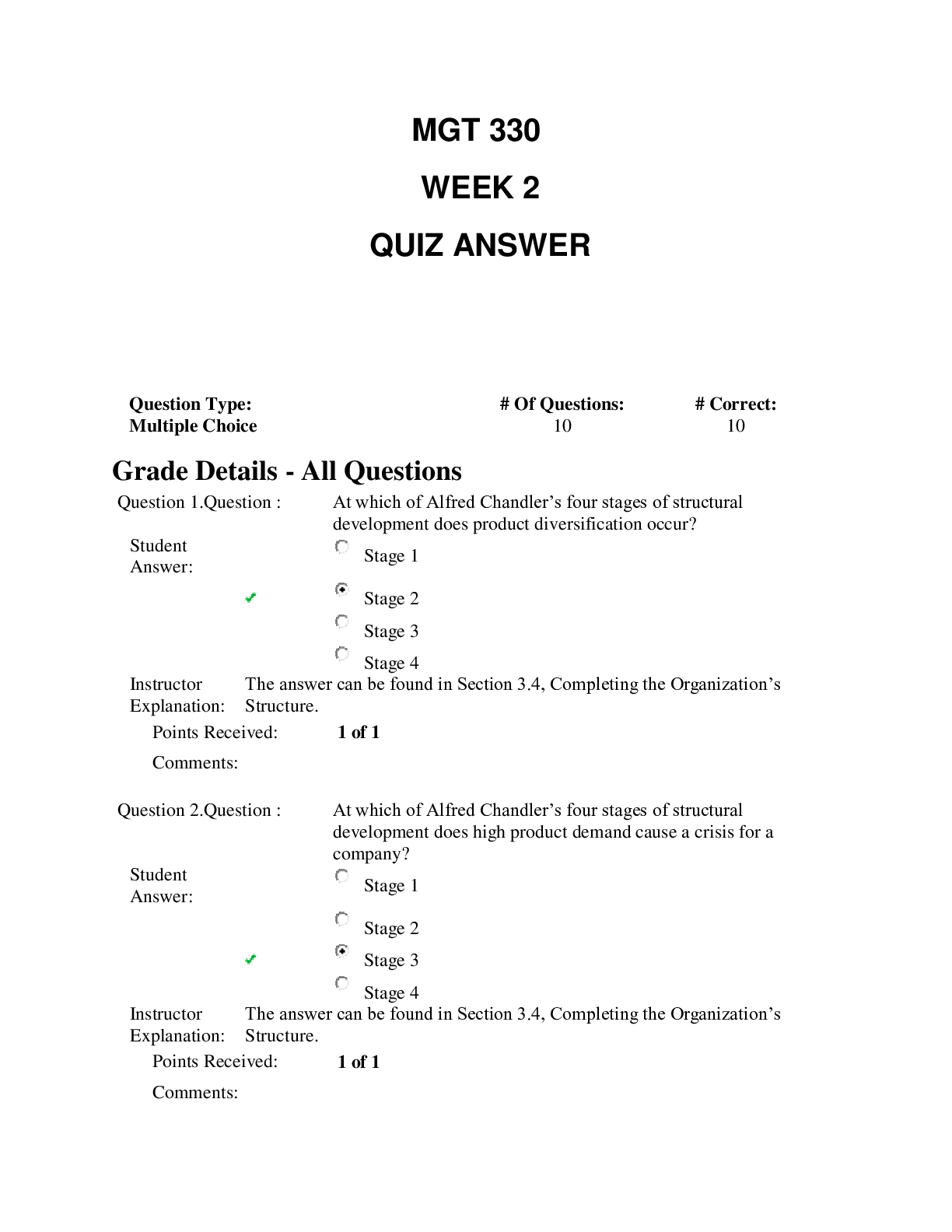
1. Question : Identify the form of the following argument. If there is a universal standard for ethics, then there is an ultimate foundation for morality. If there is an ultimate foundation for mo... rality, then humans can know the truth. Therefore, if there is a universal standard for ethics, then humans can know the truth. Student Answer: modus ponens disjunctive syllogism modus tollens not a valid form hypothetical syllogism Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 4.5, “Some Famous Deductive Argument Forms,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 2. Question : Select the proper form of the following statement, where B is “I will buy a new computer” and C is “my computer crashes.” “I will buy a new computer only if my current computer crashes.” Student Answer: If C then B If B then C B and C B or C PHI 103 Week 2 Quiz QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALL CORRECT none of these Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 4.2, “Logical Operators,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 0 of 1 Comments: Question 3. Question : A categorical statement is one that _____________. Student Answer: is a statement of propositional logic makes a statement about two categories. is always true is part of a valid argument Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.4, “Categorical Logic: Introducing Categorical Syllogisms,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 0 of 1 Comments: Question 4. Question : What is the contrapositive of the statement “All sunsets are beautiful things”? Student Answer: All non-beautiful things are non-sunsets. none of these All non-sunsets are not non-beautiful No beautiful things are sunsets. All beautiful things are non-sunsets. Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.5, “Categorical Logic: Venn Diagrams as Pictures of Meaning,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 5. Question : A sorites is __________. Student Answer: an argument with two premises and a conclusion an argument that is valid and sound an argument that strings together several subarguments an argument that has an unstated premise or conclusion an argument that is invalid and unsound Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.7, “Categorical Logic: Types of Categorical Arguments,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 6. Question : “All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore Socrates is mortal” is what type of argument? Student Answer: inductive deductive invalid argument from definition Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.3, “Types of Deductive Arguments,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 7. Question : In logic, which of the following is NOT true of all deductive arguments? Student Answer: they reason from general to particulars they can be valid or invalid if they are valid, it is impossible to have true premises and a false conclusion none of these if they are invalid, it is possible to have true premises and a false conclusion Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.1, “Basic Concepts in Deductive Reasoning,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 8. Question : Which of the following is the form of “All birds are animals, so some animals are birds”? Student Answer: All B are A so all A are B. Some A are B so all B are A. All A are B, so some B are A. none of these. All A are B, so some A are B. Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.2, “Categorical Logic: Evaluating Deductive Arguments,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 9. Question : According to modern logicians, statements of the form “All P is Q” are ________ when no P exists. Student Answer: invalid false meaningless true unsound Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.4, “Categorical Logic: Introducing Categorical Statements,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 10. Question : How do we know that the conclusion of a sound argument is true? Student Answer: it is highly probable if the argument is strong enough it is part of the definition of soundness the fact that it is true follows from the definition of soundness we don’t, some sound arguments have false conclusions Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.1, “Basic Concepts in Deductive Reasoning,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 0 of 1 Comments: Question 11. Question : “Some computers are Macs” is which type of statement? Student Answer: none of these universal affirmative particular negative universal negative particular affirmative Instructor Explanation: The answer can be found in Section 3.4, “Categorical Logic: Introducing Categorical Statements,” of With Good Reason: A Guide to Critical Thinking. Points Received: 1 of 1 Comments: Question 12. Question : Negation is __________. Student Answer: an “if and only if [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 31, 2022
Number of pages
11
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 31, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
62