Intro to Analytics Modeling(ISYE6501)
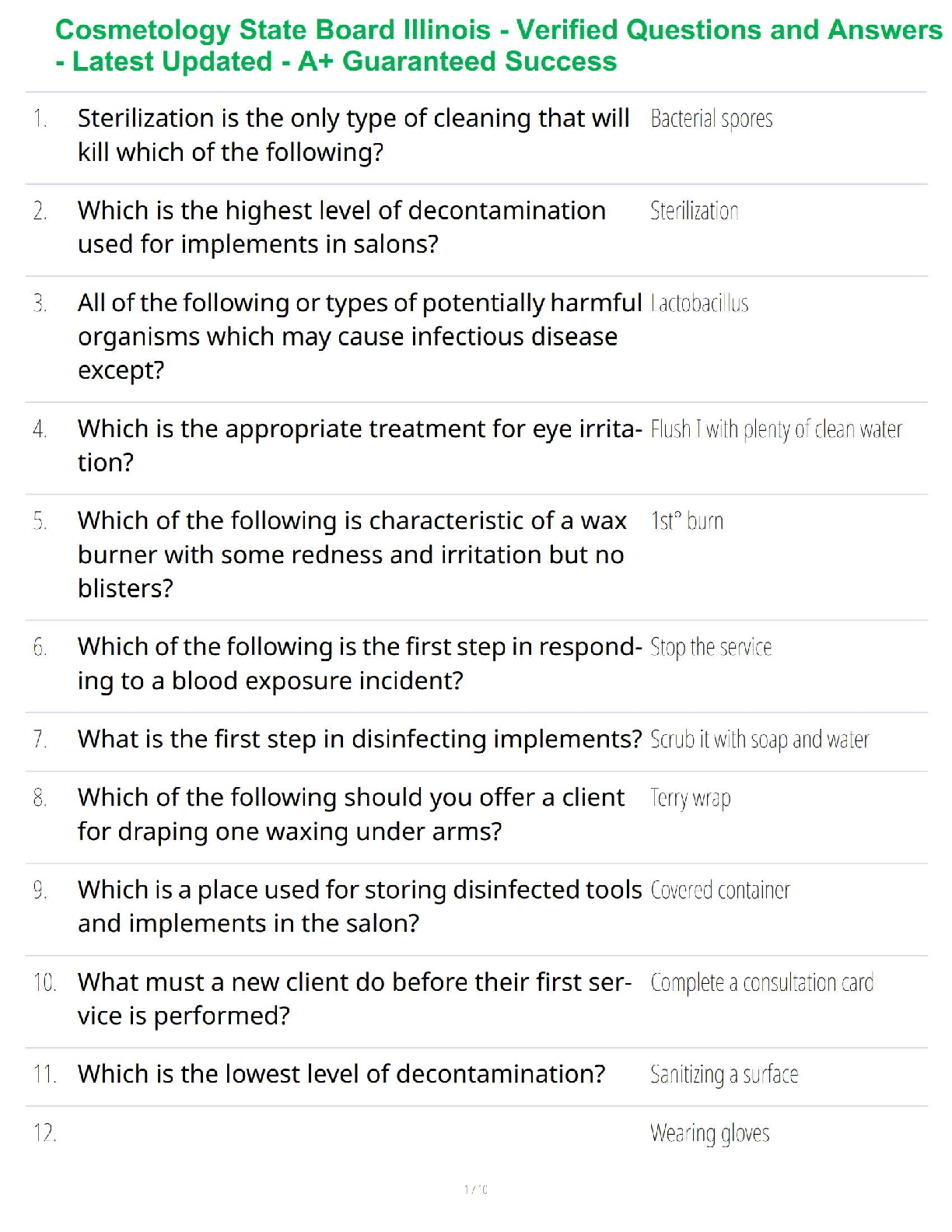
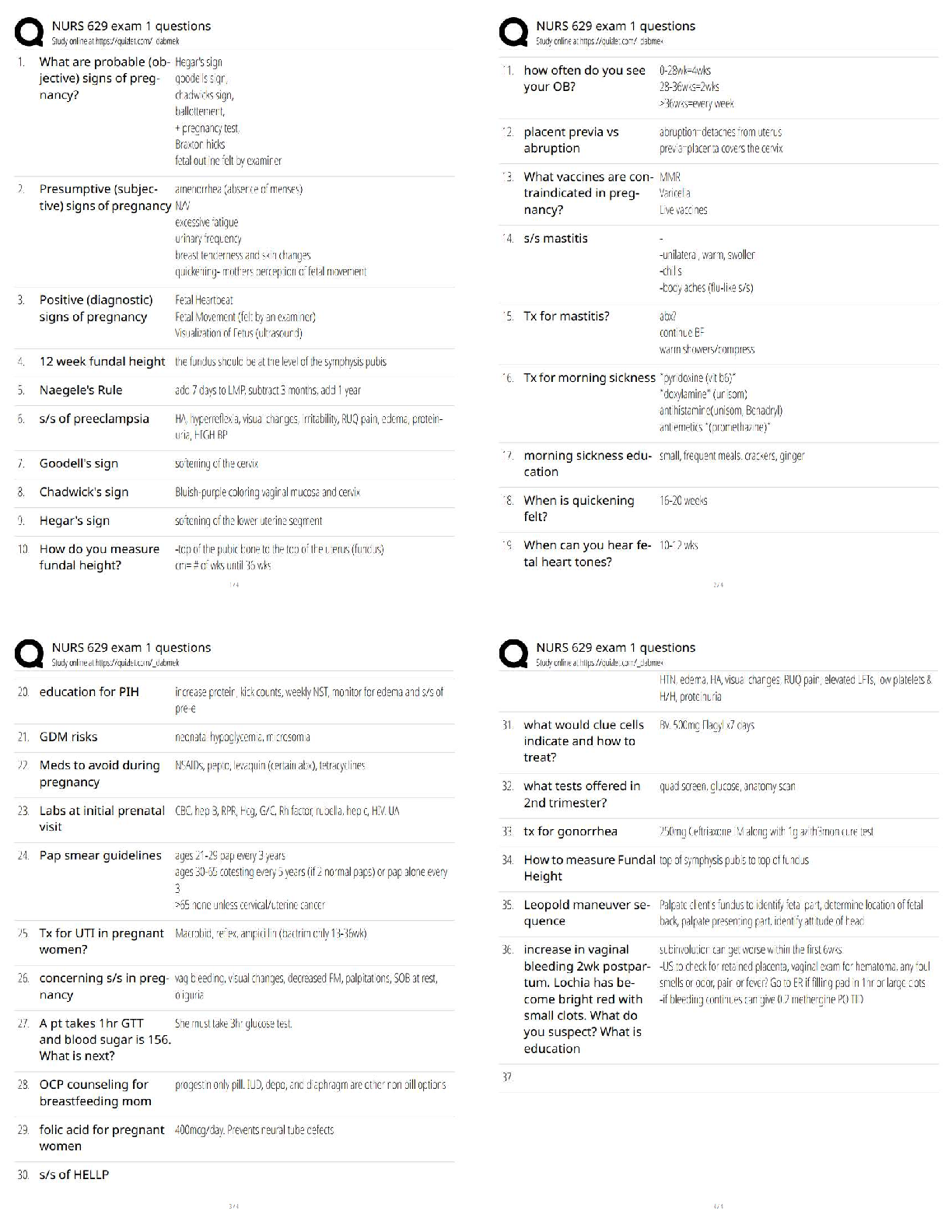
HW2
Question 4.1 Describe a situation or problem from your job, everyday life, current events,
etc., for which a clustering model would be appropriate. List some (up to 5) predict
...
Intro to Analytics Modeling(ISYE6501)
HW2
Question 4.1 Describe a situation or problem from your job, everyday life, current events,
etc., for which a clustering model would be appropriate. List some (up to 5) predictors that
you might use.
Answer: In my previous job at consulting, we were trying to help our client to find out where
they should be opening language school franchise. Some predictors could be: 1) distance
from a community college , 2) distance from a freeway, 3) number of parking lots, 4) number
of public transportations, 5) average traffic time, and etc.
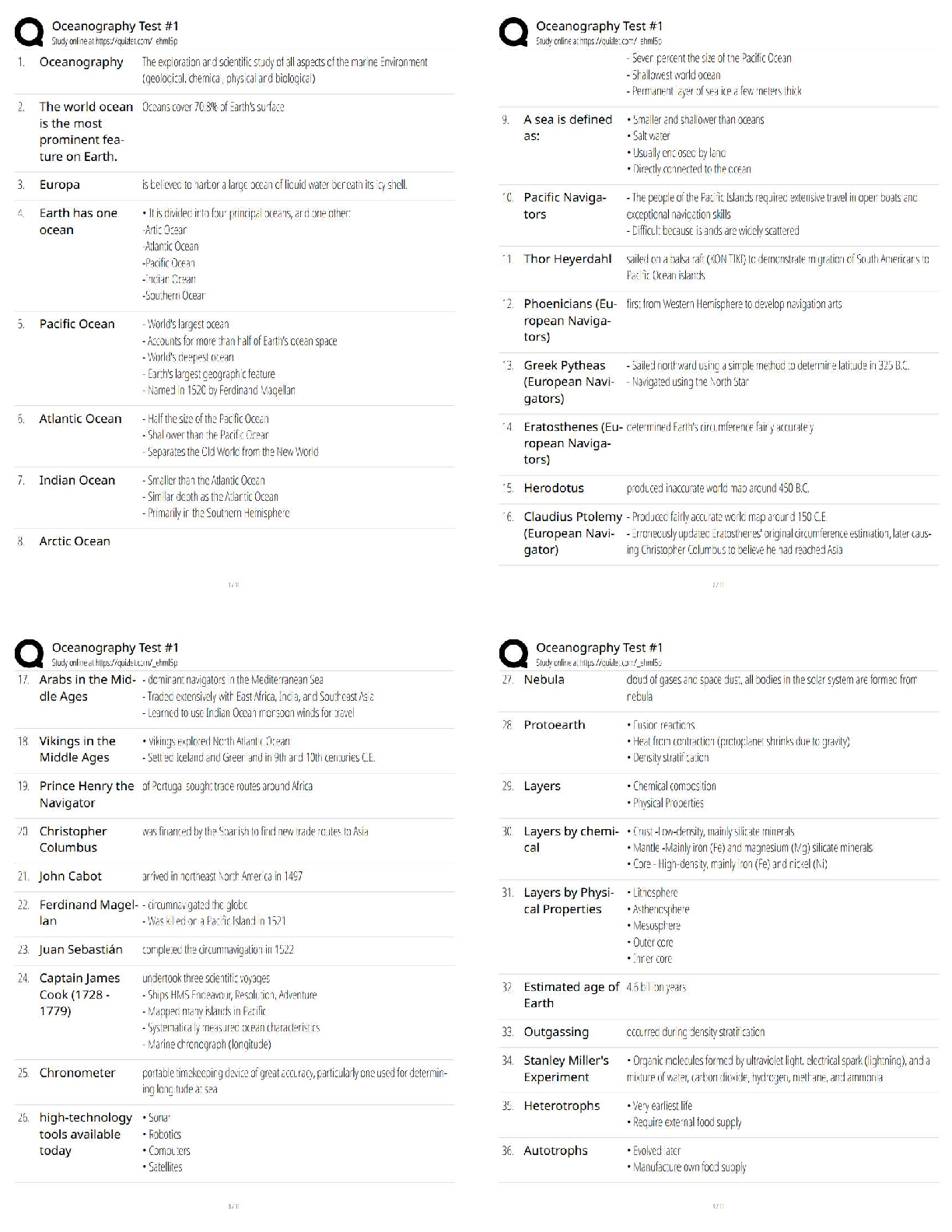
Question 4.2 The iris data set iris.txt contains 150 data points, each with four predictor
variables and one categorical response. The predictors are the width and length of the sepal
and petal of flowers and the response is the type of flower. The data is available from the R
library datasets and can be accessed with iris once the library is loaded. It is also available at
the UCI Machine Learning Repository (https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Iris ). The
response values are only given to see how well a specific method performed and should not
be used to build the model. 1) Use the R function kmeans to cluster the points as well as
possible. 2) Report the best combination of predictors, your suggested value of k, and 3) how
well your best clustering predicts flower type.
#HW 4.2
#install.packages("ggplot2",dependencies=TRUE)
#install.packages("kernlab")
#install.packages('plyr',repos="http://cran.us.r-project.org") #markdown
#install.packages("readxl") #markdown
#install.packages("MikTek")
summary(iris) # 4 variables of 150 observations
head(iris) # view heads
library(ggplot2) #scatter plot
theme_set(theme_bw())
ggplot(iris,aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col= Species)) + geom_point()
ggplot(iris,aes(x = Petal.Length, y = Petal.Width, col= Species)) + geom_point()
set.seed(200)
k.max <- 10
wss<- sapply(1:k.max,function(k){kmeans(iris[,3:4],k,nstart = 20,iter.max =
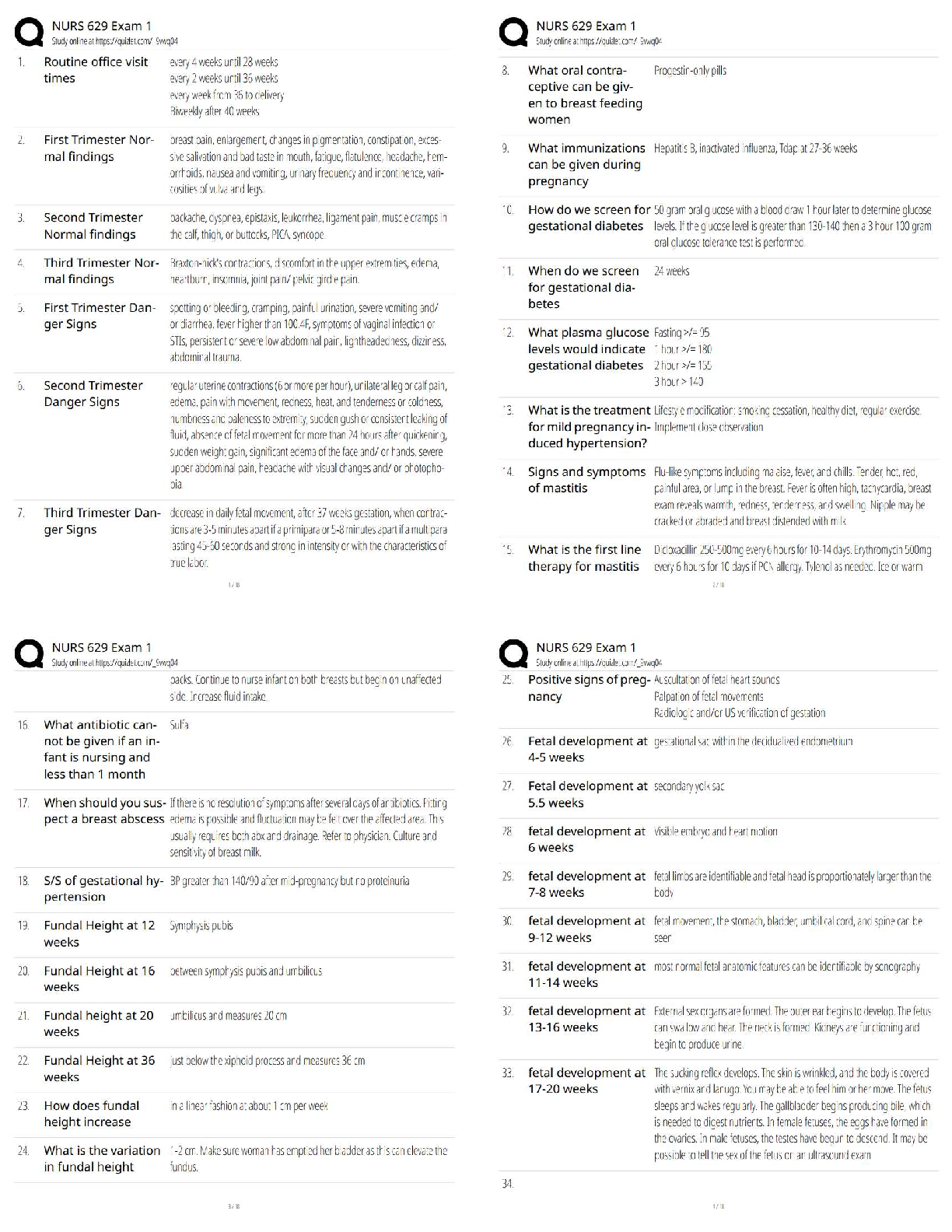
20)$tot.withinss})
wss
plot(1:k.max,# x= No of clusters,
wss, # wss for each
type= "b", #both points as also connect them
xlab = "Number of clusters(k)", ylab = "Within cluster sum of squares")
This study source was downloaded by 100000842525582 from CourseHero.com on 05-13-2022 05:27:11 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/67662046/ISYE6501-HW2docx/#based on elbow point at 3 from the graph, whic shows that 3 is the best value for k to be
used.
icluster <- kmeans(iris[,3:4],3,nstart = 30)
table(icluster$cluster,iris$Species)
ggplot(iris,aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col= Species)) + geom_point()
#cluster tries 30 times random test shows setosa is clustered the most correctly
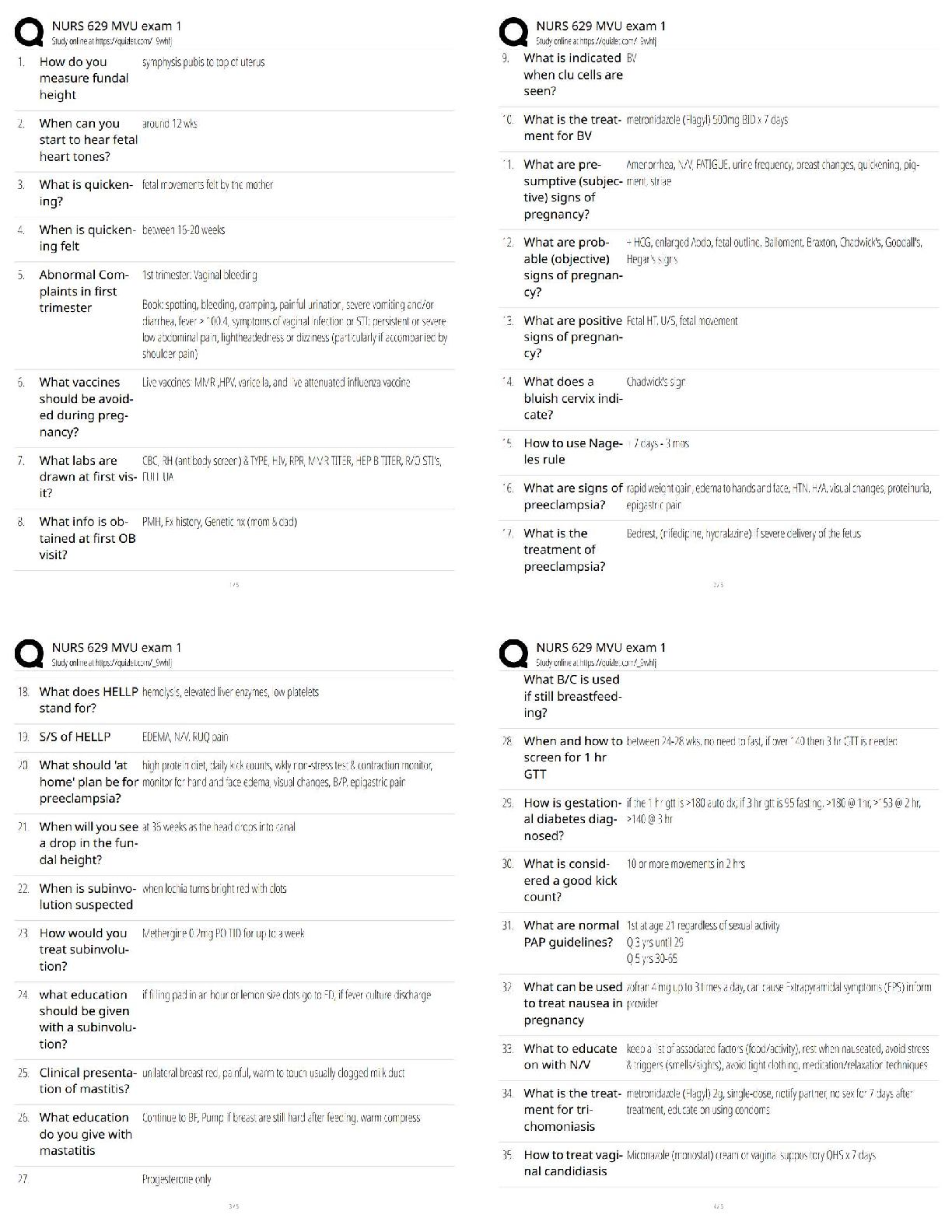
Question 5.1 Using crime data from the file uscrime.txt
(http://www.statsci.org/data/general/uscrime.txt, description at
http://www.statsci.org/data/general/uscrime.html), test to see whether there are any outliers in
the last column (number of crimes per 100,000 people). Use the grubbs.test function in the
outliers package in R.
#HW 5.1
#install.packages("outliers")# import packages
library(outliers)
set.seed(10) # as simple linear model
uscrime <- read.delim("~/Downloads/Intro to Analystics Modeling/week_2_datasummer/uscrime.txt", header=TRUE)
summary(uscrime)
head(uscrime)#checking the data
grubbs.test(uscrime$Crime) #find outlier
range(uscrime$Crime)
summary(uscrime$Crime) #checking 5 datas
plot(uscrime$Crime) #view plot
uscrime$Crime[0:20]
#conclusion : highest value 1993 is an outlier
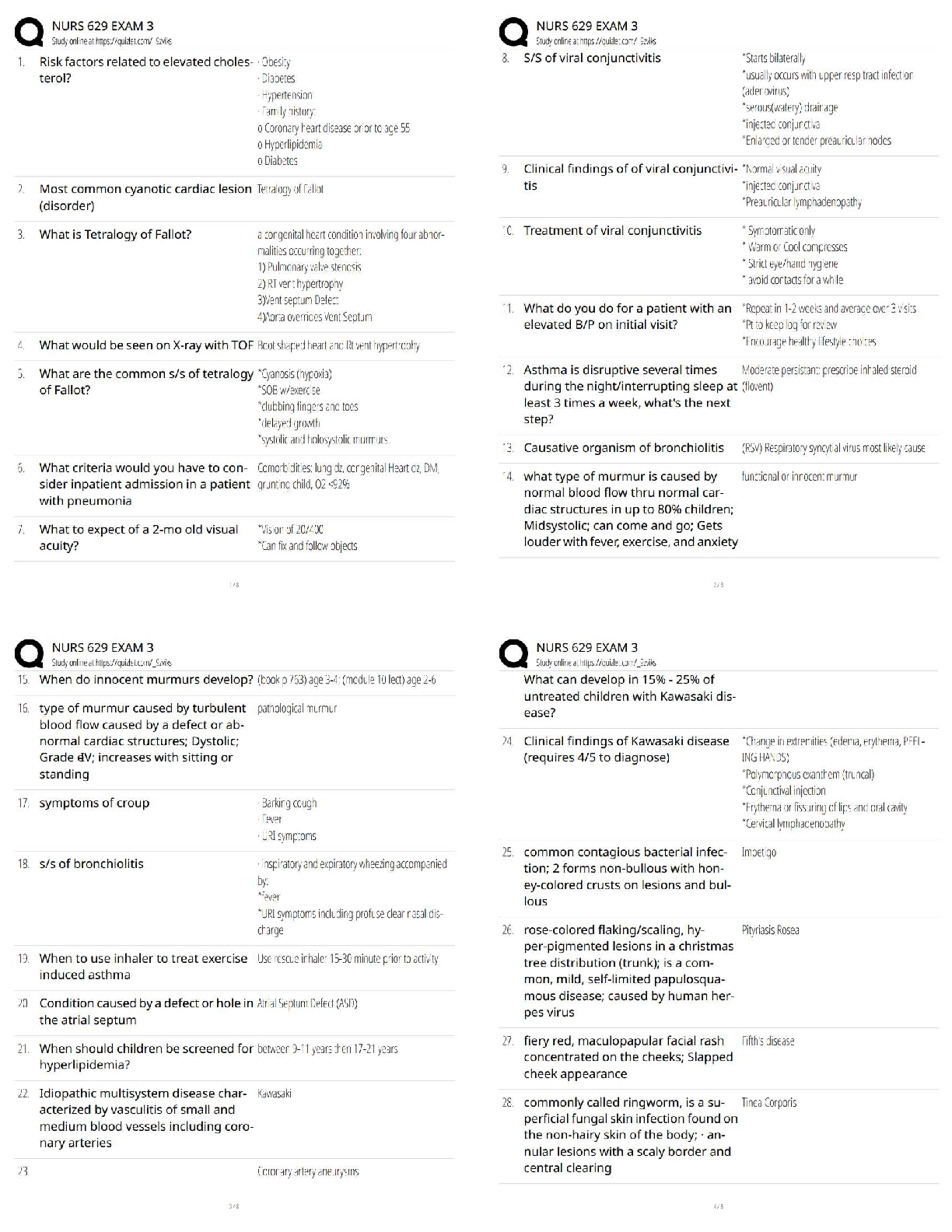
Question 6.1 Describe a situation or problem from your job, everyday life, current events,
etc., for which a Change Detection model would be appropriate. Applying the CUSUM
technique, how would you choose the critical value and the threshold?
Answer: To monitor stock price variance over time, I can apply Cumulative sums (CUSUM)
of deviations from a target value. I am trying monitor bio-tech related stocks since average
stock price of bio-tech has been higher than last month, the variance is significant enough that
I am trying to decide whether should I buy this stock or not. It will be good to know if the
price is just a outliers (a result of Covid-19 outbreak) or if they will be sustained. I would get
average (mean) of stock price and a critical value that is relatively large for this year to get
the threshold line to show detect the changes.
Question 6.2 1. Using July through October daily-high-temperature data for Atlanta for 1996
through 2015, use a CUSUM approach to identify when unofficial summer ends (i.e., when
the weather starts cooling off) each year. You can get the data that you need from the file
temps.txt or online, for example at http://www.iweathernet.com/atlanta-weather-records or
https://www.wunderground.com/history/airport/KFTY/2015/7/1/CustomHistory.html . You
can use R if you’d like, but it’s straightforward enough that an Excel 6.62.spreadsheet can
[Show More]