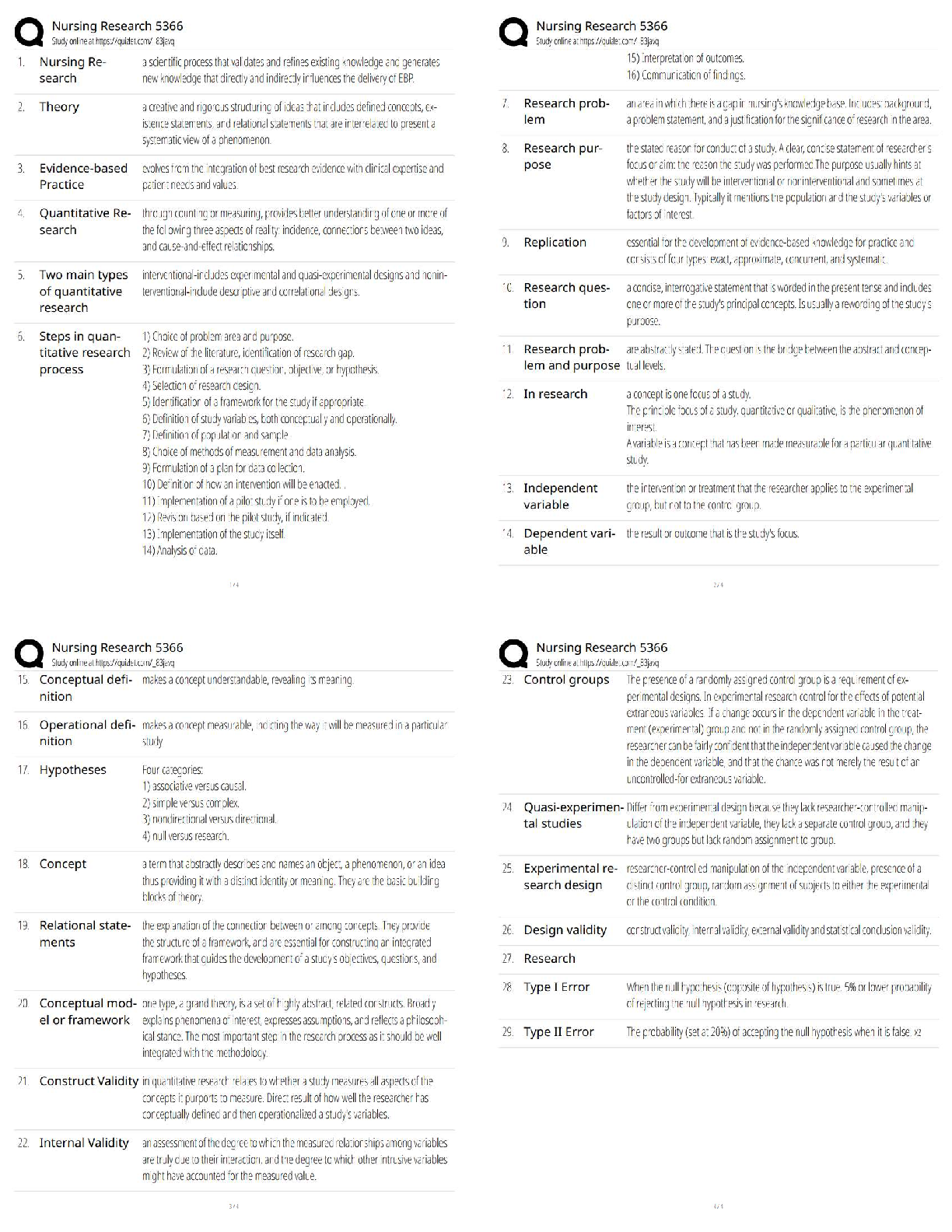
Evolve Pharmacology hesi practice
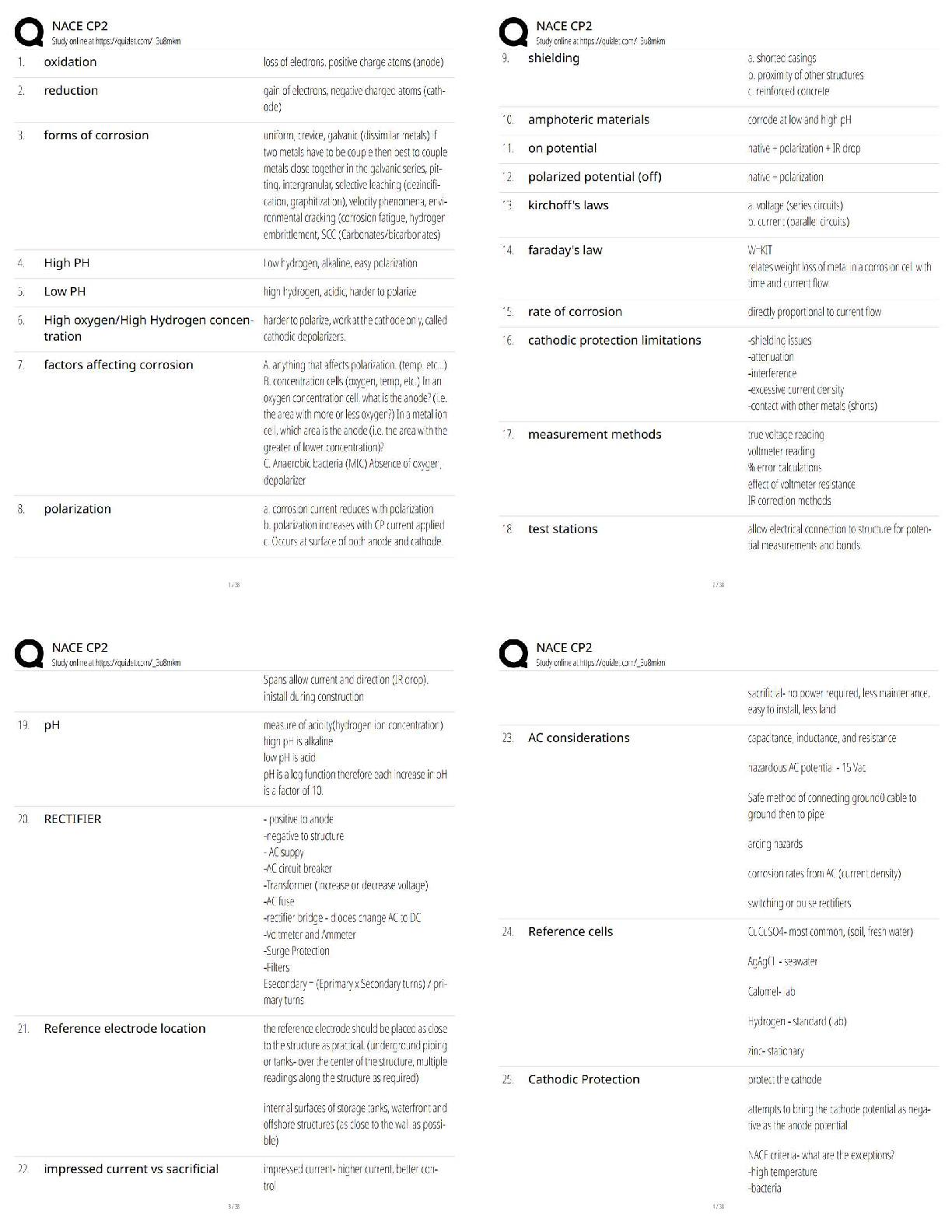
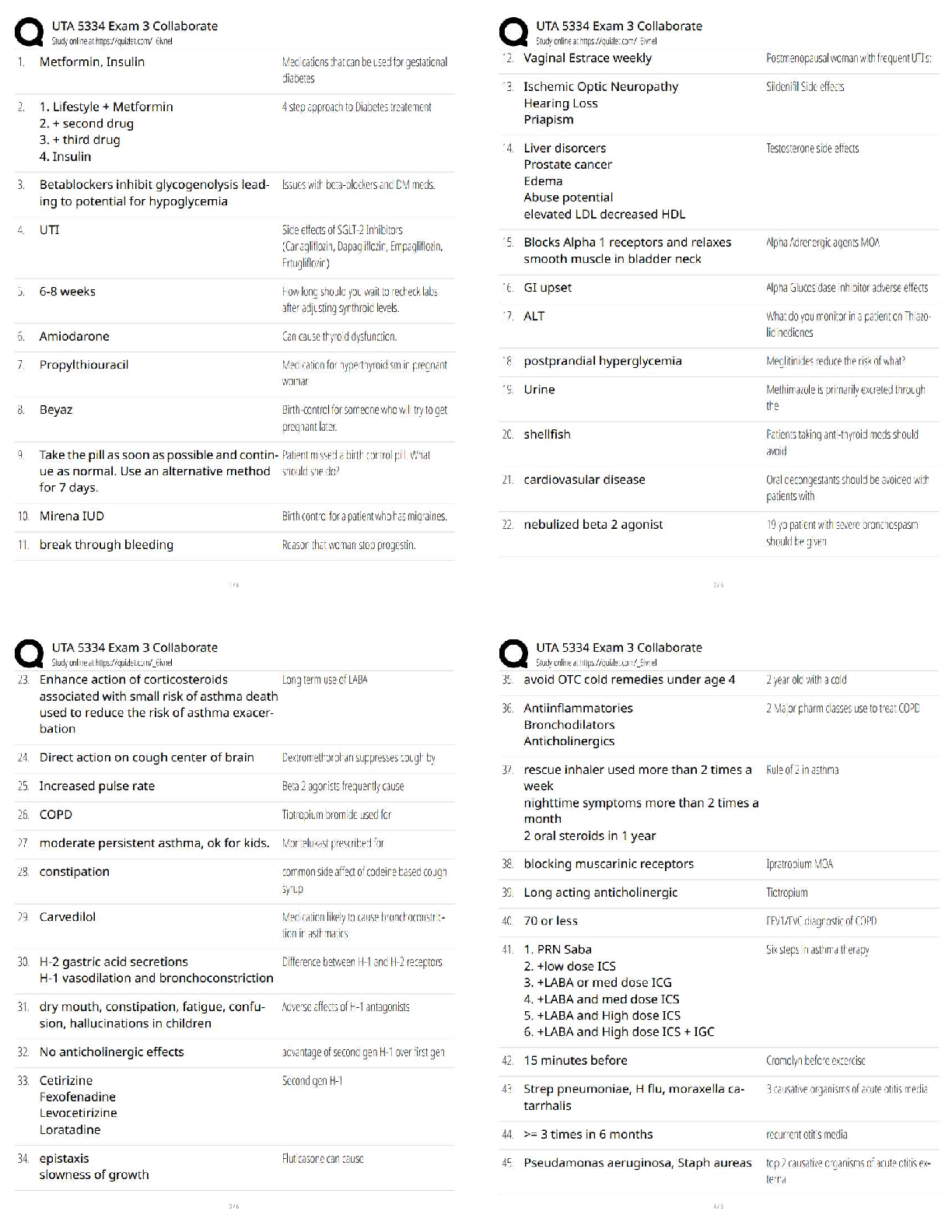
Already Graded A+
A client who has been taking phenazopyridine (Pyridium) for symptoms of urethritis and cystitis comes
to the clinic because her urine is reddish-orange. Which questi
...
Evolve Pharmacology hesi practice
Already Graded A+
A client who has been taking phenazopyridine (Pyridium) for symptoms of urethritis and cystitis comes
to the clinic because her urine is reddish-orange. Which question should the practical nurse ask to
determine if the medication has been effective?
A) How much water have you been drinking each day?
B) Does the urine color stain your toilet bowl or undergarments?
C) Have you had any relief from urinary pain, burning, or urgency?
D) Did your urine appear cloudy or have a foul odor on voiding? Correct Answer-C) Have you had any
relief from urinary pain, burning, or urgency?
Feedback:
Phenazopyridine, an over-the-counter urinary analgesic, acts on the mucosa of the urinary tract to
relieve urinary pain, burning, itching, or urgency (C) associated with urethritis and cystitis. Although
determining if the client is forcing fluids (A), experiencing staining from Pyridium's side effect (B), or
having signs of a urinary infection (D) are worthwhile assessments, the therapeutic response of Pyridium
is related to urinary discomforts only.
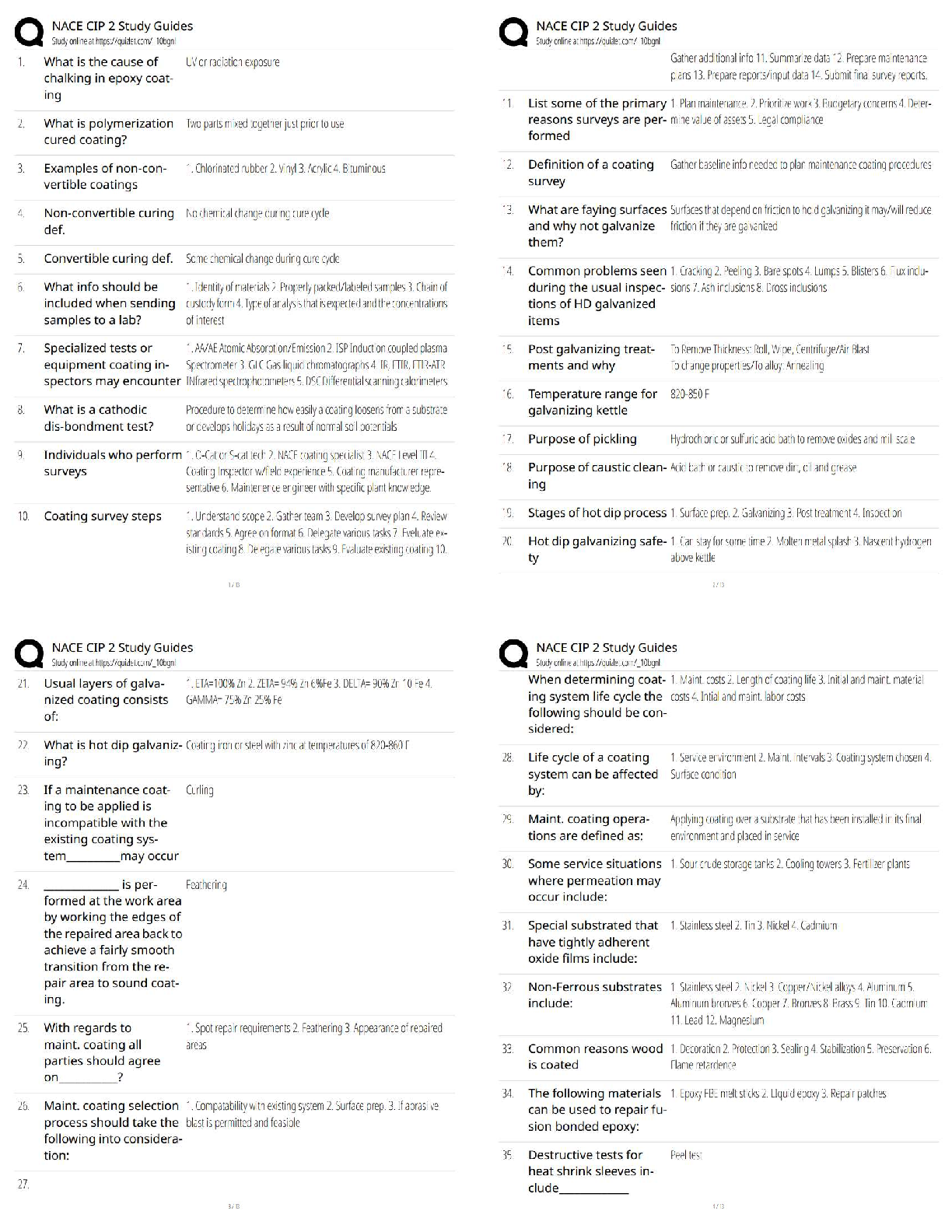
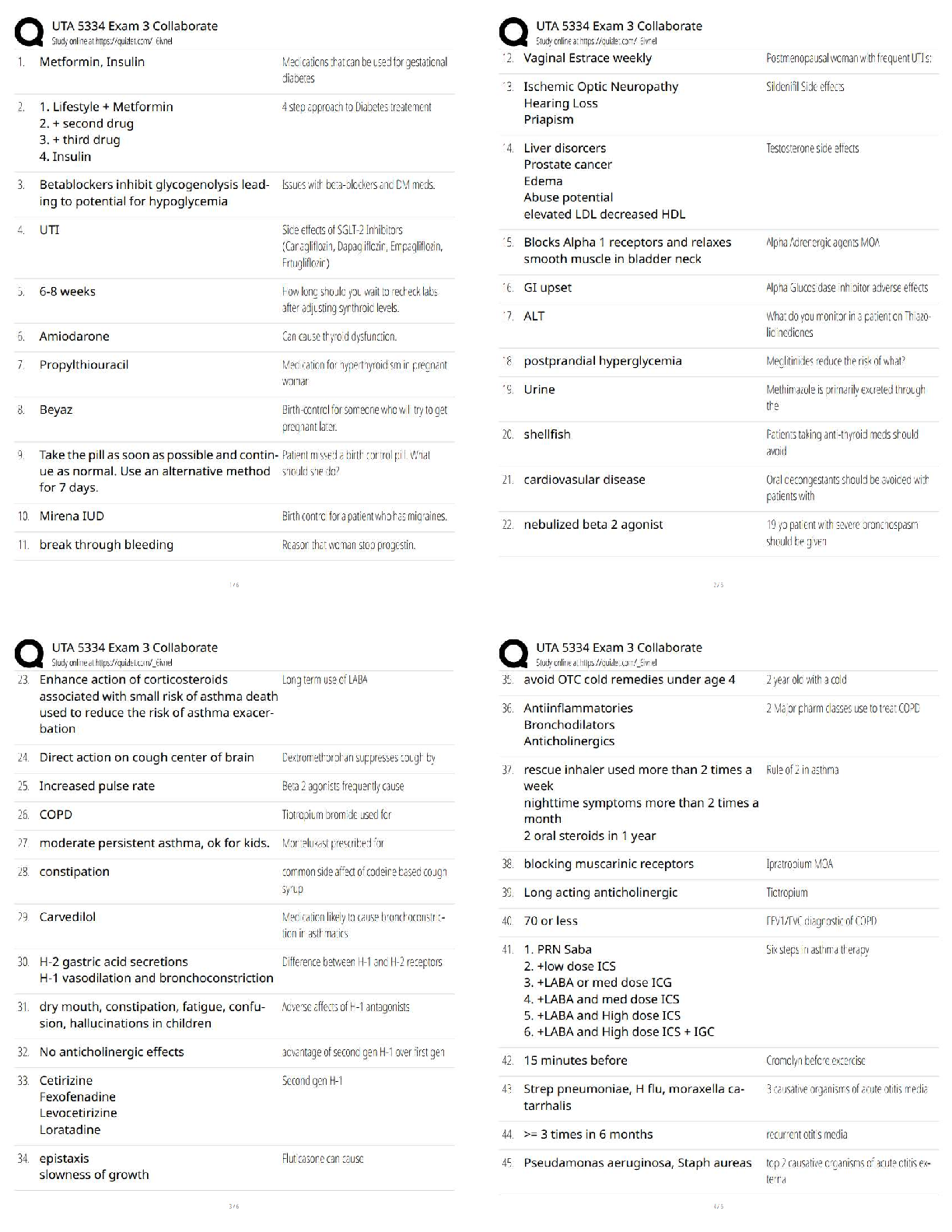
A male client who has been receiving an antineoplastic drug has developed thrombocytopenia. What
instructions should the practical nurse (PN) reinforce?
A) Use suppository form of drugs.
B) Avoid large public gatherings.
C) Rise slowly when standing up.D) Shave with an electric razor. Correct Answer-D) Shave with an electric razor.
Feedback:
Thrombocytopenia is a common side effect of bone marrow depression caused by several antineoplastic
agents. The client is experiencing a low platelet count and should use an electric razor (D) to reduce his
risk of bleeding. (A, B, and C) are not indicated for a client who needs to implement thrombocytopenia
precautions.
The practical nurse (PN) is caring for a client who has been taking prednisone (Deltasone) daily for a
year. Which adverse effect should the PN document in the client's record?
A) Photosensitvity.
B) Weight gain.
C) Loss of hair.
D) Pale skin color. Correct Answer-B) Weight gain.
Feedback:
Long term use of prednisone causes fluid retention and redistribution of fat deposition. Weight gain (B)
and moon face reflect adverse effects of long-term prednisone use and should be documented. (A, C,
and D) do not occur with treatment using prednisone.
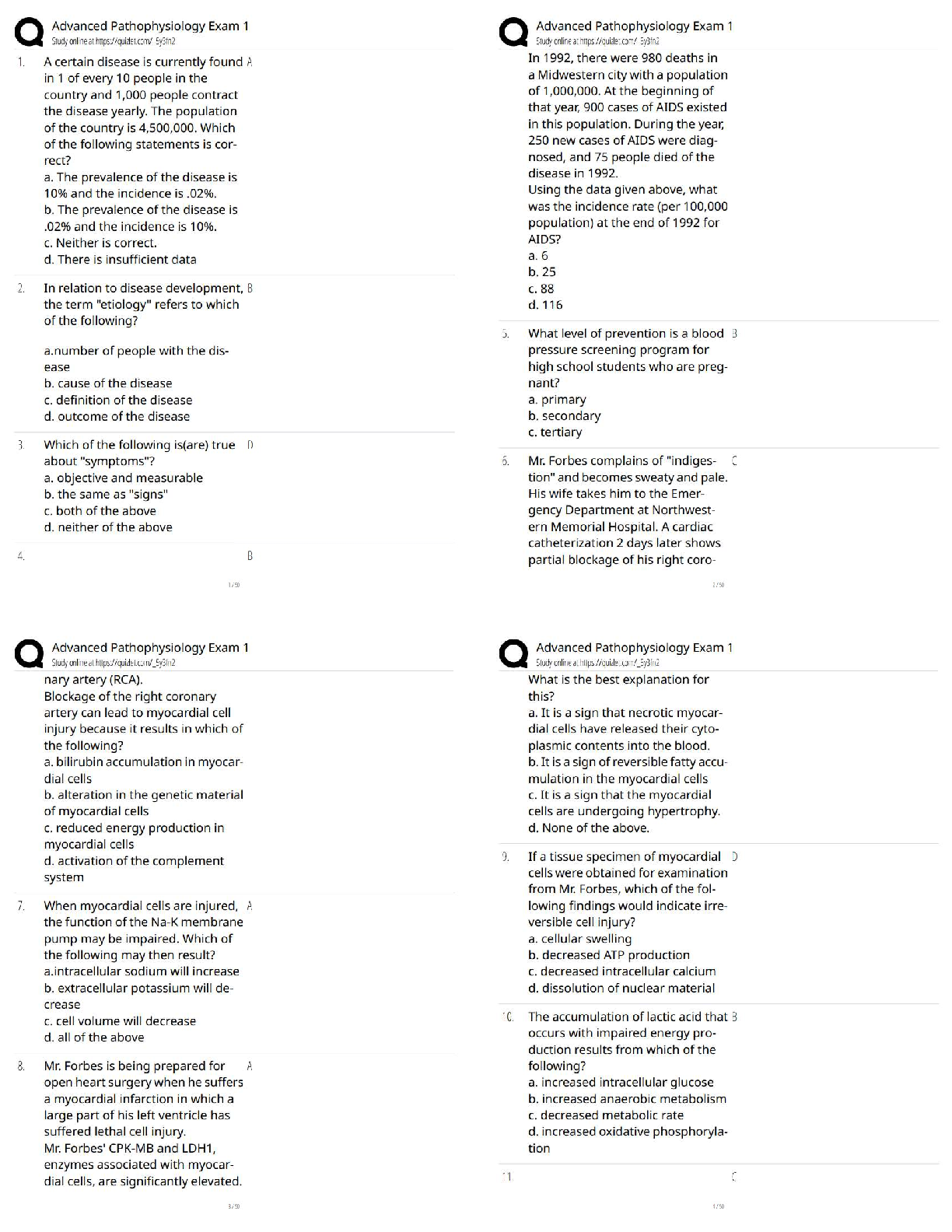
A female client with recurring headaches tells the practical nurse (PN) that she has been taking at least 4
grams of acetaminophen a day. Which laboratory studies should the PN review for this client?
A) Creatinine clearance.
B) Hepatic enzymes.C) Coagulation values.
D) Arterial blood gases. Correct Answer-B) Hepatic enzymes.
Feedback:
Liver toxicity can occur when doses of acetaminophen exceed 4 grams a day, resulting in an elevation in
hepatic enzyme values (B). (A, C, and D) do not reveal findings related to acetaminophen toxicity.
A client receives a prescription for an oral opioid analgesic for post-operative pain. Which adverse effect
should the practical nurse (PN) monitor for with the client?
A) Constipation.
B) Photosensitivity.
C) Decreased heart rate.
D) Frequent urination. Correct Answer-A) Constipation.
Feedback:
Opioid analgesics slow peristalsis, which leads to constipation (A), a common side effect of opiates. (B, C,
and D) are not associated with opioid analgesics.
Which action should the practical nurse implement when administering a buccal medication?
A) Encourage the client to swallow.
B) Administer water with medication.
C) Ensure the medication is positioned under the tongue.D) Place the medication between the upper molar teeth and cheek. Correct Answer-D) Place the
medication between the upper molar teeth and cheek.
Feedback:
Buccal medications are placed between the upper molar teeth and the cheek (D) for absorption by the
capillaries of the oral mucosa. The client should be cautioned against swallowing, not (A). Buccal
medications are not administered with water (B). (C) describes sublingual administration.
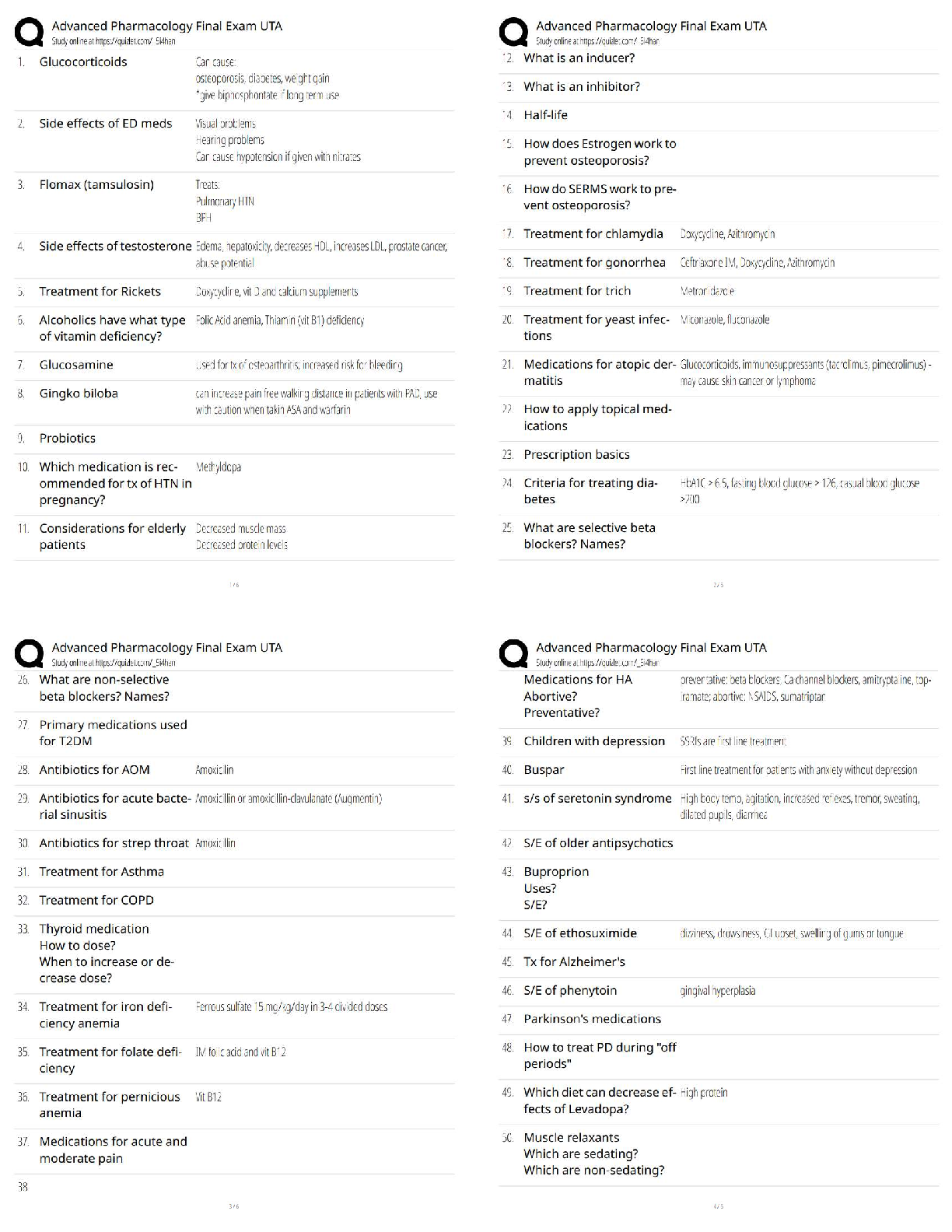
What assessment is most important for the practical nurse (PN) to obtain prior to initiating medication
therapy with phenelzine (Nardil) for a client with depression?
A) Activity level.
B) Mood and affect.
C) Understanding of diet modification.
D) The client's support system. Correct Answer-C) Understanding of diet modification.
Feedback:
To prevent a potentially lethal hypertensive crisis, a tyramine-free diet should be maintained during
antidepressant therapy with Nardil, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). It is most important to
determine if the client understands diet modification (C) before Nardil is initiated to prevent
consumption of foods that interact with Nardil. Although a client's activity level (A) and mood and affect
(B) should be monitored during antidepressant therapy, it is most important that the client understand
diet modifications. The client's support system (D) and network of family and friends is important, but
the client should understand the responsibility of dietary compliance with the medication regimen.The practical nurse (PN) is unable to arouse a client who is receiving meperidine (Demerol) for
postoperative pain. The client is stuporous, has constricted pupils, and a respiratory rate of 8
breaths/minute. Which PRN prescription should the PN give the client?
A) Naloxone (Narcan).
B) Promethazine (Phenergan).
C) Metoclopramide (Reglan).
D) Bethanechol (Urecholine). Correct Answer-A) Naloxone (Narcan).
Feedback:
Narcan (A) is an opioid antagonist and should be administered to reverse the effects of a Demerol, an
opioid, overdose. (B, C, and D) are common postoperative PRN prescriptions but are not indicated for
narcotic overdose.
On which therapeutic action should the practical nurse (PN) base an explanation to a client who is
receiving a cardiac glycoside?
A) Decreased cardiac output.
B) Increased renal perfusion.
C) Decreased rate of contraction.
D) Increased blood volume. Correct Answer-C) Decreased rate of contraction.
Feedback:
Cardiac glycosides increase the force of cardiac contraction (inotropy) and decrease the heart rate
(chronotropy) (C) by decreasing the speed of conduction through the heart (dromotropy). (A, B, and D)
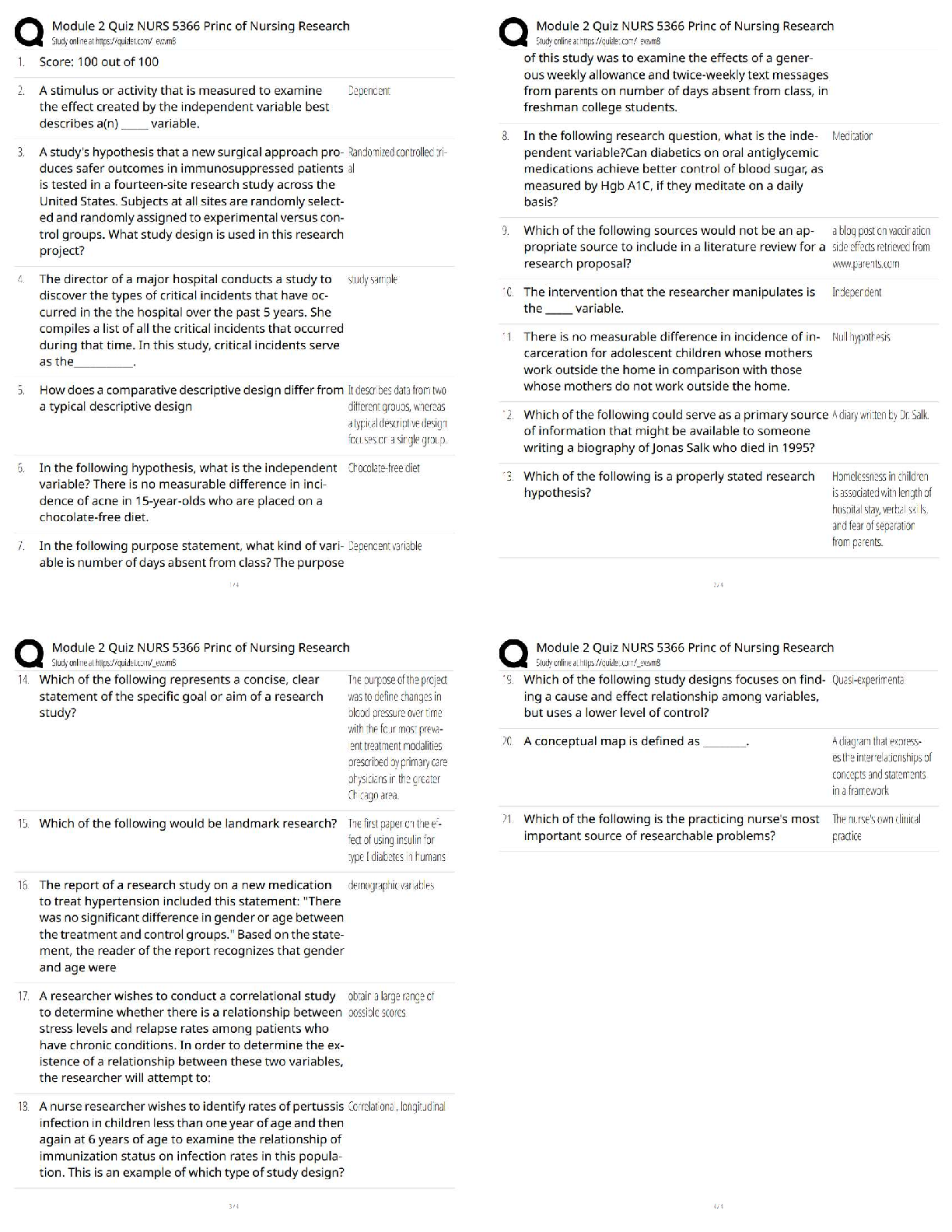
are incorrect.A client with type 1 diabetes mellitus received an early AM dose of regular insulin per sliding scale. At
10:00 AM, the practical nurse (PN) should report which signs indicative of hypoglycemia?
A) Urticaria and rash.
B) Nausea and diarrhea.
C) Irritability and confusion.
D) Fruity, acetone odor to the breath. Correct Answer-C) Irritability and confusion.
Feedback:
Irritability and confusion (C) are early signs of hypoglycemia. (A, B, and D) are not signs of hypoglycemia.
Which prescription should the practical nurse (PN) administer for a client who is experiencing an
anaphylactic reaction to an antibiotic?
A) Ephedra (ma-huang).
B) Epinephrine (Adrenalin).
C) Phenylephrin (Neo-Synephrine).
D) Fexofenadine with pseudoephedrine (Allegra D). Correct Answer-B) Epinephrine (Adrenalin).
Feedback:
Epinephrine (Adrenalin), a potent sympathomimetic, is the drug of choice for the treatment of
anaphylaxis (B). (A, C, and D) are not used for an acute immunololgical dysfunction that causes
cardiovascular effects.An older adult client receives a prescription for hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDIURIL), a thiazide diuretic
for the treatment of heart failure. Which side effect(s) should the practical nurse reinforce with the
client? (Select all that apply.)
A) Constipation.
B) Fatigue.
C) Edema.
D) Nausea.
E) Dehydration.
F) Blurred vision. Correct Answer-B) Fatigue.
E) Dehydration.
Feedback:
Hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDIURIL), a thiazide diuretic, reduces blood pressure by reducing blood
volume and reducing arterial resistance. Adverse effects of thiazides include hypokalemia, fatigue (B),
dehydration (E), hyperglycemia, and hyperuricemia. Although (A, C, D and F) may be associated with
aging or other pathology, they are not side effects commonly associated with HydroDIURIL.
A client who returns from surgery for bowel resection complains of severe pain around the incision.
Which assessment is most important for the practical nurse (PN) to obtain prior to the administration of
morphine sulfate?
A) Rate of respirations.
B) Core temperature.
C) Appearance of the incision.D) Presence of bowel sounds. Correct Answer-A) Rate of respirations.
Feedback:
Opioids cause respiratory depression, so the respiratory rate (A) should be assessed prior to
administration of morphine sulfate. (B, C, and D) do not address the concept of medication safety.
A client is receiving the third course of 5-fluorouracil (5FU) therapy for a tumor of the liver. Which action
should the practical nurse implement to reduce the client's risk for stomatitis?
A) Use commercial oral products to reduce the risk of oral infections.
B) Observe for black, tarry stools or bleeding ulcerations.
C) Increase intake of foods containing fiber and citric acid.
D) Examine mouth daily for bleeding, white spots, and ulcerations. Correct Answer-D) Examine mouth
daily for bleeding, white spots, and ulcerations.
Feedback:
5-fluorouracil (5FU) is an antimetabolite, antineoplastic agent that causes sloughing of the rapid
proliferating epithelial cells of the oral mucosa causing ulceration, bleeding, and oral candidiasis
(thrush). Daily examination of the oral mucosa (D) should be implemented to identify signs of stomatitis,
such as white spots, ulcerations, and bleeding of the mouth, so early intervention can be implemented.
Oral commercial products usually contain alcohol, which contributes to inflammation of the oral
mucosa, and should be avoided (A). Although monitoring the stool for bleeding (B) should be
implemented, stomatitis occurs in 75% of clients who receive 5FU. Foods high in fiber and citric acid
should also be avoided (C) to reduce pain and trauma to the mouth.
Which instruction should the practical nurse (PN) reinforce with a client who is taking disulfiram
(Antabuse)?A) Cigarette smoking cessation program should be started.
B) Avoid using any over-the-counter substances containing alcohol.
C) This drug is similar to alcohol but without euphoric effects.
D) Small amounts of mouthwash or cough medicine can be used. Correct Answer-B) Avoid using any
over-the-counter substances containing alcohol.
Feedback:
The use of disulfiram (Antabuse) with over-the-counter (OTC) products that contain alcohol causes
severe adverse reactions, such as severe nausea, vomiting, chest pain, hyperventilation, tachycardia,
seizures, and cardiovascular collapse, and should be avoided (B). Although a smoking cessation program
is always a good health recommendation (A), it is not a priority with Antabuse. (C) is inaccurate. Small
amounts, as little as 7 ml, of mouthwash or cough syrup that contains alcohol can precipitate a
disulfiram reaction and should not be used (D).
Which prescription should the practical nurse administer for a client who is experiencing an acute
episode of bronchial asthma?
A) Nedocromil (Tilade).
B) Albuterol (Proventil).
C) Zafirlukast (Accolate).
D) Triamcinolone (Azmacort). Correct Answer-B) Albuterol (Proventil).
Feedback:
Albuterol (Proventil) (B), an adrenergic agonist, is the first line of treatment for acute episodes of
bronchial asthma. (A, C, and D) are maintenance medications used in the prevention of asthmatic
episodes and are routinely taken every day, not during an acute episode.The practical nurse (PN) should recommend that oral contraceptives be avoided in which group of
women?
A) Women who smoke.
B) Multigravidous women.
C) Monogamous women.
D) Women with an intrauterine device. Correct Answer-A) Women who smoke.
Feedback:
Oral contraceptives pose an increased risk of thromboembolism for women who smoke (A), and this risk
is not increased in (B, C, and D).
A client with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is having symptoms of reflux despite taking
omeprazole (Prilosec) 20 mg daily. What action should the practical nurse (PN) implement?
A) Notify the healthcare provider about the symptoms.
B) Obtain vital signs every 30 minutes until symptoms are alleviated.
C) Instruct the client to stop taking the medication.
D) Tell the client to take an antacid in addition to the omeprazole. Correct Answer-A) Notify the
healthcare provider about the symptoms.
Feedback:
Omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, acts to reduce gastric acid secretion. If once daily dosing fails to
control the client's symptoms, the healthcare provider should be notified (A) for dose adjustment. (B)
will not help to reduce the client's symptoms. Unless the client shows symptoms of a hypersensitivity tothe medication, the client should not stop the medication (C). (D) should not suggested without a
prescription from the healthcare provider.
The practical nurse (PN) administers isoproterenol (Isuprel) to a client with heart block. The PN should
evaluate the client for which physiological response?
A) Thirst and dry mucous membranes.
B) Decrease in gastric motility.
C) Increased heart rate.
D) Bronchoconstriction. Correct Answer-C) Increased heart rate.
Feedback:
Isoproterenol (Isuprel) acts on beta 1 receptors in the heart, causing an increased cardiac reactivity in
AV heart block and an increase in the client's heart rate (C). (A and B) are anticholinergic responses and
are not typical with adrenergic agents, such as isoproterenol. By activating beta 2 receptors found in the
smooth muscle of bronchioles, isoproterenol causes bronchodilation, not (D).
The practical nurse (PN) should emphasize the importance of monitoring for which side effect(s) in a
client who takes a daily antilipemic agent?
A) Photosensitivity.
B) Liver dysfunction.
C) Upper respiratory infections (URI).
D) Water soluble vitamin deficiencies. Correct Answer-B) Liver dysfunction.
Feedback:Antilipemic agents (lipid-regulating agents) are metabolized by the liver and require regular monitoring
of liver function studies for hepatic dysfunction (B). Photosensitivity (A), URI (C), and vitamin deficiencies
(D) are not side-effects of antilipemics.
A client with Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) is prescribed amphetamine (Adderall). Which side effect
should the practical nurse (PN) explain is commonly experienced?
A) Difficulty sleeping.
B) Increased fatigue.
C) Improved appetite.
D) Decreased heart rate. Correct Answer-A) Difficulty sleeping.
Feedback:
Adderall is a central nervous system stimulant, which often causes the client to experience difficulty
sleeping (A). Due to central nervous stimulation, Adderall causes an increase in energy, a decrease in
appetite, and an increase in heart rate, not (B, C, and D).
An older client who takes risperidone (Risperdal), an antipsychotic, is complaining of constipation.
Which dietary changes should the practical nurse (PN) recommend?
A) Increase daily green vegetables and bran.
B) Take a laxative and stool softener daily.
C) Eat liver and turnips once a week.
D) Use a retention enema every four days. Correct Answer-A) Increase daily green vegetables and bran.
Feedback:Constipation, a side effect of antipsychotics, is managed by encouraging the client to drink additional
water and increase dietary roughage, such as bran and green vegetables daily (A). (B, C, and D) are not
routine recommendations for constipation.
A client's tissue culture results indicate the wound is infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus (MRSA). What action should the practical nurse (PN) implement first?
A) Provide sterile wound care as prescribed.
B) Give the first dose of Vancomycin (Vancocin).
C) Implement contact isolation precautions.
D) Document wound site appearance and drainage. Correct Answer-C) Implement contact isolation
precautions.
Feedback:
The risk of transmitting a hospital acquired infectious disease among clients is high with an organism
such as MRSA. Infection prevention and control practices, including contact isolation precautions,
should be implemented first (C). (A, B, and D) may be implemented after isolation precautions are in
place.
The practical nurse asks a male client who came to the clinic with an upper respiratory infection if he has
any drug allergies. The client cannot remember if he does or if he ever received penicillin. After
administering the injection of penicillin, the PN tells the client to stay for 30 minutes of observation.
Which finding should the PN identify that is indicative of a reaction to the medication?
A) Rash, itching, and hives.
B) Fever and abdominal pain
[Show More]