*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Nasm CPT Final Exam Study Guide Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions Already Passed (All)
Nasm CPT Final Exam Study Guide Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
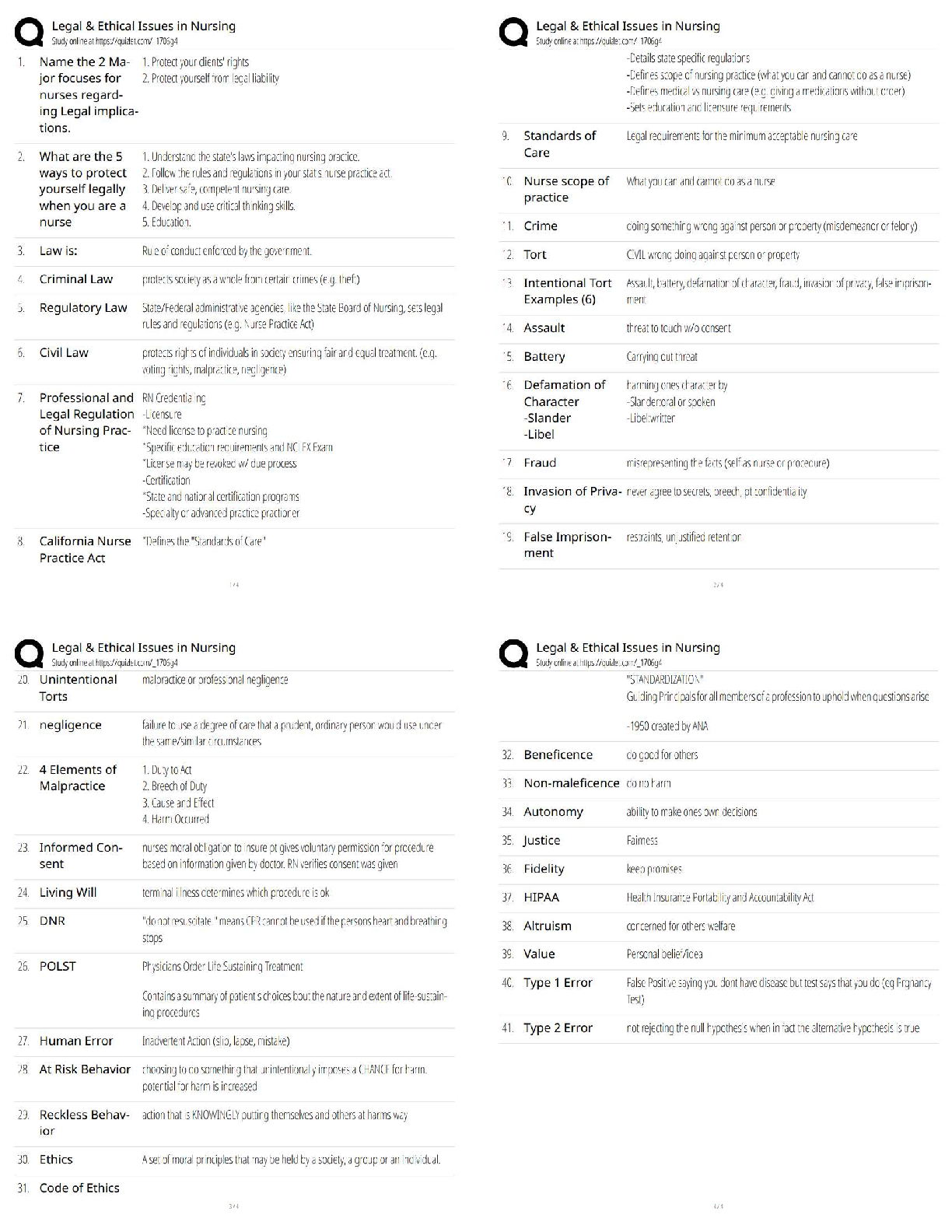
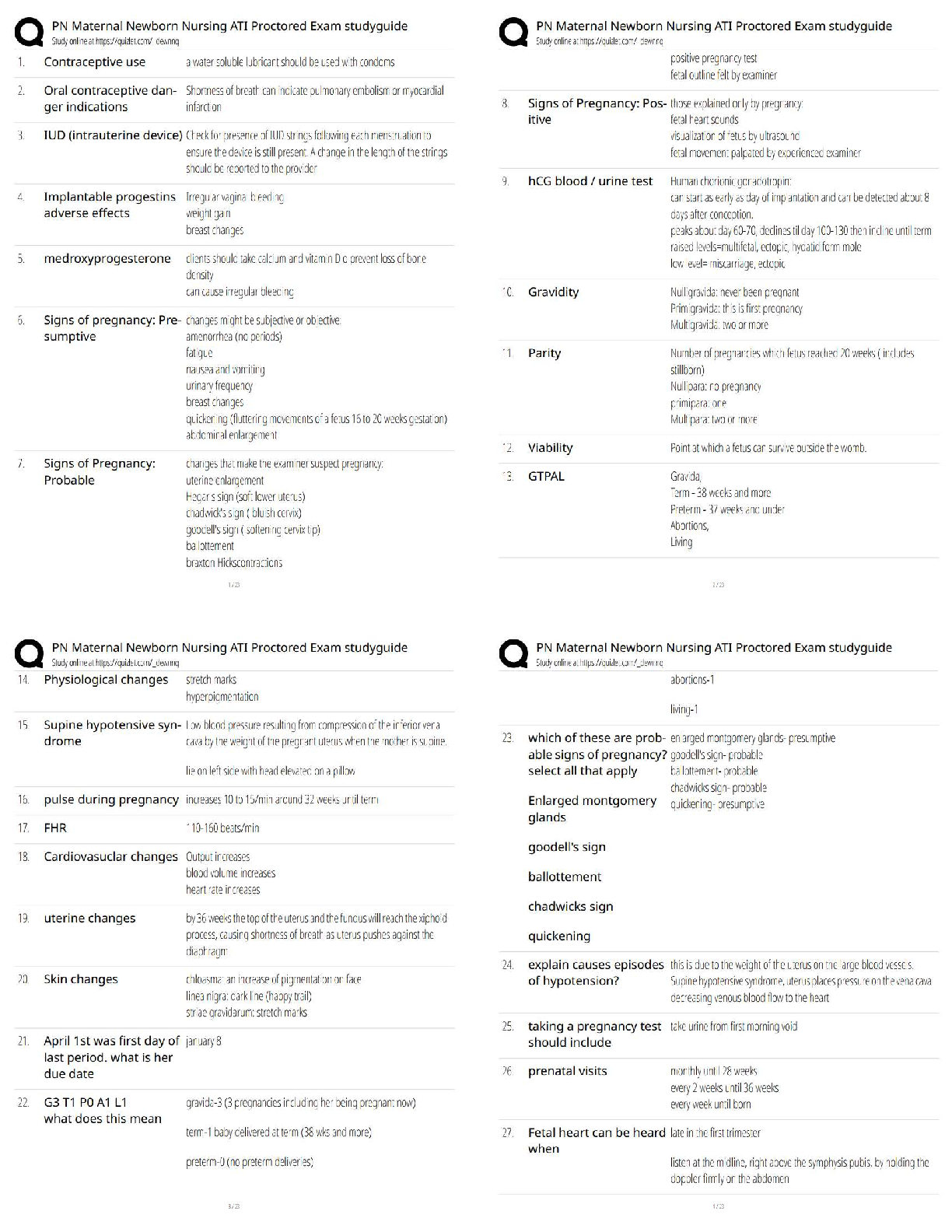
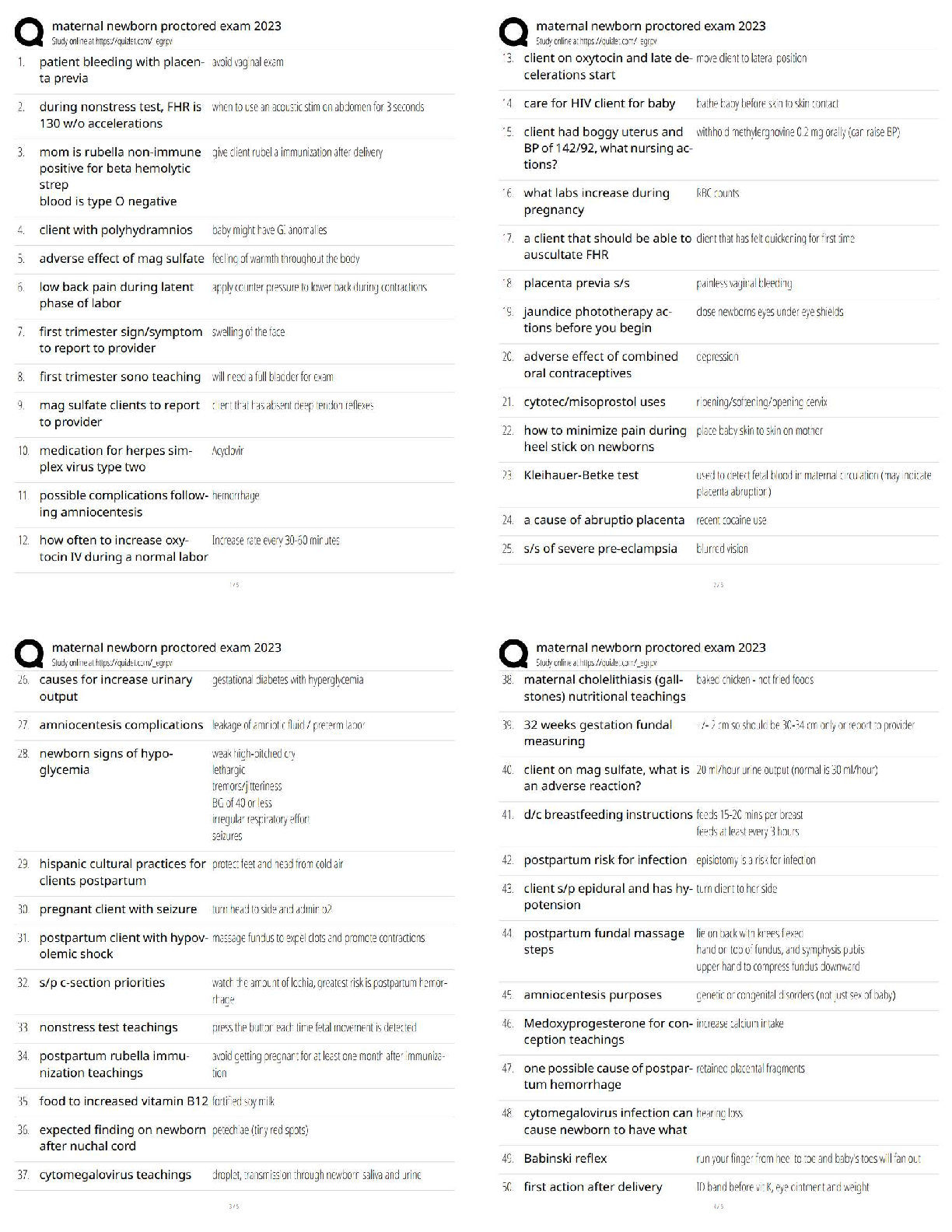
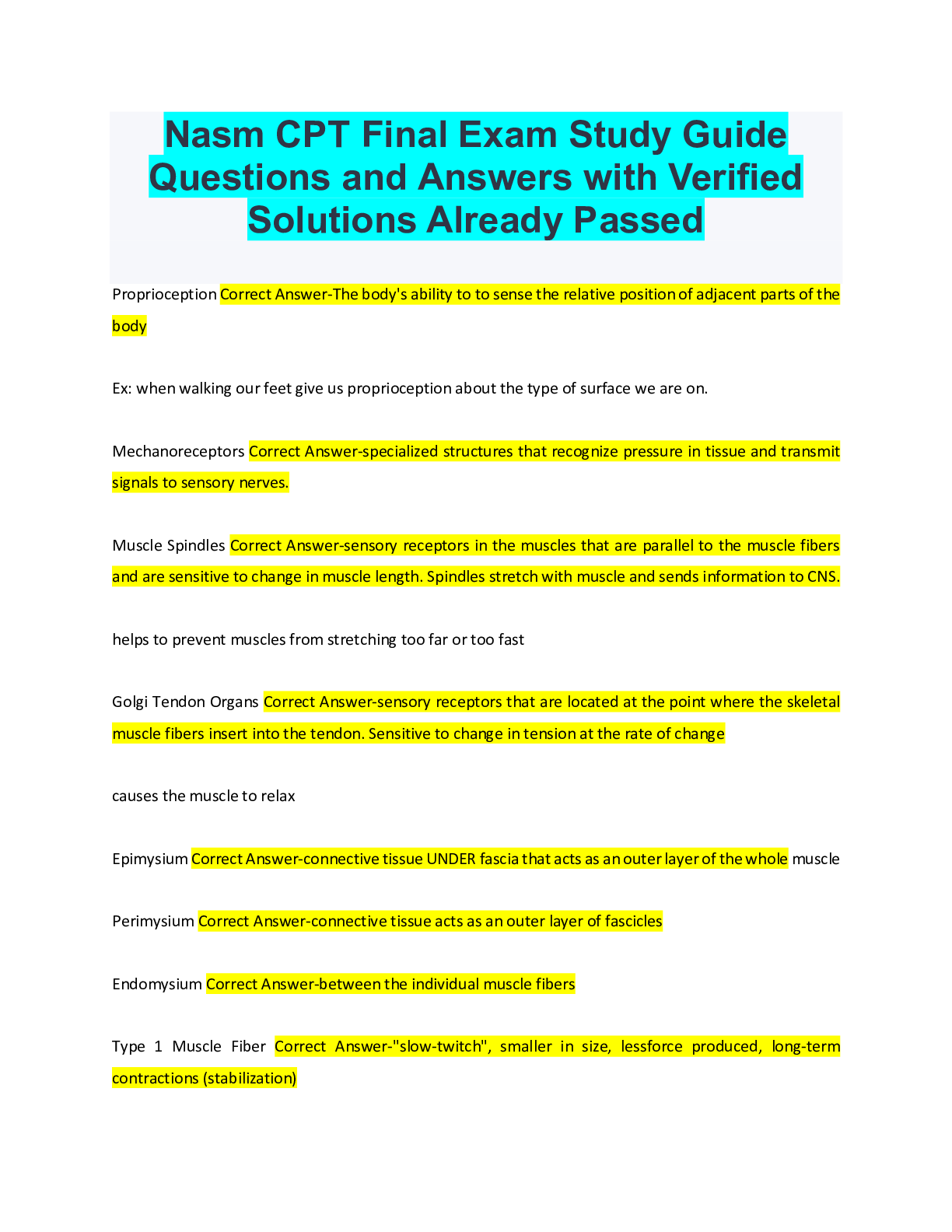
Nasm CPT Final Exam Study Guide Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions Already Passed Proprioception Correct Answer-The body's ability to to sense the relative position of adjacent parts of ... the body Ex: when walking our feet give us proprioception about the type of surface we are on. Mechanoreceptors Correct Answer-specialized structures that recognize pressure in tissue and transmit signals to sensory nerves. Muscle Spindles Correct Answer-sensory receptors in the muscles that are parallel to the muscle fibers and are sensitive to change in muscle length. Spindles stretch with muscle and sends information to CNS. helps to prevent muscles from stretching too far or too fast Golgi Tendon Organs Correct Answer-sensory receptors that are located at the point where the skeletal muscle fibers insert into the tendon. Sensitive to change in tension at the rate of change causes the muscle to relax Epimysium Correct Answer-connective tissue UNDER fascia that acts as an outer layer of the whole muscle Perimysium Correct Answer-connective tissue acts as an outer layer of fascicles Endomysium Correct Answer-between the individual muscle fibers Type 1 Muscle Fiber Correct Answer-"slow-twitch", smaller in size, lessforce produced, long-term contractions (stabilization)Type 2 Muscle Fiber Correct Answer-fast twitch, larger, quick to fatigue, force and power exercises Agonist Correct Answer-PRIME MOVER, main muscles ex: chest press-> pectoralis major Synergist Correct Answer-ASSIST PRIME MOVER, ex: chest press -> ant deltoid, triceps Stabilizer Correct Answer-stabilizes while prime mover and assist work. chest press -> rotator cuff Antagonist Correct Answer-Oppose Prime mover, chest press -> posterior delt Right Atrium Correct Answer-gather DEOXGENATED blood returning to the heart from ENTIRE BODY Left Atrium Correct Answer-gathers OXYGENATED blood coming from the LUNGS Right Ventricle Correct Answer-thin walls pumps under low pressure. Pumps to lungs Left Ventricle Correct Answer-thick walls, pumps under high pressure to rest of body Metabolism Correct Answer-all of the chemical reactions that happen in our body to maintain itself. Nutrients are acquired, transported and used by the body. Exercise Metabolism Correct Answer-bioenergetics as it relates to the unique physiologic changes and demands on body during exercise Substrates Correct Answer-where enzymes act Carbohydrates Correct Answer-Sugars, starches, and fiber. Provide the body with a source of fuel and energy required for all daily activitiesGlucose Correct Answer-a simple sugar that comes from the digestion of carbs that is transported through the blood and is used or stored as energy Glycogen Correct Answer-the stored form of carbs, when needed it converts to glucose and used Fat Correct Answer-a secondary source of energy Trigylcerides Correct Answer-come from fats, when calories are consumed but not used they are converted and stored in fat cells Protein Correct Answer-Amino acids that build and repair body tissues and structures. A third energy source, usually not until starvation. Recommended 0.8 g per day Adults, 1.2-1.7 per day strength athletes, 1.2-1.4 endurance athletes 1 g = 4 calories Gluconeogenesis Correct Answer-glucose form from non carb sources like amino acids Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Correct Answer-Energy storage and transfer unit in the cells. When chemical bonds that hold it together are broken, energy is released Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) Correct Answer-molecule produced by ATP ATP-PC system Correct Answer-simpliest and fastest, occurs without oxygen (anaerobic), provides energy for high intensity, short-duration ex: power and strentgh Glycosis System Correct Answer-produces lots of energy for 30-50 sec. Typical bc it falls in the time frame of 8-12 reps Oxidative System Correct Answer-most complexB- oxidation Correct Answer-breakdowns triclgycerides into free fatyy acids to produce more ATP Myth of Fat Burning Zone Correct Answer-higher intensity workouts require greater contribution from fat despite the increase in need of fuel source from carbs Biomechanics Correct Answer-internal and external forces acting on the human body and the effect produced Superior Correct Answer-above a reference point inferior Correct Answer-below a reference point Proximal Correct Answer-reference closest to the center of the body or reference Distal Correct Answer-refernence furthest away Anterior Correct Answer-Reference in front of the body Posterior Correct Answer-Reference in the back of the body Medial Correct Answer-Refernence to the midline of the body Lateral Correct Answer-Reference to the outside of the body Contralateral Correct Answer-refers to a position on the opposite side of the body Ipsilateral Correct Answer-positioned on the same side of the body Sagittal Plane Correct Answer-movements of flexion or extension ex: front lunge, bicep curls, squat Frontal Plane Correct Answer-movements lateralex: side lunge, side lat raises Transverse Plane Correct Answer-divides body in upper and lower halves Adduction Correct Answer-movement TOWARD the midline of the body Abduction Correct Answer-movement AWAY from the midline of the body Isotonic Correct Answer-Constant muscle tension [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 11, 2022
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 11, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
61