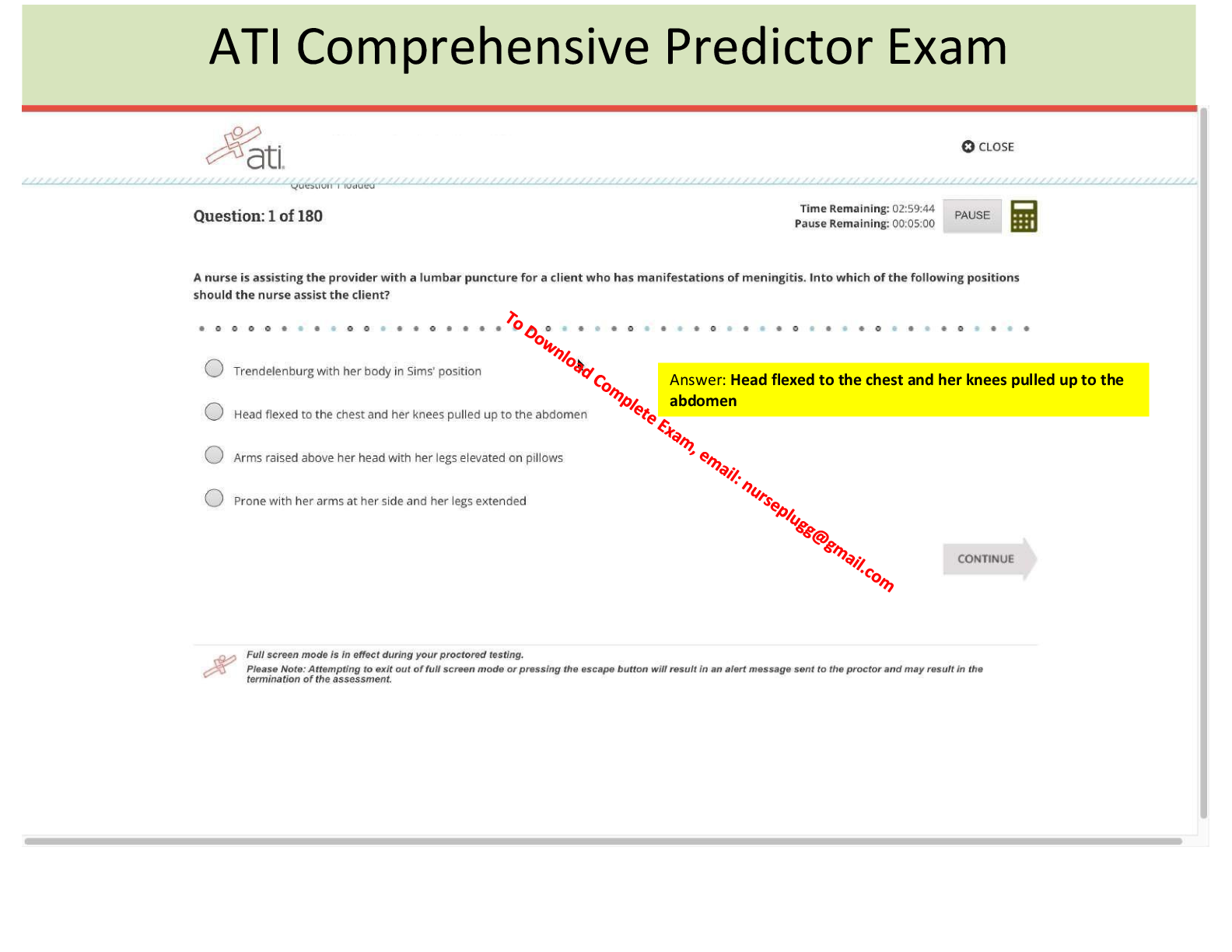
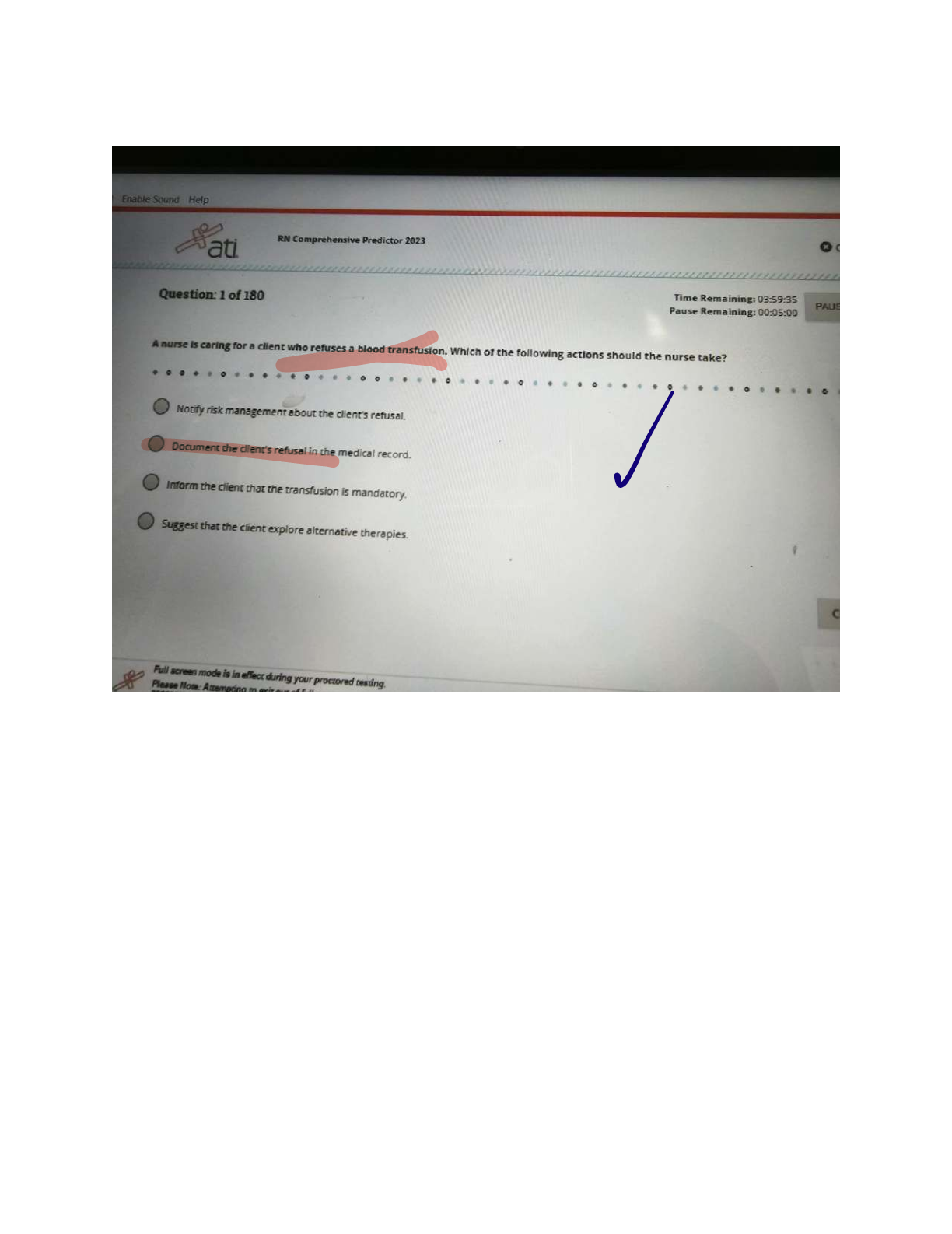
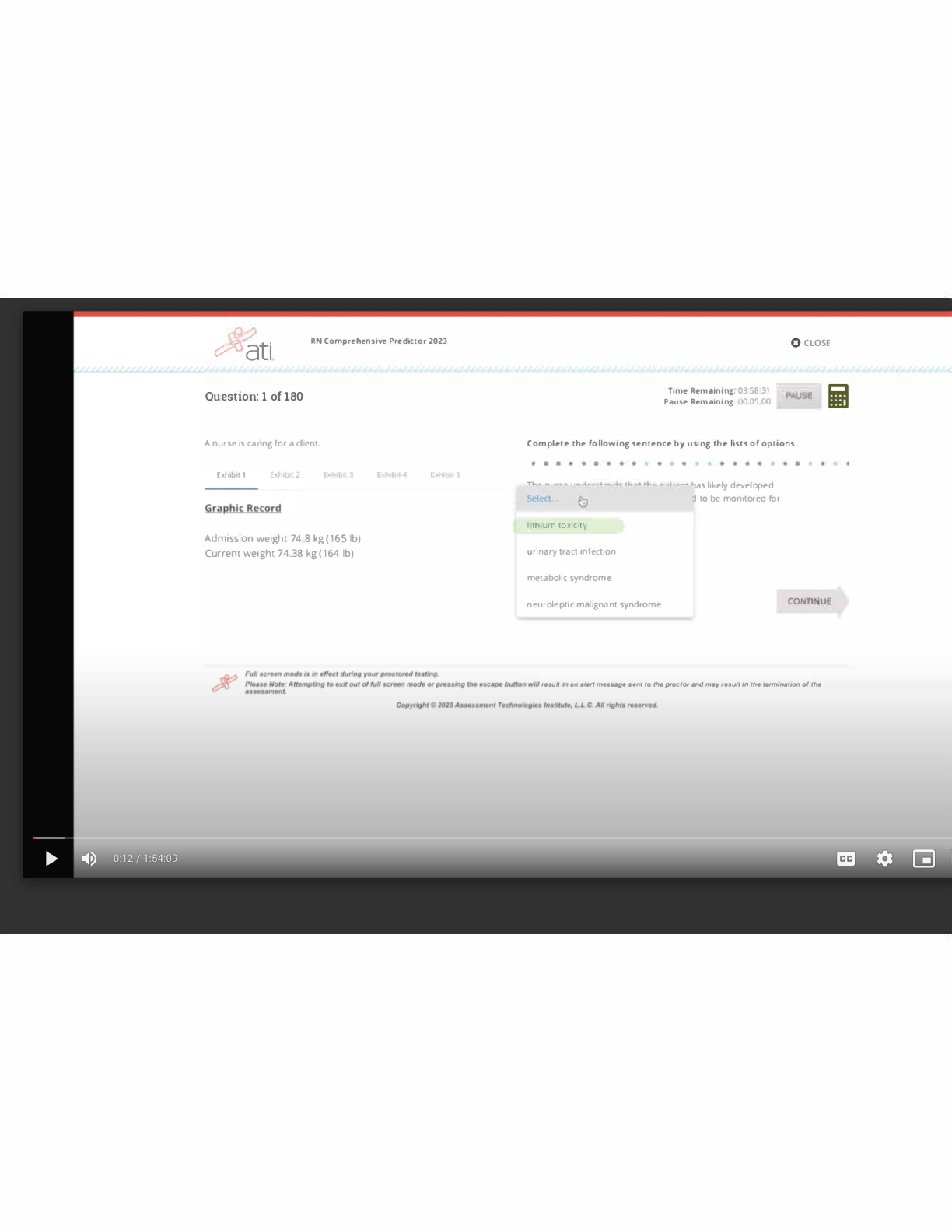
NURS 351 Exam 2 Study Guide – Nevada State College
Study guide exam 2
Ch 17 Maximizing comfort
• General anesthesia – rarely used for uncomplicated vaginal birth
o Nitrous Oxide: laughing gas for labor
¬ Nitrous
...
NURS 351 Exam 2 Study Guide – Nevada State College
Study guide exam 2
Ch 17 Maximizing comfort
• General anesthesia – rarely used for uncomplicated vaginal birth
o Nitrous Oxide: laughing gas for labor
¬ Nitrous oxide mixed with oxygen provides analgesia during the first and second stages of labor
¬ Self-administered by laboring woman
¬ Used in any stage of labor
¬ Full effect in 30-60 seconds
¬ Effect: pain relief, euphoria, less anxiety
¬ Side effect: nausea, vomiting, poor recall of labor
o Anesthesia: General anesthesia 12 (loss of consciousness)
¬ Rarely used for uncomplicated vaginal birth
¬ The woman should be premedicated with (clear) oral antacid to neutralize the acidic contents of the stomach.
¬ Because of this risk for neonatal narcosis, it is critical that the baby be delivered as soon as possible after induction of general anesthesia
o Regional analgesia and anesthesia and local 13
¬ Epidural: currently the most effective pharmacologic pain relief method for labor
¬ Combined spinal-epidural (CSE)
¬ Walking epidural – lighter version of epidural
¬ Spinal
¬ PCEA
¬ Pudendal Block
• Epidural/spinal anesthesia and associated complications – everything
o Regional analgesia and anesthesia: contraindications
¬ History of spinal surgery/ abnormalities
¬ Active or anticipated serious maternal hemorrhage
¬ Maternal hypotension
¬ Maternal coagulopathy
¬ Infection at the injection site
¬ Thrombocytopenia
¬ Increased intracranial pressure
¬ Maternal refusal or inability to cooperate
¬ Some types of maternal cardiac conditions
o Contraindicated for the woman who is receiving anticoagulation therapy
o Side Effects/complications of regional anesthesia
¬ Hypotension
¬ Changes in FHR
¬ Nausea and Vomiting
¬ Pruritis
¬ Urinary retention, Maternal temperature
¬ Postdural puncture headache
¬ High spinal
¬ Intravascular injection
¬ Epidural hematoma
• Nonpharmacological pain management
o Application of heat and cold
o Massage
o Birthing Balls
o Hydrotherapy
o Acupressure and acupuncture
o Frequent position change
o Aromatherapy
o Music
o Hypnosis
• All about pain; anxiety and pain
Definition of pain
♣ Pain tolerance refer to the level of pain a laboring woman is willing to endure
o First stage of labor (visceral pain)
o Second stage (visceral +somatic pain)
♣ Somatic pain - intence, sharp, burning, and well localized
o Third stage (similar to the first stage)
Factors influencing pain response
o Anxiety and fear
o Culture
o Previous experience
o Support system
o Environment
Non-pharmacological management of pain
o Gate-control theory – pain relieve techniques to distract from pain (massage, music, stroking, ect..)
o P.385 – BOX 17-2
o Breathing techniques – p387, BOX 17-3
Pharmacologic pain management (p392 BOX 17-4)
o Sedatives: relieve anxiety, depress CNS, induce sleep
¬ Can be given to a woman experiencing a prolonged latent phase of labor when there is a need to lessen the intensity of the contractions
¬ They can also be given to augment analgesics and reduce nausea when an opioid is used
o Barbiturates (Secobarbital) – side effects- respiratory and vasomotor depression
¬ Should be avoided if birth is anticipated within 12 to 24h
o Benzodiazepines (lorazepam - Ativan, diazepam - Valium) enhance pain relief and reduce nausea and vomiting when administered with opioids
¬ Major side effects (drowsiness, hypotension; diazepam hurts newborn thermoregulation)
o Analgesia (p 392 BOX 17-4) is partial or full relief of painful sensation using medications that decrease or alter the perception of pain (alleviation of pain)
o Anesthesia: Partial or complete loss of sensation with or without loss of consciousness (removing sensation)
¬ The type of analgesic or anesthetic chosen is determined in part by the stage of labor of the woman and by the method
o Meperidine(Demerol) and Fentanyl (Sublimaze) stimulate opioid receptors, mu and kappa
o Morphine - affinity for mu receptors
o Morphine – lesser risk for neonatal sedation compare to Demerol
o Stadol, Nubain – affinity for kappa and sigma receptors, lesser Respiratory Depression
Side effects of narcotics:
♣ Maternal/fetal sedation
♣ Maternal/fetal respiratory depression
♣ Maternal: NV, dizziness, urinary retention
♣ Fetal: Decrease in FHR variability
♣ Newborn: Decreased muscle tone and ineffective sucking reflex with difficulty initiating breathing
♣ Naloxone (Narcan) – administered to reverse the depressant effect of the opioids
Ch 18 Fetal assessment
• EFM equipment; placement
o Intermittent auscultation (IA)
¬ Listening to fetal heart sounds at periodic intervals to assess FHR
♣ Pinard fetoscope (p411)
♣ Doppler ultrasound
♣ Ultrasound stetoscope
¬ Easy to use, inexpensive, less invasive than EFM
¬ Difficult to perform on women who are obese
¬ Does not provide a permanent record
o Electronic fetal monitoring
o External monitoring (p414)
¬ Ultrasound transducer - reflects high-frequency sound waves off a moving interface: the fetal heart and valves
¬ Tocotransducer – measures UA transabdominally. Placed over the fundus above umbilicus and held securely in place using an elastic belt
• Everything about Internal monitors
o Fetal Scalp Electrode (FSE): internal monitoring of the FHR
o Intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC): monitoring uterine contractions
• Fetal heart abnormal rates: tachycardia, bradycardia
ϖ Tachycardia: >160 beats/min 10 minutes or more
Causes:
¬ Maternal infection, chorioamnionitis
¬ Fetal anemia
¬ Fetal cardiac dysrhythmias
¬ Maternal use of cocaine/meth
¬ Maternal dehydration
¬ Fetal infection
¬ Maternal hyperthyroidism
ϖ Bradycardia: <110 beats/min 10 minutes or more
Causes
¬ Uteroplacental insufficiency
¬ Umbilical cord prolapse
¬ Maternal hypotension
¬ Prolong umbilical cord compression
¬ Fetal congenital heart block
¬ Anesthetic medications
[Show More]