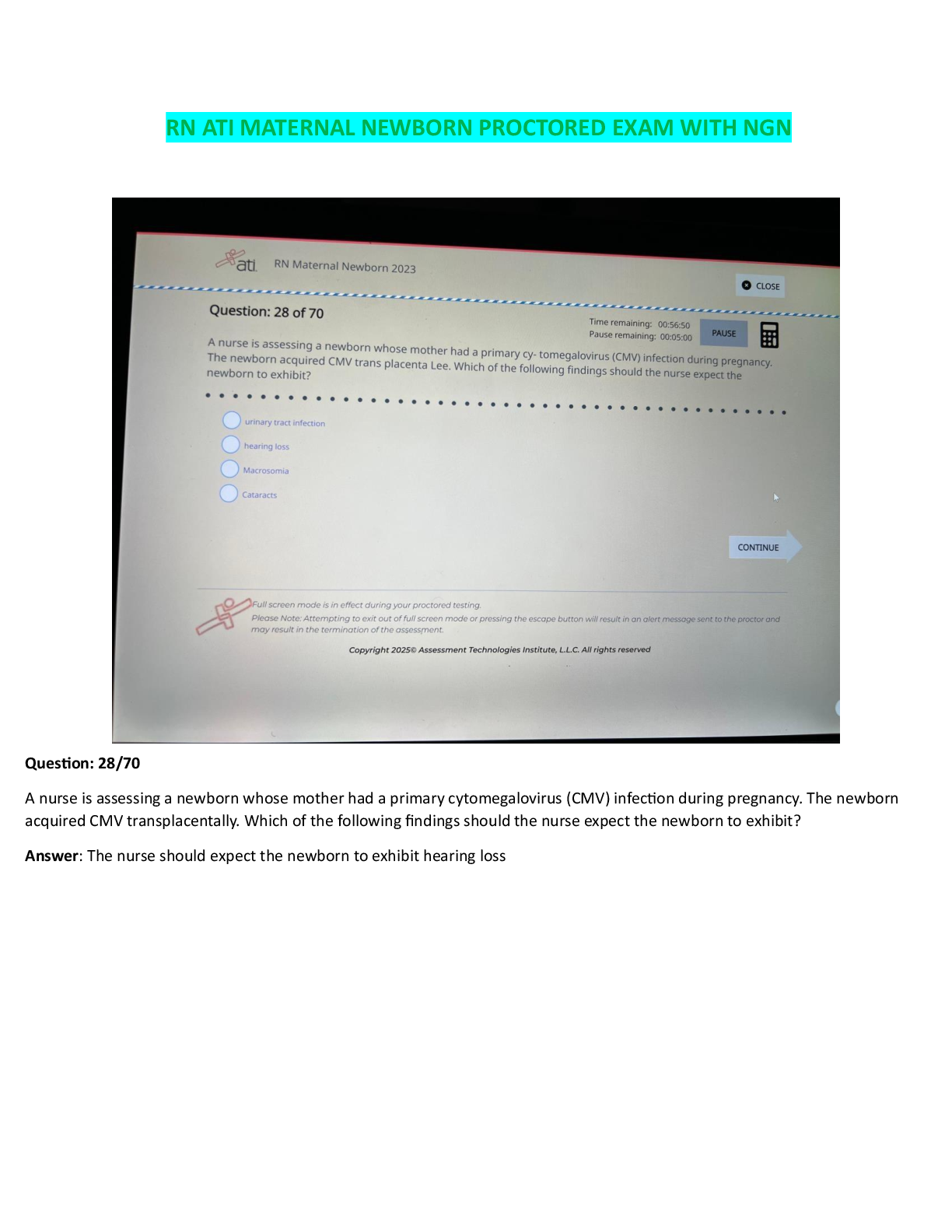
NFPT exam study guide (2022)
Document Content and Description Below
The five components of physical health - ANSWER Cardiorespiratory conditioning, muscular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, body composition
SPICES - ANSWER Social health, physical health,
...
intellectual Health, cognitive health, emotional health, spiritual health
Cardiorespiratory conditioning - ANSWER Endurance
Muscular endurance - ANSWER The amount of strength that can be repeated several times
Muscular strength - ANSWER The amount of strength in one repetition
Flexibility - ANSWER The range of motion in given joints
Body composition - ANSWER The amount of body fat relative to the total weight or as compared to the lean mass
What are three additional factors that are specific to the fitness regimens of athletes and sports teams? - ANSWER Agility, speed and Mobility
Intellectual health - ANSWER The capacity to assimilate and integrate new information into one's thinking and thought processes
Cognitive health - ANSWER Often grouped with mental health as it has mostly to do with how we process information in the brain. It includes the way we see, or conceptualized, the world around it includes brain functioning in the areas of conceptual and perceptual skill, language learning as well as many other brain development functions
Emotional health - ANSWER Includes self-esteem, self-awareness, self-acceptance, self-image and our capacities to deal with adversity and stress. This includes our ability to intimate, not just sexual, with a significant other.
Spiritual health - ANSWER This is focused on the connection of ourselves with a higher power, a sense of purpose, self-actualization, and an inner Joy. It is often described as self-acceptance, repentance for misdeeds, a willingness to give to and forgive others and a desire to seek peace with the community and World overall
Why is it important to touch on all things spices related as a personal trainer? - ANSWER Think about it and perhaps write a blog post
What are the three categories of motivating factors for positive behavior - ANSWER Predisposing factors, enabling factors and reinforcing factors
Predisposing factors include - ANSWER Knowledge, attitude, believe, values and perceptions
Enabling factors - ANSWER Skills, resources, physical and mental capabilities
Reinforcing factors - ANSWER Praise from others comma rewards, encouragement and recognition
Which factors does the personal trainer typically fall into - ANSWER Reinforcing factors. We can recognize how the other two factors promote or inhibit positive behavior and we can work to reinforce positive behavior with forms of encouragement
What are some things that can be added to life to invoke positive change? - ANSWER Taking time for Meaningful reflection, reading a book, being creative, socializing with friends and family, adding a physical component and healthy eating to daily living
What areas of exercise therapy would require a highly trained exercise physiologist or physician to prescribe appropriate regimens - ANSWER Cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, joint injury, or obesity / metabolic disorders which include diabetes and hypertension
What is the purpose of muscles - ANSWER To produce Force, maintain posture, allow for movement and produces Heat
All muscle action originates and is controlled by what? - ANSWER The brain which sends and receives signals through the nervous system
What gets pulled during a muscle contraction? - ANSWER Tendons, the strong connective tissue that connects muscles to bones
What are the two points of muscle - ANSWER Origin and insertion
Define muscle origin - ANSWER The origin is considered the point at which the muscle joins the stationary bone at the end closest to the center of the body
Define muscle insertion - ANSWER Insertion is the point at which the muscle joints moving boat. When a muscle contracts the insertion moves toward the origin
How many muscles are in the average adult body - ANSWER 656 muscles
Muscles are joined together to form muscle groups to execute bodily movement. They can get shorter and pull but they cannot push. True or false? - ANSWER True
In muscle groups, when one group pulls the other group pulls back and as one team pulls the other team relaxes. True or false? - ANSWER True
What are the three muscle types? - ANSWER Skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles
What are the two subtypes of muscles? - ANSWER Involuntary and voluntary
How many muscles are voluntary and how many bones do they control? - ANSWER 430 of our muscles are voluntary controlling 206 bones
Which type of muscles are voluntary? - ANSWER Skeletal muscles
Which type of muscles are involuntary? - ANSWER Smooth and cardiac which include the cardio vascular tissue comma heart and blood vessels, and the lining of the intestinal and respiratory tracts
What internal system supplies muscles with the necessary oxygen and nutrients to survive ? - ANSWER The cardiorespiratory system
How many bones are in the adult body? - ANSWER 206. We are born with 350
What are the five major functions of the skeleton? - ANSWER Protect vital internal organs; Sports our bodies framework, giving us an upright vertical shape; produces red and white blood cells in the bone marrow; stores minerals and fats; regulates mineral balance, releases minerals into the blood as needed
What is the largest bone in the body? - ANSWER The femur, located in the top half of the leg it allows us to walk
What are the rounded nodules, or outgrowths, on bones that generally act as sites for muscle insertions? - ANSWER Tubercles; for example, the tibial tuberosity creates an attachment point for the patellar ligament
What is a joint? - ANSWER A joint is the location at which two or more bones come together for movement and mechanical support
What is a ligament? - ANSWER Strong stretchy bands of fibrous tissue that hold joints together
What is cartilage? - ANSWER Cartilage covers the ends of each bone and is a tough flexible connective tissue that has a smooth, shiny surface
What is the name of the thin film of slippery fluid located between bones? - ANSWER Synovial fluid, keeps the bones from scratching and bumping against each other during movement
Tendon - ANSWER Connects muscle to bone
Ligament - ANSWER Connects bone to bone
How many liters of blood does the human body contain ? - ANSWER 4 - 5 liters
Blood is the transport system by which oxygen and nutrients reach the body cells and waste materials are carried away. True or false? - ANSWER True
Define hormones - ANSWER The regulatory substances transported in tissue fluids for stimulating specific cells that control the specific body process
On which side of the heart does blood enter and what color is it - ANSWER Blood enters on the right side of the heart and is dark red almost bluish and is low in oxygen
Blood travels from the right side of the heart along pulmonary arteries to the lungs, where it received fresh supplies of oxygen and becomes bright red period it then flows along pulmonary veins to the heart's left side pump. Blood then leaves the left side of the heart and travels to the rest of the body through arteries, going away from the heart, that gradually divide into capillaries. - ANSWER This is the circulatory system
In relation to the heart, blood travels in which direction through arteries? - ANSWER Away from the heart
In relation to the heart, blood travels in which direction through veins? - ANSWER Toward the heart
What occurs in the capillaries? - ANSWER Food and oxygen are released to the body's cells, and carbon dioxide and other waste products are returned to the bloodstream. After which the blood travels through veins back to the heart and whole process starts again
When we breathe the body takes in oxygen and removes what? - ANSWER Carbon dioxide
What is the technical term for the windpipe and what purpose does it serve - ANSWER Trachea, allows passage of air into the lungs
What is the name for the tubes that carry air into each lung - ANSWER Bronchi
Bronchi divide into even smaller tubes called what - ANSWER Bronchioles
What is the name for the small air sacs located at the end of each bronchiole and which I wrapped up by the capillaries - ANSWER Alveoli
What is the respiratory system - ANSWER The body system that deals with breathing
Our breathing process is controlled by which muscle - ANSWER The diaphragm which is located in the Torso underneath the lungs
Is the diaphragm contracts does it expand or flatten - ANSWER It flattens, causing the chest to expand and air to be sucked into the lungs
What test can you perform dtermine an individuals maximum oxygen intake in one breath - ANSWER VO2 max
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for sending and receiving information to and from the entire body and consists of the brain and spinal cord - ANSWER The central nervous system which is the processing hub
Which nervous system consists of nerves that attach to the CNS to the body's organs and extremities and acts as a messenger between the brain and the rest of the body - ANSWER The peripheral nervous system
What is the sublevel of the pns - ANSWER Autonomic nervous system which operates involuntary voluntary motor nerve processes
List the order of the digestive system - ANSWER Mouth, esophagus comma stomach comma pancreas, gallbladder, small intestine, liver, large intestine, rectum and anus
Esophagus - ANSWER Is a muscular tube that takes food from the throat and pushes it down through the neck and into the stomach. It moves food by waves of muscle contractions called peristalsis
Stomach - ANSWER The stomach has big muscles in its wall with contract too much food. The stomach secrete strong protein digesting juices and acids that attacked the food and a chemical whey breaking down and dissolving its nutrients. Once the food is broken down it will then move into the small intestine
Pancreas - ANSWER Is a glandular organ in the digestive and endocrine system. In the digestive system it acts much like the stomach in that it makes powerful digestive juices called enzymes that for their break down food as it enters the small intestines. This is also where insulin and glucagon are released to control blood sugar levels
Gall bladder - ANSWER This is a small bag like part that is tucked under the liver. It stores fluid called bile which is made in the liver. As food from a meal arrives in the small intestine bile flows from the gallbladder along the bile duct into the intestine. This vile acts especially to further digest fatty foods
Small intestine - ANSWER This is where most of the absorption of nutrients occur. Nutrients are small enough to pass through the lining of the small intestine and into the blood. These nutrients are then carried away to the liver and other parts of the body to be processed stored and distributed
Liver - ANSWER Blood from the intestines flows to the liver, carrying nutrients comma vitamins and minerals, and other products from digestion. The liver stores some nutrients, changes them from one form to another, and then releases them into the blood according to the activities and bodily needs
Large intestine - ANSWER Useful substances in The Leftovers, such as spare water and minerals, are absorbed through the walls of the large intestine and back into the bloodstream. The remains are formed into semi solid waste product, feces, to be removed from the body
Rectum and Anus - ANSWER The end of the large intestine comma the rectum, stores the feces which are squeezed through a ring of muscle, the anus, and out of the body
List some of the body's defense mechanisms from bad germs - ANSWER The skin, the linings of the respiratory and digestive passageways, the blood-clotting process, the white cells and other substances in the blood, the thymus gland in the chest, and a small lymph nodes or glands are located throughout the body
What is the job of the white blood cells in regards to the body's immune system - ANSWER White cells attack any germs that are present in the body.
Where are white cells located as far as our immune system - ANSWER Lymph nodes, thymus gland, spleen, tonsils and adenoids
Lymph nodes - ANSWER Act as filters or germ traps. They contain billions of white blood cells which multiply rapidly to fight off invading pathogens
Thymus gland - ANSWER Located in front of the heart and behind the sternum. It produces and educates to cell. T cells are orchestrated in the thymus for the purpose of attacking foreign substances and responding to infected cells. The thymus is larger and most active during childhood and puberty
Spleen - ANSWER Located just behind the stomach on the left side. It makes in stores various kinds of white and red blood cells. It works to decrease susceptibility and fight off infection
Tonsils and adenoids - ANSWER These help to destroy foreign substances that are breathing or swallowed. Adenoids are located at the rear of the nasal cavity where the nose and throat meet. Tonsils are patches of lymph tissue at the upper rear part of the throat
Endocrine system - ANSWER Similar to the nervous system, but it's made up of glands that mainly use hormones as information channels. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
Glands - ANSWER Located in many regions of the body release chemical Messengers called hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones transport signals from one cell to another, for the purpose of generating a specific response, regulating the varied functions of an organism, such as, mood, sleep, growth, development, and metabolism
Homeostasis - ANSWER The regulating and stabilizing of the body's internal properties.
Pituitary gland - ANSWER It's at the junction where the nervous system and the endocrine system come together at the hypothalamus. The gland is attached to the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain and secretes hormones that affect and control functions like skeletal growth, development of sex glands, blood pressure and pain relief, and the stimulating functions of other endocrine glands
Thyroid gland - ANSWER Controls how quickly the body uses energy and regulates metabolism
Adrenal gland - ANSWER Synthesizes and releases hormones in response to stress, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline
Pineal gland - ANSWER Produces the hormone melatonin which stimulates and affects our sleep and daily rhythmic patterns
Exocrine glands - ANSWER Such as salivary glands, sweat glands glands within the gastrointestinal tract excrete their product to an external environment by way of ducts
Anterior - ANSWER Front of the body
Posterior - ANSWER Back of the body
Superior - ANSWER Upper part of the body
Inferior - ANSWER Lower part of the body
Proximal - ANSWER Closest to the point of origin from the center of the body
Lateral - ANSWER Away from the middle of the body
Distal - ANSWER Furthest from the point of origin from the center of the body
Medial - ANSWER Towards the middle of the body
Bilateral - ANSWER Both sides of the body
Unilateral - ANSWER One side of the body
Deep muscle - ANSWER Toward the inner body
Superficial - ANSWER Toward the outer surface
Peripheral - ANSWER Toward the extremities
Biomechanical movement - ANSWER The study of mechanical movement of the human body within the actions of external and internal forces
Kinesiology - ANSWER Study of anatomy physiology and mechanics of human movement
Biology - ANSWER Scientific study of life and living matter including structure and function
Kinematics - ANSWER Branch of biomechanics that specifically studies the time taken to carry out an activity
Biomechanics - ANSWER Kinesiology applied to the biological function of human movement. It focuses on the effects of the forces of Life external and internal on human mechanics
Abduction - ANSWER Movement away from the body or body parts midline
Adduction - ANSWER Movement toward the body or body parts midline
Flexion - ANSWER The bending of a joint that decreases the angle
Extension - ANSWER The straightening of a joint that increases the angle
Circumduction - ANSWER The motion of a circular Movement Like rotating the foot around the ankle
Rotation - ANSWER Both internal and external rotation. Internal rotation is the movement of the body part about its axis turning inward or toward the center / midline of the body. External rotation is the movement of the body part turning outward away from the center / midline of the body
Protraction - ANSWER Anterior movement of a body part
Retraction - ANSWER Posterior movement of a body part
Hypo extension - ANSWER Extensions that is less than normal, under extended
Hyperextension - ANSWER Extension Beyond normal limits, overextended
Gliding - ANSWER Movement of non angular joints over each other
Deviation - ANSWER Departure from the midline
What are the six movements specific to hands / palms and feet - ANSWER Pronation, supination, inversion, erosion, dorsiflexion, plantar plantarflexion
Pronation - ANSWER Palm of hand turning downward into a posterior position when arm is down at side. The inward roll of the foot / arch decreased during normal walking motion
Supination - ANSWER Palm of hand turning upward into an anterior position when arm is down inside. The outward roll of the foot, underpronation / arch heightened during normal walking motion
Inversion - ANSWER Turning both feet inward so the soles face each other
Eversion - ANSWER Turning both feet outward so these soles face away from each other
Dorsiflexion - ANSWER Ankle pointing foot up towards the shin
Plantarflexion - ANSWER Ankle pointing foot downward
What are the four main types of muscle contraction - ANSWER Isometric, isokinetic, isotonic concentric and isotonic eccentric
What is the purpose of muscle contraction - ANSWER They allow for the given muscle to perform work and move within its range of motion
Range of motion - ANSWER The degree of freedom for which a joint can move through
Isometric contraction - ANSWER The load on the muscle is greater than the generated tension, results in no movement taking place
Isokinetic contraction - ANSWER The muscle contracts and shortens at a constant rate of speed, allows the muscle to gain strength evenly all through the entire range of motion. This is the quickest method for increasing muscle strength but requires equipment that increases the load as it senses the contractions speeding up
Isotonic contractions - ANSWER The load on the muscle is less than the generate attention and results in movement taking place tension is developed and mechanical work can be done
Isotonic Concentric contraction - ANSWER Causes the muscle to decrease / shorten in length and the angle of the joint to decrease. This is referred to as the positive part of a repetition. It brings the involved bones together. This is usually an active and voluntary action resulting in movement
What is the concentric phase in a squat chest press and lat pull - ANSWER Squat- standing up
Chest press- lowering the bar
Latin pull- pulling the bar down
Isotonic eccentric contraction - ANSWER Causes the muscle to increase /lengthen in length and the angle of the joint to increase. This action is referred to as the negative part of a repetition where they control the resistance is returned to the starting position of an exercise. This can be either voluntary in order to stimulate adaptation or involuntary in order to protect the joint
What is The Eccentric contraction in a squat chest press and lat pull - ANSWER Squat- lowering down
Chest press- pushing the bar up
Lat pull- letting the bar go back up
What are the four planes of motion - ANSWER Sagittal, frontal, transverse, parasagittal
What is the sagittal plane of motion and what exercises take place here - ANSWER This divides the left and right side. The motions include flexion and extension such a squat, lunge, walking, running, arm curls
What is the frontal plane of motion and what exercises take place here - ANSWER This divides the anterior from the posterior. The motions include abduction and adduction for example lateral raise, pull downs, side bends, military press homicide squats, jumping jacks , skater lunge
What is the transverse plane of motion and what exercises take place here - ANSWER Divides the inferior from the superior parts of the body. Motions include internal rotation and external rotation including rotation at the waist for example swinging a golf club or baseball bat
Oblique - ANSWER Describe the diagonal movement, or a hybrid / combination of two planes.
Internal rotation - ANSWER Also medial rotation, occurs when it rotates inward. During a military or shoulder press, you would be internally rotating the scapula
External rotation - ANSWER Occurs when the anterior aspect rotates outward. During a lat pull the scapula are being externally rotated
Pronation and supination - ANSWER Occur at the elbow to rotate the wrist or the ankle to rotate the foot. Pronation is turning the palm from the anatomical position to face backward. Turning the Palm forward is supination.
Protraction and retraction - ANSWER Projection is movement anteriorly in the transverse plane. During a seated row as the person pulls the handle back towards the thorax they are retracting their scapula
Gliding - ANSWER Is the motion in any direction of two articulating surfaces sliding past one another. This occurs in the carpal bones of the hands and tarsal bones of the feet and also between the clavicle and sternum
Another name for a joint is - ANSWER Articulation
Define a joint - ANSWER A connection between two bones or a bone and cartilage
The stability and integrity of a joint is due to ligaments that connect two bones together and how snug there fit is. T/f - ANSWER True
The the more stable The Joint the more snug fit and less range of motion it has - ANSWER True
What is relaxin - ANSWER A protein hormone that increases in production to relax the joints in pregnant women to facilitate childbirth
What factors determine the degree of movement that's possible at a given joint - ANSWER Type and structure of the joint; the structure or shape of the articulating bones which determines the fit, how flexible or inflexible The Joint ligaments are, the arrangement and strength of the associated muscles and tendons, soft tissue May limit mobility of a joint comma hormone production
What are the two classifications of joints - ANSWER Structure and function
What defines the structure of a joint - ANSWER Joints are identified by how the bones connect to each other structurally
How to find the function of a joint - ANSWER They are identified by their range of motion in the planes that the joint can move along
What are the three main classifications of joints, by mobility - ANSWER Ligamentous, cartilaginous, synovial
What is the mobility of a ligamentous joint - ANSWER Immovable. These joints have no joint cavity and are bound together by strong, fibrous connective tissue. Example bones of the skull
What is the mobility of a cartilaginous joint - ANSWER Slightly movable. These joints are attached by cartilage or fibro cartilage in his tissue. For example growth regions of immature long bones or discs between spinal vertebrae
What is the mobility of a synovial joint - ANSWER Highly movable. These joints have space between the articulating bones, filled with synovial fluid. Articular ends of the bones have cartilage that cushions the bones and decrease friction. Is synovial cavity is the space between the articulating bones. An articular capsule contains the to Bone ends in a fluid environment
Is the shoulder complex comprised of - ANSWER The sternoclavicular joint, the acromioclavicular joint, the glenohumeral joint
What is the sternoclavicular joint - ANSWER A saddle type synovial joint that occurs between the clavicle and the sternum
What is the acromioclavicular joint - ANSWER A gliding type synovial joint the other end of the clavicle that articulates with the scapula
What is the glenohumeral joint - ANSWER A ball-and-socket joint with multiaxial movement. It is the place where the humerus joins the scapula
Where is the humerus bone located - ANSWER Is the upper arm bone
What is the clavicle - ANSWER Also known as the collarbone
What is the scapula - ANSWER Known as the shoulder blade. They are secured to the axial skeleton by multiple muscles exerting multiple lines of pull
What is a saddle joint - ANSWER The permits movement in two planes / axes of movement it allows for flexion, extension, action, abduction and circumduction. It has a small amount of rotational movement
What is a pivot joint - ANSWER They have similar Mobility to a ball-and-socket joint and they are also known as cylindrical joints
Knee joint facts - ANSWER Largest joint in the human body Kama it is comprised of articulations at 3 long bones the femur the tibia and the fibula,
Femur facts - ANSWER Connected to two parallel floor lamp Bones the tibia and the fibula
Tibia and fibula facts - ANSWER These are the bones of the lower leg, the tibia is larger than the fibula medial to the fibula. The tibia articulates at the proximal end with the femur and at the distal end with the talus bone in the ankle. The Joint between the tibia and femur is known as the tibiofemoral joint. The head of the fibula, or the proximal end, articulates with the tibia just below the level of the knee joint. The distal end of the fibula articulates with the talus bone of the foot
Tibiofemoral joint - ANSWER Located between the flat surface of the tibia in the condyles of the femur, with the patella in front of it
Patella - ANSWER Also known as the kneecap. This is a sesamoid bone that is seated in the patellar quadriceps tendon. The tendon attaches on the tibia at the tibial tuberosity. The patella helps to resist the stress that is placed on the patellar tendon during movement of the knee.
What is the prime movement of the knee joint - ANSWER Flexion and extension, or bending and straightening the leg
What type of joint is the knee joint - ANSWER Hinge but it also includes condyloid joints of the tibial femoral and it partly gliding joint of the patella femoral joint
Which muscle in the knee laterally rotates the femur and the tibia, unlocking the meat and movements that require flexing the leg or bending the knee - ANSWER Popliteus
What are the three supportive structures of the knee - ANSWER The collateral ligaments, the cruciate ligaments, and the menisci
Define ACL and PCL - ANSWER Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments respectively. The ACL resist hyperextension in the PCL resists hyperflexion. Injuries in sports or most likely to originate from the lateral side therefore damaging the ACL
Define menisci - ANSWER There are two in each need the medial and lateral menisci are then cartilage in the knee. They provide for cushioning at the Joint services for the femur and tibia
What is the purpose of the medial collateral ligament and the lateral collateral ligament - ANSWER These ligaments resist lateral and medial displacement and rotation. They attach the femur to the tibia
What two bones make up the forearm and connect to the wrist joint - ANSWER The radius and the ulna
Name the primary wrist joint - ANSWER The radiocarpal
Name the joint Leona and radius form - ANSWER Radioulnar joint; this is a distal joint and is a pivot type synovial. The bump at the end of the wrist is the head of the ulna bone
Name the ankle joint - ANSWER Talocrural; hinge joint with movement in only one plane
3 bones join together to make the talocrural joint - ANSWER The palace, the tibia and the fibula
What are the only two motions that can occur directly at the talocrural joint - ANSWER Plantarflexion and dorsiflexion
The tibia and fibula are joined by what ligaments - ANSWER Tibiofibular which produced a socket that the body of the talus fits snugly into
What is the subtalar joint - ANSWER It is where the talus and the calcaneus meat. It allows for inversion and eversion of the foot
What are the three joints that make up the shoulder complex - ANSWER Acromioclavicular comma glenohumeral, and scapula
What does the acromioclavicular joint allow in the shoulder movement - ANSWER Elevation and depression
What does the glenohumeral joint allow for in the movement of the shoulder - ANSWER Extension, abduction, abduction, rotation
What movement does the scapula allow - ANSWER Protraction and retraction
Which joints are located in the elbow - ANSWER Humeroradial ,humoroulna, radioulna
What movement the humeroradial and humeroulna allow - ANSWER Flexion and extension
What movement does the Radioulna allow - ANSWER Pronation and supination of the forearm and hand
What is considered a connective tissue - ANSWER Attendance, ligaments, fascia
What purpose does connective tissue serve - ANSWER Protect and insulate internal organs, find together and support other tissue in the body and compartmentalize or divide structures, like skeletal muscle
Is adipose tissue a connective tissue - ANSWER Yes and it is a major site for storage of energy
Is blood considered a connective tissue - ANSWER Yes it serves as a major transport system in the body
What is a ligament - ANSWER Ligament attaches bone to bone and provides integrity and strength both inside and outside the synovial joint. They are strong and less elastic than tendons and are less likely to return to their normal resting length when overstretched and they are more prone to tearing
What is a tendon - ANSWER A tendon connects muscle to bone cartilage or an adjoining muscle. They're formed from fibrous tissue and can be ruptured however they are much stronger than muscle and the periosteum of the bone
What is fascia - ANSWER Athan sheet of fibrous tissue that is loose but strong and provides support and some protection by enclosing the muscle or sheet of fibrous tissue that is loose but strong and provide support and some protection by enclosing the muscle or organ. Trauma, inactivity and muscle tension can reduce blood flow and cause painful inflammation of the fascia its corresponding muscle. If this persists fibrosis can occur
myofascial release is a soft tissue therapy that helps to break the cycle of this condition by stimulating the stretch reflex, improving blood flow and relaxing contracted muscles - ANSWER True
What is a prime mover - ANSWER major skeletal muscles that are primarily responsible for movement of the resistance in a given exercise
What is another name for the prime mover - ANSWER Agonist
In a concentric contraction the muscles that are shortening are The Agonist - ANSWER True
during the eccentric contraction, the muscles that are lengthening are the Agonist - ANSWER True
What is an antagonist muscle - ANSWER Text to return a limit to its original place they oppose the movement of The Agonist
What are antagonist muscle examples - ANSWER Pectorals to latissimus dorsi, anterior and posterior deltoids, left and right external obliques, quadriceps to hamstrings, biceps and triceps, forearm flexors to forearm extensors
What is a synergist muscle - ANSWER It neutralizes the extra motion from The Agonist and are sometimes referred to as neutralizers, they make sure that the force of the movement is acceptable for the desired plane of motion
What is a fixator muscle - ANSWER It provides stabilization to support the rest of the body during their respective movement and is sometimes referred to as stabilizer
What are the prime mover movers of the chest press - ANSWER Pectoralis Major which are critical to the pushing movements of the upper body and function primarily to adduct, flex and medially rotate the arm at the shoulder joint.
Pectoralis minor - ANSWER Originates at 3rd 4th and 5th ribs and inserts at Superior Service / medial portion of the character a process of the scapula. The main function is to do press and protract the scapula. A good exercise for this muscle are dips
Deltoids - ANSWER These are shoulder muscles stretching from the clavicle to the humerus and they are made up of three parts the anterior lateral and posterior deltoids. They are the prime movers for arm abduction and originate through the anterior border / lateral part of the clavicle around through the upper part / posterior border of the scapula and they insert together at the middle / anterior surface of the humerus. They work with the chest and back muscles for abduction and adduction of the humerus and for extension and flexion of the shoulder joint at the humorous. They also assist the chest muscles while working for overhead pushing movements.
What is a good exercise for the deltoids - ANSWER Anterior and lateral raises and shoulder presses
Rotator cuff - ANSWER Located beneath the deltoids and as a group of four muscles that originated from the scapula and connect to the head of the humerus. They act to support the arm keeping the head of the humerus family and its shoulder socket during movements of the muscles at the shoulder joint
What are the four muscles of the rotator cuff - ANSWER Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
Supraspinatus - ANSWER Abducts the arm
Infraspinatus - ANSWER Externally rotates the arm
Teres minor - ANSWER Externally rotates the arm
Subscapularis - ANSWER Internally rotates the humerus
Biceps brachii - ANSWER Originate at the scapula and stretch downward to insert at the radial tuberosity. It works as the prime mover to supinate the forearm and flex the elbow
Tricep brachii - ANSWER 3 bundles of muscle that originate at different points joining at the proximal end of the ulna at the elbow. They work together for the extension of the elbow
Name the forearm muscles - ANSWER Brachioradialis comma pronator teres Kama flexor carpi radialis flexor carpi ulnaris flexor digitorum superficialis, palmaris longus Kama extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digiti minimi, extensor digitorum, anconeus
What are the prime movers for a knee extension - ANSWER The Quadriceps
Name the 4 muscles that make up the quadriceps - ANSWER Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medial is and vastus internedius
All but which quad muscle originates at the femur - ANSWER The rectus femoris which is located at the middle, front of the thigh, and originates from the ilium
All four quad muscles insert at the - ANSWER Tibial tuberosity of the tibia. The quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament
Best exercise for the adduction muscles - ANSWER Sumo squat
Hamstrings are made up of which three muscles - ANSWER Biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus
What are the prime movers for flexion at the knee joint - ANSWER Hamstrings
What is flexion at the knee joint - ANSWER Bringing the foot up and back toward the glutes
All but which muscle originate at the tuberosity of the ischium and insert at the medial portions of the tibia - ANSWER Biceps femoris, which originates on the posterior crest/ridge of the femur and inserts into the lateral portions of the fibula
Best exercise for the hammies - ANSWER Hamstring curl
What are the Calves - ANSWER Two muscles-gastrocnemius and the soleus. Both insert into the cacaneus (heel bone). Gatrocnemius are superficial and originate from the femur. The soleus is the deep muscle that originates from the superior posterior area of the tibia.
What is the primary function for the gluteus maximus - ANSWER Hip extension
What is the primary function for the gluteus medius and minimus - ANSWER Hip abduction
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages





.png)