ABCTE PTK Exam Study 391 Questions with Correct
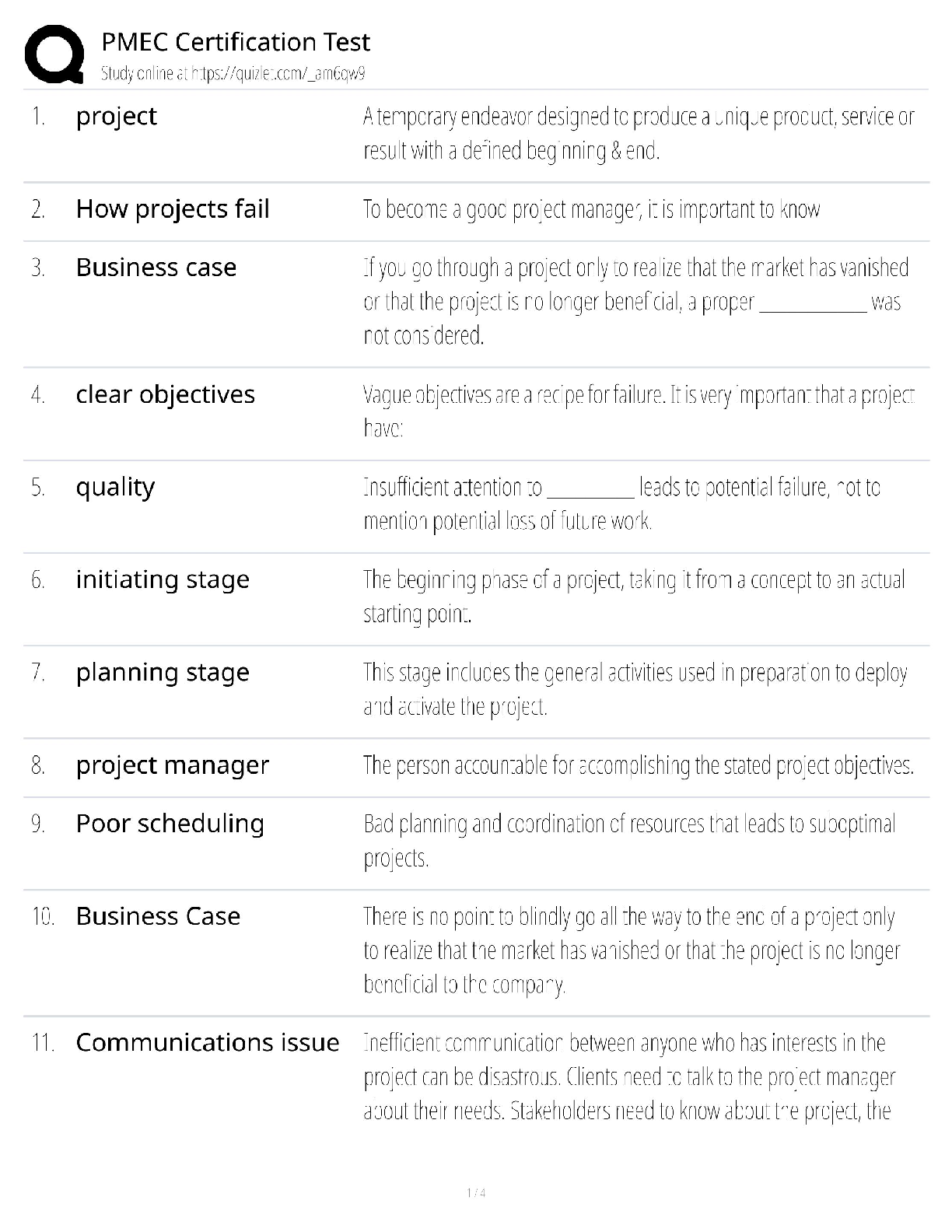
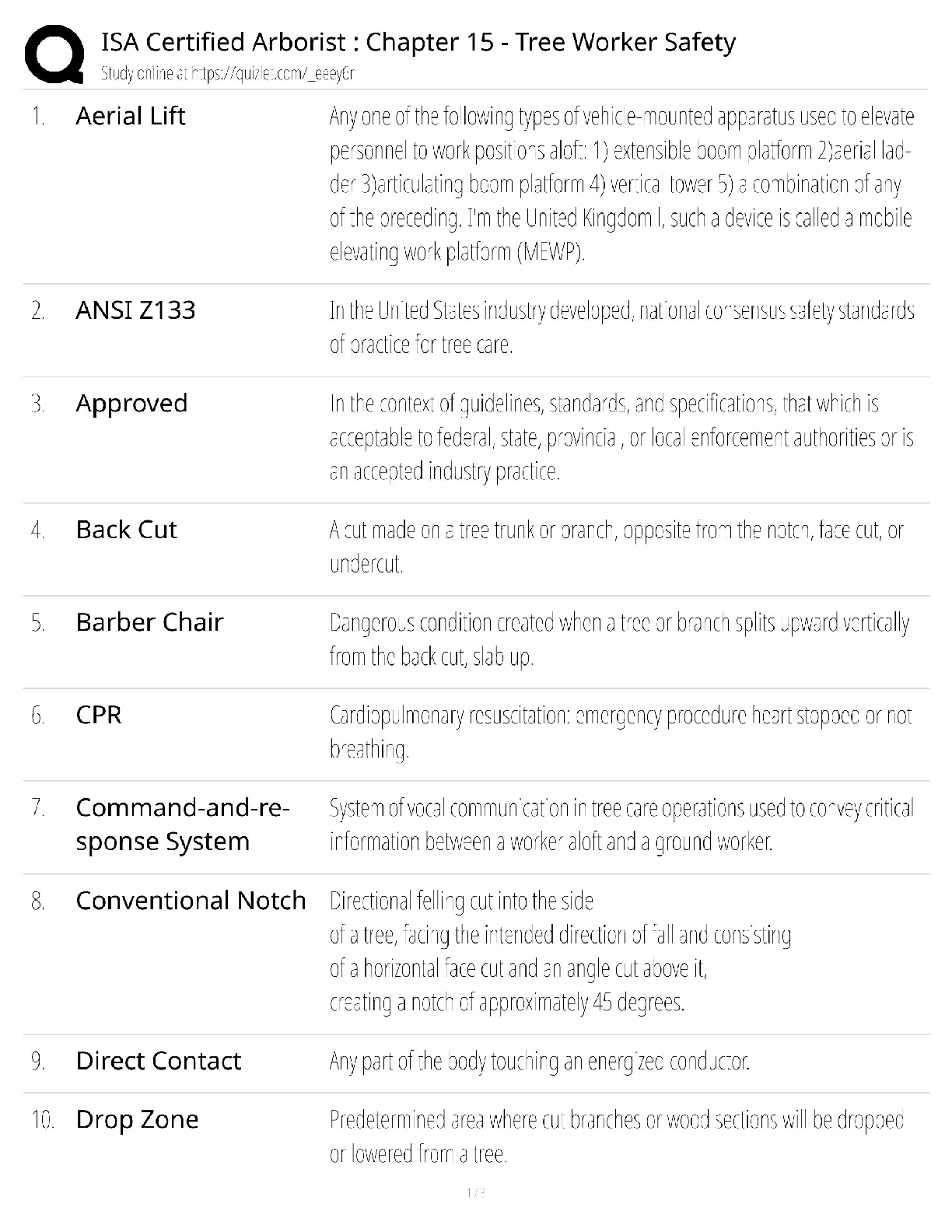
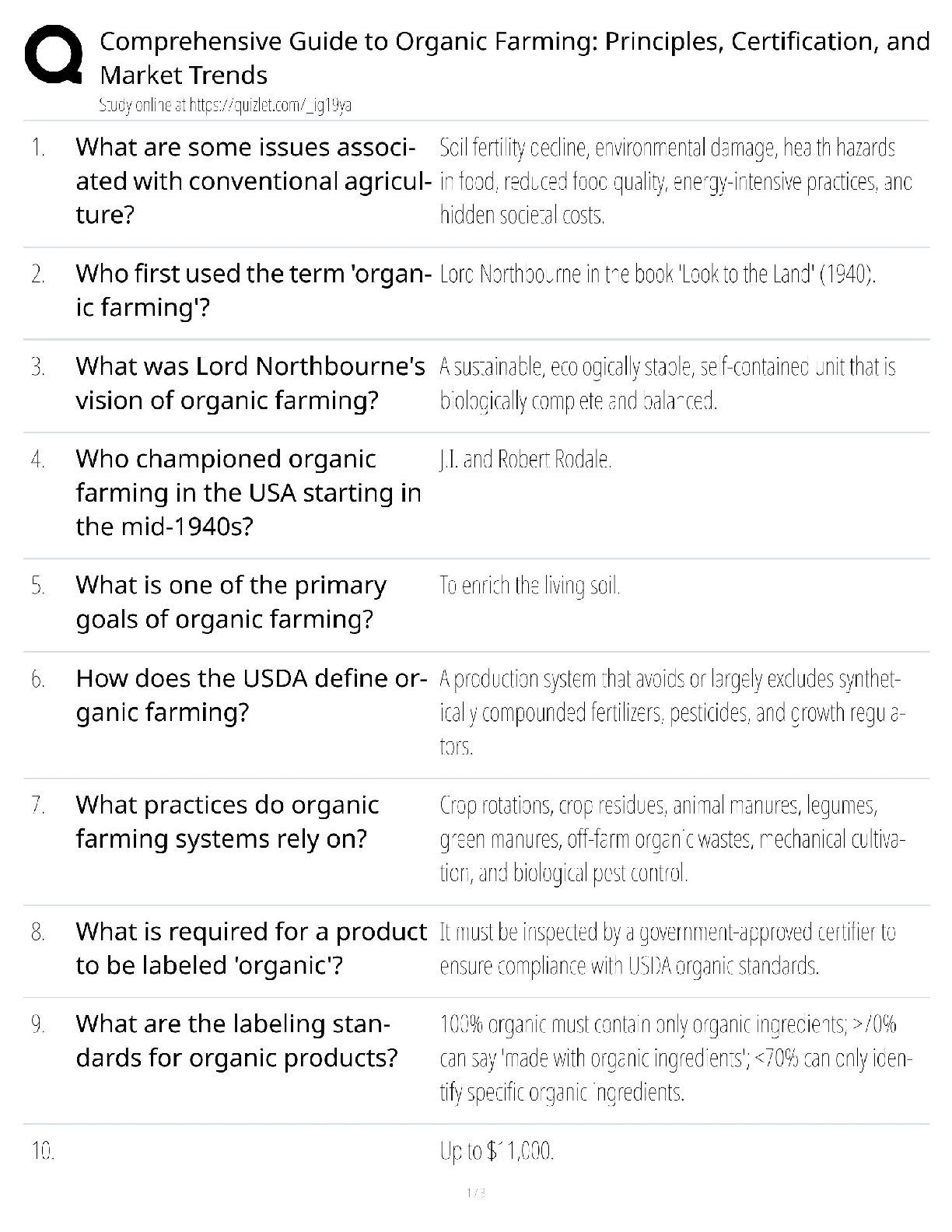
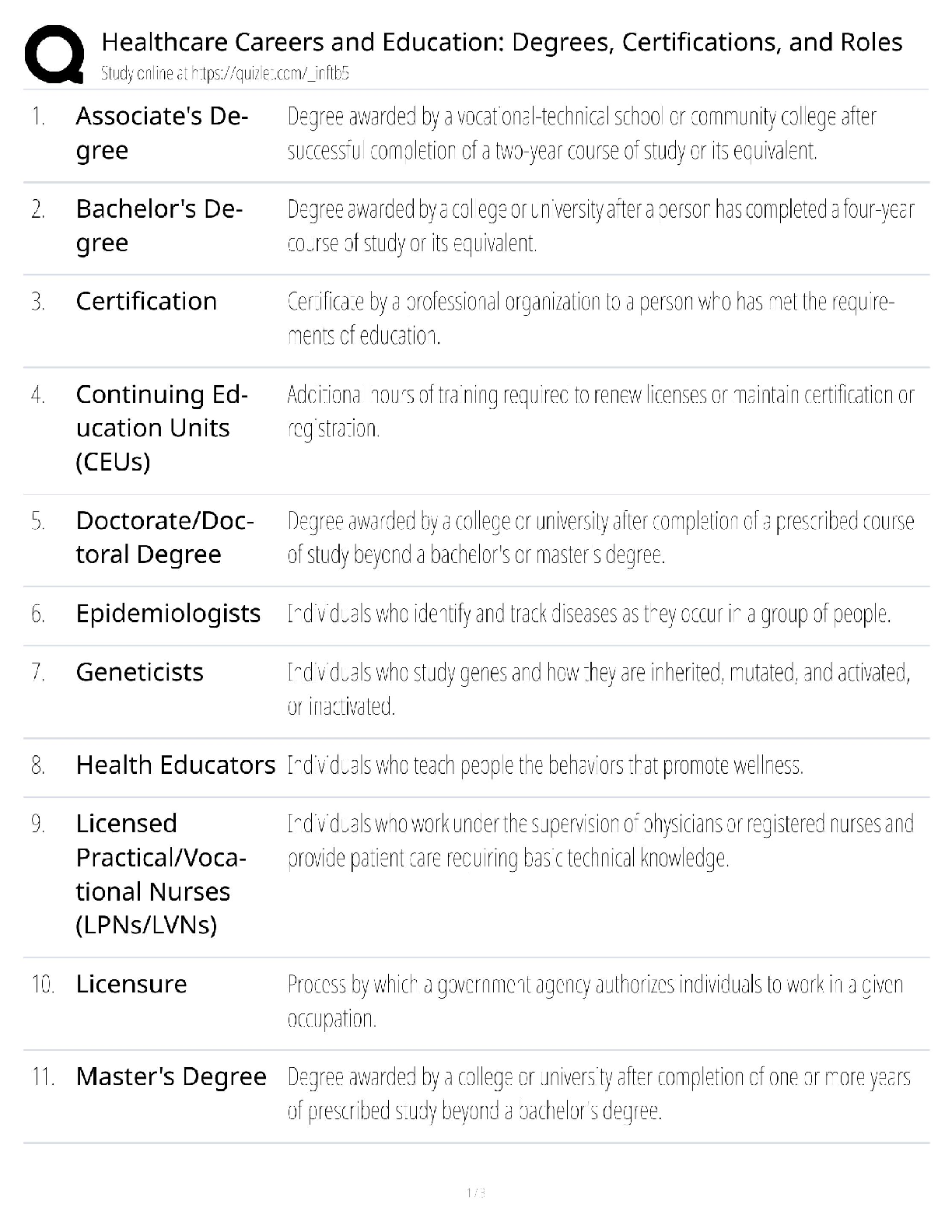
Answers
The highest level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as: assess, create,
compare, solve, judge, recommend, rate, relate, criticize, evaluate, summarize,
a
...
ABCTE PTK Exam Study 391 Questions with Correct
Answers
The highest level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as: assess, create,
compare, solve, judge, recommend, rate, relate, criticize, evaluate, summarize,
appraise. >>> Evaluate
The second highest level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as design,
compose, invent, hypothesize, develop, construct, produce, plan, create, organize. >>>
Synthesis
A middle level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as compare, analyze,
classify, distinguish, categorize, differentiate, infer, survey, select, prioritize. >>>
Analysis
A middle level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as organize, generalize,
prepare, produce, choose, apply, solve, draw, show, paint. >>> Application
a lower level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as match, restate, paraphrase,
give examples, express, illustrate, explain, defend, distinguish, summarize, interpret,
interrelate. >>> comprehension
The lowest level in Bloom's Taxonomy. Includes verbs such as select, list, name, define,
describe, memorize, label, identify, recite, state, recognize. >>> knowledge
Curricular standards communicate what? >>> what, when, and how to teach
what lesson plans are designed to meet or achieve >>> standards
the most important educational document >>> the lesson plan
what does curriculum contain? >>> objectives, sample lessons, assessments,
procedures, materials/equipment needed, activities, samples of student work
what the student is supposed to learn >>> objective
methods of determining effectiveness of the lessons >>> assessments
What was the purpose of No Child Left Behind and the Every Student Succeeds Act?
>>> to create a standardized curriculum for each subject area
what is curriculum? >>> what the students are supposed to learn as a result of a
specific educational sequence of eventsanchor papers >>> the reference for all other work; what is expected by students
Who can help translate curriculum? >>> administrators and content specialists
order the steps of instruction: re-design, teach, repeat, review, give assessment, write
assessment, identify time limit of unit, evaluate instruction, review for assessment >>>
1. identify time limit of unit
2. write assessment
3. teach
4. review for assessment
5. give assessment
6. evaluate instruction
7. re-design
8. repeat
Objectives should be specific enough that they can be used as ____________
questions. >>> Exam
Lesson Objectives: what the students will ___________________ by the end of the
lesson. >>> accomplish
Agenda Items: what the class will ___________ to meet the lesson objectives. >>> do
Pacing of material is dependant upon 3 things >>> 1. nature of students
2. nature of material
3. goals of the teacher
periodic measuring devices that indicate student growth and also verify successful
lessons >>> assessments
should you schedule assessments based on the calendar date or the progress of the
class? >>> based on progress of the class
Who do you need to know before you begin planning lessons? >>> your students
who can help you get to know your students? >>> prior teachers, counselors,
administrators, other colleagues
How much repetition is enough? >>> as much as possible until mastery is acheived
What should inform your instruction? >>> assessments
Name three important things to consider when choosing a seating arrangement. >>> 1.
visibility of students
2. movement by the teacher
3. space for isolation4. students should always be in front of the teacher
5. utilize a second teacher's desk in the room
6. considers the distance between students
what is fostered when students are seated close together or in groups? >>> interaction
between students
when should you prepare class rules and their consequences? >>> BEFORE school
begins
Name some ways to create a positive learning environment. >>> 1. greet students at
the door
2. display examples of student work
3. make the classroom feel open, welcoming, and caring
Definition= The learning and practice of teaching >>> Pedagogy
Lessons are intended for the _________________ of the audience, not for the
____________________ of the teacher. >>> benefit
convenience
What are the steps of the Learning Cycle based on Piaget's learning theory? >>> 1.
exploration
2. concept introduction
3. concept application
In Piaget's learning cycle, exploration is what? >>> the beginning of instruction
addresses the concrete level of thinking- lower order thinking skills
teacher's job is to replace misconceptions with correct knowledge
When beginning a lesson, you should provide... >>> a context for the material
In Piaget's learning cycle, concept introduction is... >>> the teaching stage
the guided discovery stage- students are constructing meaning based on the teacher's
lessons
In Piaget's learning cycle, concept application is... >>> where students apply what they
have learned to new situations
students formulate a new idea or understanding
should lead directly into the exploration stage of the next curricular conceptwhat are some ways to identify what the students already know? >>> 1. offer a pre-test
on the material
2. group discussion
3. student interviews
4. classroom participation
how can you provide context for learning new concepts? >>> create "bridges" between
the old and the new
what are some ways to stimulate active learning? >>> 1. minimize unnecessary info or
distractions
2. utilize sufficient relevant examples
3. organize curriculum around a central theme or idea
4. require review, memorization, repetition, and mnemonic devices
5. provide study and memory aides prior to the lesson
warm-up, lecture, demonstrations, gallery walk, using graphic organizers, and
questioning are all teaching strategies to use with what types of groups? >>>
whole/large groups
what is a "bell ringer"? >>> daily work that is completed by the students as soon as they
enter the room
allows the teacher time to complete clerical tasks
this is the most common and efficient whole group teaching strategy >>> lecture
what is the engagement time of most students during a lecture? >>> 15-20 minutes
what type of teaching is demonstrated by the teacher showing students a technique,
process, or procedure
example- the teacher shows the class how to write the letters in the alphabet before the
students practice it themselves >>> directed-teaching
what type of whole group teaching strategy is most relied upon in the classroom, but
should never take the place of the teacher's lesson plan? >>> worksheets
how can worksheets benefit a lesson? >>> 1. provide additional practice
2. provide repetition
3. can serve as a review of the material
4. helps refresh student's memories
name some sources of technology utilized in the classroom. >>> 1.
computers/laptops/tablets2. LCD projectors
3. SMART boards
4. the Internet
5. WebQuest
Name 5 graphic organizers. >>> 1. Venn Diagram
2. Quadrant/Frayer Model
3. KWL Chart
4. T-Chart
5. Outline
6. Concept Map/Web/Cluster
7. Timeline
8. Portfolio
9. Flow Chart
10. Flashcards
What is a KWL chart? >>> a graphic organizer that allows students to iterate what they
Know, what they Want to know, and what they have Learned about a concept.
completed as 3 columns.
Recall questions are best used for which age group? >>> elementary students
Which type of questions are theoretical questions with hypothetical answers? Usually
contain more than one answer >>> open-ended questions
probing questions promote... >>> thoughtful inquiry
deeper thinking by the student
Which type of questions can provide an assessment of knowledge attainment? >>>
guiding questions
How long does it take for new learning to be understood and transferred into long-term
memory? >>> 5 seconds
Do the quality of answers increase or decrease with increased wait time? >>> increase
An instructional response that asks the student to re-word their thinking so that the
teacher can collect more info or provide clarity. >>> Clarifying
a type of instructional response that restates or summarizes a student answer using
different wording. >>> paraphrasingan instructional response that uses a neutral tone, promotes the flow of the lesson,
continues thinking, and offers a non-committal response to the students. >>> NonJudgmental
an instructional response that imparts advice to the students >>> Advisory
the manner in which students conduct themselves >>> student deportment
What is a piggyback response? >>> where an answer builds upon the previous answer
What is the SQ3R/SQ4R instructional strategy useful for? >>> useful in getting students
to interact with reading passages.
What are the elements of SQ3R/SQ4R? >>> 1. survey
2. Questions
3. Reading/Relate
4. Recite
5. Review
How are students grouped when they are differentiated? >>> they are grouped by
academic need
What is scaffolding? >>> breaking learning into parts
What is think-pair-share? >>> an instructional strategy for small groups where students:
1. think- individually come to an answer
2. pair- work in pairs to combine responses into a new one
3. share- present new, combined reponses
what is the RAFT instructional technique? >>> 1. Role
2. Audience
3. Format
4. Topic
what is a portfolio? >>> a collection of student work that demonstrates their level of
achievement
can be used as assessment technique
What are tiered assignments? >>> differentiation based on academic ability and
preferred modality of learning
What things do an effective lesson closure contain? >>> 1. summary of objectives
2. connections between prior and future lessonsWhat can a well-constructed lesson minimize? >>> Disruptions
Every lesson has 3 things... >>> 1. a beginning
2. a middle
3. an end
applying behavior, knowledge, and skills acquired during a learning event
the ability to effectively use acquired content knowledge and skills >>> learning transfer
What is a teacher-centered lesson plan? >>> one where the teacher does most of the
work
students are passive learners
Example= lecture
what is a student-centered lesson? >>> one where the student does most of the work
(accomplishing a task)
students are motivated, active learners
students are allowed to talk and answer questions
Which is more effective for transfer of learning- a teacher-centered lesson or a studentcentered lesson? >>> student-centered
What is meta-cognition? >>> awareness and understanding of one's own thought
processes.
a successful teacher views discipline as a ___________________ and a
________________________. >>> process; product
what is practical knowledge? >>> learning from others
what is professional knowledge? >>> learning on the job
knowing __________ to teach is just as important as knowing ____________ to teach.
>>> how; what
New teachers can learn a lot from __________________ teachers. >>> successful
what is the difference between a lockdown and a shelter-in-place? >>> a lockdown is
when students and staff are locked in their rooms
a shelter-in-place is when students and staff are locked inside the school; more secureThe ability to effect a meaningful, positive change with lasting effects is called what?
>>> significance
Deliberate instruction includes intentional lessons. They also... >>> 1. are well-planned
2. have a clearly-stated objective
3. show an understanding of the audience
The Whole Child Approach to Education strives to train up students who are... >>> 1.
stewards of the world
2. citizens of the world
Name some skills that "global learners" possess. >>> 1. communication skills
2. cultural competency
3. problem-solving skills
4. collaboration skills
5. teamwork skills
On the first day of school, what are the most important things to do in order to establish
classroom management? >>> 1. learn student names as quickly as possible
2. be positive
3. be prepared
4. begin class with a warm-up activity
5. greet students as they come in the door
6. familiarize students with the class rules/expectations
never miss an opportunity to praise a child for... >>> 1. effort
2. quality work
3. good behavior
what do warm-up activities at the beginning of class do to benefit the student? >>> 1.
focuses the student on learning
2. can serve as a review of previously learned content
what do warm-up activities at the beginning of class do to benefit the teacher? >>> 1.
works to control disruptions
2. provides an opportunity to perform clerical duties
3. helps to fill the entire instructional time
A teacher should position themselves so that they can see as many
__________________ as possible. >>> students
where is the best place to sit when administering a whole-class test to students? >>>
behind themHow should homework relate to the learning process? >>> it should extend it; there
should not be any new learning taking place during homework time, but merely be an
extension of what has already been learned
serve as a form of repetition and practice
Name some subtle disciplinary strategies. >>> 1. the "evil eye"
2. proximity
3. ask the student to stop their misbehavior
4. get the misbehaving student involved with the lesson
5. move the student's seat
6. use humor
subtle disciplinary strategies do not interrupt the ____________ of the lesson. >>> flow
a subtle disciplinary strategy that includes non-blinking eye contact with the
misbehaving student >>> the "evil eye"
what disciplinary strategy is LEAST disruptive to the lesson flow? >>> proximity
No disciplinary tactic works for ____________ student ______________ time >>>
every; every
mentally participating to the speaker >>> active listening
a condition that inhibits the ability of the student to concentrate >>> ADD (Attention
Deficit Disorder)
a condition that not only inhibits the ability to concentrate but also causes the learner to
be impulsive, easily distracted, and overly active. >>> ADHD (Attention Deficit
Hyperactive Disorder)
the feelings, emotions, and attitudes of individuals >>> Affective Domain
a rigid set of standards or rules for performing a task >>> algorithm
matching what is taught and tested to learning goals or standards >>> alignment
moving from knowledge to the ability to use the information >>> application
a standardized test that is designed to predict future performance levels in a given
subject >>> Aptitude test
classroom management in which rules are given and applied consistently but without
hostility >>> assertive disciplinea measure of what students know (declarative information) and are able to do
(procedures) >>> assessment
fitting new knowledge into existing processes >>> assimilation
foundation skills such as reading and math that form the basis for other skills >>> basic
skills
changing an undesirable behavior through a prescribed learning theory >>> behavior
modification
the goals of the learning stated as observable behavior >>> behavioral objectives
a baseline of data usually grade and/or subject specific >>> benchmark
learning based on how the brain works >>> brain-based learning
a teaching strategy in which students generate many ideas without concern about
quality >>> brainstorming
federal program in which money is given to districts that have a high number of
disadvantaged students >>> Title I
the place in the lesson where the teacher makes sure that students have mastered the
learning before moving to the next step in the lesson >>> checking for mastery
the place in the lesson where the teacher checks to make sure that students understand
before moving on in the teaching process. >>> checking for understanding
the mood of the classroom including teacher-student interactions, student-student
interactions, and the belief system in the classroom >>> classroom climate
the process of managing student behavior in the classroom >>> classroom control
the classroom climate as well as the teacher's ability to manage behavior and the tasks
of the class >>> classroom management
the part of the lesson in which the teacher summarizes the learning >>> closure
teaching that includes modeling, observation of student behaviors and immediate
feedback >>> coaching
the mental operations of thinking >>> cognition
thought and reasoning usually divided into two categories- knowledge or factual, and
processes >>> cognitive developmentobjectives that measure knowledge and/or processes demonstrated by the student >>>
cognitive objectives
the collective feelings or emotions of a group >>> cohesiveness
a test to measure the ability of students to meet a given set of objectives, usually state
or national objectives >>> competency test
a graphic representation of relationships between and among a given set of criteria >>>
concept map
a learner-centered approach based on the idea that students construct knowledge for
themselves based on what they already know and by interaction with new information
>>> constructivism
questioning in which the number of possible answers is very limited, usually to one
possible answer >>> convergent questioning
a teaching strategy in which students work together in groups toward a common goal
>>> cooperative learning
required curriculum for all students >>> core
thinking that leads to new ideas or ways of looking at things >>> creative thinking
a standardized test designed to measure a student's level of mastery of a given set of
standards, goals, or objectives >>> criterion-referenced test
occurs when all elements of society are valued and the language and traditions of the
groups are maintained >>> cultural pluralism
learning that moves from general concepts to specific concepts >>> deductive learning
reasoning that moves from general ideas to a specific conclusion >>> deductive
reasoning
Maslow used this term to describe the basic needs of survival, safety, belonging, and
self-esteem >>> deficiency needs
a test designed to identify areas of strength and weakness in a student >>> diagnostic
test
the control of student behavior in the classroom >>> discipline
a teaching technique that follows the following processes:1. identify the problem
2. develop a hypothesis
3. test the hypothesis
4. arrive at a conclusion >>> discovery learning
practice that is repeated over time, usually at pre-set intervals >>> distributed practice
thinking that leads to a conclusion or product that is unique to the individual >>>
divergent thinking
a disorder in which the individual has difficulty learning to read, write, and spell >>>
dyslexia
the ability to understand the feelings and actions of other >>> empathy
questions that require judgment to be made >>> empirical questions
The amount of time students are actively engaged in learning activities is known as
_______ >>> engaged time
the intentional design and delivery of information by the teacher to the students.
Processes:
1. teacher models/demonstrates skills
2. substantial time for practice and opportunity to apply the skills
3. opportunity for feedback >>> explicit instruction
motivation that is triggered by rewards outside the individual >>> extrinsic motivation
Free Appropriate Public Education that is guaranteed by federal law to special
education students >>> FAPE
assessment that takes place throughout the lesson >>> formative assessment
the gathering of data, during the time the program is being developed, to guide the
development process >>> formative evaluation
structural organizers that visually help students to organize and see relationships in the
learning >>> graphic organizers
a method of grouping in which students of varying abilities, interests, achievement
levels, and backgrounds are grouped together >>> heterogeneous grouping
a method of grouping in which students with the same abilities, interests, achievement
levels, and backgrounds are grouped together >>> homogeneous groupingan act that provides special education and services for children with disabilities >>>
IDEA
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act
the phase of instruction that occurs after skills and strategies have been explicitly taught
and practiced under teacher direction or supervision.
Involves the application of newly taught skills in familiar formats or tasks and reinforces
skill acquisition >>> independent practice
a teaching strategy in which the student learns through discovery >>> indirect teaching
making a general conclusion based on several examples >>> inductive reasoning
asking questions to obtain information >>> inquiry
the learning, idea, or processes becomes a part of the l
[Show More]