ACE personal training certification, Questions with accurate answers, rated A
Document Content and Description Below
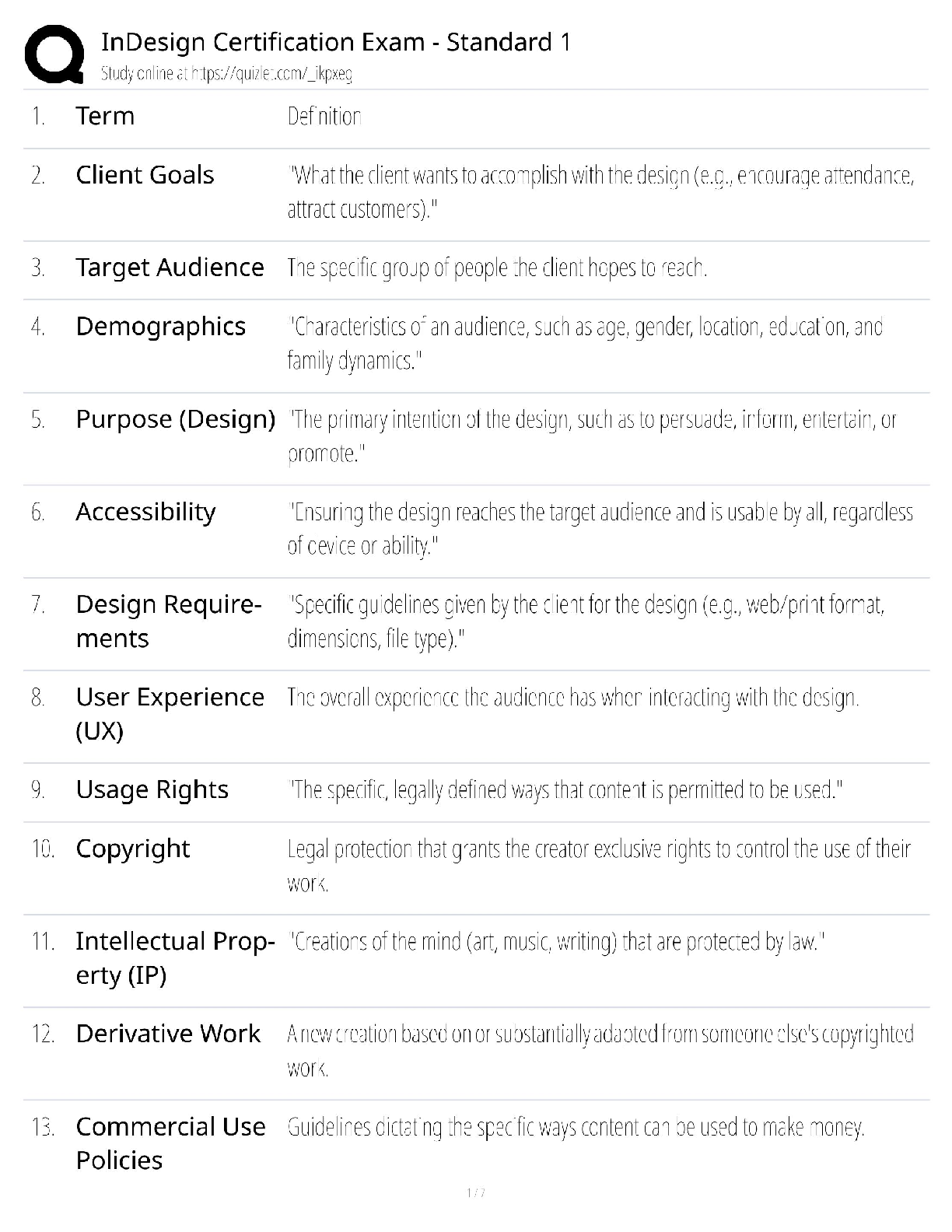
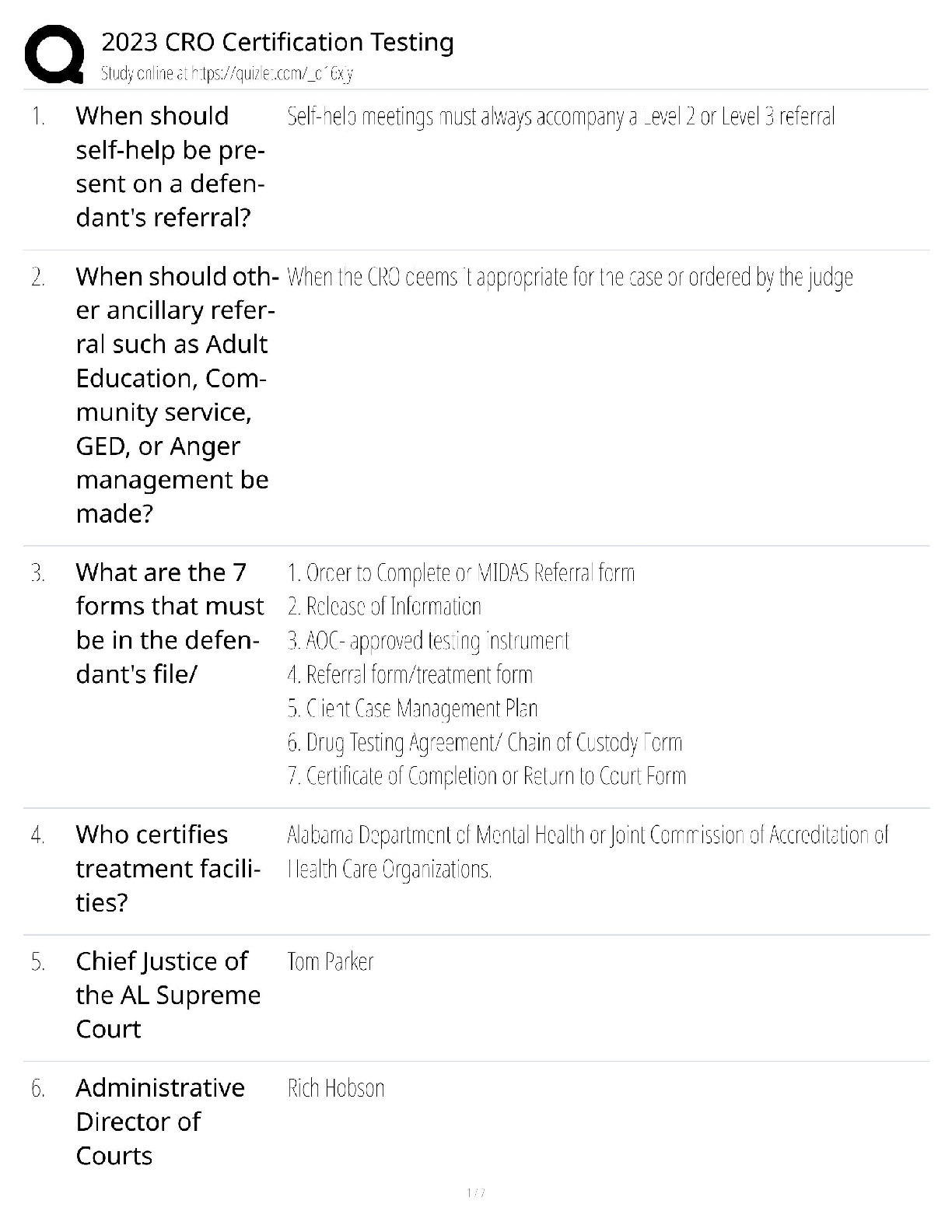
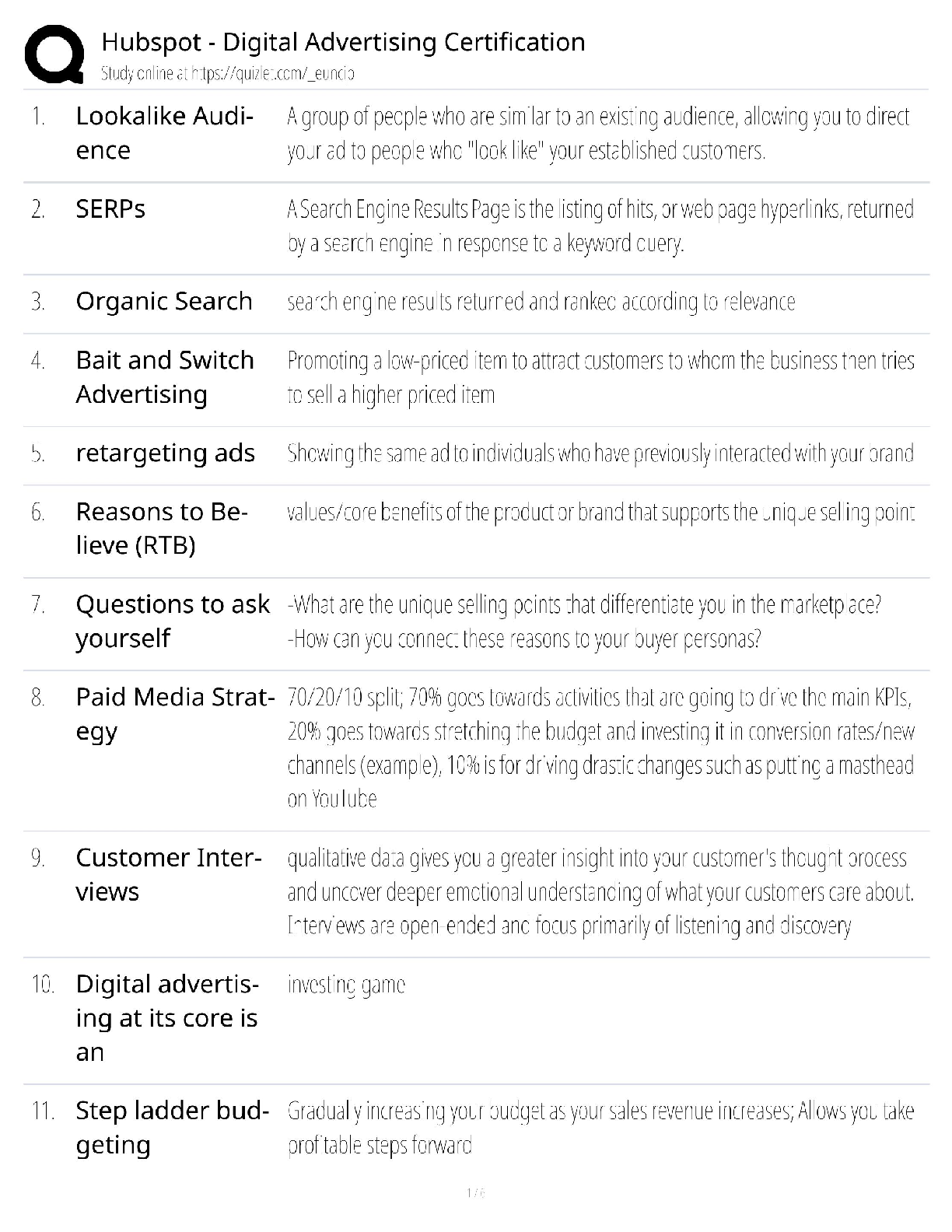
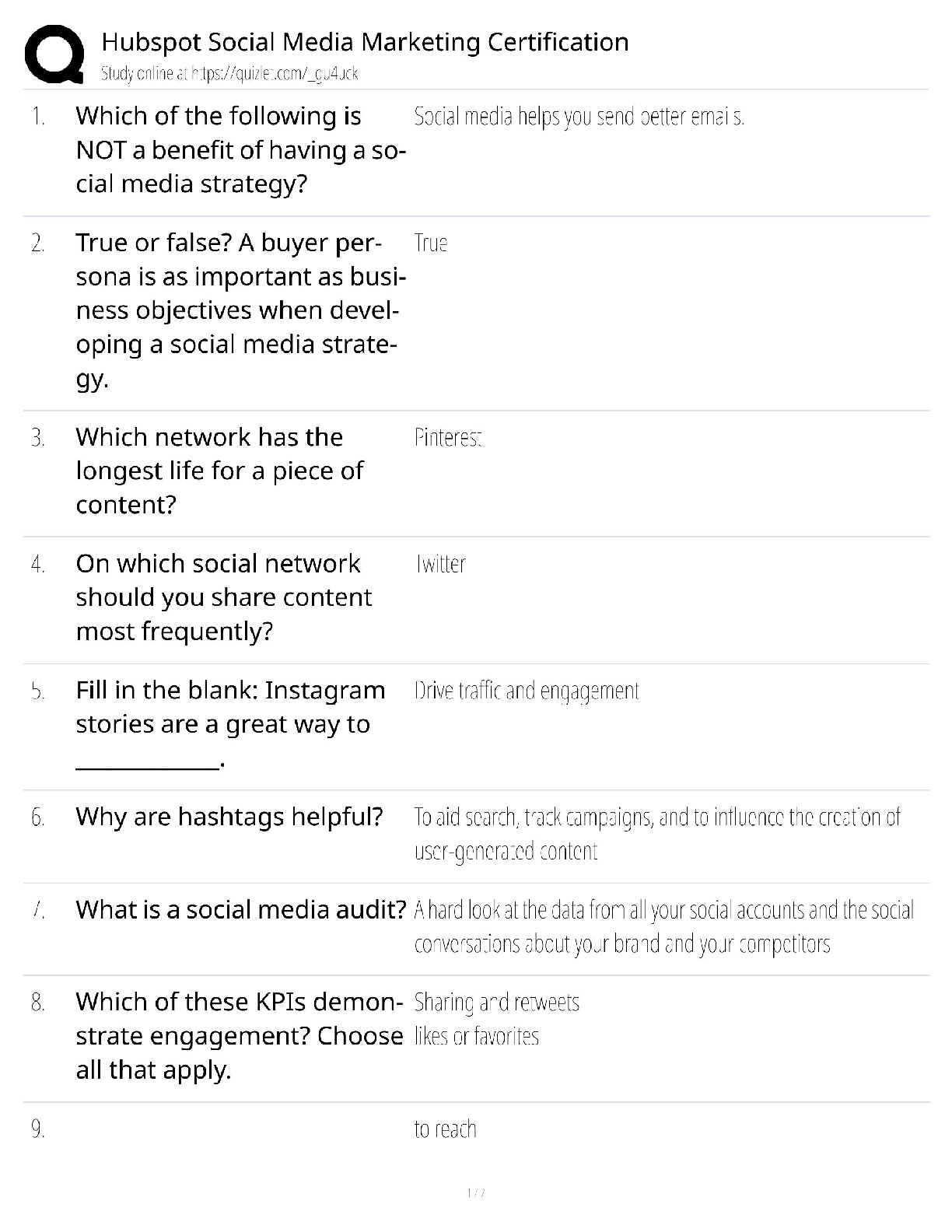
ACE personal training certification, Questions with accurate answers, rated A
Define intrinsic and extrinsic motivation - ✔✔Intrinsic is exercising for the pure joy of working out.
Extrinsic
...
is exercising for any other reason.
Give an example of intrinsic and extrinsic feedback - ✔✔Intrinsic: Client adjusts his own workout based on his perception of difficulty
Extrinsic: Trainer gives performance feedback
Define situational and contextual motivation - ✔✔Situational: How the client feels during exercise
Contextual: How the client feels, sees, thinks about exercise
Name 5 strategies for dealing with negative social influencers - ✔✔Avoid, deal with person after workout, explain to the person how the negativity affects your workout, anticipate responding to the nsi, get that person involved with your struggle
Name 3 types of high risk relapsers - ✔✔People with poor time management skills, lack of social support, busy schedules
5 personal attributes influencing exercise participation and adherence - ✔✔Demographic: Age, education, income, gender
Health status: sick people or people with heart disease diabetes ect exercise less
Activity history: past exercise participation
Psychological traits: self motivated
Knowledge attitudes and beliefs: health perception
2 Environmental factors that influence exercise participation and adherence - ✔✔Access to facilities: Location
Time: Lack of time is the most common excuse for not exercising
Social interactions that influence exercise participation and adherence - ✔✔If a spouse or a friend is on board the client will be more likely to stick with the program
2 Physical activity factors that influence exercise participation and adherence - ✔✔Intensity of program: drop pout rate is 2x higher with vigorous activity
Injury: program drop out is directly related to injury.
4 stages of the client trainer relationship (RIPA) - ✔✔Rapport: 1st impression of trainer. client evaluates Apperance, environment, interaction, posture, communication ect.
Investigation: Trainer evaluates client using health and fitness data, medical history, exercise history ect.
Planning: Give and take. Client and trainer work together to set SMART goals, generate and discuss alternatives, formulate a plan, and evaluate the exercise program.
Action: Start working out. Usually a combination of exercises for the client to do with the trainer and at home.
Define motivational interviewing. - ✔✔A way of speaking with people that motivates them to change their behavior. Usually this is used when clients are not ready to commit to an exercise program.
Describe how voice quality, eye contact, facial expression, hand gestures, and body positions should looks and what kind of communication are they? - ✔✔They are non-verbal communication.
Eye contact: Direct but friendly.
Voice quality: confident but not too loud
Facial expression: genuine emotion
Hand gestures: flexed, not fidgeting
Body position: open *Aggressive= hands on hips*
4 Styles of communication - ✔✔Preaching: lecture type = bad
Educating: informational
Counseling: working together to find and solve problems
Directing: during exercise directing works
Give an example of each interviewing technique: Minimal encourager, paraphrasing, reflecting, probing, clarifying, informing, confronting, questioning, deflecting. - ✔✔Minimal encourager: "Explain what you mean by.."
Paraphrasing: "I understand your ideal wright is.."
Reflecting: "it sounds like.." Restate the main points
Probing: Ask additional questions to gather more info
Clarifying: Verifying what the client is saying
Confronting: Using mild to strong feedback
Questioning: Open ended questions to information given
Deflecting: Changing the focus to another person if it relates
Define SMART goals.
When do you make SMART goals? - ✔✔Specific: Clear on what client wants accomplished
Measurable: How will the client measure progress
Attainable: Can be done with the limits and within time frame
Relevant: Relevant to the interests of the client
Time: Specific time frame/ time line
You make smart goals during the planning stage.
Name and describe the 3 stages of learning (CAA) - ✔✔Cognitive: Clients try to understand a new skill
*Use tell, show, do technique*
Associative: Begin to master the basics and re ready for more specific feedback that will help them refine the motor skill
Autonomous: Clients are preforming skill naturally, trainer is doing less teaching and more monitoring.
Define product goals and process goals - ✔✔Product goals: Outcome. Something achieved (weight loss, increase in strength ect.)
Process goals: Action. Something a client does (# of workouts per week ect)
Define the health belief model and name the 3 stages - ✔✔The health belief model states that people will engage in a healthy behavior based on the perceived threat they feel regarding a health problem.
Perceived seriousness: How serious they think contracting an illness is basically how scared they are of health illnesses
Perceived susceptibility: How at risk they think they are for getting an illness.
Cue to action: an event or symptom that wakes them up and motivates them to change.
*The more scared, at risk or bad the situation is the more likely they are to workout*
Define self efficacy and name 6 sources of it - ✔✔Self efficacy is the belief in ones self to be able to succeed
Sources:
Past performance experience: strongly influence feelings
Vicarious experiences: Clients knowledge of success stories ect
Verbal persuasion: Feedback/ statements form others
Physiological state appraisals: clients judgments about abilities
Emotional state appraisals: mood and feelings
Imaginal experiences: perceived notion of what exercise will be like.
Define the 5 stages of change in the transtheoretical model of behavioral change (stages-of-changes-model) - ✔✔1. Precontemplation: sedentary, not considering an exercise program, do not see activity as important or relevant to them
2. Contemplation: sedentary, starting to consider exercise important, and have begun to see the negative consequences of being inactive, they are still not ready to make a change.
3.Preperation: some sporadic light activity, mentally and physically preparing to adopt and exercise program and are ready to lead an active lifestyle, but are inconsistent
4.Action: client engages in regular physical activity but are have been doing so for less then 6 months
5. Maintenance: regular activity for longer then 6 months
For each stage of change describe a goal for the process of change to the next stage. - ✔✔Precontemplation: Goal is to make inactivity relevant issue and to make them start thinking about becoming active.
Contemplation: Goal is to get involved in some type of activity
Preparation: Goal is to get to regular physical activity participation
Action: Goal to maintain regular physical activity
Maintenance: Goal is to prevent relapse and continue activity
Describe decisional balance - ✔✔The number of pros and cons related to exercise.
Precontemplators and contemplators perceive more cons:
Cons: sweating, sore muscles, time, cost, bordem
Describe positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement - ✔✔Positive: When positive stimulus is given for good behavior
Negative: removal or avoidance of negative stimulus for bad behavior
Example: A client is late for a session and you don't say anything, they are likely to be late again because they think its okay.
What aspects are involved with the investigation stage of the client trainer relationship? - ✔✔Health and exercise history
Readiness to change behavior
Personality style
Assessments
Describe downfalls and benefits of the PAR-Q - ✔✔Benefits: quick easy and noninvasive
Downfalls: limited by lack of detail and may overlook major risks
**Cardiovascular disease Risk factors (8)- State the factor and the value at which the factor warrants +1 point
1 Negative risk factor and value - ✔✔AGE: male >_45 female>_55 (+1)
FAMILY HISTORY: father- sudden death before 55 (+1)
mother-sudden death before 65
CIG. SMOKING: Yes (+1)
SEDENTARY: not doing 30 min per session, 3x per week (+1)
OBESITY: BMI>_ 30 or girth 40 in (men) 35 in (women) (+1)
HYPERTENSION: SBP>_140 DBP>_90 mmHg (+1)
DISLIPIDEMIA: LDL(cholesterol) >_130 HDL<_40 (+1)
PREDIABETES: glucose>_100
HDL cholesterol: >_60 (-1)
How many points/symptoms classify someone as low risk, moderate risk, and high risk - ✔✔Low: <2 points
Moderate: >_2 points
High: Known cardiovascular disease or symptoms
Describe what an informed consent form entails and limitations - ✔✔Informs the client about the risks associated with the activity.
Not a liability waiver and doesn't provide legal immunity.
Describe what an agreement and release of liability waiver entails and limitations - ✔✔Used to release the trainer from liability for injuries, clients give up their right to file suit.
Doesn't protect trainer from being sued for negligence
Describe what a Health history questionnaire entails (name at least 5 types of information collected).
What is meant by lifestyle information? - ✔✔Collects detailed medical and health information
-Past and present exercise information
-Medications/ supplements
-Recent or current illness or injuries including acute/ chronic pain
-Surgery/ injury history
-Family medical history
-Lifestyle information (nutrition, stress, work, sleep)
Describe what a medical release form entails - ✔✔Provides trainer with medical information, physical activity limitations, and guidelines given by physician.
Define atherosclerosis - ✔✔process in which fat builds up on the walls of the arteries causing them to thicken and when this happens in the arteries to the heart you get CAD.
Define angina - ✔✔Pressure or tightness, usually in the chest but can be in the arm shoulder or jaw
Name 3 common respiratory problems - ✔✔Bronchitis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
What injuries should be screens for (most common) in the musculoskeletal system? - ✔✔Sprains(ligaments) strains(muscles/tendons)
herniated disk
bursitis( swelling or inflammation of the bursa)
Tendinitis
Arthritis
Describe an overuse injury (how it happens and examples) - ✔✔Poor training techniques and overusing.
Runners knee, tennis elbow, swimmer shoulder
Iliotibial band syndrome (pain along the outside of the thigh and knee)
Name 2 metabolic diseases that may interfere with exercise - ✔✔diabetes and thyroid condition.
Effects of each on RHR, exercising HR, MHR
Beta blockers
Diuretics
Antihistamines
Antidepressants
diet pills containing amphetamines
caffeine
and Nicotine - ✔✔Beta blockers: Down, Down, Down
Diuretics: No change, No change, No change
Antihistamines: No change, no change, no change
Antidepressants: No change or up, no change, no change
diet pills containing amphetamines: up, up, no change
caffeine: no change or up, no change or up, no change
and Nicotine: no change or up, no change or up, no change
What two arteries can be used to take heart rate - ✔✔Coronary: neck
Radial: Wrist
How many bpm in a typical:
Slow RHR
Normal RHR
Fast RHR - ✔✔Slow: <60 bpm
Normal: 60-100 bpm
Fast: >100 bpm
Blood pressures SBP and DBP:
Normal
Prehypertension
Hpertension Stage 1 & 2 - ✔✔Normal: SBP<120 DBP<80
Prehypertension: SBP 120-139 DBP 80-89
Hypertension Stage 1: SBP 140-159 DBP 90-99
Stage 2: SBP >_160 DBP <_100
Describe the Borg scale for RPE - ✔✔Scale from 6-20 where the number (+0) corresponds to HR.
6=nothing
13= somewhat hard
15= hard
19= very very hard
Describe the category ratio scale - ✔✔0-10
3= moderate
5=strong
7=very strong
10= very very strong
Define flexion and extention - ✔✔Flexion: Decreasing the angle between two bones
Extension: Increasing the angle between two bones
*usually extension is bringing the area back to normal or straightening it*
Show what flexion and extension of the vertebral column (trunk/core) looks like - ✔✔Standing straight flexion is hinging forward at the hips
Extension is bringing the body back straight
Show what flexion and extension of the shoulder joint looks like - ✔✔Flexion: Bringing the arm straight out in front of the body
Extension: Bringing the arm back to the body
Show what flexion and extension of the elbow joint looks like - ✔✔Flexion: Bringing the hand up to the shoulder (bicep curl)
Extension: Bringing the hand back down to the side
Show what flexion and extension of the wrist looks like - ✔✔Flexion: palm to underside of the wrist
Extention: Top of the hand to the top of the wrist
Show what flexion of the knee joint looks like - ✔✔Flexion: Standing straight (on one leg) the foot lifts toward butt
Extension: The foot comes back down to normal standing position
Show what flexion and extension of the hip joint looks like - ✔✔Flexion: swinging the leg forward out in front of the body
Extension: swinging the leg backward behind the body
Describe plantar flexion and dorsiflexion - ✔✔Plantarflexion: foot points down
Dorsiflexion: foot points up
Describe lateral flexion - ✔✔Standing straight and leaning to one side or the other with upper body only
Describe the three planes of motion - ✔✔Saggital: Cuts the body down the middle into left and right sides
Frontal: Cuts the body in half to back and front sides
Transverse: Cuts the body at the waist into upper and lower
What movements can be done in the Saggital plane? - ✔✔Flexion, extension, Dorsiflexion, Plantarflexion
What movements can be done in the frontal plane? - ✔✔Abduction, adduction, elevation, depression, inversion, eversion
What movements can be done in the transverse plane? - ✔✔Rotation, pronation/ supination (rotating the hand and wrist)
Major muscles that act at the shoulder girdle (STRLP) - ✔✔Serratus anterior
Trapezius
Rhomboids
Levetor scapulae
Pectoralis minor
Describe where the serratus anterior is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔It connects the shoulder blade to the rib cage
Primary functions: abduction and upward rotation of the scapula
Describe where the trapezius is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Spans from the bottom of the scull to the shoulder back in and down the spine to the bottom of the back.
Upper: Upward rotation and elevation of the scapula
Middle: Upward rotation and adduction of the scapula
Lower: Depression of the scapula
Describe where the Rhomboids are and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Connect the spine to the spine to the shoulder blade
Primary function: Adduction, downward rotation, and elevation of the scapula
Describe where the levetor scapulea is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Runs down the neck to the shoulder blade
Primary function: to elevate the scapula
Describe where the pectoralis minor is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Internal muscle that connects the tip of the shoulder blade to the front of the rib cage
Primary functions: depression, downward rotation, and abduction of the scapula
What are the prime movers in the adduction of the scapula? - ✔✔Rhomboid major/minor and trapezius
What are the prime movers in the abduction of the scapula? - ✔✔Pectoralis minor and serratus anterior
Major muscles that act at the shoulder (DTRLP) - ✔✔Deltiod
Teres major
Rotator cuff
Lattisumus dorsi
Pectorlais major
Describe where the Deltoid is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Shoulder cap
Primary function: Abduction internal/external rotation of the shoulder
Describe where the teres major is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Armpit muscle
Primary functions: Extension and adduction of the shoulder
Describe where the Rotator cuff is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔SITS: Suprsinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
Right next to/ behind deltiod
Primary Functions: Abduction, external/internal rotation
Describe where the lattisimus dorsi is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Stretches all the way from the armpit to the hip and into the sternum
Primary Functions: Extension, Adduction, horizontal abduction
Describe where the Pectoralis major is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Boob muscle
Primary Functions: Flexion, extention, and adduction of the shoulder
What are the prime movers for adduction at the shoulder? - ✔✔Pectoralis major and lattisimus dorsi
Give an example of an exercise that works the pectoralis major and one that works the lattisimus dorsi - ✔✔Pec major: Pushups, pull ups, bench press
Lat. Dorsi: Chin ups, lat pull down
*any exercise that involves pulling the arms downagainst resistance
Major muscles that act on the elbow and forearm BBBT - ✔✔Biceps Brachii
Bronchialis
Brachioradialis
Triceps Brachii
Describe the Biceps Brachii and its primary function - ✔✔Bicep (above elbow inside arm)
Flexsion at the elbow
Describe where the Brachilalis is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Small muscle inside elbow under bicep above Brachioradialis
Flexion of the elbow
Describe where the Brachioradialis is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Inside forearm
Flexion at the elbow
Describe where the Tricep is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Behind bicep
Extension at the elbow
Major muscles that act at the trunk (RETIE) - ✔✔Rectus abdominis
Erector spinea
Transverse abdominis
Internal oblique
External oblique
Describe where the Rectus abdominis is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Six pack muscles
Flexion of the trunk and lateral flexion of the trunk
Describe where the Erector spinae is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Down the spine
Extension of the trunk and lateral flexion of the trunk
Describe where the transverse abdominis is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Deep inside muscle of the abdomen
Stabalizes and compresses abdomen
Describe where the Internal oblique is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Under the exteranl oblique
Rotates the trunk
Describe where the External oblique is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Outermost layer of the abdomen wall (on theside)
Rotation of the trunk
Muscles that act at the hip joint RGGIBS - ✔✔Rectus femoris
Gluteous maximus
Gluteous medius and minimus
IT band (illiotibial)
Biceps femoris
Sartorious
Describe where the Rectus femoris is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Long Quadricep muscle
Flexion
Describe where the Gluteous maximus is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Biggest butt muscle
Extension and external rotation
Describe where the Gluteous medius and minimus are and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Medius is above maximus and minimus is deep inside
They both do abduction
Describe where the Bicep femoris is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Hamstring muscle
Extension
Describe where the Sartorious is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Longest muscle in the body crosses both the hip and knee
Flexion of the knee and external rotation of the hip
What is the primary mover for leg extension at the knee? - ✔✔rectus femoris
Describe where the Anterior tibilais is and what its primary functions are - ✔✔The front of the lower leg (shin)
Dorsiflexion at the ankle
Describe where the Gastrocenemius and soleus are and what its primary functions are - ✔✔Behind the lower leg (Calf muscle)
Plantarflexion at the ankle
Decribe the difference between the centeral nervous system and the peripheral nervous system - ✔✔CNS is covered by bone for the spinal cord and brain
the peripheral nervous system is for the extremities
Describe the difference between the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton - ✔✔Axial: Head neck and trunk bones
Appendicular: Extremities
Describe the difference between arteries and veins - ✔✔Arteries carry blood away from the heart
Veins carry blood to the heart
What is fasciae? - ✔✔Connective tissue that provides lubrication for muscle fibers and allows muscles to change shape. Responsible for 41% of the total resistance experienced during a joint movement
Describe Lordosis - ✔✔Increased anterior lumbar curve
The bottom of the back is curved too far inward
Describe Kyphosis - ✔✔Increased posterior thoracic curve
The upper back in curved to far outward
And an increased anterior lumbar curve
Describe flat back - ✔✔Decreased anterior lumbar curve and the neck sits to far outward
*opposite of lordosis
Decribe sway back - ✔✔Decreased anterior lumbar curve and increased posterior thoracic curve
*Combo of flat back and kyphosis
Describe scoliosis - ✔✔Lateral spinal curvature
What muscles are tight and what muscles are lengthened with Lordosis - ✔✔Tight: Hip Flexors, lumbar extensors, and lattisimus dorsi
Lengthened: Hip extensors & external obliques
What muscles are tight and what muscles are lengthened with Kyphosis - ✔✔*Same as lordosis for lower but for the upper body deviation:
Tight: Anterior chest and shoulders and neck extensors
Lengthened: Upper back extensors, scapular stabilizers, Neck flexors
What muscles are tight and what muscles are lengthened with Flat back - ✔✔Tight: Rectus abdominis, upper back extensors, Neck extensors,
Lengthened: Iliacus/psoas major (hip), internal oblique, lumbar extensors, Neck flexors
What muscles are tight and what muscles are lengthened with Sway back - ✔✔Tight: Hamstrings, posterior obliques, lumbar extensors, neck extensors
Lengthened: Iliacus/pasoas major, internal oblique, lumbar extensors, neck flexors
What muscles are commonly tight and which are usually lengethened (when talking about lordosis, kyphosis, sway and flat back) - ✔✔Tight: Neck extensors
Lenghtened: Neck flexors and obliques
What kind of factors are these when it comes to posture:
Repetitive movements
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 45 pages

.png)
 (1).png)