Finance > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ACCT 3332 Final Exam 2022 with complete solution, Question, Rated A+ (All)
ACCT 3332 Final Exam 2022 with complete solution, Question, Rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
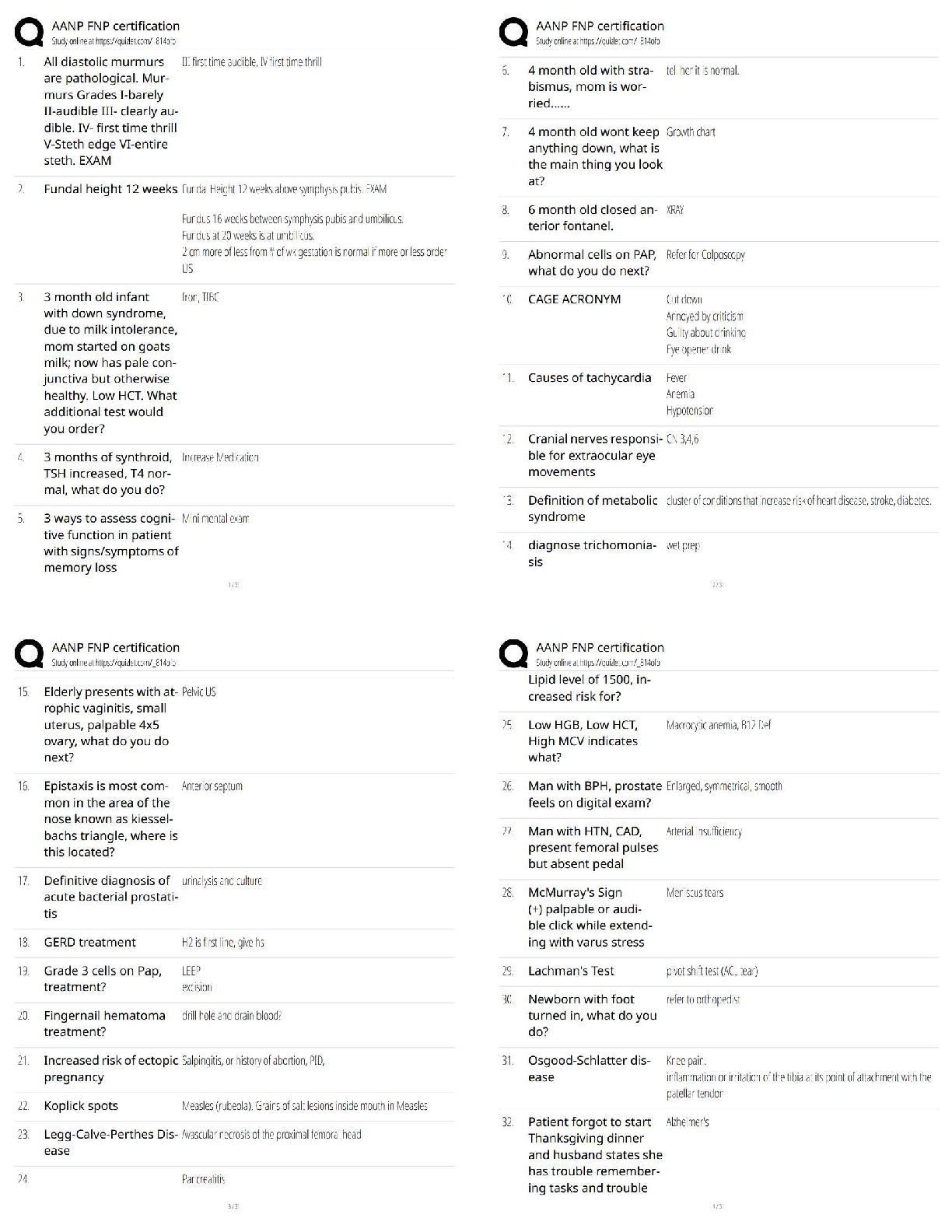
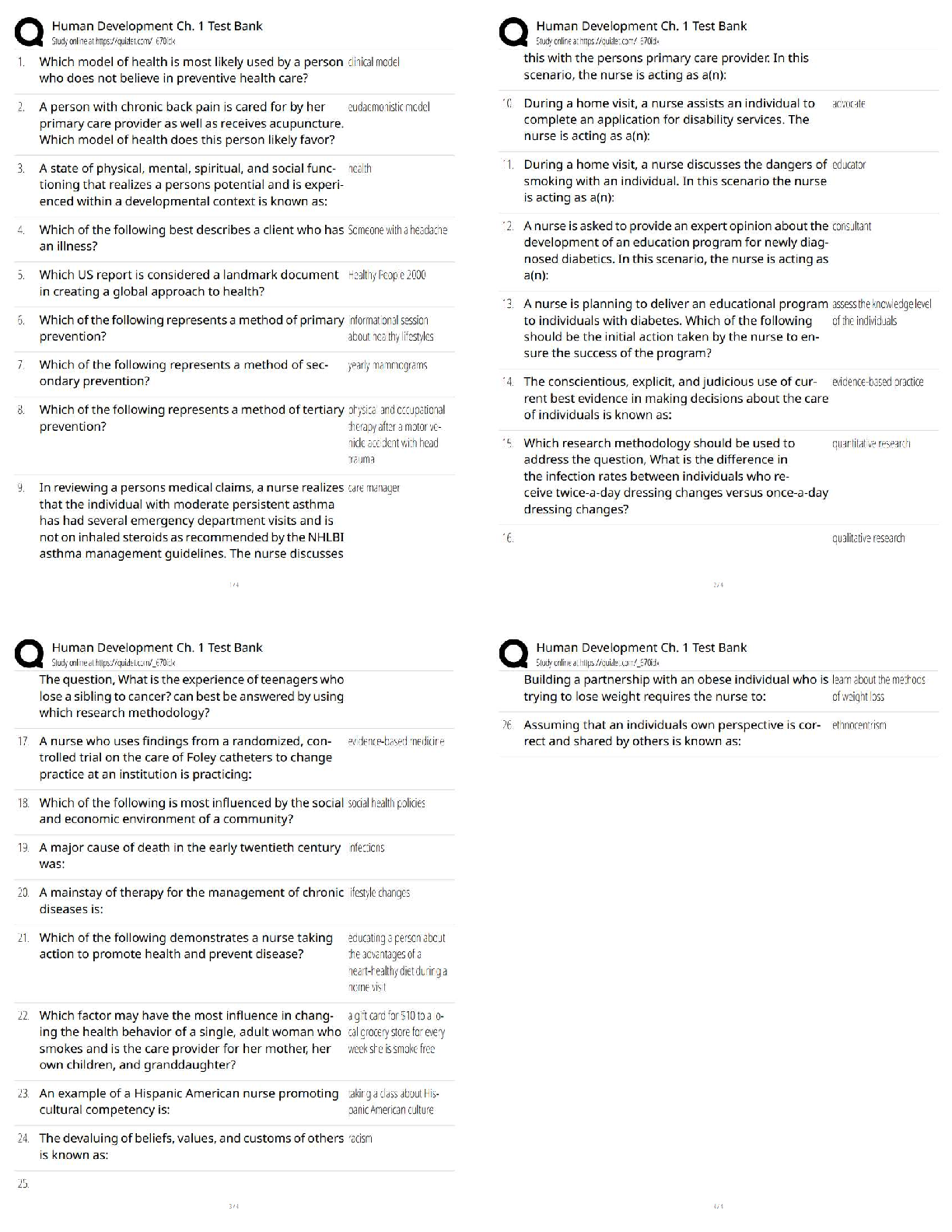
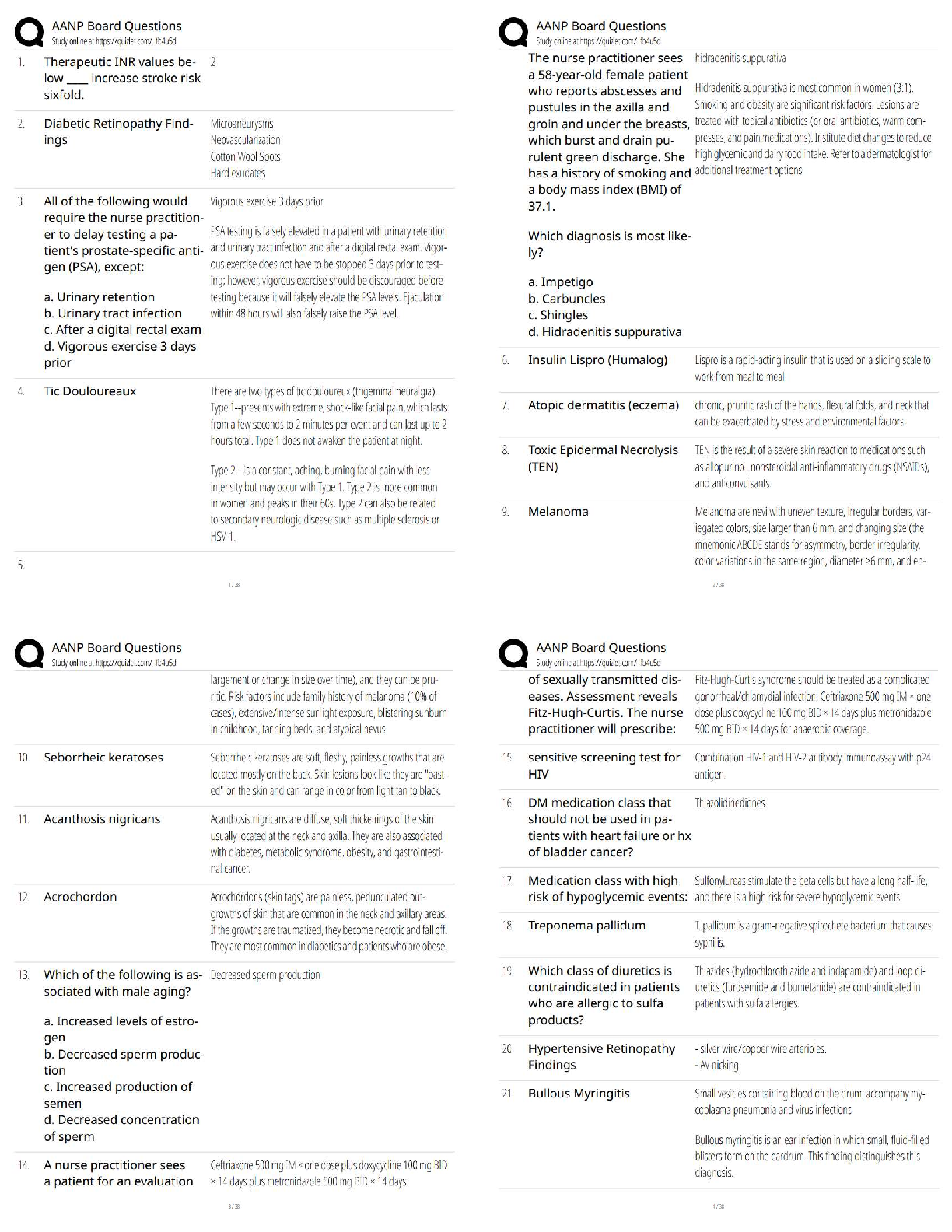
ACCT 3332 Final Exam 2022 with complete solution P. Chang & Co. exchanged land and $9,000 cash for equipment. The book value and the fair value of the land were $106,000 and $90,000, respectively. C ... hang would record equipment at and record a gain/(loss) of: Equipment Gain (loss) $99,000 $(16,000) $90,000 $(25,000) $108,000 $16,000 $106,000 $(9,000) -Answer- $99,000 $(16,000) Kross Co. exchanged land and $18,000 cash for equipment. The book value and the fair value of the land were $212,000 and $180,000, respectively. Assuming that the exchange has commercial substance, Kross would record equipment at and record a gain (loss) of Equipment Gain (loss) $198,000 $(32,000) $180,000 $(50,000) $216,000 $32,000 $212,000 $(18,000) -Answer- $198,000 $(32,000) Software development costs are capitalized if they are incurred Prior to point at which technological feasibility has been established After technological feasibility has been established but prior to the product availability date After commercial production has begun None of these is correct. -Answer- After technological feasibility has been established but prior to the product availability date Vijay Inc. purchased a 3-acre tract of land for a building site for $320,000. On the land was a building with an appraised value of $120,000. The company demolished the old building at a cost of $12,000, but was able to sell scrap from the building for $1,500. The cost of title insurance was $900 and attorney fees for reviewing the contract was $500. Property taxes paid were $3,000, of which $250 covered the period subsequent to the purchase date. The capitalized cost of the land is: $336,400. $336,150. $334,650. $201,150. -Answer- $334,650.On July 1, 2009, Larkin Co. purchased a $400,000 tract of land that is intended to be the site of a new office complex. Larkin incurred additional costs and realized salvage proceeds during 2009 as follows: Demolition of existing building on site $75,000 Legal and other fees to close escrow $12,000 Proceeds from asle of demolition scrap $10,000 What would be the balance in the land account as of December 31, 2009? $400,000. $475,000. $477,000. $487,000. -Answer- $477,000. Asset retirement obligations: Increase the balance in the related asset account. Are measured at fair value in the balance sheet. Are liabilities associated with the restoration of an operational asset. All of these are correct. -Answer- All of these are correct. Assets acquired under multi-year deferred payment contracts are: Valued at the present value of the payments required by the contract Valued at their fair value on the date of the final payment Valued at the sum of the payments required by the contract None of these -Answer- Valued at the present value of the payments required by the contract The exclusive right to benefit from a creative work, such as film, is a: Patent. Copyright. Trademark. Franchise. -Answer- Copyright. In a nonmonetary exchange of equipment, if the exchange has commercial substance, a gain is recognized if: The fair value of the equipment received exceeds the book value of the equipment received. The book value of the equipment received exceeds the fair value of the equipment surrendered. The fair value of the equipment surrendered exceeds the book value of the equipment surrendered. None of these is correct. -Answer- The fair value of the equipment surrendered exceeds the book value of the equipment surrendered.Below are data relative to an exchange of similar assets by Grand Forks Corp. Assume the exchange has commercial substance. Old Equipment Cash Book Value Fair Value Paid Case A $50,000 $60,000 $15,000 Case B $40,000 $35,000 $8,000 In Case B, Grand Forks would record a gain/(loss) of: $ 5,000 $ 3,000 $(5,000) $(3,000) -Answer- $(5,000) Research and development expense for a given period includes: The full cost of a newly acquired operational asset that has an alternative future use. Depreciation on a research and development facility. Research and development conducted on a contract basis for another entity. Patent filing and legal costs. -Answer- Depreciation on a research and development facility. If a company incurs disposition obligations as a result of acquiring an asset: The company recognizes the obligation at fair value when the asset is acquired. The company recognizes the obligation at fair value when the asset is disposed. The company records the difference between the fair value of the asset and the obligation when the asset is acquired. None of these. -Answer- The company recognizes the obligation at fair value when the asset is acquired. Simpson and Homer Corporation acquired an office building on three acres of land for a lump-sum price of $2,400,000. The building was completely furnished. According to independent appraisals, the fair values were $1,300,000, $780,000, and $520,000 for the building, land, and furniture and fixtures, respectively. The initial values of the building, land, and furniture and fixtures would be: $1,300,000, $780,000, $520,000. $1,200,000, $720,000, $480,000. $720,000, $1,200,000, $480,000. None of these. -Answer- $1,200,000, $720,000, $480,000. Goodwill is:Amortized over the greater of its estimated life or forty years. Only recorded by the seller of a business. The excess of the fair value of a business over the fair value of all net identifiable assets. None of these. -Answer- The excess of the fair value of a business over the fair value of all net identifiable assets. Donated assets are recorded at: Zero (memo entry only). The donor's book value. The donee's stated value. Fair value. -Answer- Fair value. Productive assets that are physically consumed in operations are: Equipment. Land. Land improvements. Natural resources. -Answer- Natural resources. Below are listed data relative to an exchange of equipment by Pensacola Inc. Assume the exchange has commercial substance. Old Equipment Cash Book Value Fair Value Paid Case A $75,000 $80,000 $12,000 Case B $60,000 $56,000 $10,000 In Case A, Pensacola would record the new equipment at: $68,000. $63,750. $67,250. $80,000. -Answer- $68,000. The acquisition costs of tangible operational assets do not include: The ordinary and necessary costs to bring the asset to its desired condition and location for use. The net invoice price. Legal fees, delivery charges, installation, and any applicable sales tax. Maintenance costs during the first 30 days of use. -Answer- Maintenance costs during the first 30 days of use. Ruth Corporation acquired an office building on three acres of land for a lump-sum price of $1,200,000. The building was completed furnished. According to independent appraisals, the fair values were $650,000, $390,000 and $260,000 for the building, land,and furniture and fixtures, respectively. The initial values of the building, land, and furniture and fixtures would be: $650,000, $390,000, $260,000 $360,000, $600,000, $240,000 $600,000, $360,000, $240,000 None of these -Answer- $600,000, $360,000, $240,000 Ro Stores exchanged land and cash of $15,000 for similar land. The book value and the fair value of the land were $270,000 and $300,000 respectively. Assuming that the exchange lacks commercial substance, Ro would record land-new at and record a gain (loss) of Land Gain (loss) $315,000 $ 0 $315,000 $30,000 $285,000 $30,000 $285,000 $ 0 -Answer- $285,000 $ 0 Research and development (R&D) costs: Generally pertain to activities that occur prior to the start of production. May be expensed or capitalized, at the option of the reporting entity. Must be capitalized and amortized. None of these is correct. -Answer- Generally pertain to activities that occur prior to the start of production. Lake Incorporated purchased all of the outstanding stock of Huron Company paying $950,000 cash. Lake assumed all of the liabilities of Huron. Book values and fair values of acquired assets and liabilities were: Lake would record goodwill of: $ 0. $ 75,000. $445,000. $250,000 -Answer- $250,000 Juliana Corporation purchased all of the outstanding stock of Caldwell Inc., paying $2,700,000 cash. Juliana assumed all of the liabilities of Caldwell. Book values and fair values of acquired assets and liabilities were: Juliana would record goodwill of: Book Value Fair Value Current assets (net) $420,000 $450,000 Property, plant, & equip. (net) $1,600,000 $2,250,000 Liabilities $500,000 $600,000 $1,180,000.$ 600,000. $ 880,000. $ 100,000. -Answer- $ 600,000. When selling operational assets for cash: The seller recognizes a gain or loss for the difference between the cash received and the fair value of the asset sold. The seller recognizes a gain or loss for the difference between the cash received and the book value of the asset sold. The seller recognizes losses, but not gains. None of these. -Answer- The seller recognizes a gain or loss for the difference between the cash received and the book value of the asset sold. Holiday Laboratories purchased a high speed industrial centrifuge at a cost of $420,000. Shipping costs totaled $15,000. Foundation work to house the centrifuge cost $8,000. An additional water line had to be run to the equipment at a cost of $3,000. Labor and testing costs totaled $6,000. Materials used up in testing cost $3,000. The capitalized cost is: $455,000. $446,000. $437,000. $435,000. -Answer- $455,000. Assets acquired in a lump-sum purchase are valued based on: Their assessed valuation. Their relative fair values. The present value of their future cash flows. Their cost plus the difference between their cost and fair values. -Answer- Their relative fair values. Below are data relative to an exchange of similar assets by Grand Forks Corp. Assume the exchange has commercial substance. Old Equipment Cash Book Value Fair Value Paid Case A $50,000 $60,000 $15,000 Case B $40,000 $35,000 $8,000 In Case A, Grand Forks would record the new equipment at: $65,000. $75,000. $50,000. $60,000. -Answer- $75,000.The fixed asset turnover ratio provides The amount of sales generated per dollar of fixed assets The rate of decline in asset lives The rate of replacement of fixed assets The decline in book value of fixed assets compared to capital expenditure -Answer- The amount of sales generated per dollar of fixed assets Greig Company purchased a high speed industrial centrifuge at a cost of $840,000. Shipping costs totaled $30,000. Foundation work to house the centrifuge cost $16,000. An additional water line had to be run to the equipment at a cost of $6,000. Labor and testing costs totaled $12,000. Materials used up in testing cost $6,000. The capitalized cost is $870,000 $874,000 $892,000 $910,000 -Answer- $910,000 Horton Stores exchanged land and cash of $5,000 for similar land. The book value and the fair value of the land were $90,000 and $100,000, respectively. Assuming that the exchange HAS commercial substance, Horton would record land-new at and record a gain/(loss) of: Land Gain (loss) $105,000 $ 0 $105,000 $10,000 $95,000 $ 0 $95,000 $10,000 -Answer- $105,000 $10,000 Horton Stores exchanged land and cash of $5,000 for similar land. The book value and the fair value of the land were $90,000 and $100,000, respectively. Assuming that the exchange LACKS commercial substance, Horton would record land-new at and record a gain/(loss) of: Land Gain (loss) $105,000 $ 0 $105,000 $10,000 $95,000 $ 0 $95,000 $10,000 -Answer- $95,000 $ 0 Axcel Software began a new development project in 2008. The project reached technological feasibility on June 30, 2009 and was available for release to customers at the beginning of 2010. Development costs incurred prior to June 30, 2009 were$3,200,000 and costs incurred from June 30 to the product release date were $1,400,000. 2010 revenues from the sale of the new software were $4,000,000 and the company anticipates additional revenues of $6,000,000. The economic life of the software is estimated at four years. 2010 amortization of the software development costs would be: $ 0. $ 350,000. $1,840,000. $ 560,000. -Answer- $ 560,000. Below are listed data relative to an exchange of equipment by Pensacola Inc. Assume the exchange has commercial substance. Old Equipment Cash Book Value Fair Value Received Case A $75,000 $80,000 $12,000 Case B $60,000 $56,000 $10,000 In Case B, Pensacola would record a gain/(loss) of: $ 4,000. $ (4,000). $ (10,000). None of these is correct. -Answer- $ (4,000). Bloomington Inc. exchanged land for equipment and $3,000 in cash. The book value and the fair value of the land were $104,000 and $90,000, respectively. Bloomington would record equipment at and record a gain/(loss) of: Equipment Gain (loss) $87,000 $3,000 $104,000 $(5,000) $87,000 $(14,000) None of these is correct. -Answer- $87,000 $(14,000) Grab Manufacturing Co. purchased a ten-ton draw press at a cost of $180,000 with terms of 5/15, n/45. Payment was made within the discount period. Shipping costs were $4,600, which included $200 for insurance in transit. Installation costs totaled $12,000, which included $4,000 for taking out a section of a wall and rebuilding it because the press was too large for the doorway. The capitalized cost of the ten-ton draw press is: $171,000. $183,600. $187,600. $185,760. -Answer- $187,600.The exclusive right to display a symbol of product identification is a: Patent. Copyright. Trademark. Franchise. -Answer- Trademark. The basic principle used to value an asset acquired in a nonmonetary exchange is to value it at: Fair value of the asset(s) given up. The book value of the asset given plus any cash or other monetary consideration received. Fair value or book value, whichever is smaller. Book value of the asset given. -Answer- Fair value of the asset(s) given up. Alamos Co. exchanged equipment and $18,000 cash for similar equipment. The book value and the fair value of the old equipment were $82,000 and $90,000, respectively. Assuming that the exchange lacks commercial substance, Alamos would record a gain/(loss) of: $26,000. $ 8,000. $(8,000). $ 0. -Answer- $ 0. Amortization of capitalized computer software costs is: Either the percentage-of-revenue method or the straight-line method at the company's option. The greater of the percentage-of-revenue method or the straight-line method. The lesser of the percentage-of-revenue method or the straight-line method. Based on neither the percentage-of-revenue nor the straight-line method. -Answer- The greater of the percentage-of-revenue method or the straight-line method. Depreciation, depletion, and amortization: All refer to the process of allocating the cost of operational assets over future periods. All generally utilize the same methods of cost allocation. Are all handled the same in arriving at taxable income. All of these are correct. -Answer- All refer to the process of allocating the cost of operational assets over future periods. On September 30, 2009, Bricker Enterprises purchased a machine for $200,000. The estimated service life is 10 years with a $20,000 residual value. Bricker records partialyear depreciation based on the number of months in service. Depreciation for 2009, using the straight-line method is: $13,500. $15,000. $ 4,500. $ 5,000. -Answer- $ 4,500. On March 31, 2009, M. Belotti purchased the right to remove gravel from an old rock quarry. The gravel is to be sold as roadbed for highway construction. The cost of the quarry rights was $164,000, with estimated salable rock of 20,000 tons. During 2009, Belotti loaded and sold 4,000 tons of rock and estimated that 16,000 tons remained at December 31, 2009. During 2010, Belotti loaded and sold 8,000 tons, but estimated at December 31, 2010, that 12,000 tons remained. Belotti would record depletion in 2010 of: $54,667. $65,600. $52,480. $55,760. -Answer- $52,480. In 2008, Antle Inc. had acquired Demski Co. and recorded goodwill of $245 million as a result. The net assets (including goodwill) from Antle's acquisition of Demski Co. had a 2009 year-end book value of $580 million. Antle assessed the fair value of Demski at this date to be $700 million, while the fair value of all of Demski's identifiable tangible and intangible assets (excluding goodwill) was $550 million. The amount of the impairment loss that Antle would record for goodwill at the end of 2009 is: $150 million $ 95 million $ 0 None of these is correct -Answer- $ 0 In testing for recoverability of an operational asset, an impairment loss is required if the: Asset's book value exceeds the undiscounted sum of expected future cash flows. Undiscounted sum of its expected future cash flows exceeds the asset's book value. Present value of expected future cash flows exceeds its book value. None of these. -Answer- Asset's book value exceeds the undiscounted sum of expected future cash flows. Fryer Inc. owns equipment for which it paid $90 million. At the end of 2009, it had accumulated depreciation on the equipment of $27 million. Due to adverse economic conditions, Fryer's management determined that it should assess whether an impairment should be recognized for the equipment. The estimated undiscounted future cash flows to be provided by the equipment total $60 million, and the equipment's fair value at that point is $40 million. Under these circumstances, Fryer:Would record no impairment loss on the equipment. Would record a $3 million impairment loss on the equipment. Would record a $23 million impairment loss on the equipment. None of these is correct. -Answer- Would record a $23 million impairment loss on the equipment. Wilson Inc. owns equipment for which it paid $70 million. At the end of 2009, it had accumulated depreciation on the equipment of $12 million. Due to adverse economic conditions, Wilson's management determined that it should assess whether an impairment should be recognized for the equipment. The estimated undiscounted future cash flows to be provided by the equipment total $60 million, and the equipment's fair value at that point is $50 million. Under these circumstances, Wilson: Would record no impairment loss on the equipment. Would record an $8 million impairment loss on the equipment. Would record a $20 million impairment loss on the equipment. None of these is correct. -Answer- Would record no impairment loss on the equipment. Fellingham Corporation purchased equipment on January 1, 2007, for $200,000. The company estimated the equipment would have a useful life of 10 years with a $20,000 residual value. Fellingham uses the straight-line depreciation method. Early in 2009, Fellingham reassessed the equipment's condition and determined that its total useful life would be only six years in total and that it would have no salvage value. How much would Fellingham report as depreciation on this equipment for 2009? $24,000 $27,333 $36,000 $41,000 -Answer- $41,000 Cutter Enterprises purchased equipment for $72,000 on January 1, 2009. The equipment is expected to have a five-year life and a residual value of $6,000. Using the straight-line method, depreciation for 2010 and the equipment's book value at December 31, 2010 would be: $14,400 and $43,200. $28,800 and $37,200. $13,200 and $39,600. $13,200 and $45,600. -Answer- $13,200 and $45,600. North Company purchased a machine for $180,000 on January 1, 2017. The machine is expected to have a four-year life, with a residual value of $20,000 at the end of four years. Using the straight-line method, depreciation for 2014 and book value at December 31, 2018 would be$40,000 and $80,000 $45,000 and $90,000 $45,000 and $70,000 $40,000 and $100,000 -Answer- $40,000 and $100,000 Archie Co. purchased a framing machine for $45,000 on January 1, 2009. The machine is expected to have a four-year life, with a residual value of $5,000 at the end of four years. Using the double-declining balance method, depreciation for 2010 and book value at December 31, 2010, would be: $10,000 and $5,000. $10,000 and $10,000. $11,250 and $6,250. $11,250 and $11,250. -Answer- $11,250 and $11,250. In 2017, Dewey Inc had acquired Cheatam Co and recorded goodwill of $490 million as a result. The net assets (including goodwill) from Dewey's acquisition of Cheatam Co. had a 2014 year-end book value of $1,160 million. Dewey assessed the fair value of Cheatam at this date to be $1,400 million, while the fair value of all of Cheatam's identifiable tangible and intangible assets (excluding goodwill) was $1,100 million. The amount of the impairment loss that Dewey would record for goodwill at the end of 2018 is $0 $190 million $300 million None of these is correct -Answer- $0 Recognition of impairment for tangible operational assets is required if book value exceeds: Fair value. Present value of expected cash flows. Undiscounted expected cash flows. Accumulated depreciation. -Answer- Undiscounted expected cash flows. Accounting for a change in the estimated service life of equipment: Is handled prospectively. Requires retroactive restatement of prior year's financial statements. Requires a prior period adjustment. Is handled currently as a change in accounting principle. -Answer- Is handled prospectively. Archie Co. purchased a framing machine for $45,000 on January 1, 2009. The machine is expected to have a four-year life, with a residual value of $5,000 at the end of fouryears. Using the double-declining balance method, depreciation for 2009 and book value at December 31, 2009, would be: $22,500 and $22,500. $22,500 and $17,500. $20,000 and $25,000. $20,000 and $20,000. -Answer- $22,500 and $22,500. On March 31, 2017, Bedrock Company purchased the right to remove gravel from an old rock quarry. The gravel is to be sold as roadbed for highway construction. The cost of the quarry rights was $328,000 with estimated salable rock of 40,000 tons. During 2017, Bedrock loaded and sold 8,000 tons of rock and estimated that 32,000 tons remained at December 31, 2017. During 2018, Bedrock loaded and sold 16,000 tons, but estimated at December 31, 2018 that 24,000 tons remained. Bedrock would record depletion in 2017 of $49,200 $61,500 $65,600 $82,000 -Answer- $65,600 Gains on the cash sales of fixed assets: Are the excess of the book value over the cash proceeds. Are part of cash flows from operations. Are reported on a net-of-tax basis if material. Are the excess of the cash proceeds over the book value of the assets. -Answer- Are the excess of the cash proceeds over the book value of the assets. Archie Co. purchased a framing machine for $45,000 on January 1, 2009. The machine is expected to have a four-year life, with a residual value of $5,000 at the end of four years. Using the straight-line method, depreciation for 2009 and book value at December 31, 2009, would be: $10,000 and $30,000. $11,250 and $28,750. $10,000 and $35,000. $11,250 and $33,750. -Answer- $10,000 and $35,000 Cutter Enterprises purchased equipment for $72,000 on January 1, 2009. The equipment is expected to have a five-year life and a residual value of $6,000. Using the straight-line method, the book value at December 31, 2009 would be: $57,600. $51,600. $58,800. $52,800. -Answer- $58,800 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 86 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 20, 2022
Number of pages
86
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 20, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
112