Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Biology 1010 Exam 1 2022 (WITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS) (All)
Biology 1010 Exam 1 2022 (WITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS)
Document Content and Description Below
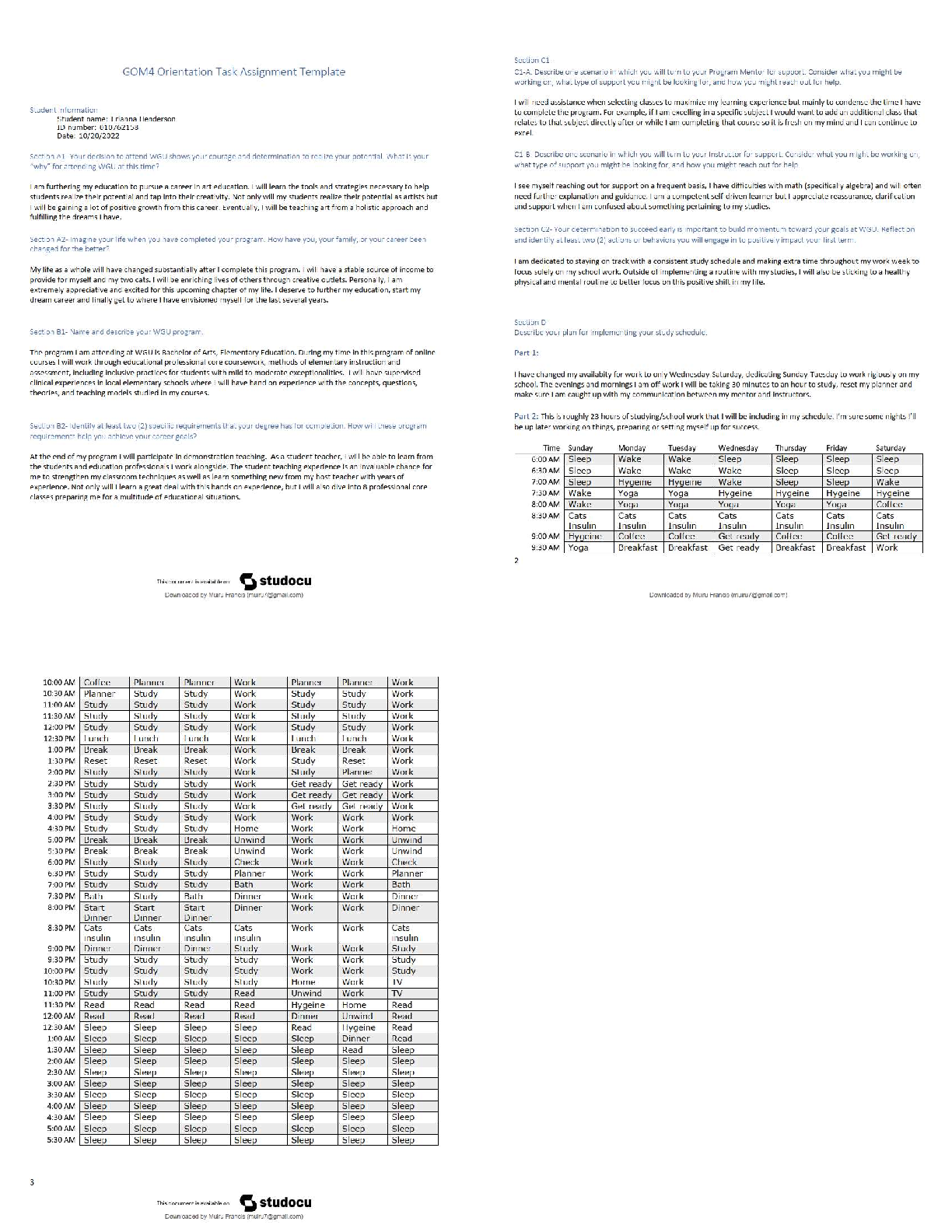
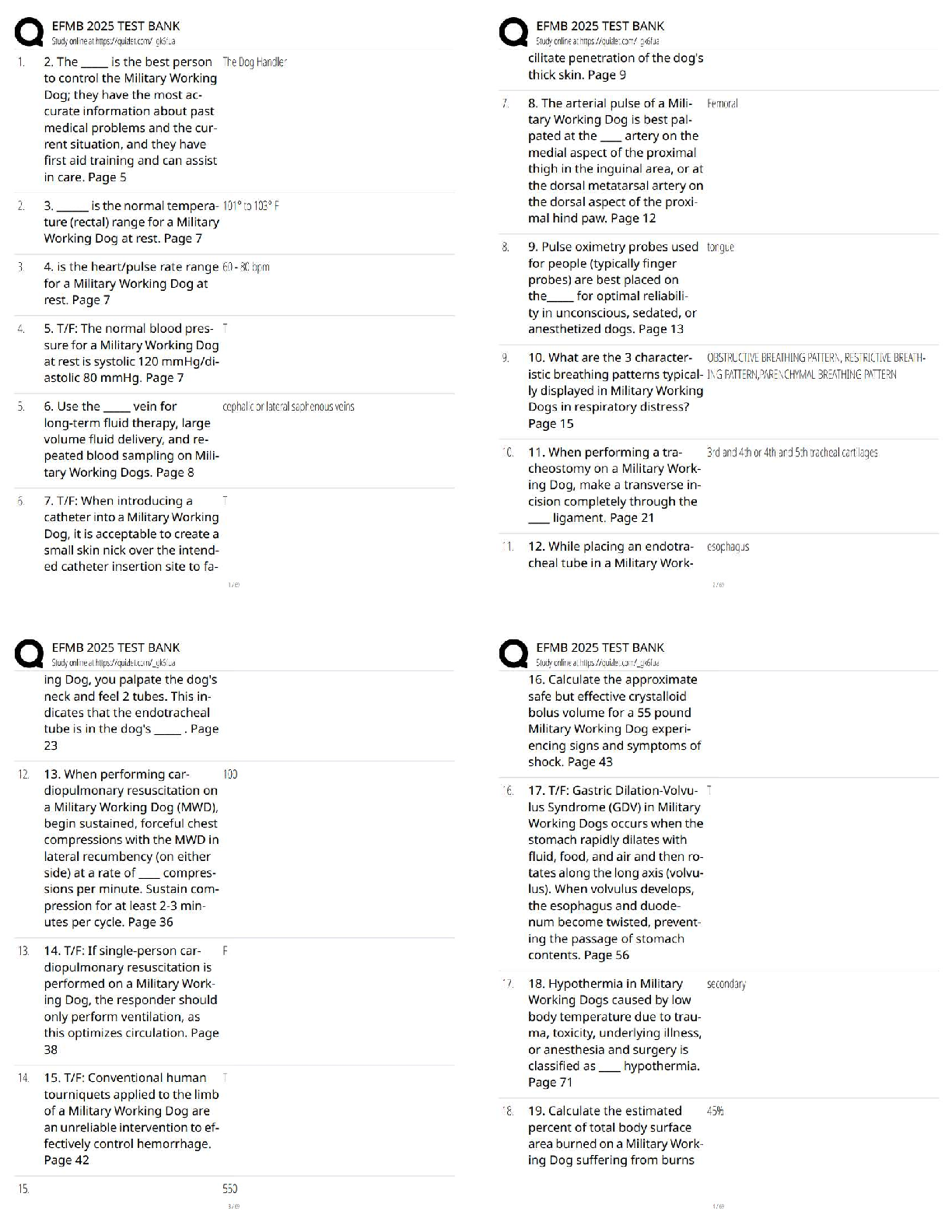
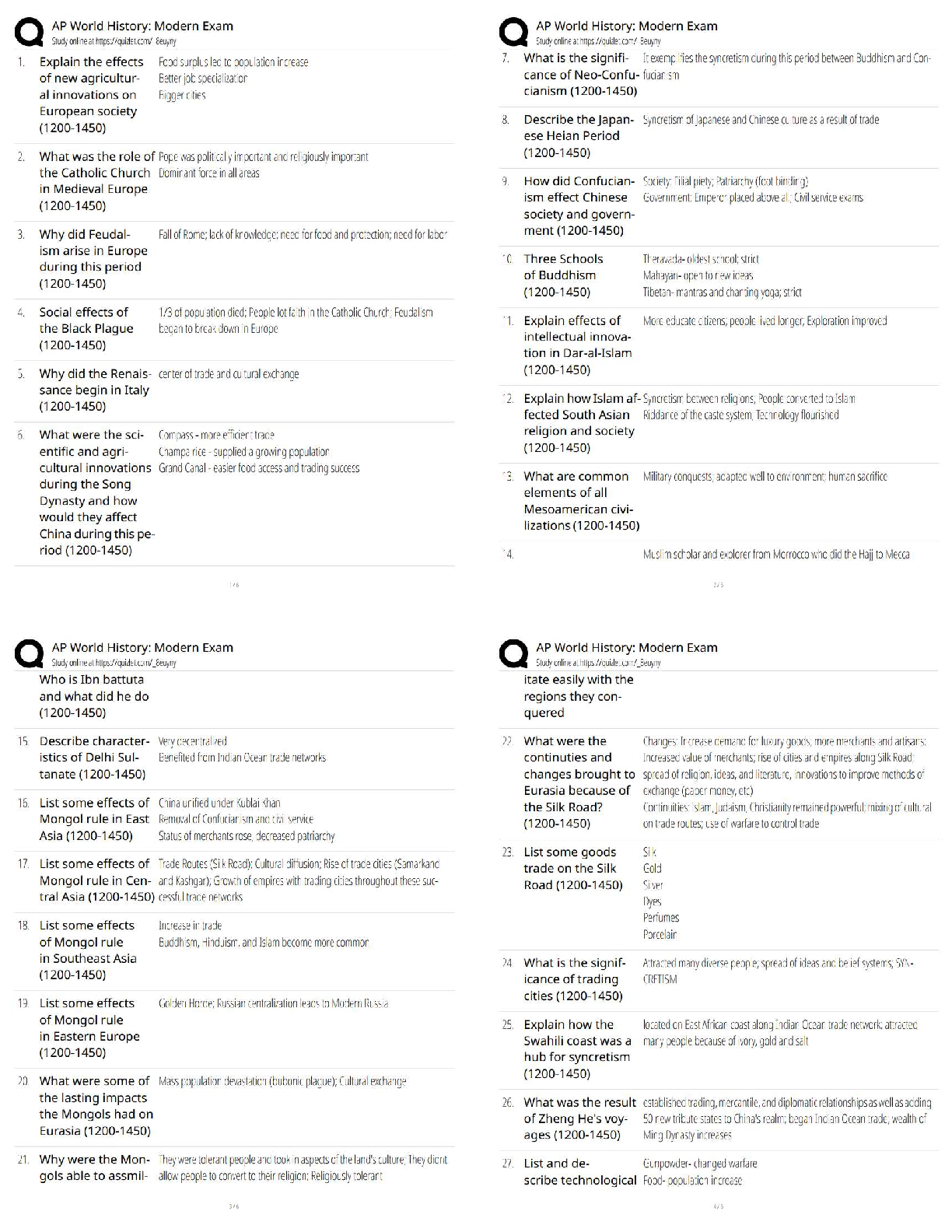
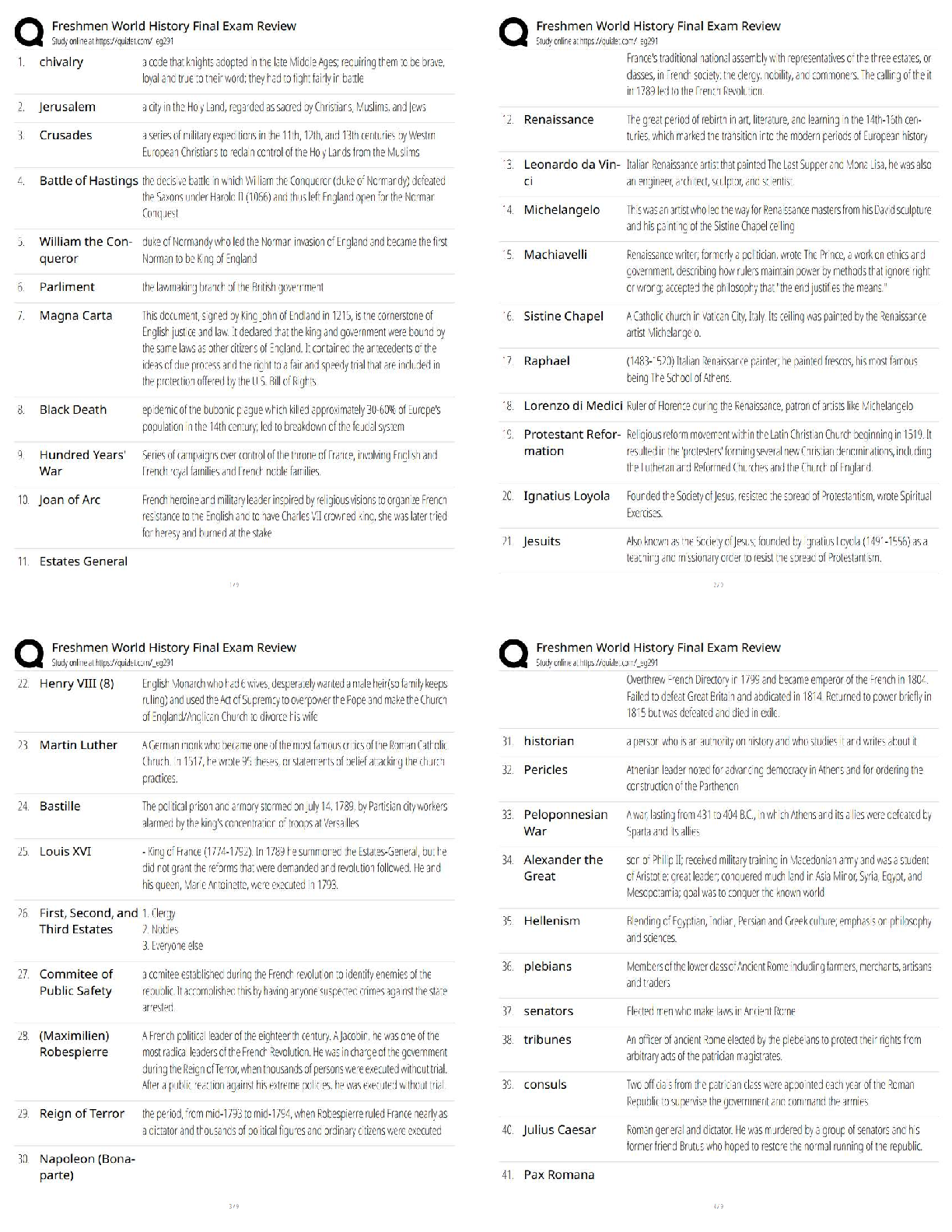
BIOLOGY 1010 EXAM 1 Biological Diversity - ANSWERDiverse species throughout the world. There are 1 million species on the planet. These species are catagorized by broad to detailed. Domains - AN ... SWERa taxonomic category above the kingdom level; the three domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya 3 Domain Names - ANSWER1. Domain Bacteria 2. Domain Archaea 3. Domain Eukarya Every living thing (that we know of) belongs to one of these categories. Domain Bacteria - ANSWER(simple) Prokaryotes. most abundant life form. prokaryote - ANSWERdont have any organelles (means that w/n organism theres no smaller compartments) see this image under microscope. Domain Archaea - ANSWERalso prokaryotes (but not bacteria). unlike bacteria b/c live in unbarable conditions like hot springs & volcanoes. Domain Eukarya - ANSWEReukaryotes. Includes protist(a), plants, fungi, and animals. eukaryotes - ANSWERorganisms made up of one or more cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Under a microsocpe you can see many of these compartments. These compartments provide services for the cell. These can turn into complex organisms. looks like this under microscope. protist(a) - ANSWERusually single celled things. plantae - ANSWERphotosynthesise fungi - ANSWERrange from mushrooms to athletes foot to STDs. Classified by their type of reproduction. animalia - ANSWERusually critters bigger than 1 cell. [ex] cats, dogs, humans. they are multicellular (as opposed to a protist) a cell - ANSWERsmallest unit of living matter. seperated from external environment by membrane(s). all living things are composed of these. evolution - ANSWERSpecies change over time by a means of natural selection. species have to change in order to survive in their environment. Charles Darwin's Theory of Evolution - ANSWERpulished theory in 1850's. He called it DESCENT W/ MODIFICATION (things change throughout generations). Organisms adapt to their environment. Each organisms have challenges that cause them to modify their conditions. natural selection - ANSWERspecies either live long enough to pass on their genes, or dont. Biology as a Real Science refers to... - ANSWERusing the scientific method to help solve whats causing curiosity. 5 steps of scientific method - ANSWER1. make observation 2. questions (about your observation) 3. make up a hypothesis (educated guess) 4. make prediction 5. test/expirament (to see if your prediction or hypothesis will work, if fails, have to make a new prediction or hypothesis). biology - ANSWERthe study of organization How is life organized? - ANSWERLife is organized into a heirarchy or levels. Hierarchy of Levels - ANSWERa) Atom b) molecule (atoms merged together) c) cell (molecules merged together) smallest living unit d) tissue (two or more cells form together) e) organ (two or more tissues working together) f) organ system (two or more organs [ex] digestive systems) g) organism [ex] blue whales/humans h) population (interbreeding group of same organism) i) community (all populations in a particular area). j) ecosystem (all communities-living & non-living) Definition of Life - ANSWER1. order/organization, 2. reproduction (living things make copies of themselves) 3. respond to environment [ex] sweating, run from danger 4. ability to transform energy (cells use: cell respiration & other forms of life use photosynthesis) 5. response to environmental stimuli, 6. increase in size and complexity 7. living things have DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) -genetic material passes on information. elements - ANSWERA molecule composed of one kind of atom; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus. Around the nucleus is the subatomic particle called an "electron", usually symbolized by " e- " b/c negatively charged. Must have one or more electrons. All atoms have different numbers of electrons. The outer most orbital determines everything in an element. It's very active. electron - ANSWERNegatively charged particle; located outside the atomic nucleus. Electrons reside in orbitals (orbit around nucleus). hydrogen atom - ANSWERexample of an element with only one electron. Helium Atom - ANSWERexample of an element with only two electrons. carbon atom - ANSWERexample of an organic element. (6 electrons) chemical bond - ANSWERan electrical force linking atoms. can occur in three ways: 1) give up electron 2) take an electron 3) share electrons. Three types of chemical bonds: - ANSWER1. Ionic Bond 2. Covalent Bond 3. Hydrogen Bond Ionic bond - ANSWERA chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron to form a positive ion and the other atom gains to electron to form a negative ion. [ex] Sodium's outside e- very active/lonely. sodium gives chlorine the electron to become a positively charged ion, and then chlorine becomes negative. Once one is negative and one is positive, they join and become an ionic bond= table salt. positive ion - ANSWERwhen an ion has less electrons than protons Covalent Bond - ANSWERa bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. [ex] two hydrogen atoms share an electron = H2 Hydrogen Bond - ANSWERWeak chemical bond formed by the attraction of positively charged hydrogen atoms to other negatively charged atoms. Only 10% as strong as a ionic or covalent bond. It is a Polar molecule= like a water molecule. One side is negative and the other positive. [ex] when two hydrogen atoms from one water molecule attach to the oxygen atom of another water molecule. Organic Compounds - ANSWERformed by carbon and hydrogen atoms; carbohydrates (CHO)- sugars and starches. Seperated into four catagories: 1. Monosaccharide 2. Disaccharide 3. Polysaccharide 4. Lipids Monosaccharides - ANSWERSimple sugar; can occur in two different shapes = ring or chain. [ex] ring- fructose or glucose Disaccharides - ANSWERTwo molecules: monosaccharide + monosaccharide. Involves dehydration synthesis= dehydrating two monosaccharides. [ex] if you take glucose and join it with fructose, you get sucrose (cane sugar). hydrolysis= reverses dehydration synthesis. Adds water. [ex] add water to sucrose= glucose & fructose. Polysaccharide - ANSWERMore than two molecules. [ex] glycogen (a way we store our excess glucose) & starch. [ex] chitin- makes up the outside of some bugs. Their "skeleton" =Exoskeleton. Lipids - ANSWERa) Fats b) Steroids c) Phospholipids (write down what all these do) fats - ANSWERLipids that store e [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 22, 2022
Number of pages
7
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 22, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
84








.png)