Deficits in Social Emotional Reciprocity
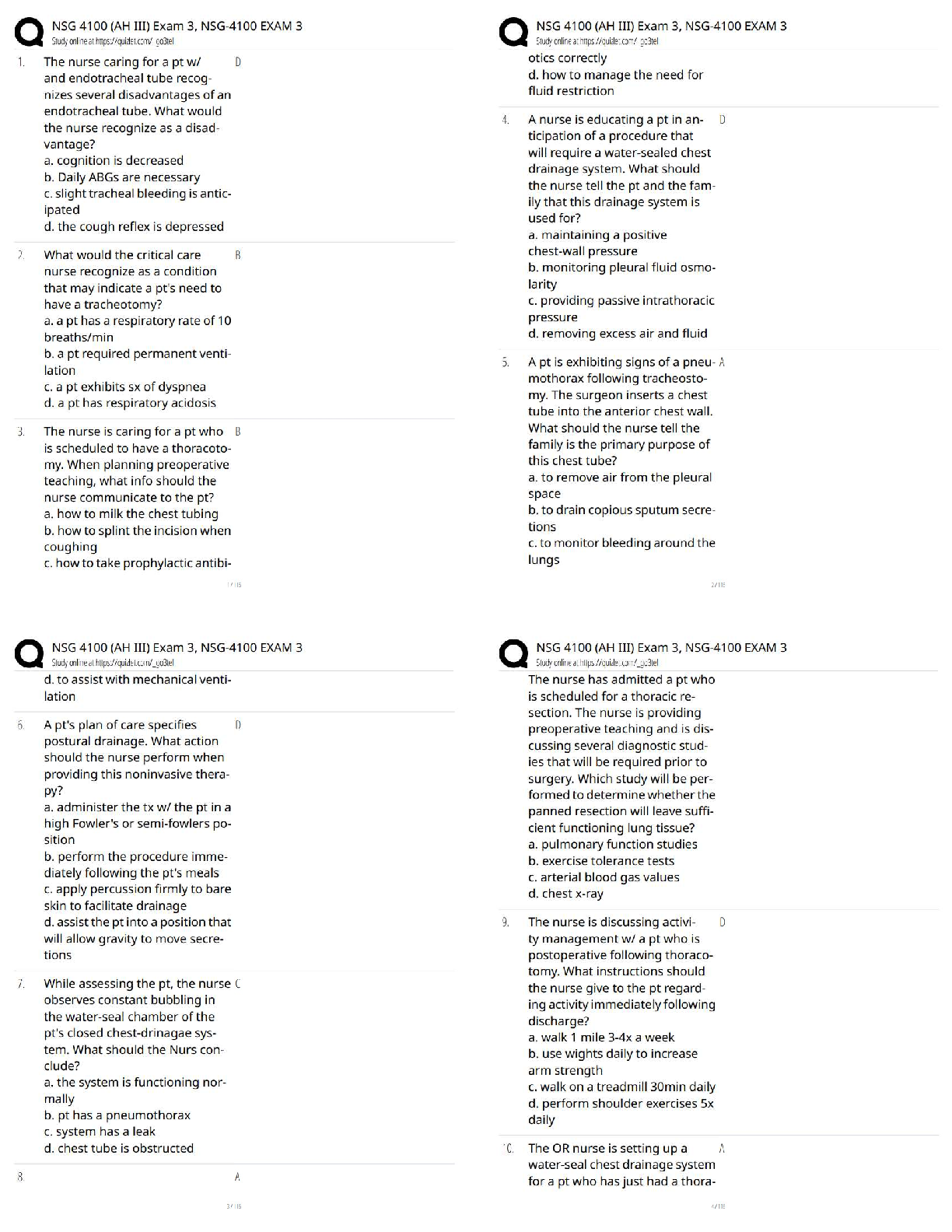
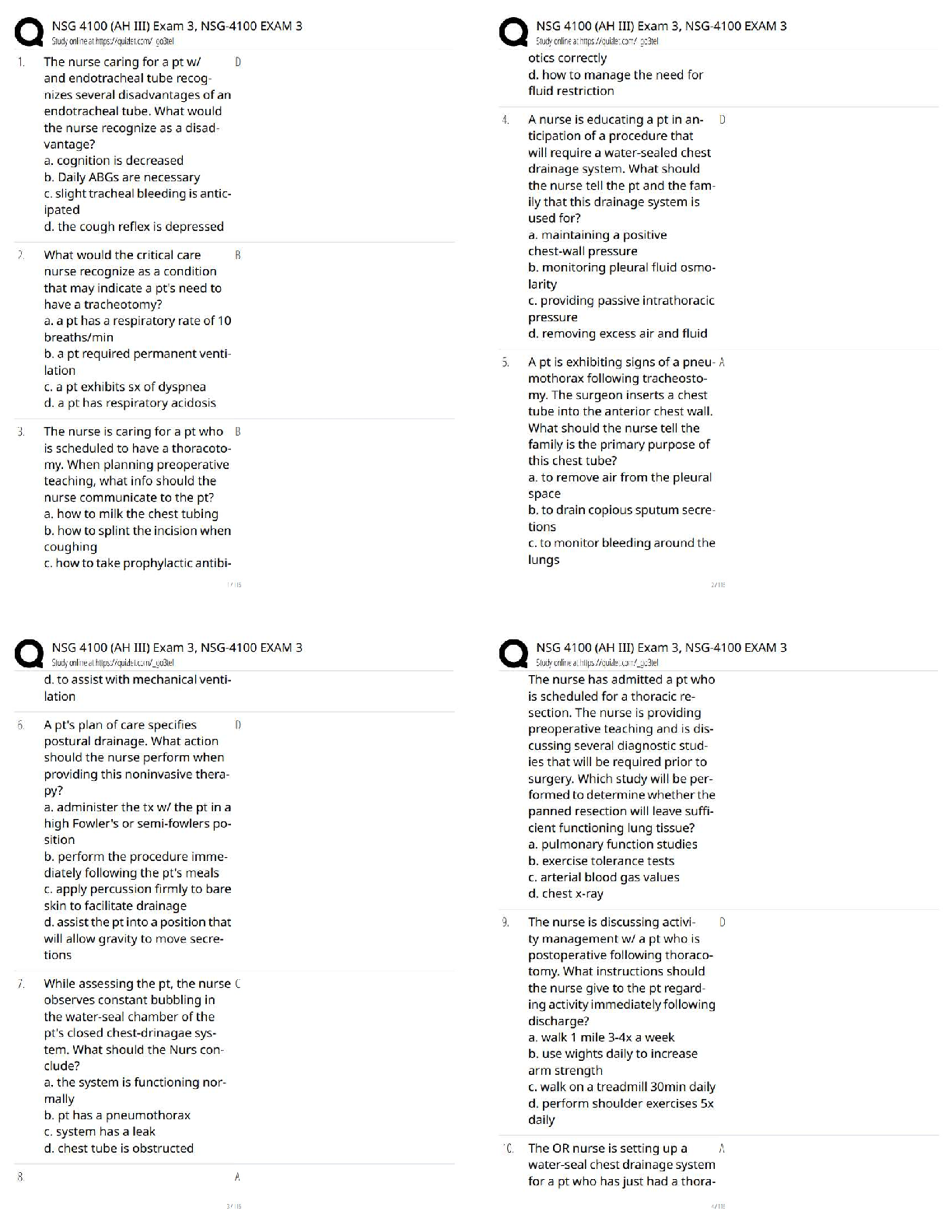
Range from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversations; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect: to failure to initiate or respond to
...
Deficits in Social Emotional Reciprocity
Range from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversations; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect: to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions.
Deficits in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction
Manifested by absent, reduced, or atypical use of eye contact (relative to cultural norms), gestures, facial expressions, body orientation, or speech intonation.
Deficits in developing maintaining and understanding relationships
Ranging from difficulties adjusting behavior to suit various social context; to difficulties in sharing imaginative play or in making friends; to absence of interest in peers
Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects or speech
Simple motor stereotypies, lining up toys or flipping objects, echolalia, idiosyncratic phrases (language with a private meaning; only makes sense to those familiar with the situation where the phrases came from)
Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or non-verbal behavior
Extreme distress at small changes, difficulties with transitions, rigid thinking patterns, greeting rituals, need to take same route or eat same food everyday
Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus
Strong attachment to or preoccupation with unusual objects, excessively circumscribed or perseverative interest
Hyper or Hypo reactivity to sensory input or unusual interests in sensory aspects of environment
Apparent indifference to pain/ temperature, adverse response to specific sounds or textures, excessive smelling or touching of objects, visual fascination with lights or movement.
Levels of severity across social communication and restrictive, repetitive behaviors
Level 1 Requiring support
Level 2 Requiring substantial support
Level 3 Requiring very substantial support
Postive Reinforcement
Sally took off her shoe independently yesterday, her mother clapped her hands and said, "Way to go Sally!" Sally took her shoes off independently again today. The clapping and "way to go" were the postive reinforcer.
Negative Reinforcement
When you start your car, an annoying noise is sounded. The noise turns off when you put your seatbelt on. The next time you get in the car you put your seatbelt on before you start the car, so you do not hear the noise.
Postive Punishment
Jose hit Lisa because he wanted her to play with him. The teacher reprimands Jose and told him not to hit her again. Jose then asked Lisa to play with him the next day.
Research regarding treatment intensity
Comprehensive undertaking that involves the child's entire family and a team of professionals. One-on-one treatment 30-40 hours per week
Early intensive behavioral intervention research
ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) Early intensive intervention helps all ages, but those who start before age 2 were most likely to make dramatic gains.
Foundational Autism Research
IAN (Interactive Autism Network) a project collecting information online from families of children with autism, ABA which may help build the foundation for later social skills training
Difference between evidence-based interventions vs. non-evidence based interventions
-Evidence-based: a body of formal research indicates the effectiveness of the treatment. (occupational therapy, speech therapy, ABA, social skills therapy) -Non-evidence based: has not been proven effective ( Hippo therapy (horse-back riding), GFCF diet (Gluten free, Casein free)
Negative Punishment
Jake loves PE. He spits at the teacher during PE class. The teacher sent him to stand in the hall. The next PE class Jake did not spit.
Positive Reinforcement
A type of reinforcement in which the Presentation of the stimulus is contingent upon the response, resulting in an Increase in the future probability of that response.
[Show More]
.png)
.png)











.png)