Module 2 Exam
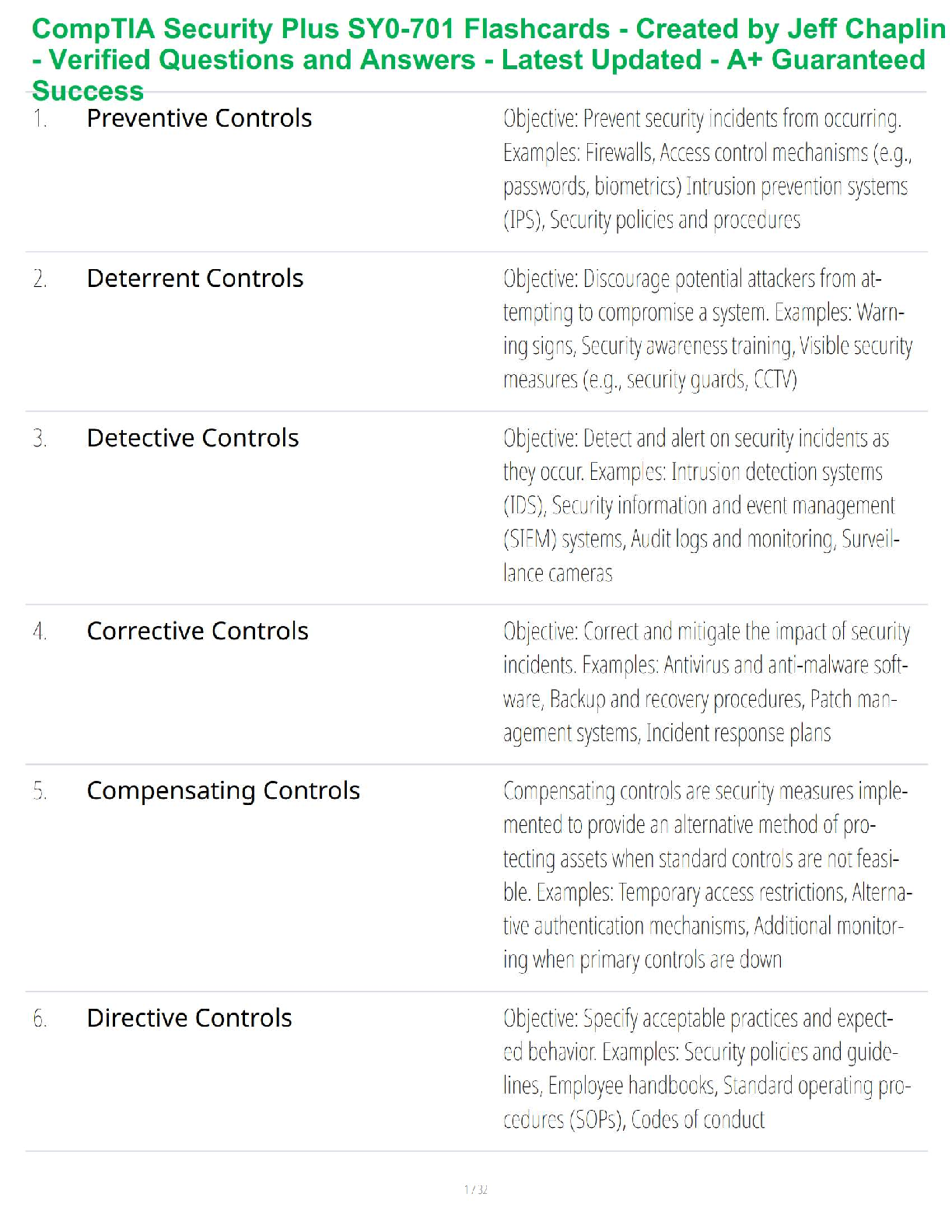
• Here is your test result.The dots represent the choices you have made.
• The highlighted questions are the questions you have missed.
• Remediation Accessed shows whether you accessed those links.'N' r
...
Module 2 Exam
• Here is your test result.The dots represent the choices you have made.
• The highlighted questions are the questions you have missed.
• Remediation Accessed shows whether you accessed those links.'N' represents links not
visited and 'Y' represents visited links.
Back to Status page
contains 27 Questions
1) Which stage of the issue management (IM) process is characterized by the following
scenario: After a higher-grade sealant was used to stop a screen fogging issue, the issue
status was updated on the issue register, and will be tracked until the screen passes
testing. [2.15.1 - Identify the components of the issue management process.]
[Remediation Accessed :N]
Issue monitoring
Issue analysis
Issue planning
Issue corrective action
2) What would be the appropriate corrective action for the following issue: As part of your
program, a major training exercise is scheduled to take place that includes the use of
handheld radios to monitor the exercise itself. Five months before the training exercise,
planners discover strong interference signals in the training area that prevent the radios
from operating effectively. They looked at eliminating the risk by taking an alternate
approach to replace the current radios and use different radios that achieve the same
desired effect. [2.15.2 - Select the appropriate corrective action for high or moderate
issues.]
Avoid
Ignore
Control
Transfer
3) Your expansion program for a base in a foreign territory has been periodically delayed
due to protestors blocking the streets to prevent construction vehicles from entering the
base. Based on the situation, a corrective action plan is in place, but construction is now at
a standstill. What would be the most appropriate step to manage and track this issue?
[2.15.3 - Given a scenario, identify the steps to track a resolution of issues against an
issue corrective action plan.]
Review the issue level and adjust the corrective action plan.
Monitor the issue to collect only estimated cost information.
Feed the information into future process steps.
Update the issue infrequently at informal meetings.
4) During the Technology Maturation and Risk Reduction (TMRR) phase, the goal is to
primarily reduce types of risk, including life cycle costs, engineering and which of the
following? [2.16.1 - Identify Risk Management considerations during acquisition life
cycle phases.]
Integration
Security
Design
Management
5) Which phase of the acquisition lifecycle would use proactive risk management activities
to address risk associated with new requirements, follow-on increments, or deferred
activities? [2.16.2 - Identify proactive risk management activities that support the
acquisition life cycle phases.]
Production and Deployment (P&D)
Technology Maturation and Risk Reduction (TMRR)
Engineering and Manufacturing Development (EMD)
Materiel Solution Analysis (MSA)
6) Which of the following is the main difference between an opportunity and an issue?
[2.2.1 - Identify the differences between risks, issues, and opportunities.]
Issues can only have a negative impact on a project.
Issues cannot be managed with as much precision as opportunities.
Issues can be analyzed and tracked; opportunities cannot.
Issues are resolved through resource reallocations; opportunities can only be addressed
through innovation.
7) Which step of the Department of Defense (DoD) Risk Management Process provides an
estimate of each risk’s likelihood and consequence? [2.3.1 - Identify the five steps of the
DoD Risk Management Process]
Analysis
Identification
Mitigation
Monitoring
8) Which of the following is a critical success factor to ensure effective risk management
(RM)? [2.4.1 - Given a scenario, identify the critical success factors to ensure effective
risk management.]
Risk management roles, responsibilities, and relationships
Experienced program management
Clearly detailing project requirements in the Request for Quotation (RFQ)
Establishing priority risk categories
9) A program generally should have 3-5 framing assumptions. Which of the following is an
attribute of a framing assumption? [2.5.2 - Choose appropriate examples of assumptions
that are considered and assumed true.]
•Consequences cannot be easily mitigated
Does not significantly affect program expectations
Is derivative of other assumptions
Is generically applicable to all programs
10) Which of the following is an objective of risk process planning? [2.6.1 - Select risk
process planning objectives.]
Ensures sound risk management (RM) principles, tools, and techniques are applied to
the RM program
Answers only the question "why are these tools used to execute the RM process?"
Describes the roles and responsibilities of all program personnel
Ensures sound Earned Value Management (EVM) principles, tools, and techniques are
applied to the RM program
11) Within a program at the management level, which of the following entities reviews the
risks owned by the Integrated Product Teams (IPTs)? [2.6.2 - Identify typical potential
program risk management organizational structures.]
IPT Risk Management Board (RMB)
Program Risk Management Board (RMB)
Risk Owner
Program manager (PM)
12) How should the government mitigate risk to ensure the most successful outcome?
[2.6.3 - Explain the importance of government and contractor risk management.]
Share risk responsibilities with the contractor.
Transfer all or most risk responsibilities to the contractor.
Assume most risk responsibilities, rather than transferring to the contractor.
Manage the most critical risks and have the contractor manage less critical risks.
13) When should the Program Risk Process (PRP) Document be written? [2.6.4 - Using a
scenario, apply specific content of a Program Risk Process (PRP) Document.]
As soon as possible when starting a new project.
Before reaching the first milestone.
Before the Request for Proposal (RFP) is issued.
Within the first 90 days following the kick-off meeting.
14) At the working level, which of the following is a responsibility of the Integrated
Product Team (IPT) during the risk management (RM) process? [2.6.5 - Identify key
elements of risk management as it relates to the role of IPT.]
Identify the need for RM training for IPT personnel.
Identify and submit candidate risks while supporting execution of the RM process.
Determine whether new or updated risk analyses and mitigation plans are adequate.
Review and validate identified program-level risks.
15) Which of the following sets of documents provides risk root causes for each phase of a
program? [2.7.1 - Identify risk identification tools and methods.]
Technical reviews
Testing results
Trend analyses
Prototyping results
16) The following describes which type of category of risk: In an effort to stem
cyberattacks aimed at Navy fighter jet communications and other essential systems, a new
program is launched to reengineer the system integration to improve overall system
security. If the initial reprogramming adjustments do not pass testing, the communication
system will require a complete reprogramming effort, requiring an additional 1½ years to
the schedule. [2.7.2 - Identify program risks and their associated root causes.]
Technical
Business
Programmatic
17) The following describes which source of potential risk: The program development
team uses an intranet to exchange documents between multiple centers. The Information
Technology (IT) team reported that the system has received over 7,000 attempted security
break-ins in the last two weeks alone. [2.8.1 - Identify typical risk sources in
acquisition.]
Security
Management
External Factors
Requirements
18) It has been reported that fiscal policy changes may result in a 10% reduction (about
$150,000) in funding for your program in the coming fiscal year. Your team estimates that
there is a 40% chance that this reduction will be realized. Based on the likelihood and
consequence table, what are the appropriate likelihood (L) and consequence (C) values?
Level Probability of
Occurrence Schedule Impact Cost Impact
1 >1% to ¡Ü20% Minimal or no schedule impact ( <5 days) <$20,000
2 >20% to ¡Ü40% Able to meet key dates (1 - 4 weeks) $20,000 -
<$100,000
3 >40% to ¡Ü60% Minor schedule slip, able to meet key
milestones (¡Ý4 weeks - 3 months)
$100,000 -
<$150,000
4 >60% to ¡Ü80% Significantly impacts ability to meet key
milestones (¡Ý3 months - 4 months)
$150,000 -
<$200,000
5 >80% to ¡Ü99% Schedule slip requires major schedule
rebaselining (>4 months) ¡Ý$200,000
[2.9.1 - Apply data provided in a risk report, including likelihood or probability criteria
and consequences criteria.]
L = 2; C = 4
L = 3; C = 3
L = 2; C = 5
L = 4; C = 4
19) The validity of a framing assumption (FA) is monitored by tracking which of the
following? [2.5.1 - Identify the attributes that define the framing assumptions in an
acquisition program.]
Metrics, expectations, and implications during execution
The number of risks and issues over the life of the program
The number of high level risks identified
The degree to which unexpected risks and issues surface during Milestone (MS) B
20) Which type of risk analysis has the highest chance of injecting bias into the risk
identification process? [2.10.1 - Given a scenario, apply risk analysis tools and techniques
for quantitative and qualitative analysis and assessment of risk levels.]
Expert interviews
Lessons learned
Product Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) risk analysis
Delphi Technique
21) Which of the following is presented with the resultant histogram of Monte Carlo
simulations? [2.10.2 - Using a simulation, apply program schedule analysis.]
[Remediation Accessed :N]
Mean, or average, completion date of the project
Final delivery dates for each task of the project
Task durations for a specific part of the project based on comparisons with similar
systems
Final costs based on the completion date of the project
22) Based on the results of a simulation, there is an 80% chance that the project will end
one week behind schedule. Using the table provided, what would the cumulative schedule
risk be, based on a one calendar week schedule delay?
Level Probability of Occurrence Schedule Impact
1 0% to 19% 0 to 5 days
2 20% to 39% 6 to 10 days
3 40% to 59% 11 to 15 days
4 60% to 79% 16 to 20 days
5 80% to 100% 21 to 25 days
[2.10.3 - Identify program risk levels based on the results from simulations.]
Probability 5; Schedule Impact 2
Probability 2; Schedule Impact 2
Probability 2; Schedule Impact 5
Probability 5; Schedule Impact 5
23) Your government program team is developing a new underwater helmet equipped with
enhanced visualization technology. Condensation issues threaten the visibility of the screen
and your team does not have the means to deal with the risk. You contract with a separate
group of industry materials and mechanical engineers since they can better address that
specific risk and offer a set of solutions back to you as you monitor their progress.
This is an example of which mitigation strategy? [2.11.1 - Choose potential risk
mitigation strategies as they relate to risk events.]
Transfer
Control
Avoidance
Acceptance
24) Your team is analyzing cost and schedule data performance to a baseline plan. Which
monitoring tool would be most appropriate? [2.12.1 - Identify the various tools and
techniques used in risk monitoring.]
Earned value analysis
Risk information form
Management indicator system
Technical performance measurements (TPMs)
25) What type of information can be gathered from a cost risk analysis (CRA)? [2.13.1 -
Identify program management functions and tools that integrate with the Risk Management
Process in support of a program.]
Early estimations of cost overruns and the ability of the system to achieve the
program’s life cycle cost objectives
A summary of the final costs for the program at completion of the program's life cycle
A list of cost overruns to date and indications of where cost savings can be made in
future tasks
A summary of cost trends derived from similar programs and an indicator of how
those may translate into cost risks in the current program
26) Opportunities are which of the following? [2.14.1 - Identify the components of
opportunity management and risk management.]
Future benefits to a program's cost, schedule, and/or performance baseline, usually
achieved through reallocation of resources
Any future effects to a program's cost, schedule, and/or performance, usually achieved
through adjustments to design and/or technical specifications
Any future potential events that could affect the success of a program, usually
identified through quantified cost and schedule analyses
All future positive events in a program achieved by successful early design, planning,
and coordination among program stakeholders
27) Your program, which has never managed more than two projects at a time, is scheduled
to kick off five projects within a two-week period. This will require more rigid
organizational, communication, and management skills to ensure success moving forward.
Which of the following best describes this situation? [2.14.2 - Given a scenario, apply the
differences between risk management and opportunity management.]
It is only a risk.
It is only an opportunity.
It is neither risk nor opportunity.
Need more information to determine if it is a risk or an opportunity.
[Show More]